Electroosmosis method and apparatus for dehydration for large area high moisture percentage earth body
A high-water content, large-area technology, applied in soil protection, construction, infrastructure engineering, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing peak voltage, uniform water content, and reducing contact resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
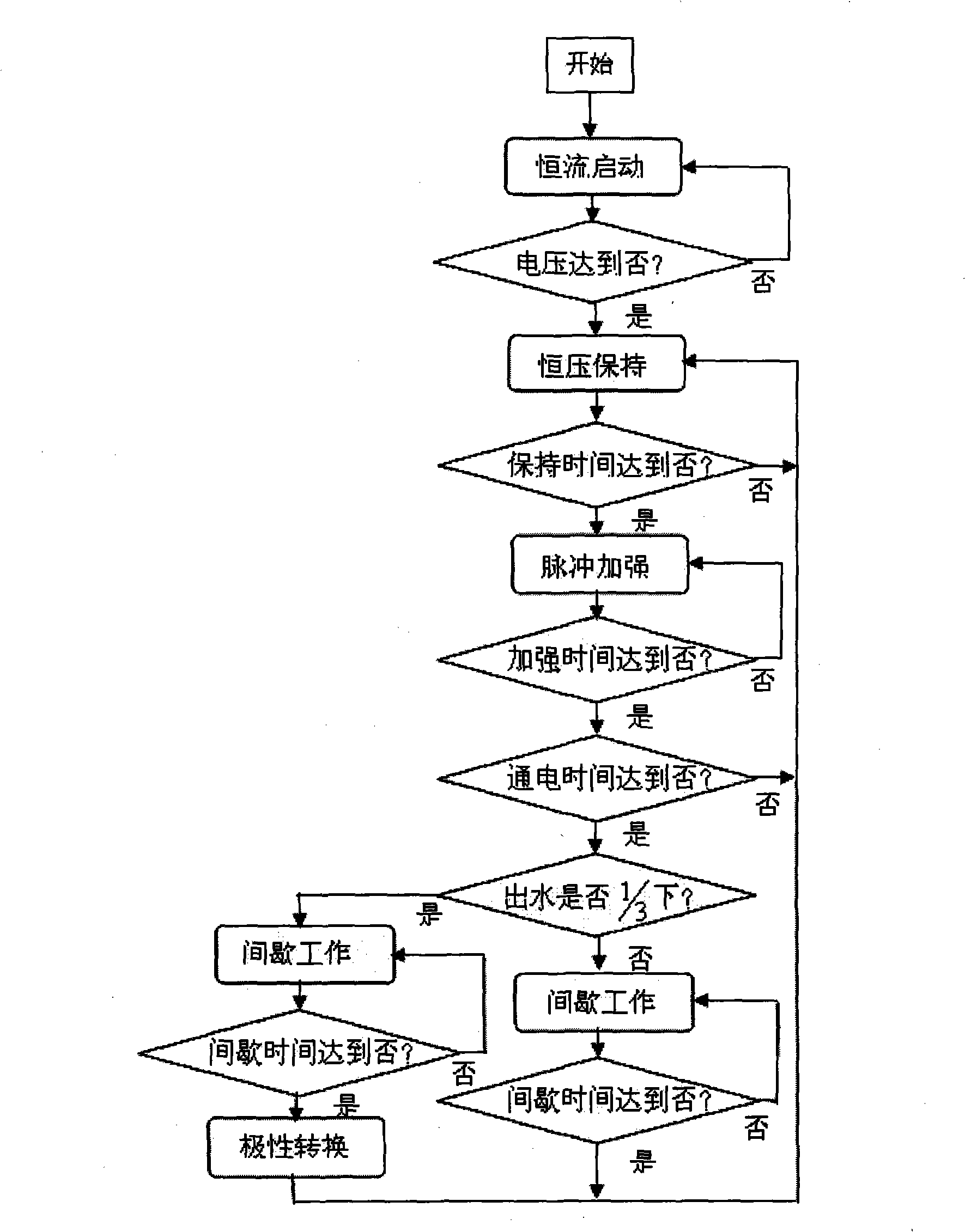
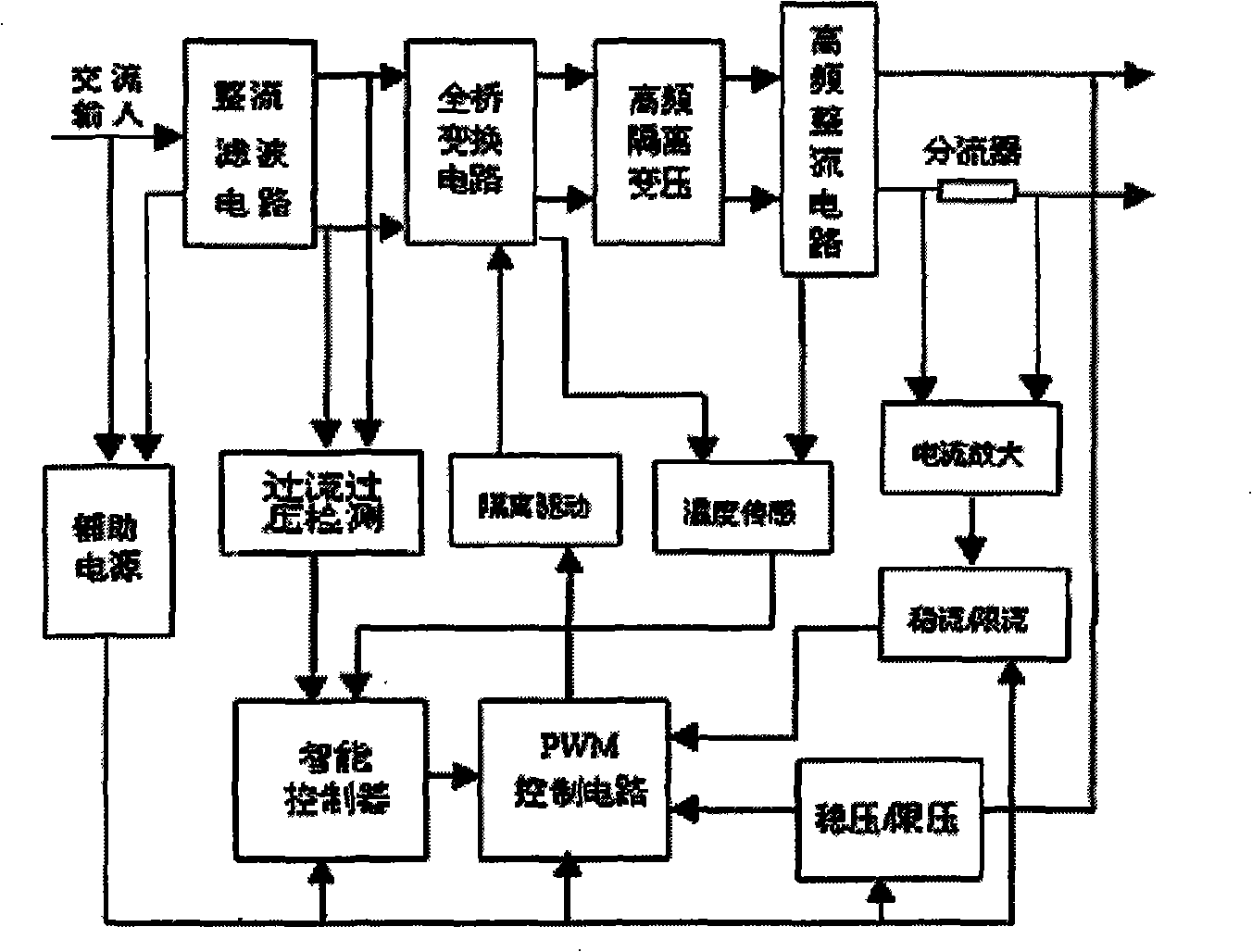
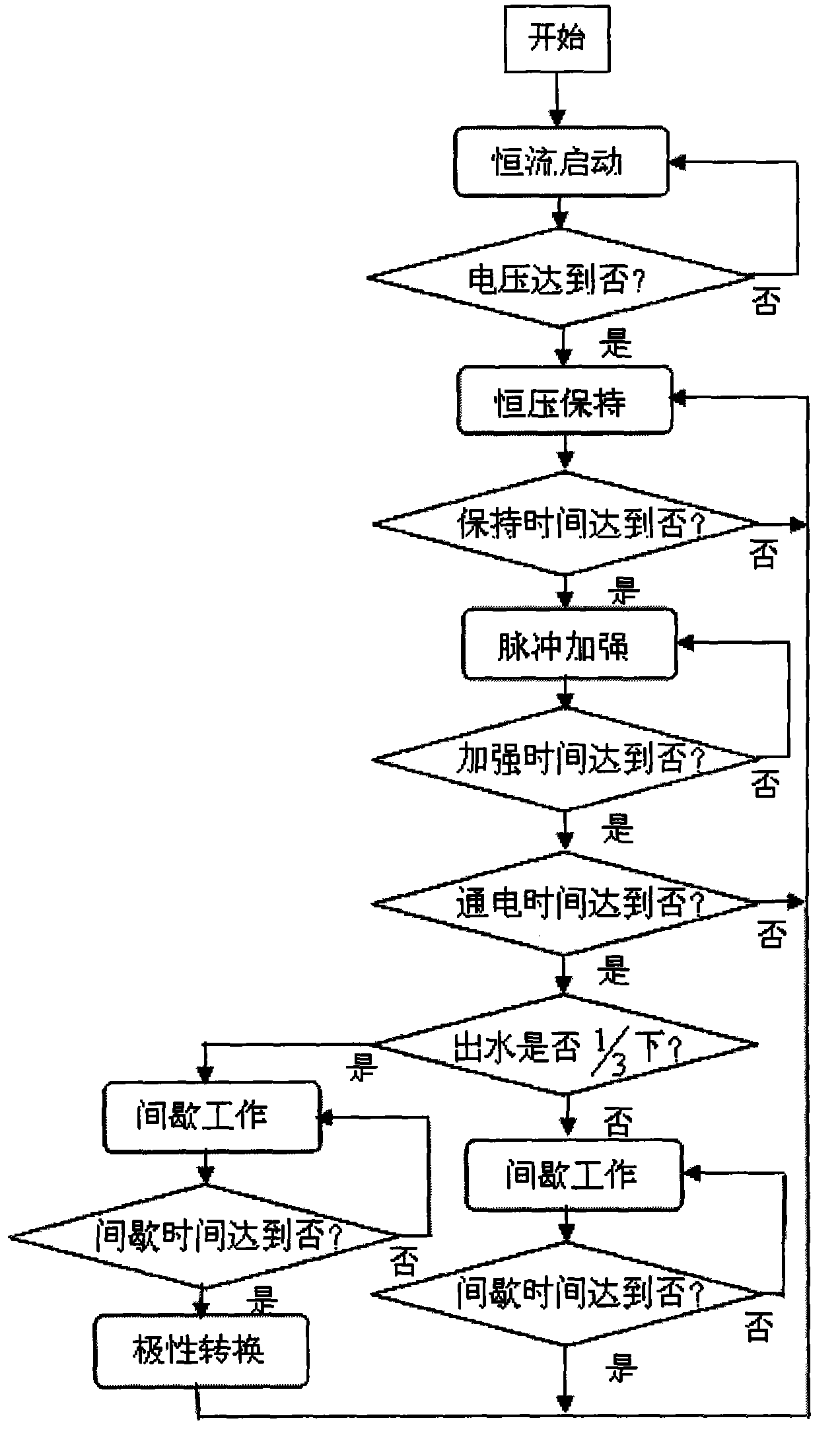
[0028] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of electroosmosis method that is used for the dehydration of large area high moisture content soil, its operation steps are as follows:
[0029] 1. Positioning, burying electrodes, inserting drainage boards
[0030] Accurately position according to the layout requirements and then bury the electrodes and insert the drainage board. The height above the ground is 0.1m, and the coarse sand is poured. The negative and positive electrodes are arranged in parallel and staggered. The corresponding electrode of the infiltration device; in order to prevent the current from excessive diversion from the soil surface, reduce the