Mixed vibration control device and method based on negative stiffness and variable damping and application
A negative stiffness and variable technology, applied in the direction of vibration suppression adjustment, non-rotational vibration suppression, shock absorbers, etc., can solve the problems of unavailable, high reliability, low cost, etc., and achieve high reliability without affecting stability , low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
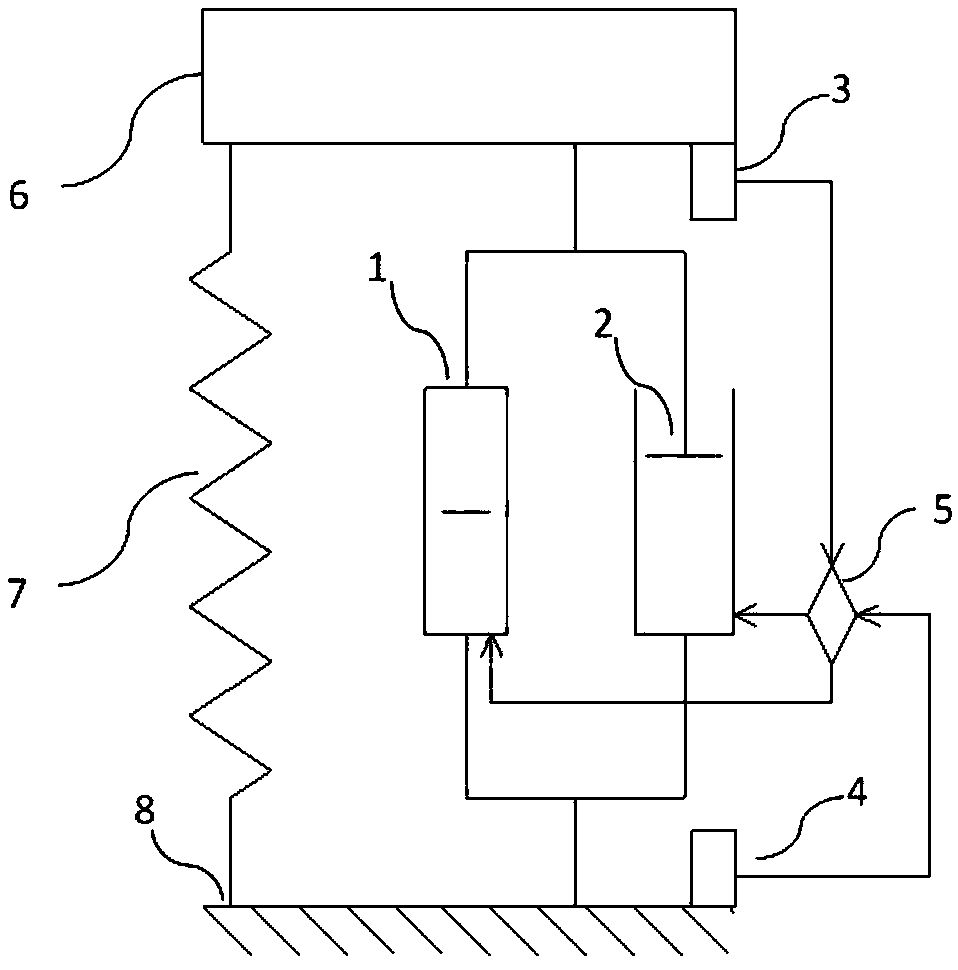
[0090] Taking the vibration isolation table as an example, the vibration isolation table is simulated as a single-degree-of-freedom system, and the present invention is installed in the vibration isolation table, arranged in parallel with the support spring 7 of the vibration isolation table, one end is connected to the sprung element 6, and the other end is connected to the base 8 .
