Controlled steering of a flexible needle
A technology to control system, tissue properties, applied in trocars, surgical navigation systems, diagnostics, etc., can solve problems such as computational complexity, not allowing real-time simulation and control of needle insertion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
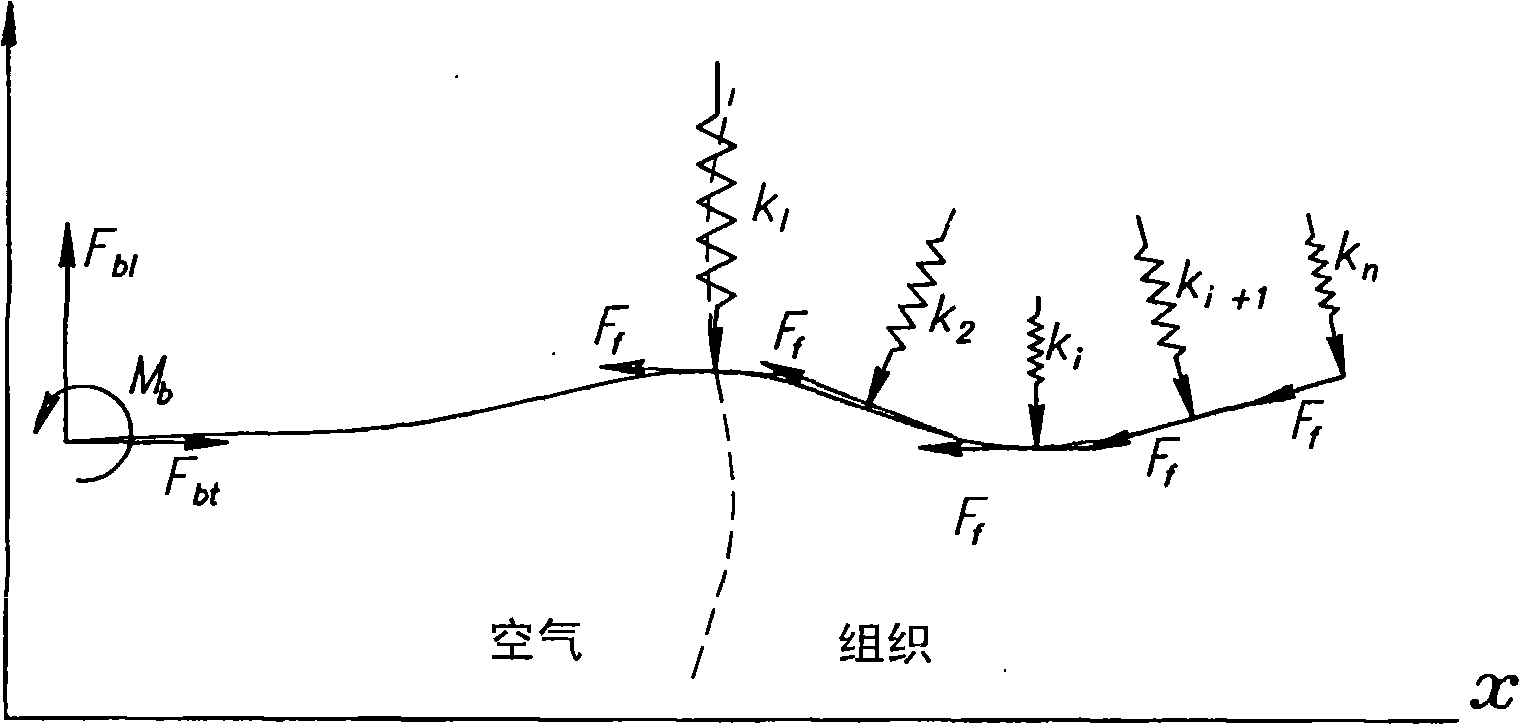
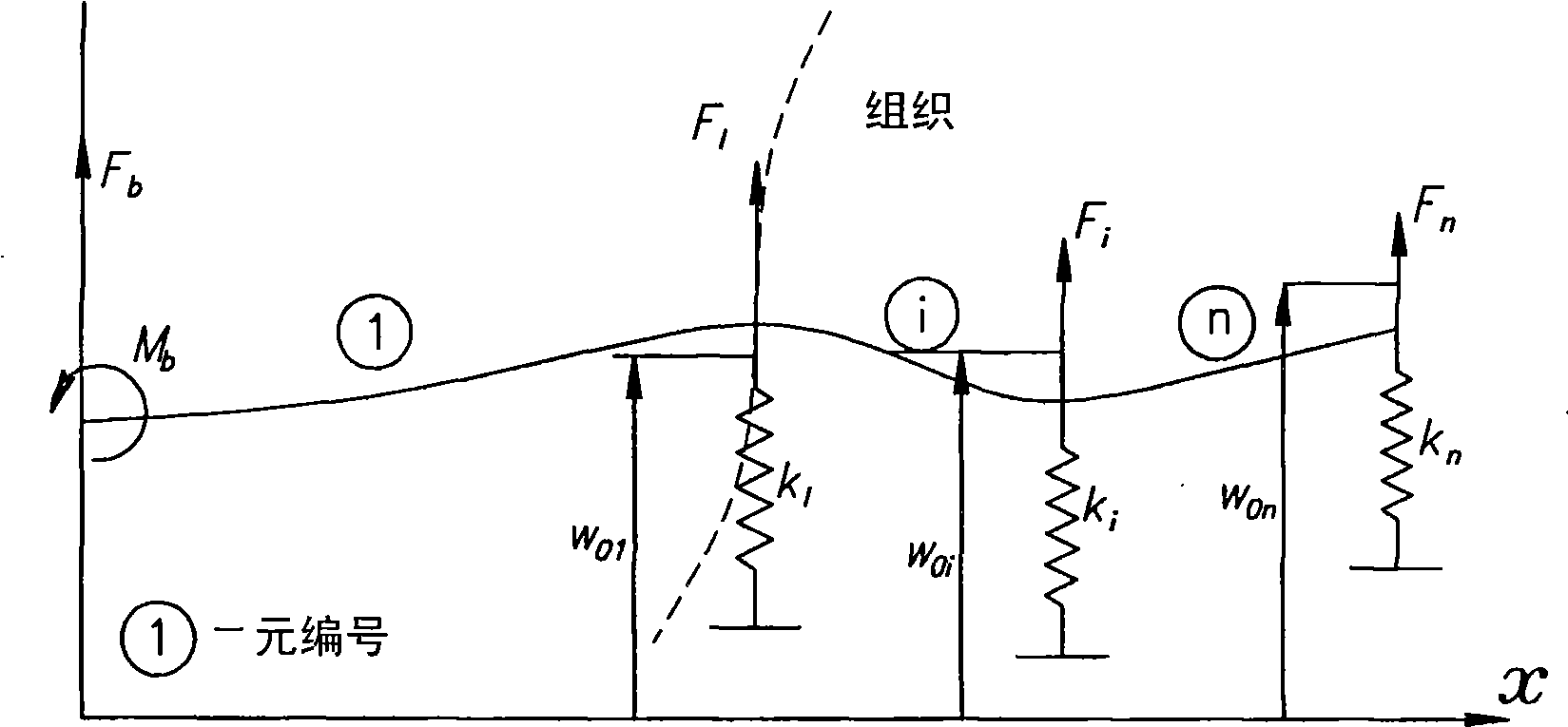
[0062] now refer to figure 1 , which schematically shows the tissue and needle interaction model represented by a series of distributed virtual springs with coefficient k 1 、k 2 、…k n , as used for the first time in the above-mentioned article MICCAI2003 published by the present inventors. exist figure 1 , the tissue surface is indicated by a dashed line. The model of flexible needle movement is based on the assumption of quasi-static motion; the needle is in equilibrium at each step. It is known that the deflection and strain of the needle are nonlinearly related due to the interaction with the biological soft tissue. However, for small displacements it is reasonable to assume a linear lateral force response. Therefore, the tissue force acting on the needle is modeled as a lateral virtual spring distributed along the curve of the needle and a friction force F tangential to the needle f The combination. Since the elastic modulus of the tissue changes according to the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com