Initial position detection method for permanent magnet synchronous electric motor rotor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor initial position technology, applied in the control of generators, motor generators, electromechanical transmissions, etc., can solve the problems of complex installation, large impact on rotor structure, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
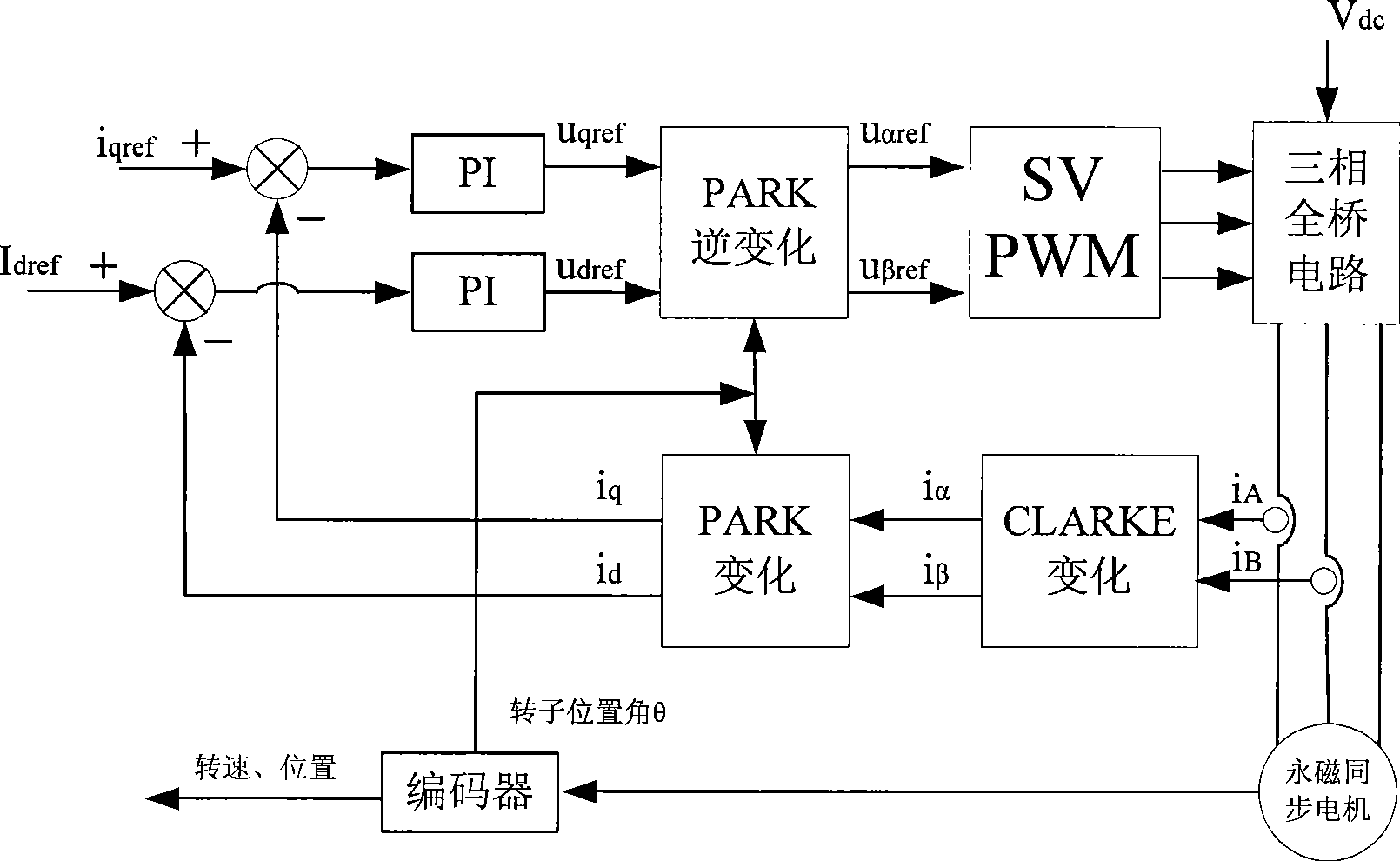
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, in the current loop of permanent magnet synchronous motor vector control, two-phase currents in the three-phase currents of the motor are usually sampled (the sum of the three-phase currents is zero, so the other phase can be calculated), and then through the CLARKE change and The feedback current value id, iq is obtained by the change of PARK, the difference between the reference current idref, iqref and the feedback value id, iq is adjusted by PI to obtain udref, uqref, and then uαref, uβref are obtained by inverse change of PARK, and finally the voltage is changed by SVPWM Pulses are applied to a permanent magnet synchronous motor.