effect of electroosmosis and the occurrence of electric corrosion effect, the exposed metal parts above the ground of the cathode and anode should be cleaned before energization, and a layer of asphalt should be applied to reduce the electric current. Consumption; the two ends of the connection between the drain board and the...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0047] (1) Constant current start: 6 electrodes are embedded in the soil at a depth of 5 meters, and the current of each electrode is set to 0.5 amperes, the initial current is 1.5 amperes and the target voltage value is 30 volts, and the steady current output mode is adopted, that is, the output current The initial current is constant at 1.5 amperes, and the output voltage increases with the electroosmotic dehydration at this time;
[0048] (2) Constant voltage maintenance: When the output voltage reaches the set target voltage value of 30 volts, it will switch to a regulated output, that is, the output voltage is constant at the target voltage value;
[0049] (3) Pulse strengthening: During the constant voltage holding process, the output voltage is superimposed on the target voltage value with a positive pulse voltage. The pulse voltage is 27 volts. When there is no pulse, the output voltage is the target voltage value. The cycle i...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0055] (1) Constant current start: 2 electrodes are embedded in the soil to a depth of 5 meters, and the current of each electrode is set to 0.2 amperes, the initial current is 1.0 amperes and the target voltage value is 25 volts, and the steady current output mode is adopted, that is, the output current The initial current is constant at 1.0 ampere, at this time the output voltage increases with the electroosmotic dehydration;
[0056] (2) Constant voltage maintenance: When the output voltage reaches the set target voltage value of 25 volts, it will switch to a regulated output, that is, the output voltage is constant at the target voltage value;
[0057] (3) Pulse strengthening: During the constant voltage holding process, the output voltage is superimposed on the target voltage value with a positive pulse voltage. The pulse voltage is 20 volts. When there is no pulse, the output voltage is the target voltage value. The cycle is 20 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com