Cement compositions comprising humic acid grafted fluid loss control additives and methods of using them
A technology of cement composition and additives, applied in drilling compositions, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory properties and inability to provide ideal levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
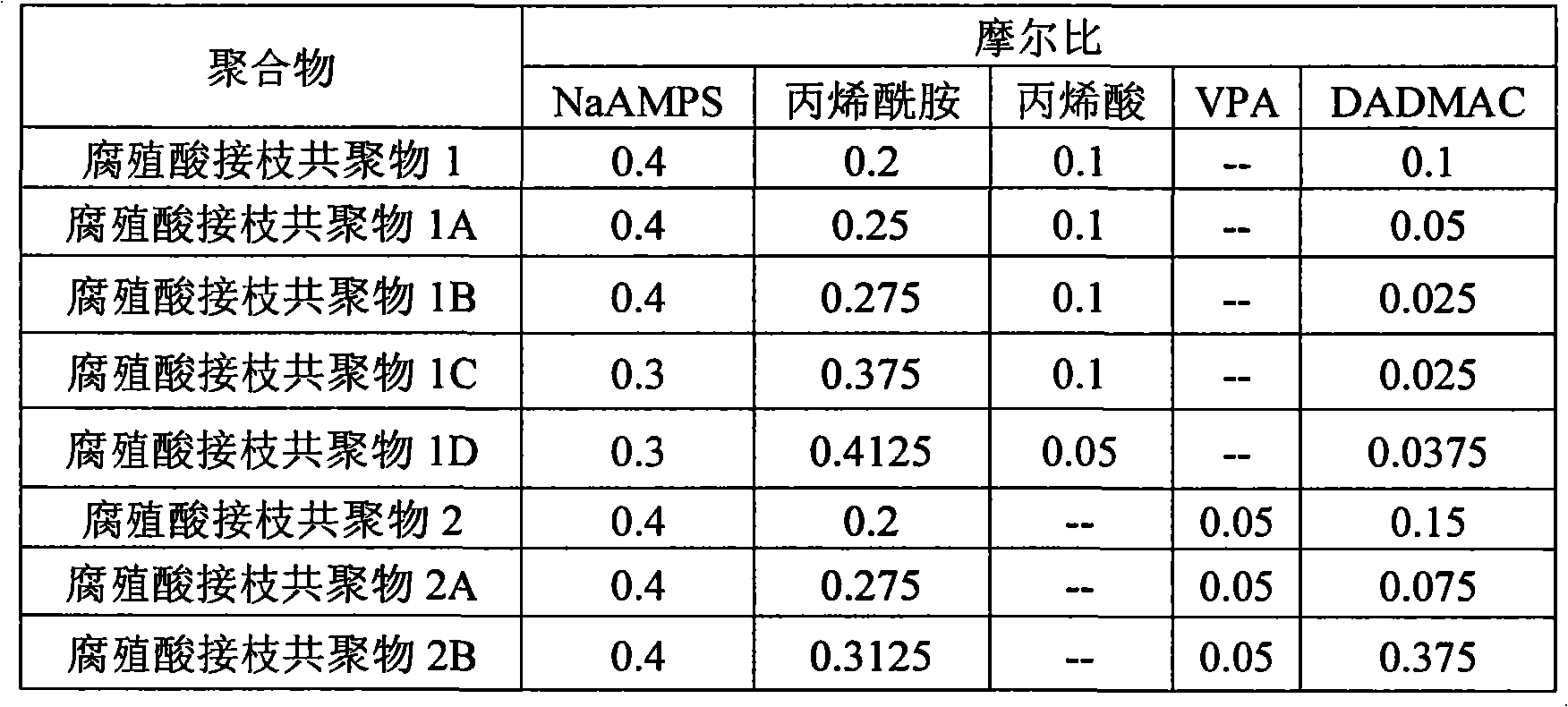
[0033] A copolymer comprising a humate backbone grafted with at least four monomers selected from the following procedure is prepared according to the following procedure: acid, acrylamide, acrylic acid, VPA, DADMAC and their salts. First, sodium humate, water, defoamer, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) were added to the reactor vessel. Then to the container, add 58% by weight of Sodium salt solution of acid, 48% by weight solution of acrylamide, acrylic acid (or VPA as described in the table below), and DADMAC. The mixture was heated and maintained at a temperature of about 158°F (70°C) for one hour while purging with nitrogen. After one hour, ammonium persulfate was added to initiate polymerization. The mixture was maintained at about 158°F (70°C) for two hours. After two hours, sodium metabisulfite was added and the mixture was allowed to cool. When the mixture reached room temperature, 50% sodium hydroxide solution was added to adjust the pH range to about...
