Methods and compositions for selecting soybean plants resistant to phytophthora root rot
A soybean plant, resistant technology, applied in the field of plant breeding and disease resistance, can solve the problem of deficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
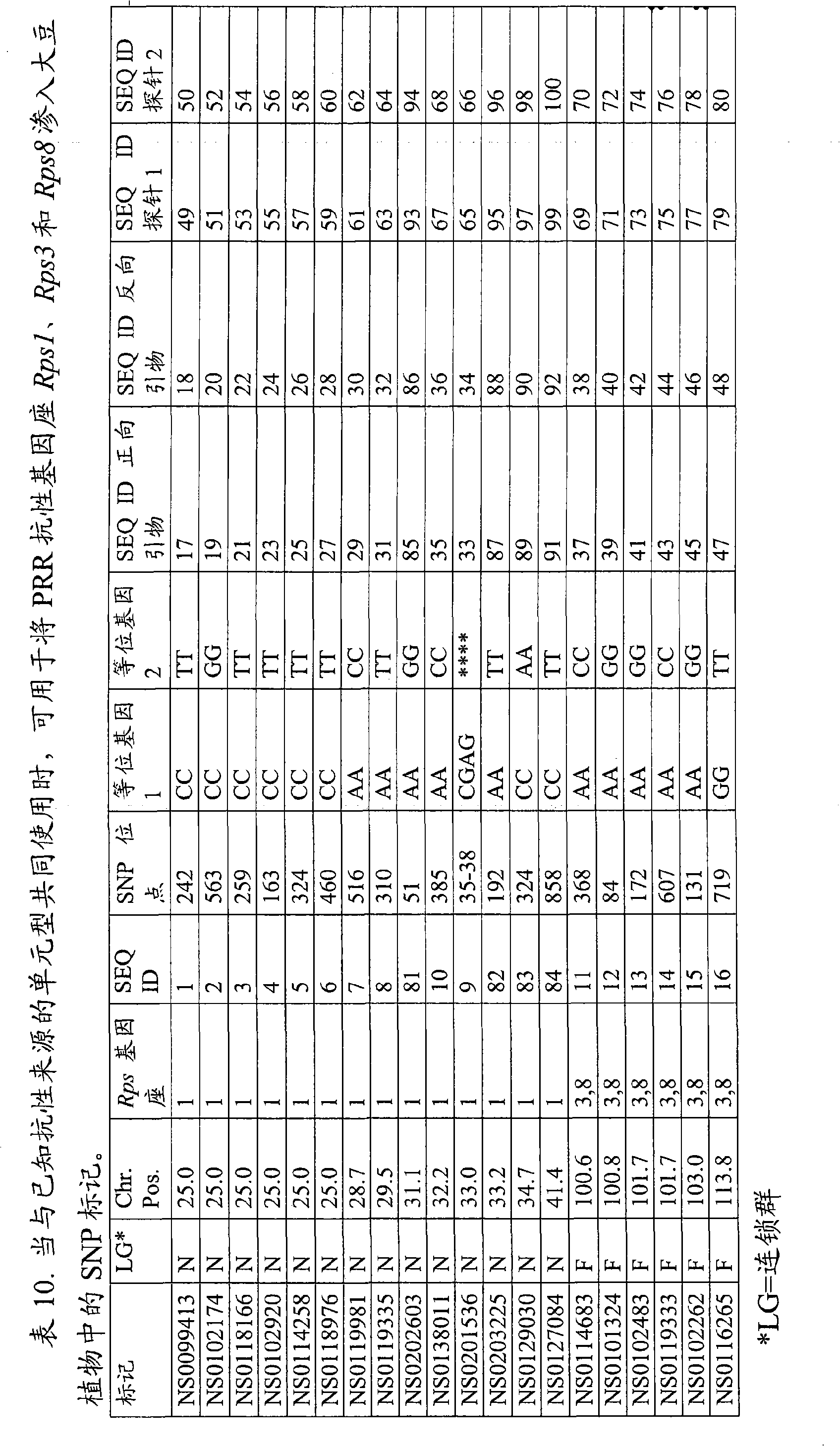
[0216] Example 1. Variation of SNP markers for introgression of PRR resistance loci when used with haplotypes of known origin of resistance
[0217] Phytophthora soybean is the causative agent of Phytophthora root rot (PRR) and causes significant losses in soybean yields in the United States. Planting resistant varieties is an effective way to control PRR. The breeding of PRR resistant soybean can be greatly facilitated by using marker assisted selection for PRR resistant alleles. Segregating populations were generated to demonstrate SNP markers useful for detection, selection, and introgression of PRR resistance loci into plants.
[0218] Table 1 includes the phenotypic rating scales and definitions used herein for the Examples below. The percentage of surviving plants after P. sojae inoculation was used for classification. This rating provides the basis for all disease ratings and determinations of resistance or susceptibility in the Examples below.
[0219] Table 1: Des...
Embodiment 2
[0247] Example 2: Selection of the Rps1k locus conferring PRR race 4 resistance using SNP markers.
[0248] Using knowledge of PRR resistant germplasm, SNP markers were used to breed PRR resistance (Table 11). F3 populations generated by crosses of two sources of PPR resistance - AG3602 (source of Rps1c) and AG3505 (source of Rps1k) - were screened using two SNP markers. A total of 466 individuals were screened. SNP markers NS0119335 and NS0118166 were used to select for Rps1k (source of PRR race 4 resistance) based on the AG3505 haplotype. Sources of Rps1 resistance include, but are not limited to, AG3602, AG3505, and DKB28-53.
[0249] Table 11. Haplotypes of two sources of PRR resistance.
[0250]
Embodiment 3
[0251] Example 3. Monitoring of introgression of the PRR resistance locus Rps1k using SNP markers.
[0252] F3 individuals produced by crossing two soybean lines AG3602(Rps1c) and AG3505(Rps1k) were genotyped. The Rps1k locus confers resistance to PRR race 4. A total of 466 F3 plants were screened with two SNP markers NS0119335 and NS0118160. Table 12 reports the results of the phenotypic validation of the genotype screen for PRR race 4. Screening with NS0119335 predicted PRR response with 85.7%. Screening with NS0118160 predicted PRR response with 83.8%.
[0253] Table 12. Results of phenotypic screening after haplotype selection based on resistance source.
[0254] mark
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com