Method for fast paving urban road surfaces and special reinforced concrete block
A technology for reinforced concrete and road pavement, which is applied to roads, roads, and pavements paved with prefabricated blocks. Short laying cycle and the effect of reducing water accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0025] Specific implementation mode one: as Figure 1-12 As shown, the urban road pavement rapid laying method described in this embodiment is realized according to the following steps:
[0026] Step 1, pre-preparing a large number of reinforced concrete blocks (regular hexagonal reinforced concrete blocks) as required;
[0027] Step two, leveling the roadbed;
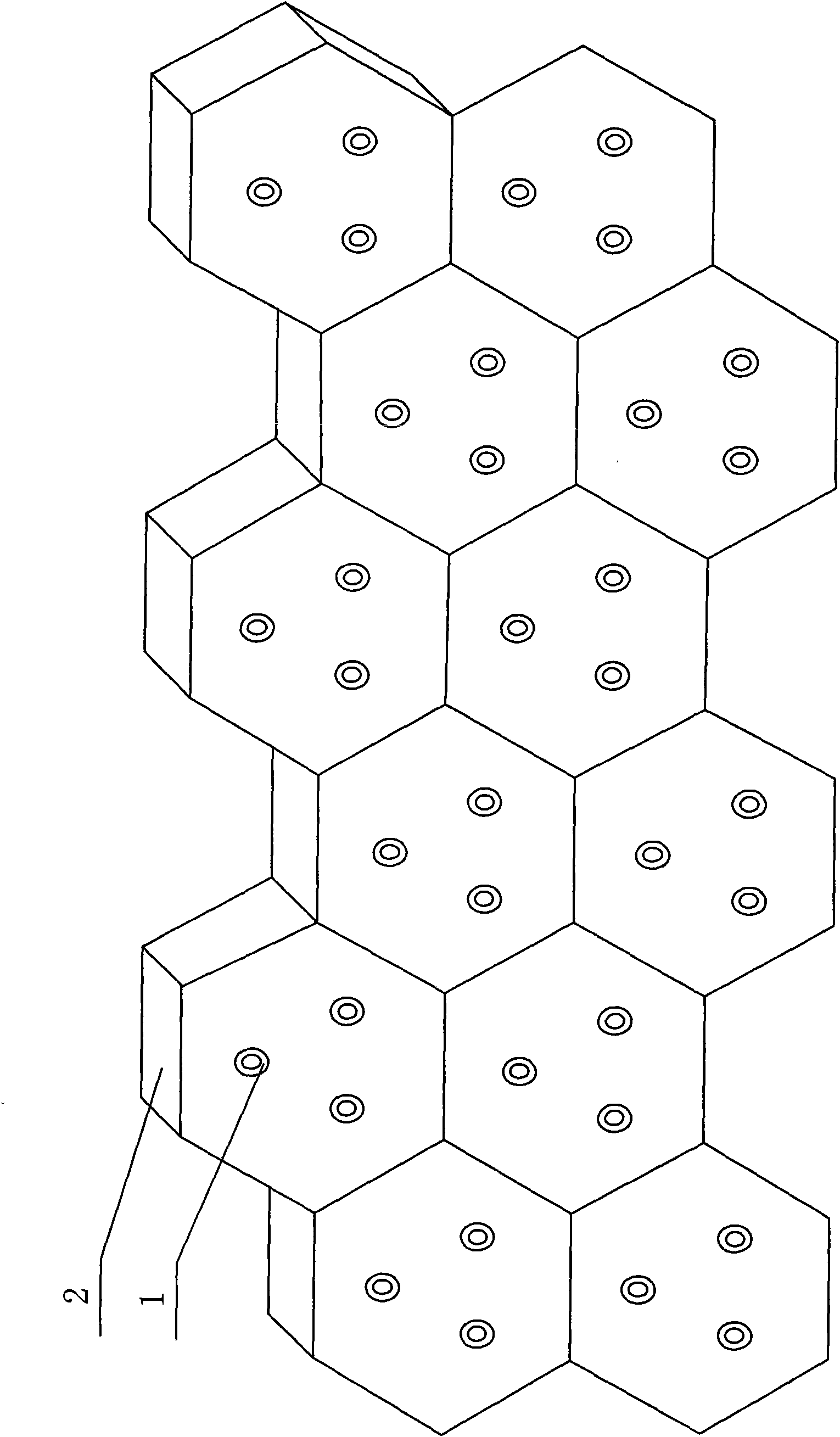
[0028] Step 3: Lay the reinforced concrete blocks one by one on the leveled roadbed with lifting equipment (crane), and the upper surfaces of several reinforced concrete blocks are spliced together to form the road surface.