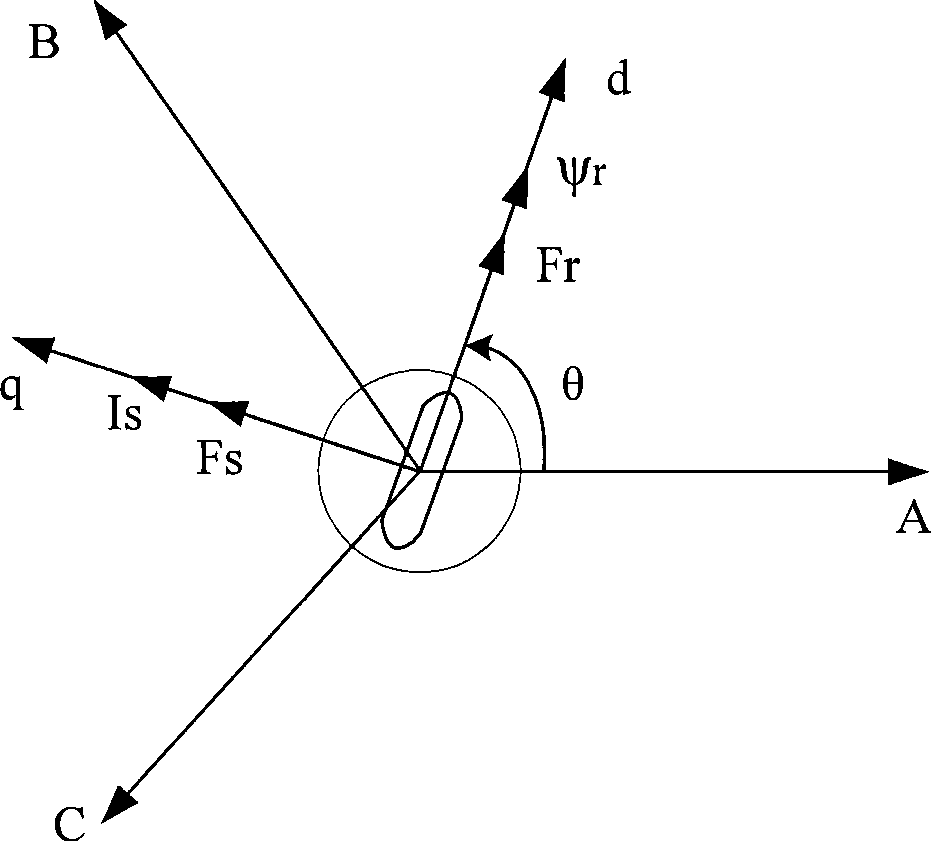
[0027] see figure 2 , the stator current vector Is is adjusted by the two quantities of id and iq, and the coordinate changes required to obtain the feedback values of id and iq are based on the rotor position angle θ, so if the rotor position angle θ is inaccurate, it is bound to It will cause the stator ...
