Buried low-resistance metal word lines for cross-point variable-resistance material memories
A resistance material and memory technology, applied in the field of variable resistance material random access memory, can solve the problems of complex memory unit size and processing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] Embodiments of devices, devices, or articles described herein can be manufactured, used, or shipped in a variety of orientations and orientations. Variable resistance material memory devices may include materials such as alloys. Variable resistance material memory devices may include materials such as metalloid components. Variable resistance material memory devices may include materials such as metal oxides. Variable resistance material memory devices may include materials such as chalcogenides. These several materials can vary widely in quality and performance.
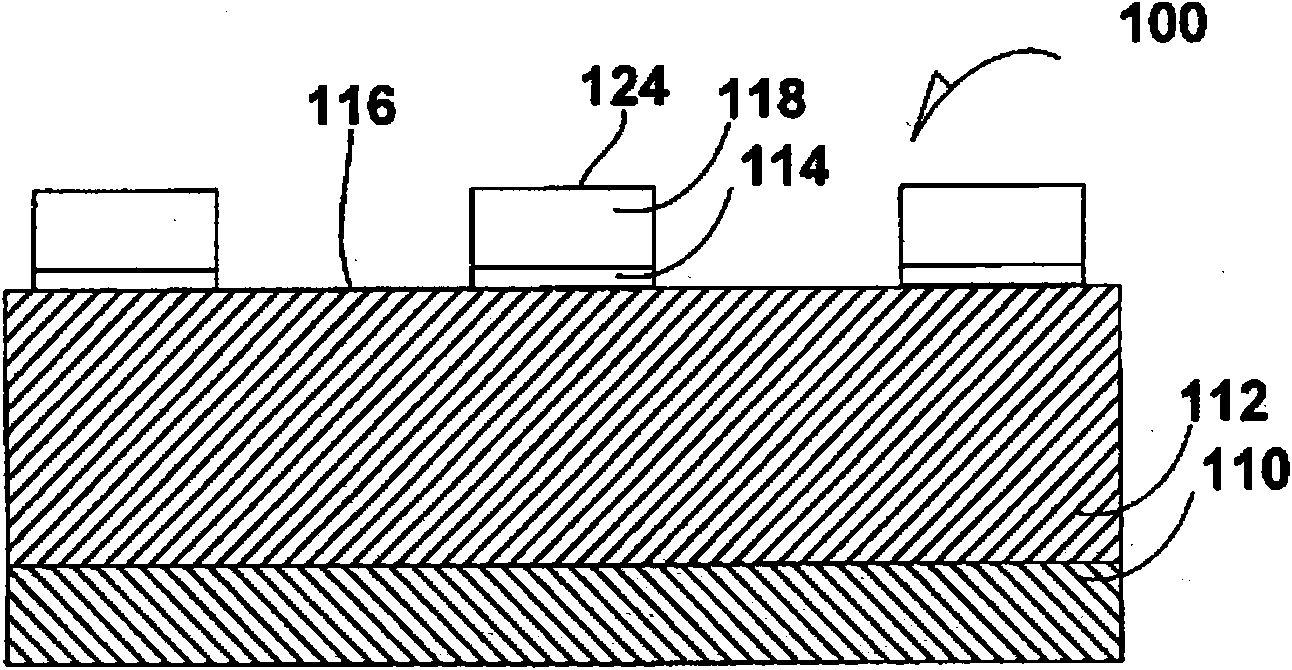
[0019] Figure 1a A cross-sectional front view of a semiconductor device 100 during processing according to an embodiment is shown. A semiconductive lower substrate 110 has been formed below a semiconductive upper substrate 112 . In an embodiment, the semiconductive lower substrate 110 is P− doped as compared to the N+ doped semiconductive upper substrate 112 .