Embodiment 2
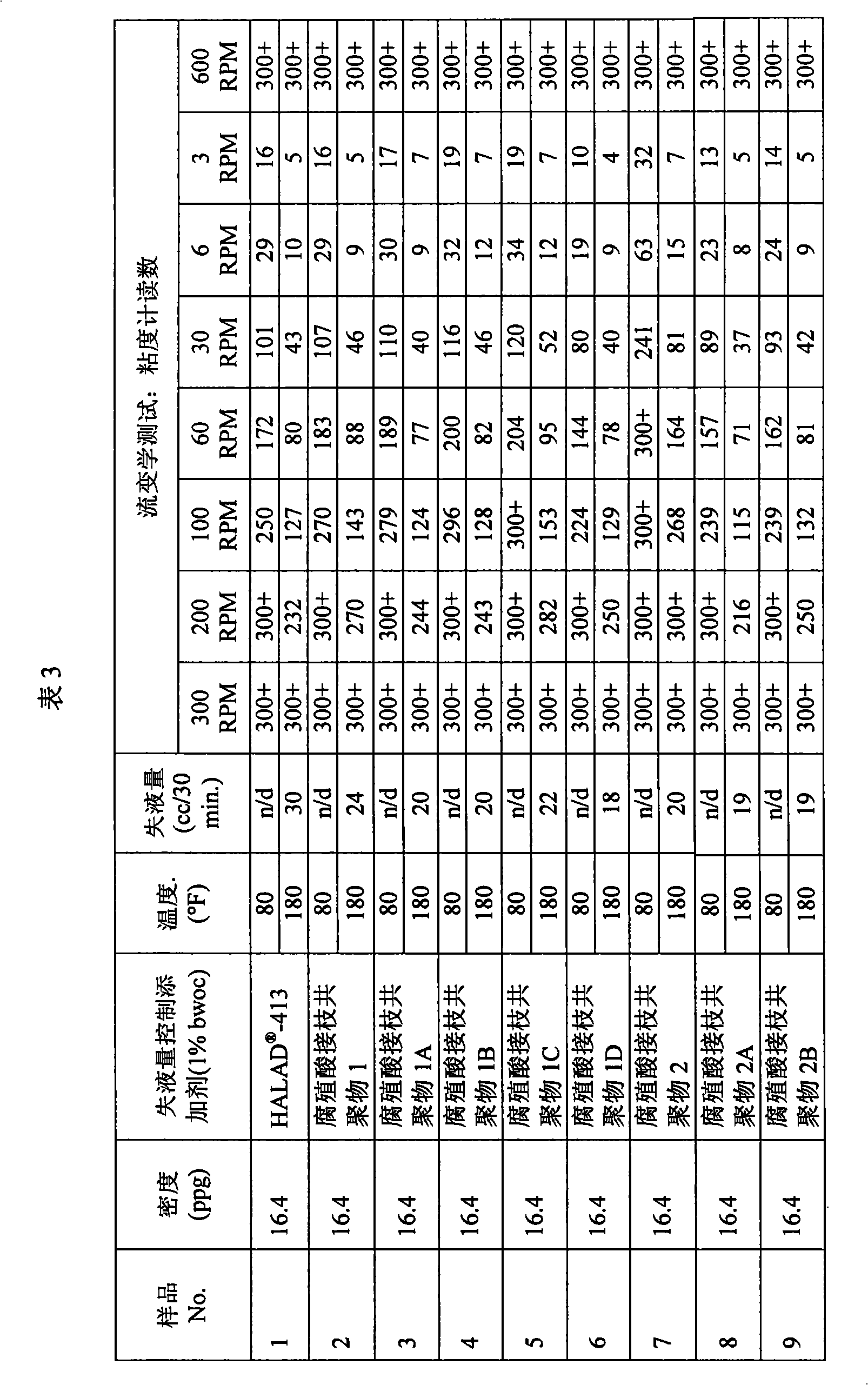
[0034] The following series of tests were conducted to compare the performance of exemplary embodiments of the fluid loss control additives of the present invention to those described in U.S. Pat. No. 4,676,317 -413 Fluid Loss Additive Comparison. Accordingly, a sample cement composition was prepared comprising the following components: Portland Class H cement, -12 retarder (0.6% bwoc), free water control additive (0.1% bwoc), fluid loss control additive (1% bwoc) and sufficient water to provide a density of 16.4 ppg. -12 Retarder is a cement set retarder available from Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. Additionally, the free water control additive used was hydroxyethyl cellulose from Halliburton Energy Services, Inc.
[0035] Regarding fluid loss control additives, sample No.1 contains -413 fluid loss additive as a fluid loss control additive. Sample Nos. 2-9 contained an exemplary embodiment of the fluid loss control additive of the present invention having a humic a...
