Passive millimeter wave imaging system
A millimeter-wave imaging, passive technology, applied in radio wave measurement system, radio wave reflection/re-radiation, utilization of re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems of low image resolution, long imaging time, poor real-time performance, etc., and achieve image resolution High efficiency, short imaging time, and reduced system cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
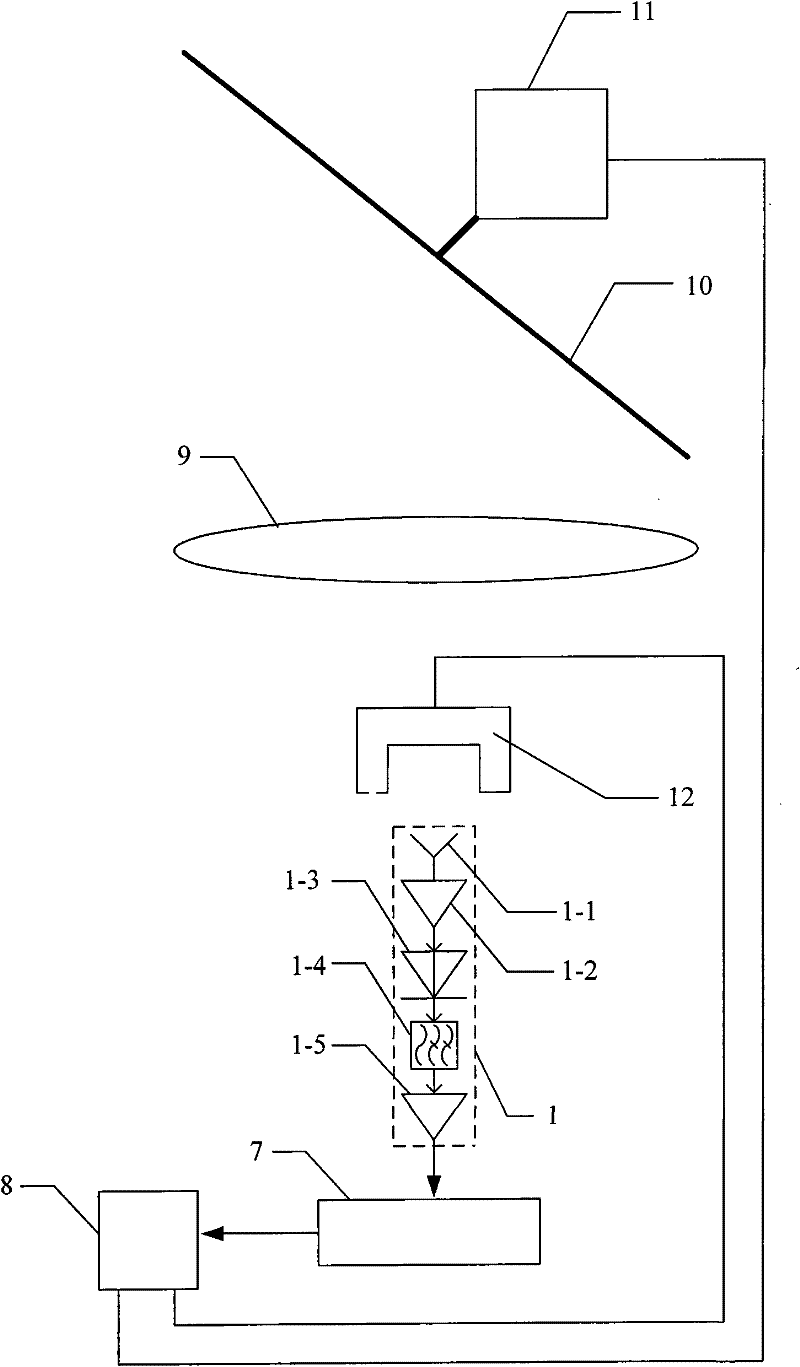
[0007] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Illustrate this specific embodiment, passive millimeter-wave imaging system, it comprises dielectric lens 9 and metal reflection plate 10, passive millimeter-wave imaging system also comprises radiometer system 1, digital acquisition circuit 7 and computer 8; Said radiometer system 1 is made up of A receiving antenna 1-1, a millimeter-wave band high-gain low-noise amplifier 1-2, a high-sensitivity square-law detector 1-3, a low-pass filter 1-4, and a low-frequency amplifier 1-5 are composed; the receiving antenna 1-1 The signal output end is connected to the signal input end of the millimeter-wave band high-gain low-noise amplifier 1-2, and the signal output end of the millimeter-wave band high-gain low-noise amplifier 1-2 is connected to the signal input end of the high-sensitivity square law detector 1-3 Connection, the signal output end of the high-sensitivity square law detector 1-3 is connected with the signal in...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0012] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the passive millimeter-wave imaging system described in Embodiment 1 is that it also includes a stepping motor 11 with a controller, and the stepping motor 11 with a controller The shaft of the rotor is fixedly connected with the center of the metal reflector 10; the stepper motor control signal output end of the computer 8 is connected with the control signal input end of the stepper motor 11 with the controller. The stepping motor 11 with a controller is used to drive the metal reflector 10 to rotate.
