Method for optionally cutting off fault point of double branch circuits at low voltage side of transformer
A technology for transformer low-voltage side and branch lines, applied in the direction of emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of expanding the scope of ground fault power outages, reducing the reliability of power supply for users, and damaging the interests of users, so as to reduce the scope of removal and reduce The effect of improving the range of blackouts and improving the reliability of power supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The embodiments described in the present invention are illustrative, rather than limiting, so the present invention is not limited to the embodiments described in the specific implementation, any other implementation obtained by those skilled in the art according to the technical solution of the present invention way, also belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
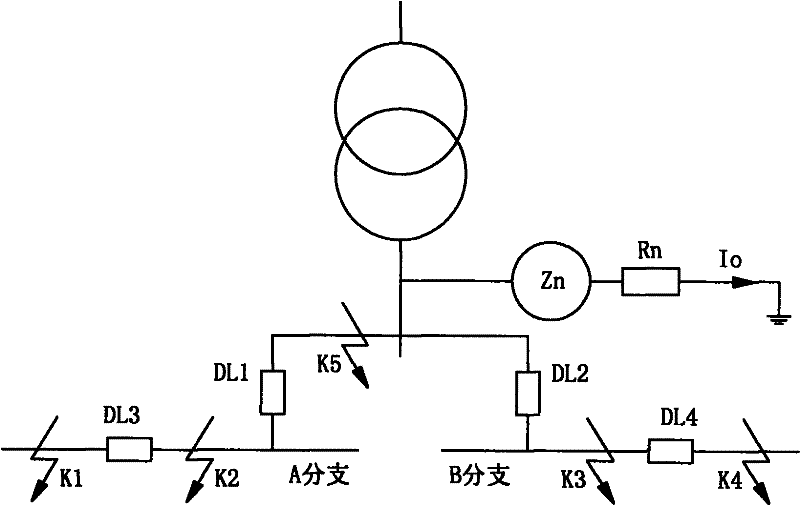
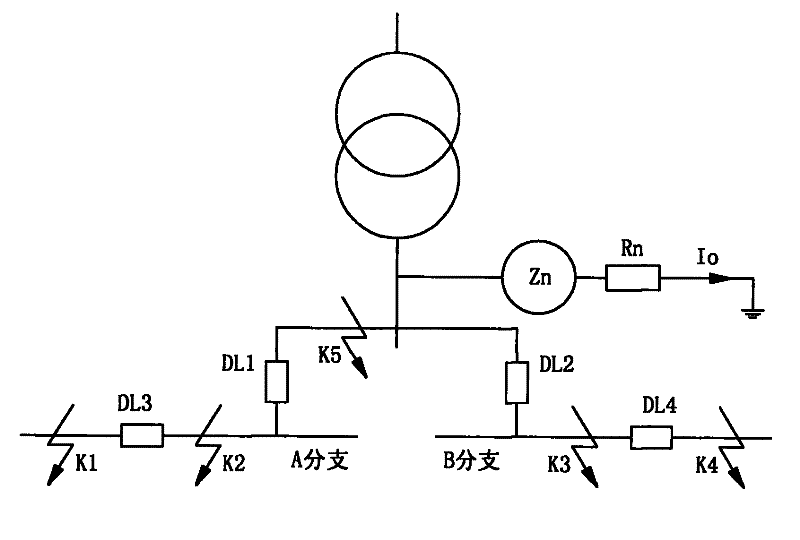
[0021] The current common transformer low-voltage side line structure is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the low-voltage side has two branches, branch A and branch B. When a fault occurs at any point K1 to K5 in the figure, the existing protection scheme will cut off branch A and branch B in turn, and cannot intelligently judge the fault. point.
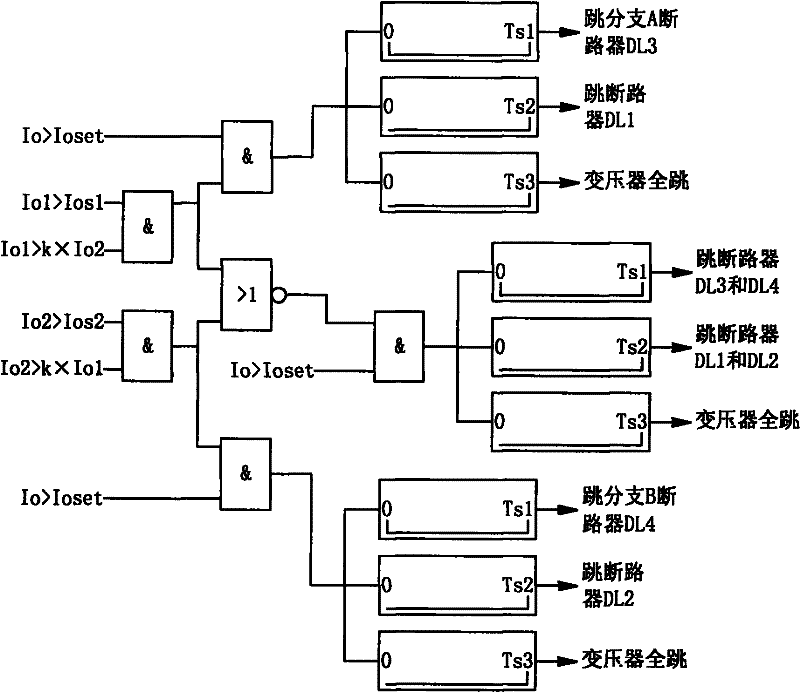
[0022] The invention provides a method for selectively removing the fault point in the double-branch line on the low-voltage side of the transformer. The main steps are: when a ground fault occurs, first measure the ground transformer Z N The zero-s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com