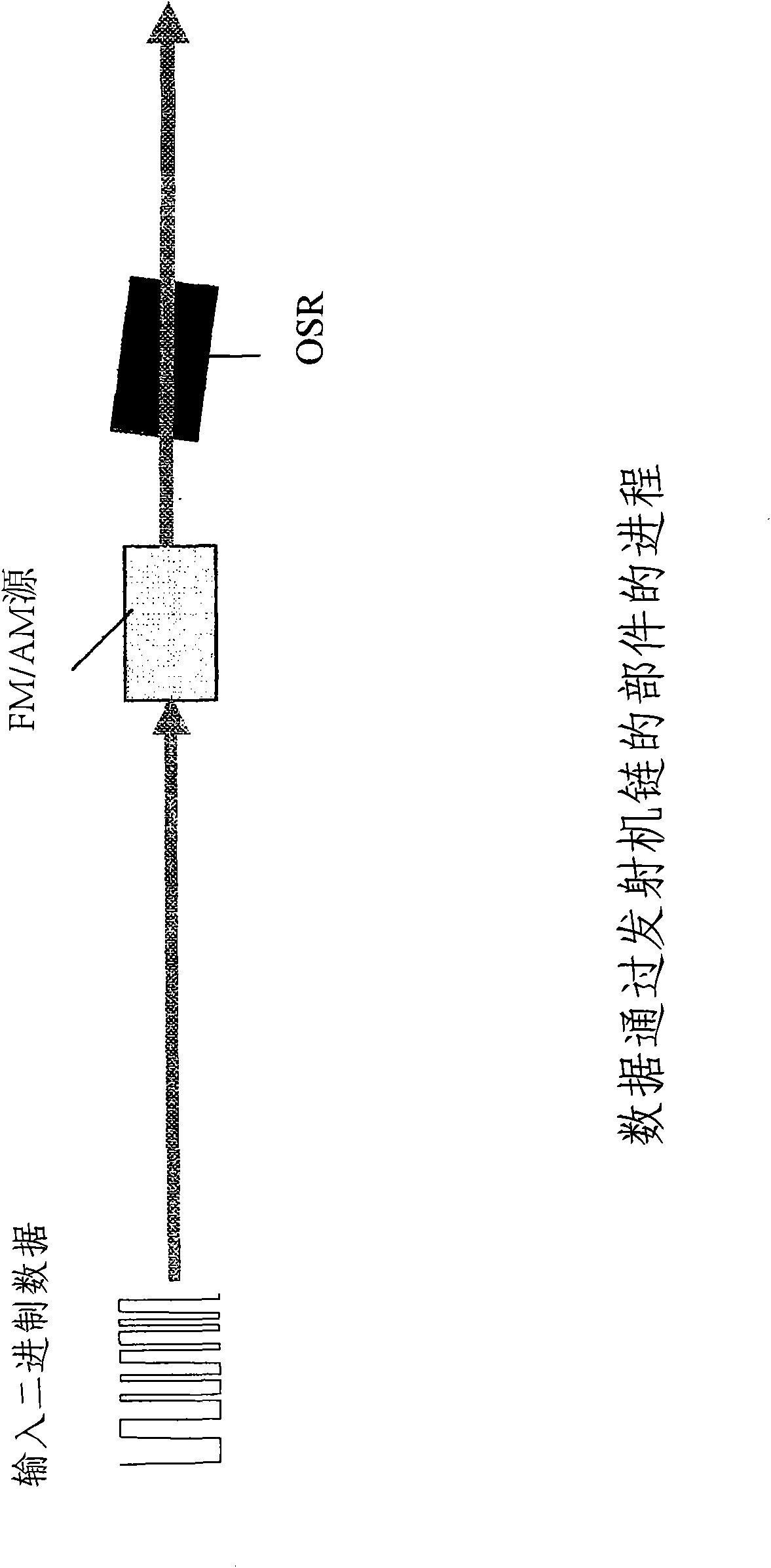
Optical transmission using semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA)
A technology of optical amplifiers and semiconductors, applied in the field of frequency modulation of laser diodes, chirp management and direct modulation of lasers, which can solve problems such as signal distortion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] Intracavity loss modulation and / or intracavity phase modulation to improve signal transmission
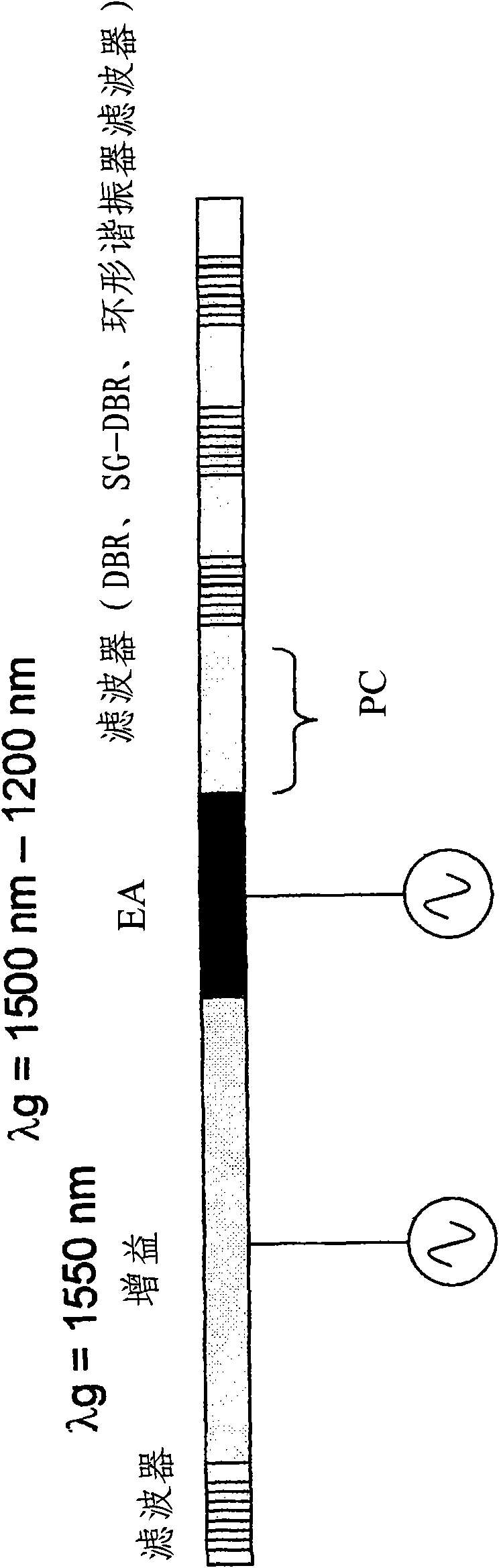
[0062] figure 2 A preferred embodiment of the invention is shown in which an electroabsorption (EA) modulator is integrated inside a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser cavity. The EA section is reverse biased. Applying a reverse bias voltage to the EA increases cavity losses, which increases the threshold gain for lasing. This increases the threshold carrier density, which results in a blue shift of the lasing frequency, ie provides frequency modulation.