[0013] The metal reflector in this embodiment can change the propagation direction of the electromagnetic wave by using the reflection effect of the metal on the electromagnetic wave, and use the stepper motor 11 to drive the metal reflector 10 to rotate around the axis to complete the longitudinal scanning of the target to be measured. The side of the metal reflector 10 facing the lens should have relatively hig...
specific Embodiment approach 3
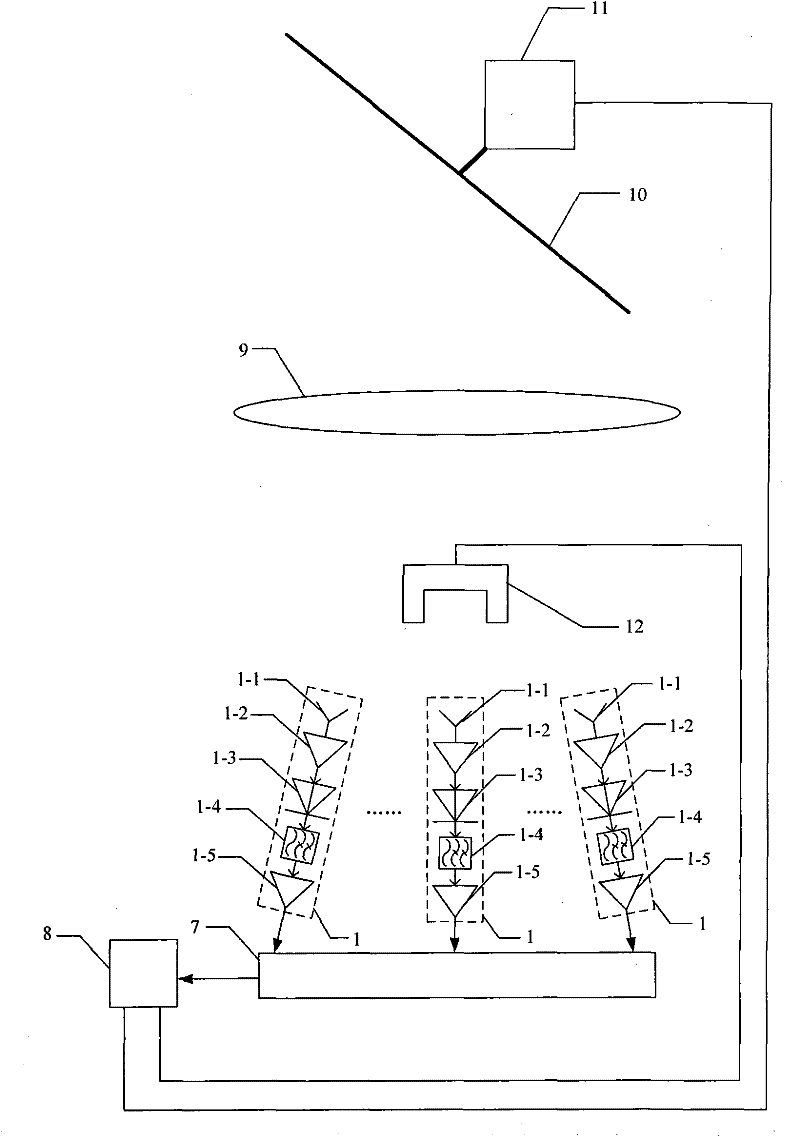
[0014] Specific implementation mode three, combination figure 2 This specific embodiment is described. The difference between this specific embodiment and the passive millimeter-wave imaging system described in the first or second specific embodiment is that the radiometer system 1 is a multi-group radiation array arranged according to the spatial Nyquist sampling law. meter system 1, and the receiving antenna 1-1 of each radiometer system 1 points to the center of the dielectric lens 9, and the phase center of the receiving antenna 1-1 of each radiometer system 1 is to the center of the illumination surface of the dielectric lens 9 The points are all at the same distance.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com