Embodiment 2
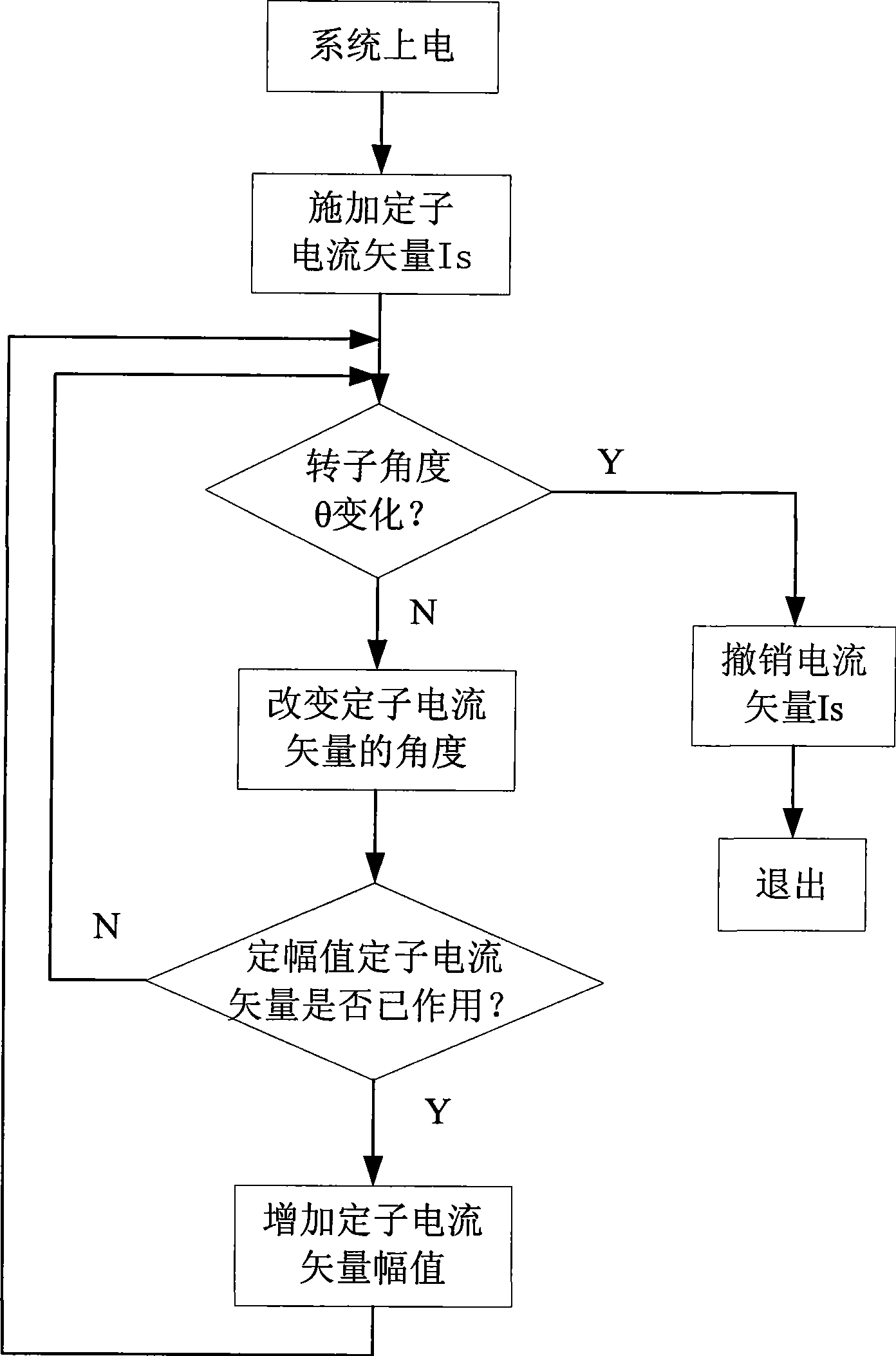
[0035] see Figure 5 , in this embodiment, the system is powered on first, and then the initial stator voltage vector Us1 is applied to the stator of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. Because the initial voltage vector Us1 is too large, the direction of the stator voltage vector Us and the rotor position angle are not 90 degrees, causing the rotor to rotate, which makes the detection of the initial rotor position angle θ inaccurate.
[0036] Then use the incremental photoelectric encoder feedback pulse to detect whether there is a slight displacement of the rotor. The accuracy of the incremental photoelectric encoder is ±360 / (P×4) mechanical angle, and P is the bus number of the incremental photoelectric encoder. The bus number of quantitative photoelectric encoders can reach 2000, which ensures the accuracy of rotor initial position detection.
[0037] If the rotor has a micro position, cancel the effect of the initial voltage vector Us1 immediately, and obtain the ini...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com