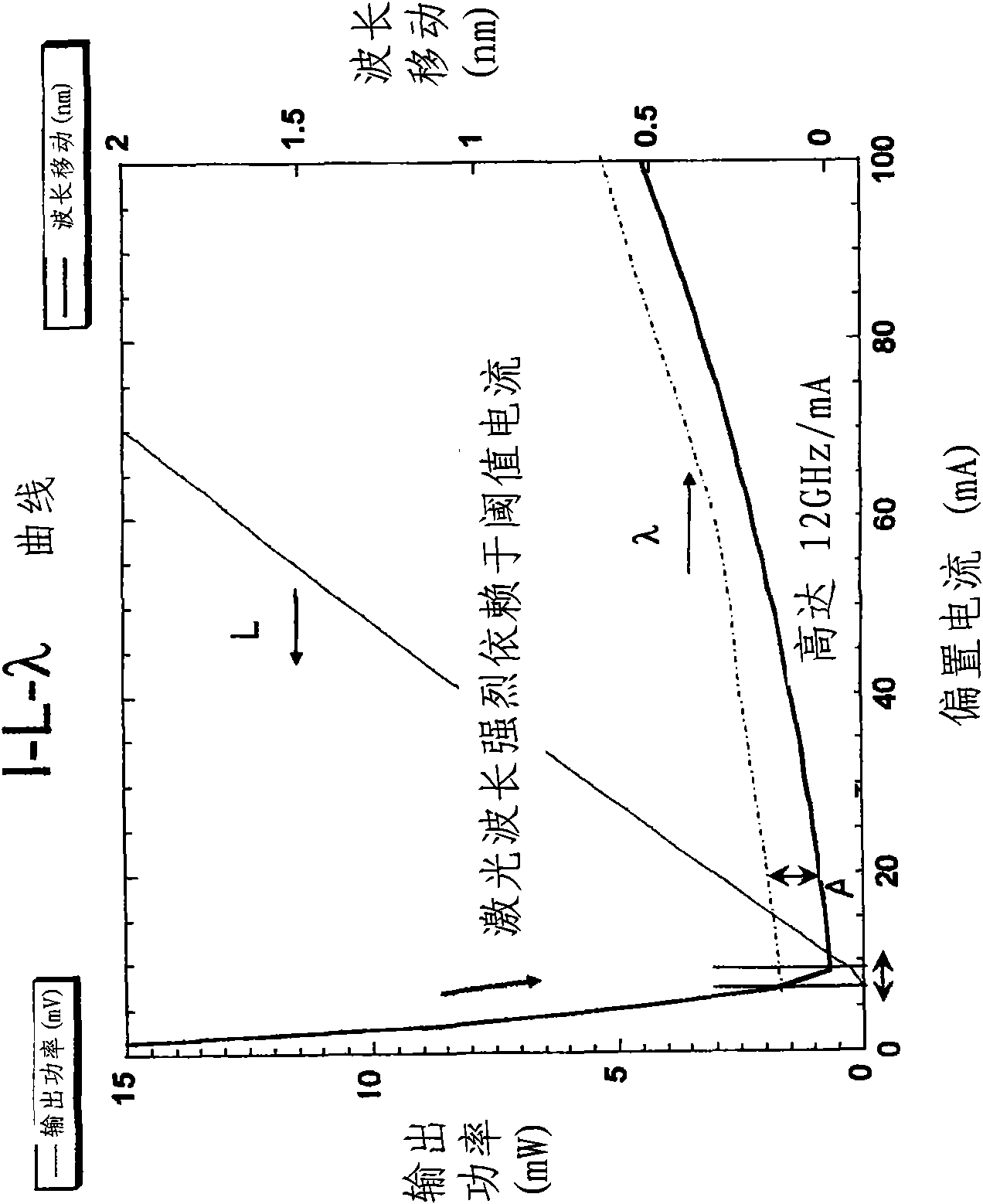
[0063] by reference image 3 , to be able to understand the larger FM efficiency produced by loss modulation, image 3 Lasing wavelength is shown as a function of current injected into a traveling wave (CW) laser. It is known that the laser wavelength of a CW semiconductor laser depends on a threshold current. When more carriers are injected into the laser below the threshold, the wavelength is blue-shifted. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com