Embodiment 3
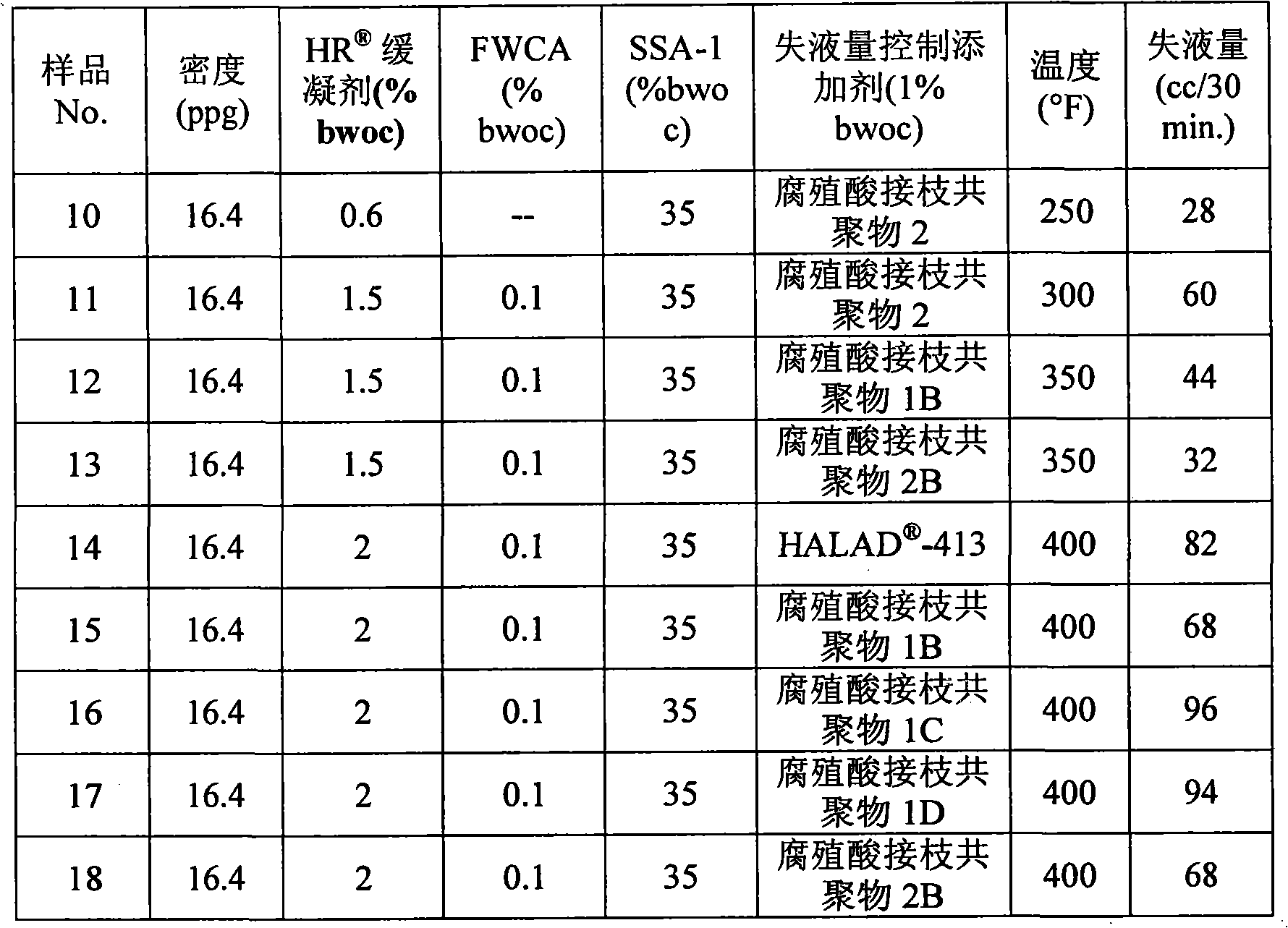
[0038] The following additional tests were performed at elevated temperatures to compare the performance of exemplary embodiments of the fluid loss control additives of the present invention with -413 Fluid Loss Additive Comparison. Accordingly, a sample cement composition was prepared comprising the following components: Portland Class H cement, -12 set retarder, free water control additive, SSA-1 strength stabilizer, fluid loss control additive and sufficient water to provide a density of 16.4 ppg. The free water control additive used was hydroxyethyl cellulose from Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. Sample No. 10 contained no free water control additive. SSA-1 is a strength stabilizer (crystalline silica) from Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. The specific fluid loss control additives contained in each sample are listed in the table below.
[0039] After preparation, perform a fluid loss test at 1,000 psi and the temperature listed in the table below. For this series o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com