[0029] Issues to be aware of when laying pavement with reinforced concrete blocks:
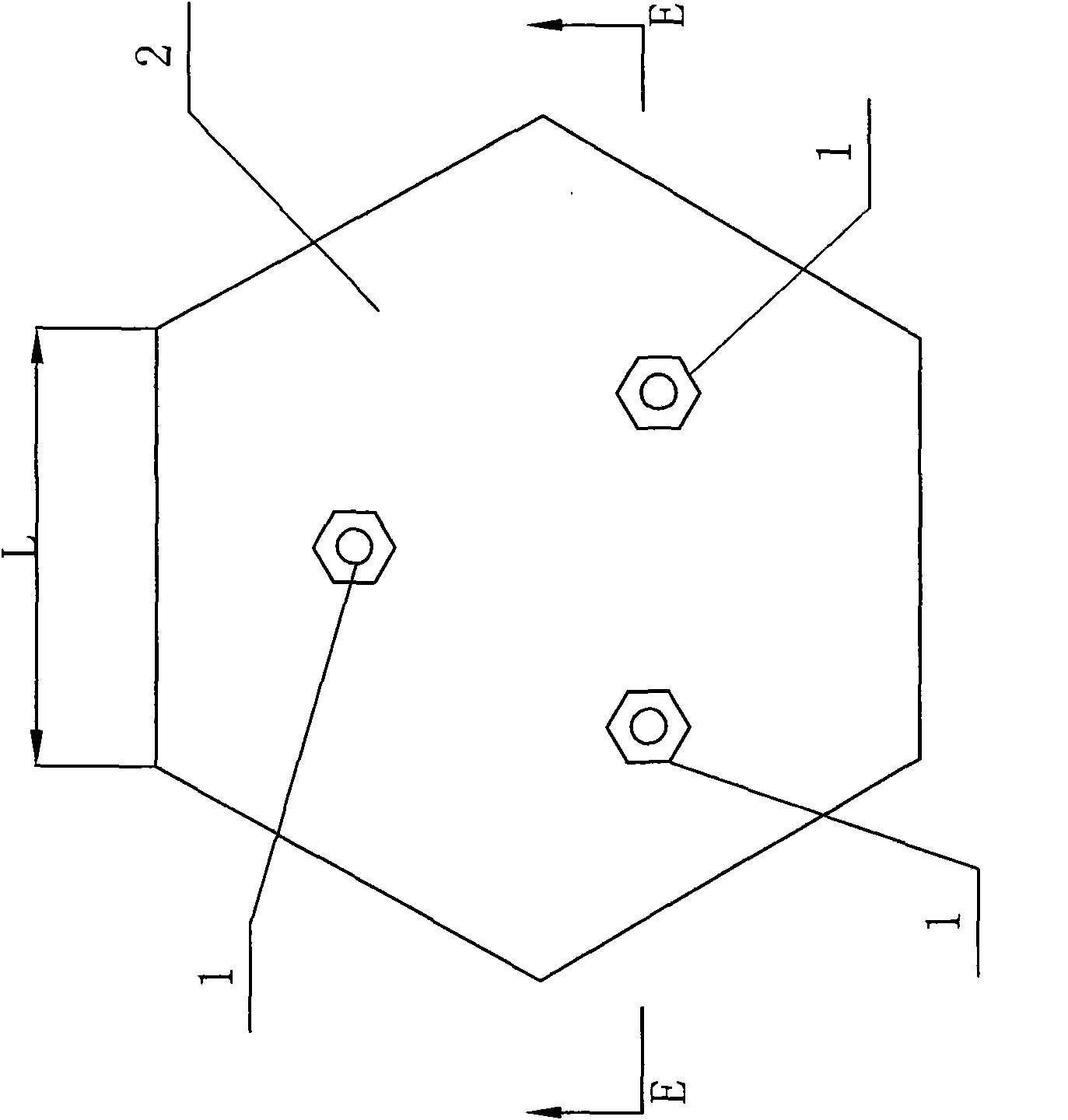
[0030] 1. Shape of reinforced concrete block
[0031] The shape of the reinforced concrete block is preferably a regular hexagon, because the road surface will bear a large force when the car brakes during driving. If a hexagonal reinforced concrete block is used, it can be guaranteed that the force borne by...