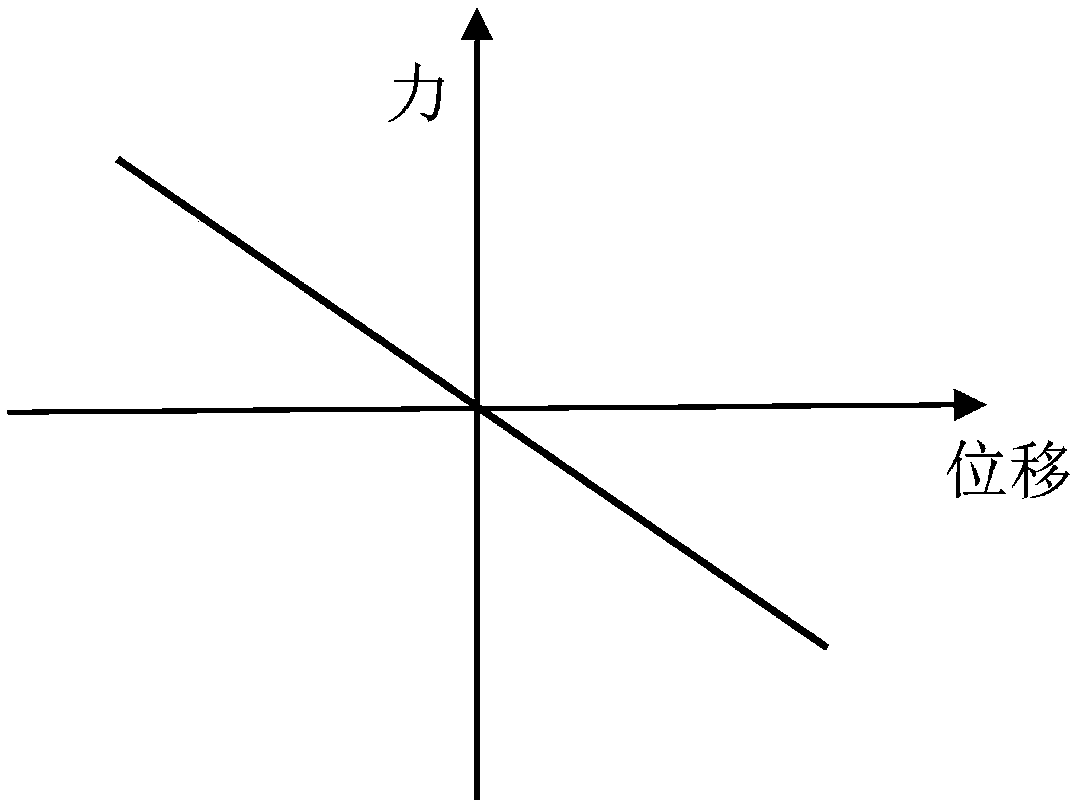
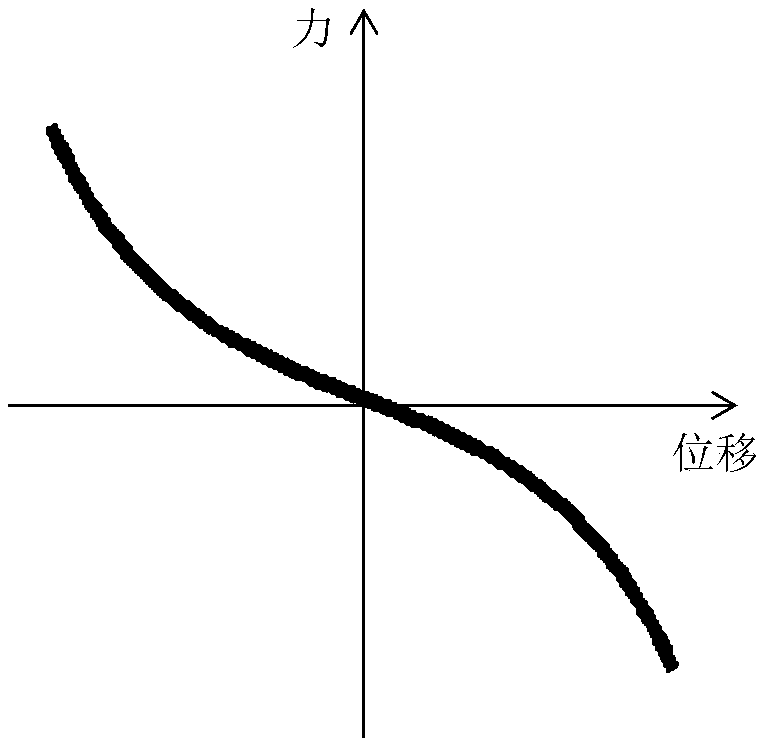
[0091] The relevant parameters are: the sprung element 6 is 1 kg, the stiffness of the supporting spring 7 is 3000N / m, the stiffness coefficient of the negative stiffness element 1 is -2400N / m, the minimum damping coefficient that the variable damping element 2 can provide is 2Ns / m, the maximum The damping coefficient is 50Ns / m, the control algorithm is a linear quadratic regulator (LQR), and the base input excitation is velocity white noise.
[0092] Figure 12 It is the absolute vibration velocity time course diagram of the sprung element 6 of the vibration isolation table, comparing the vibr...
Embodiment 2
[0096] The invention can also be applied to vehicle suspensions. refer to Figure 19 , the vehicle is simulated as a commonly used 1 / 4 vehicle dual-degree-of-freedom system, the hybrid vibration control device of the present invention is installed in the vehicle suspension, so that it is arranged in parallel with the suspension system of the vehicle, the vehicle body 9, the vehicle chassis 10. The vehicle tires 11 are installed under the vehicle chassis 10, and the support spring 7 for reducing the vibration effect and the hybrid vibration control device of the present invention are installed between the vehicle chassis 10 and the vehicle body 9.
[0097] The relevant parameters are: the mass of the vehicle body 9 is 504.5kg, the mass of the vehicle chassis 10 is 62kg, the stiffness of the suspension support spring 7 is 13.1kN / m, the stiffness coefficient between the vehicle chassis 13 and the ground is 252kN / m, and the input excitation is velocity white noise. The control a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Stiffness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Stiffness coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Stiffness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com