Partial block erase architecture for flash memory
A flash memory, memory block technology, applied in static memory, read-only memory, digital memory information and other directions, can solve problems such as complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
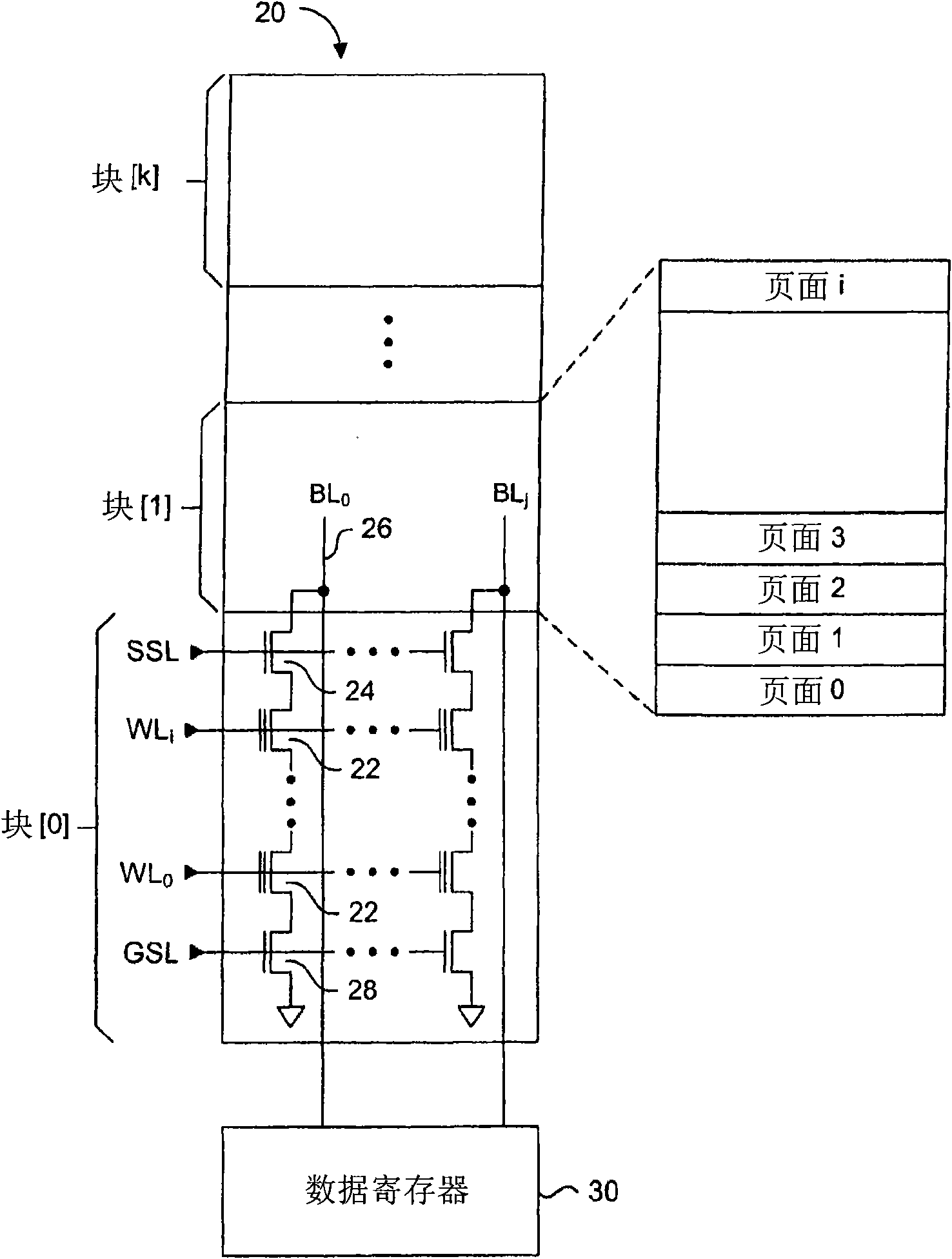
[0035] [0020] In general, embodiments provide methods and systems for increasing the lifetime of flash memory devices. Each physical memory block of a flash memory device can be divided into at least two logical sub-blocks, where each of the at least two logical sub-blocks is erasable. Therefore, only the data of that logical block is erased and reprogrammed, while the unmodified data in other logical blocks avoids unnecessary program / erase cycles. The logical sub-blocks to be erased are dynamically configurable in terms of size and position within the block. Wear leveling algorithms are used to spread data across the physical and logical sub-blocks of the memory array to maximize the life of the physical blocks.