specific Embodiment approach 2
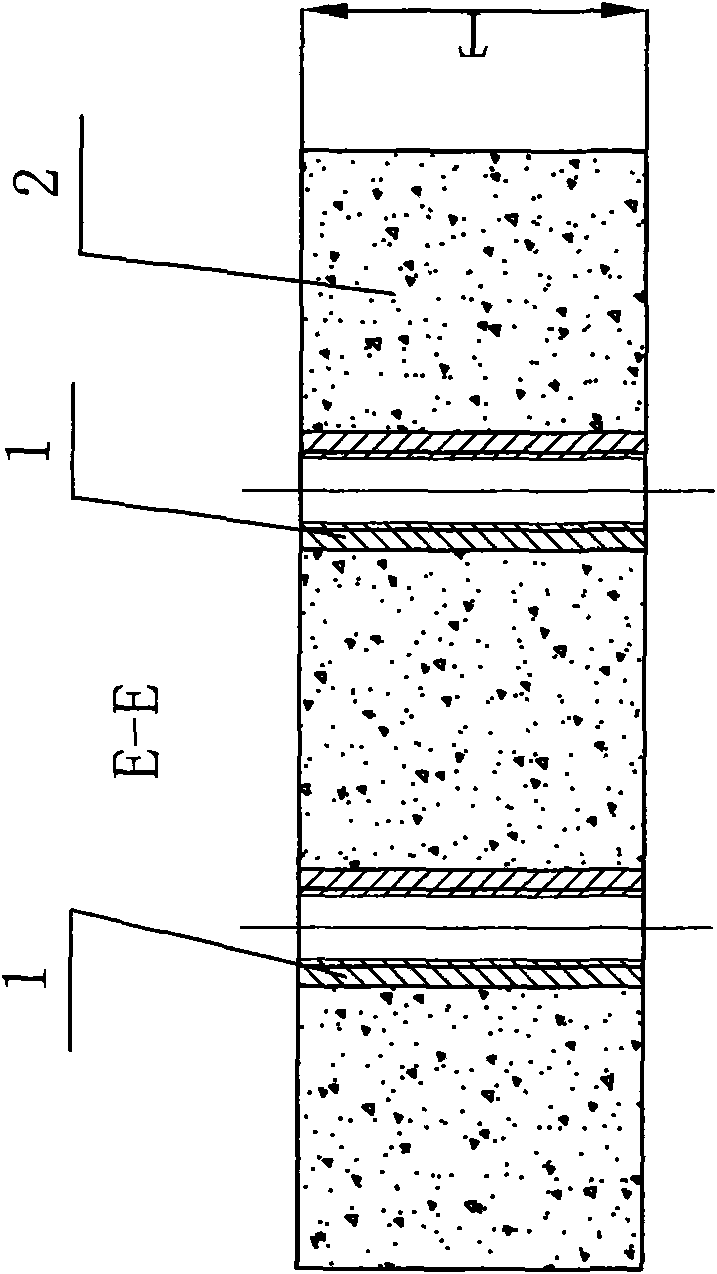
[0037] Specific implementation mode 2: In step 3 of this implementation mode, a gap of 5-20 mm is left between every two reinforced concrete blocks. When installing reinforced concrete blocks, a gap of 5-20 mm should be maintained between every two reinforced concrete blocks. This gap can compensate for the manufacturing error of the reinforced concrete blocks and reduce the constraints between the reinforced concrete blocks during maintenance. Force to facilitate the lifting of damaged reinforced concrete blocks. In addition, this gap also facilitates the infiltration of rainwater and reduces water accumulation on the road surface; it can also ensure that the road surface will not bulge due to thermal expansion and contraction. Other steps are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0038] Specific implementation mode three: as Figure 1-12 As shown, at least three nuts 1 for lifting rings are preset on the main body 2 of the special reinforced concrete block for realizing the method described in the first embodiment described in this embodiment, and the nuts 1 for the at least three lifting rings are connected with the inside of the reinforced concrete block. The steel bars are welded together, and the two ends of the nut 1 for each suspension ring are exposed outside.
[0039] The present invention is to lay hexagonal reinforced concrete blocks produced by the factory according to certain rules on the already leveled roadbed. A plurality of hexagonal reinforced concrete blocks are combined to form a large plane, which is formed by continuing to extend and lay. The pavement of the entire road, such as image 3 shown. image 3 The side length and thickness of each regular hexagon can be appropriately changed according to the lifting capacity of the work...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com