Electric rotating machine
A technology for rotating electrical machines and stator cores, applied in synchronous generators, electromechanical devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as stator coil heat dissipation and stator, and achieve the goal of suppressing poor insulation, suppressing the increase of reluctance, and suppressing temperature rise Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
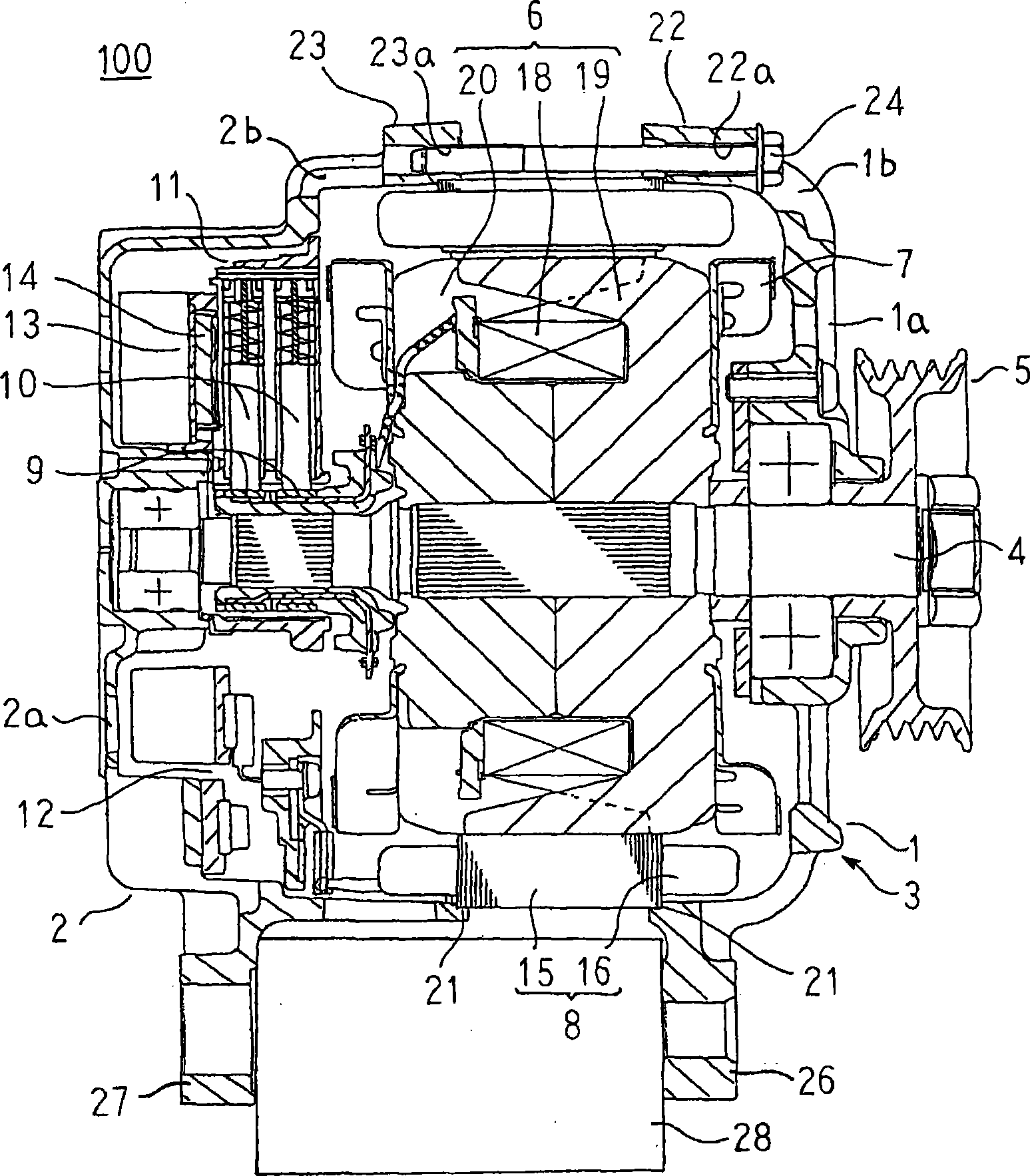
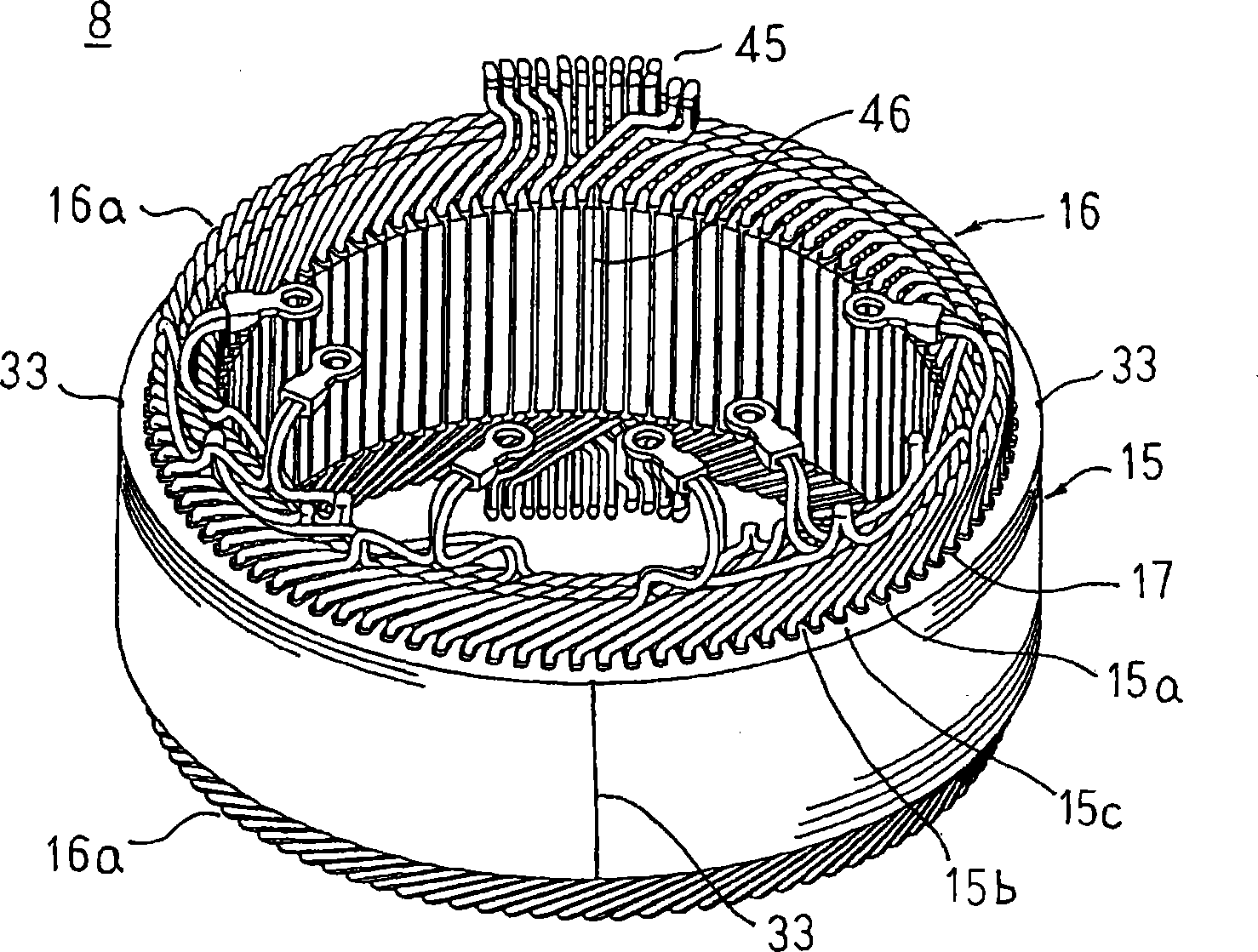
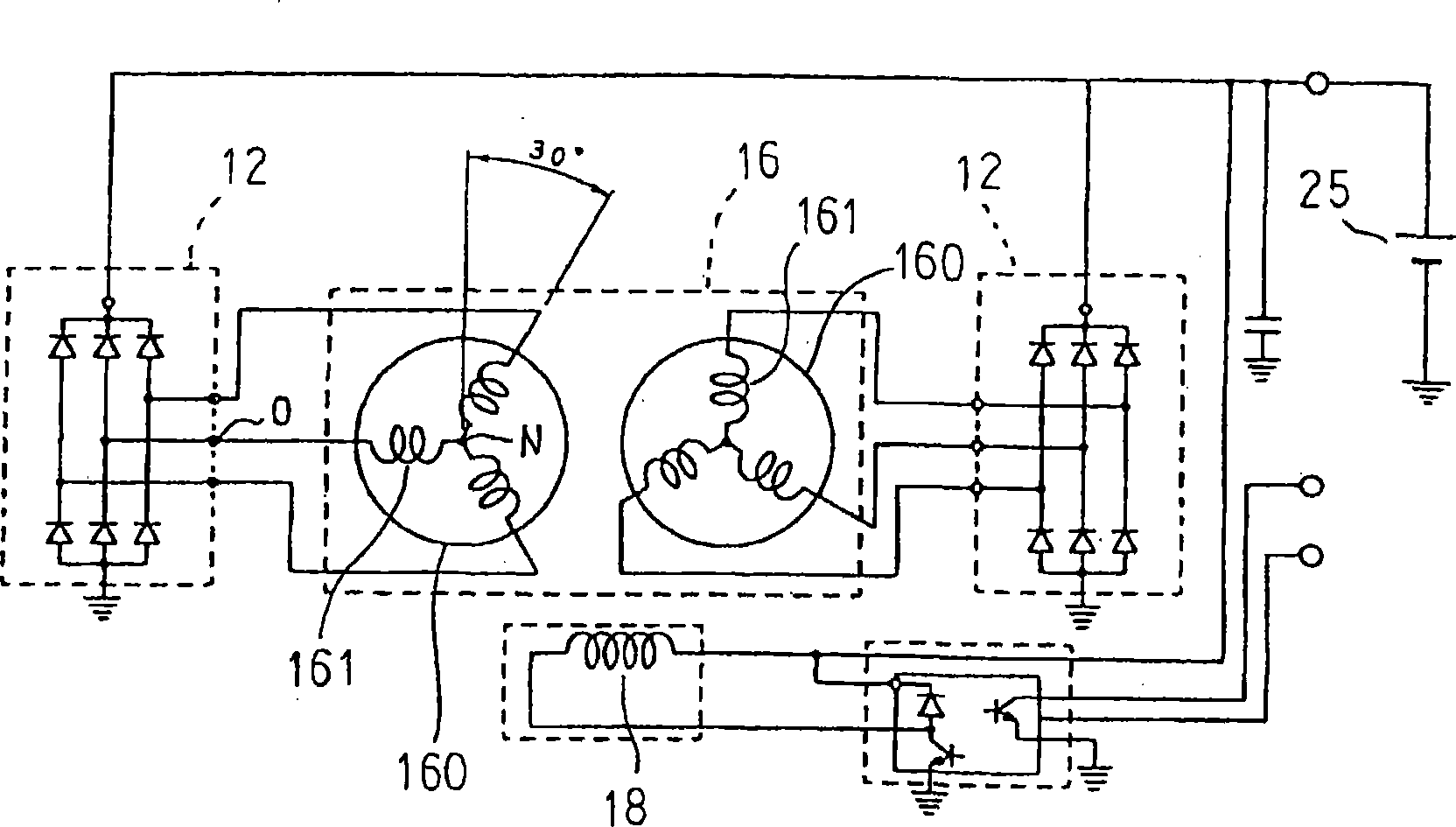
[0028] figure 1 Is a longitudinal cross-sectional view showing a vehicle alternator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 2 Is a perspective view showing a stator applied to a vehicle alternator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, image 3 Is a circuit diagram showing a vehicle alternator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, Figure 4 It is a cross-sectional view of a main part for explaining the fixing structure of the stator of the vehicle AC generator according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0029] in Figure 1 to Figure 4 Among them, the vehicle alternator 100 includes a housing 3, which is