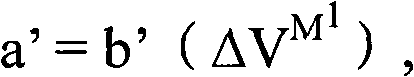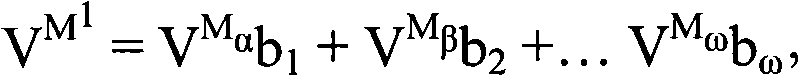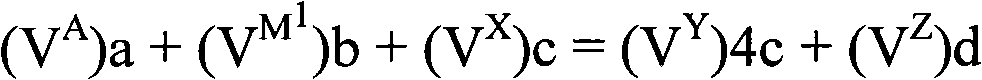Electrodes comprising mixed active particles
A technology of electrodes and mixtures, applied in battery electrodes, non-aqueous electrolyte battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient voltage, insufficient charging capacity, and uneconomical
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0187] After the preparation of the first step, the second step of the reaction is continued to react the lithium metal phosphate (provided in the first step) with a lithium salt, preferably lithium fluoride (LiF). LiF is mixed with lithium metal phosphate in proportion to provide a lithiated transition metal fluorophosphate product. Lithiated transition metal fluorophosphates have the ability to donate lithium ions to the electrochemical potential.
[0188] In addition to the previously described two-step method, a one-step reaction method can also be used to prepare this preferred material of the present invention. In one method of the invention, the starting materials are mixed thoroughly and then reacted together when heating is initiated. Typically, the mixed powders are compressed into pellets. The pellets are then heated to high temperature. This reaction can be performed under an air atmosphere or a non-oxidizing atmosphere. In another approach, lithium metal phosp...
Embodiment 1
[0240] Contains LiFe 0.9 Mg 0.1 PO 4 and LiCoO 2 The blends of the invention are prepared as follows. Each active material is prepared separately and then mixed to form a blend of active material particles for use in the electrode.
(a) The first active material LiFe 0.9 Mg 0.1 PO 4 was prepared as follows. The following sources comprising Li, Fe, Mg and phosphate were provided, containing the respective elements in a molar ratio of 1.0:0.9:0.1:1.0.
0.50 mole Li 2 CO 3 (mol.wt.73.88g / mol), 1.0 mole Li 36.95g
0.45 mol Fe 2 o 3 (159.7g / mol), 0.9 mole Fe 71.86g
0.10 mole Mg(OH) 2 (58g / mol), 0.1 mole Mg 5.83g
1.00 moles (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 (132g / mol), 1.0 mole phosphate 132.06g
0.45 moles of elemental carbon (12g / mol) (=100% mass excess) 5.40g
[0241] The above starting materials were mixed and ball milled to mix the particles. Afterwards, the particle mixture is pelletized. The pelletized mixture was heated in a furnace at 750° C. for 4-20 hours in an argon...
Embodiment 2
[0246] Contains LiCo 0.8 Fe 0.1 Al 0.025 Mg 0.05 PO 3.975 f 0.025 and LiFe 0.95 Mg 0.05 PO 4 The blends of the invention are prepared as follows. Each active material is prepared separately and then mixed to form a blend of active material particles for use in the electrode.
(a) The first active material LiCo 0.8 Fe 0.1 Al 0.025 Mg 0.05 PO 3.975 f 0.025 was prepared as follows. The following sources were provided comprising Li, Co, Fe, Al, Mg, phosphate and fluoride, containing the respective elements in a molar ratio of 1.0:0.8:0.1:0.025:0.05:1.0:0.025.
0.05 mole Li 2 CO 3 (mol.wt.73.88g / mol), 0.1 mole Li 3.7g
0.02667 mol Co 3 o 4 (240.8g / mol), 0.08 mole Co 6.42g
0.005 mol Fe 2 o 3 (159.7g / mol), 0.01 mole Fe 0.8g
0.0025 mol Al(OH) 3 (78g / mol), 0.0025 mole Al 0.195g
0.005 mole Mg(OH) 2 (58g / mol), 0.005 mole Mg 0.29g
0.1 mole (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 (132g / mol), 0.1 mole phosphate 13.2g
0.00125 mol NH 4 HF 2 (57g / mol), 0.0025 mole F 0.071g
0.2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com