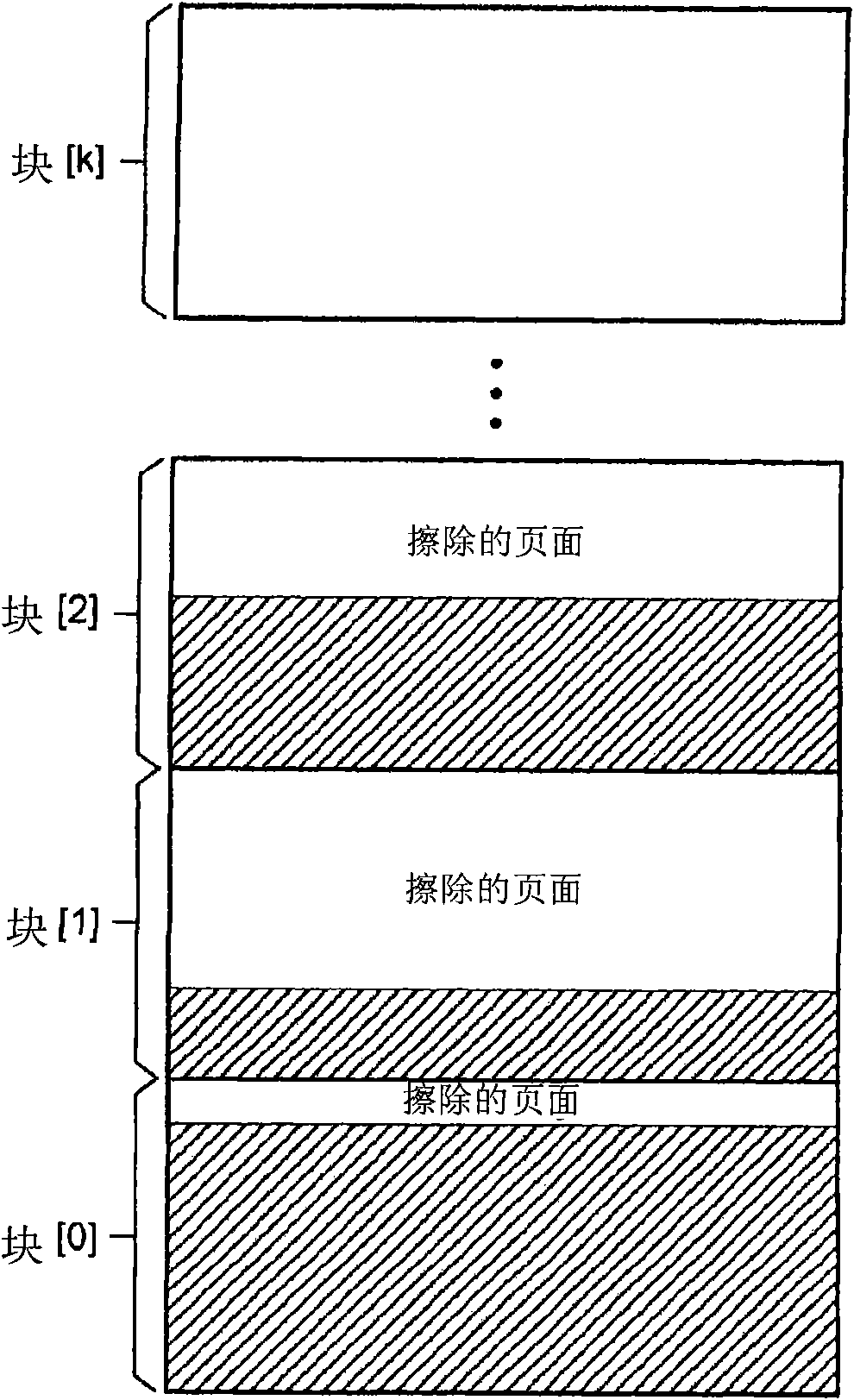
[0036] 【0021】 image 3 is a conceptual illustration of physical memory blocks (block[0] to block[k]) of the flash memory device according to the present embodiment. Each physical block can selectively erase logical sub-blocks, where the erased sub-blocks can incl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com