composed of a front frame 1 and a rear frame 2 that are roughly cup-shaped and made of aluminum as frames; and a shaft rotatably supported on the housing 3 4; a pulley 5 fixed on the end of the shaft 4 extending toward the front side of the housing 3; a rotor 6 fixed on the shaft 4 and housed in the housing 3; fixed...
Embodiment approach 2
[0053] Picture 12 It is a cross-sectional view of a main part for explaining the fixing structure of the stator of the vehicle alternator according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0054] in Picture 12 In this case, the insulating film 29 covers the outer peripheral surface of the stator core 15.
[0055] The other structure is the same as that of the first embodiment described above.
[0056] In this second embodiment, similar to the above-mentioned first embodiment, the strip-shaped magnetic thin plates 31 are laminated and integrated to form a rectangular parallelepiped laminated core 32, and the laminated core 32 with the winding assembly 40 is bent into a cylindrical shape. Both ends of the laminated core 34 bent into a cylindrical shape are face-to-face and welded to form the stator core 15. Next, an insulating resin made of, for example, an epoxy resin is applied to the outer circumferential surface of the stator core 15 to form the stator core 15 in ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0061] Figure 13 It is a cross-sectional view of a main part for explaining the fixing structure of the stator of the vehicle alternator according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0062] in Figure 13 In the stator core 15A, for example, a strip-shaped magnetic thin plate 31 with a plate thickness (t1) of 0.3 mm is laminated a predetermined number of sheets, and then a strip-shaped magnetic thin plate 31A with a plate thickness (t2) of 1.0 mm is laminated on The two ends of the laminated body of the band-shaped magnetic thin plates 31 are welded into a single body of the laminated body of the band-shaped magnetic thin plates 31 and 31A, then bent into a cylindrical shape, and welded to the abutting portions of the both end surfaces.
[0063] The other structure is the same as that of Embodiment 1 described above.
[0064] In the third embodiment, the strip-shaped magnetic thin plates 31A made of thick plates are arranged at both ends of the laminated body that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com