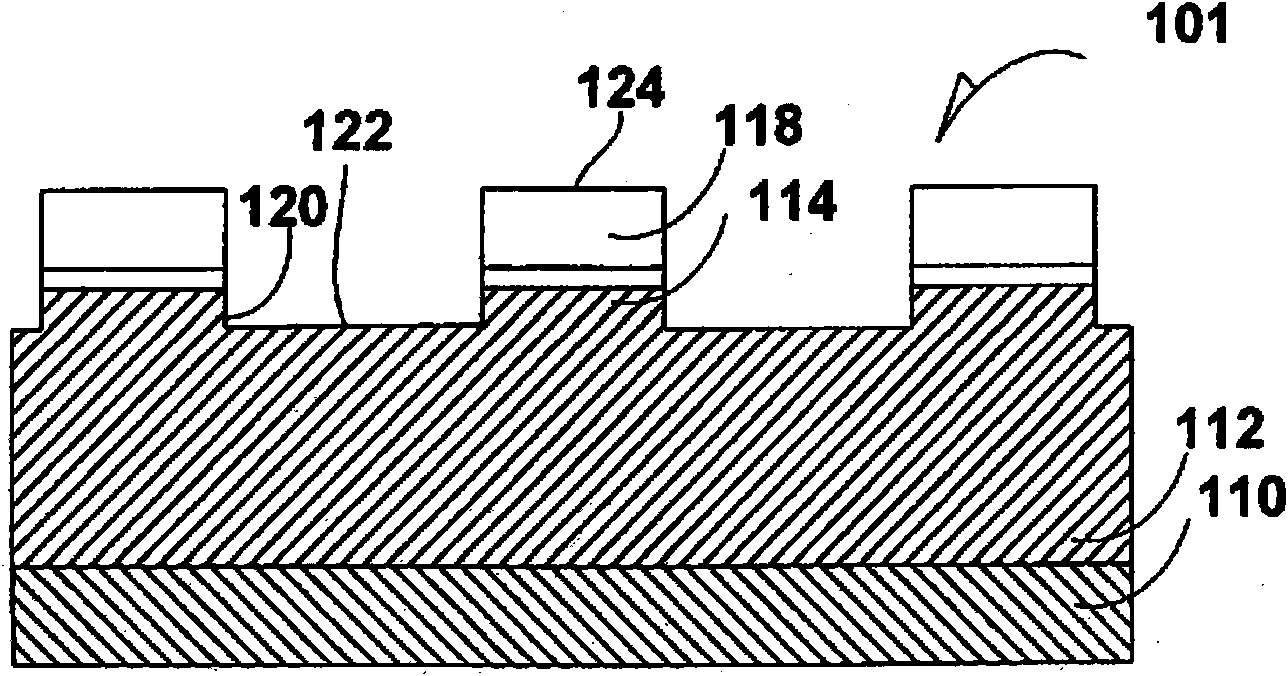
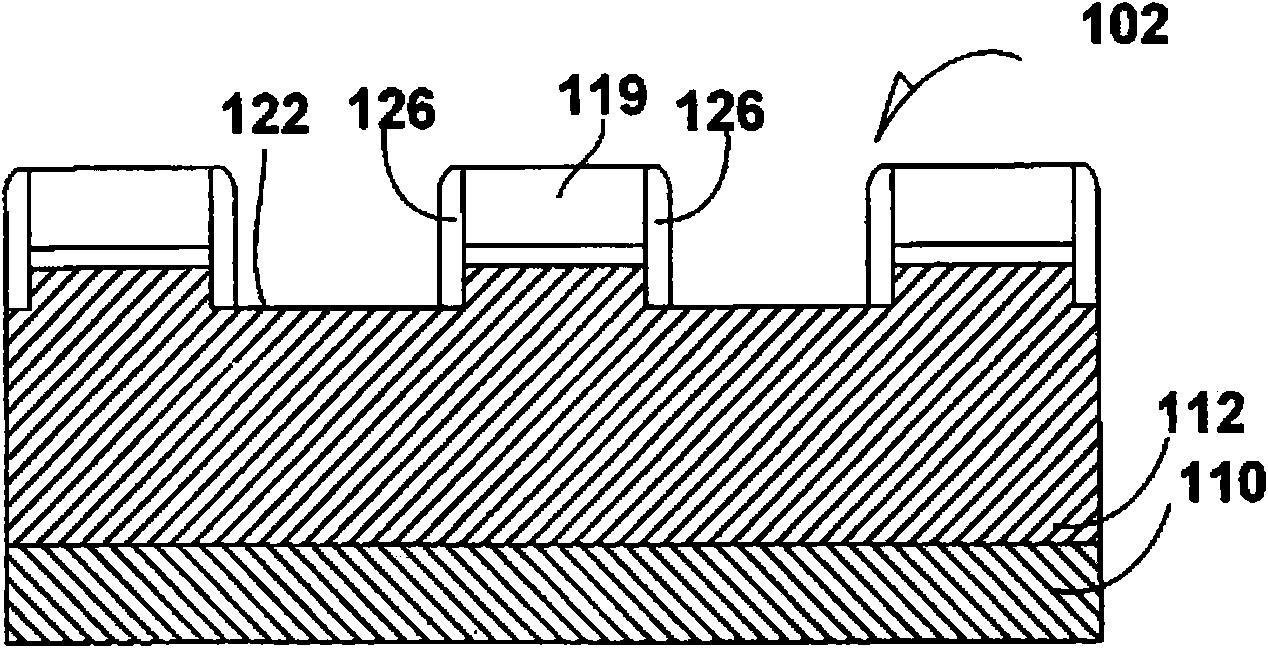
[0020] A dielectric film 114 , such as s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com