Remediation method of decabromodiphenyl oxide contaminated soil
A technology of decabromodiphenyl ether and a restoration method is applied in the field of restoration of decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated soil, can solve problems such as disappearance, decreased activity of fungi, inability to realize soil pollution restoration, etc., and achieves good effect, simple operation, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 Research on Porous Bacteria Remediation of Decabromodiphenyl Ether Contaminated Soil and the Amount of Bacteria
[0023] The red soil in the Arboretum of South China Agricultural University in Guangzhou was collected. After the soil was sampled, it was air-dried in the laboratory and passed through a 60-mesh sieve for later use.
[0024] Mix decabromodiphenyl ether with the above-mentioned treated soil samples evenly at room temperature, put them in a dark place, and prepare decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated red soil with a decabromodiphenyl ether content of 2.5 mg / kg.
[0025] This embodiment sets four experimental groups:
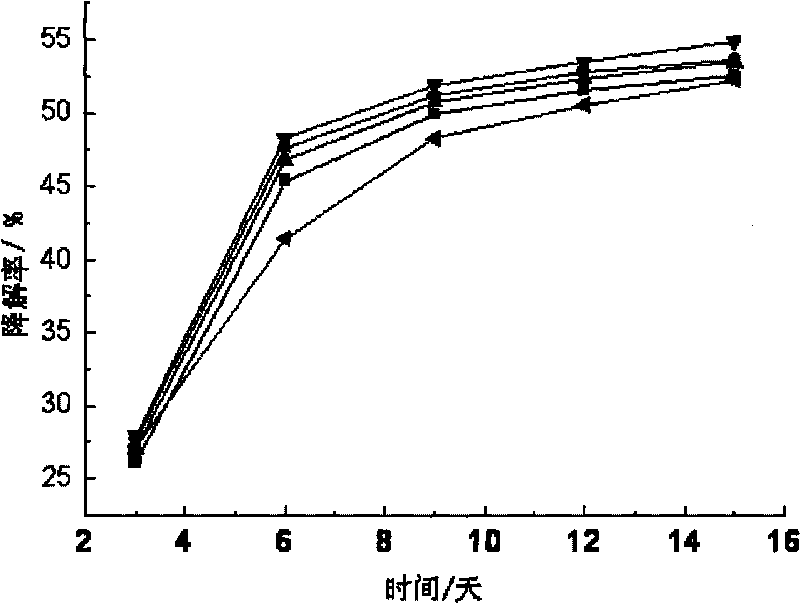
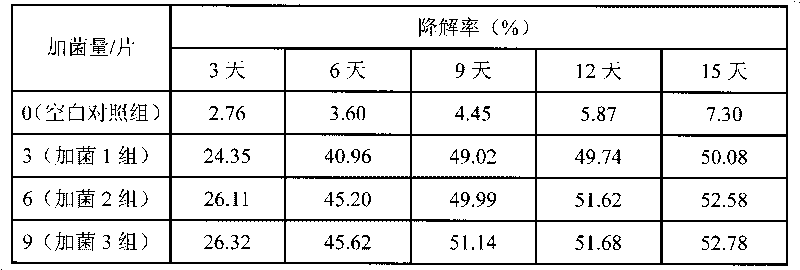
[0026] Blank control group: take no bacterial species added to the decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated red soil as the blank control group;
[0027] Bacteria addition group 1: add polypore bacteria flakes to decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated red soil and mix evenly, the ratio of bacteria addition is 3 flakes / 10g soil;
[0028] Ba...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The condition optimization of the soil to be tested in embodiment 2
[0041] The present embodiment is mainly optimized for the treatment method of the soil to be tested. The soil sample adopts the decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated red soil of 2.5 mg / kg prepared in Example 1, and is divided into two experimental groups:
[0042] (1) Non-sterilized group: this group does not adopt sterilization treatment to the decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated red soil of 2.5mg / kg prepared in Example 1, directly according to the dosage ratio of 6 pieces / 10g soil, the polypore Add to decabromodiphenyl ether contaminated red soil and mix evenly;
[0043] (2) Sterilization group: This group first carries out conventional sterilization treatment to the decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated red soil of 2.5mg / kg prepared in Example 1, and then according to the addition ratio of 6 pieces / 10g soil, the porous Bacteria were added to the sterilized decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated red s...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The restoration effect detection of embodiment 3 different soil samples
[0051] In this example, 5 kinds of soil samples were collected, namely red soil, red soil, brick red soil, paddy soil and vegetable field soil. Among them, the red soil came from Huanong Arboretum, the paddy soil and vegetable garden soil came from Huanong Village, and the red soil came from Zhanjiang. Red Soil Lai comes from Shaoguan.
[0052] After the soil sampling was returned, it was placed in the laboratory in a natural style, and passed through a 60-mesh sieve for later use. The 2.5 mg / kg decabromodiphenyl ether-contaminated red soils of the above five kinds of soils were prepared respectively, and the preparation method was the same as in Example 1.
[0053] 10g of soil was used for each treatment, and 3 replicates were set up, and the amount of polypore bacteria added was 6 pieces / 10g of soil.
[0054] Before the test, the initial concentration of decabromodiphenyl ether in the test soi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com