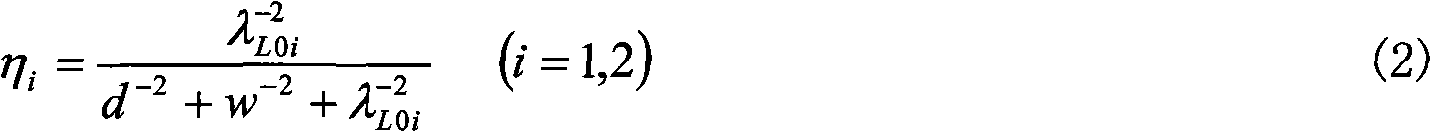All-solid-state laser gyroscope
A technology of laser gyroscope and laser gain, which is applied in the fields of laser technology, optical technology and inertial measurement, and can solve the problems of complex structure of laser gyroscope, difficulty of miniaturization and on-chip integration of gas gain medium, limited life of leaky laser gyroscope, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
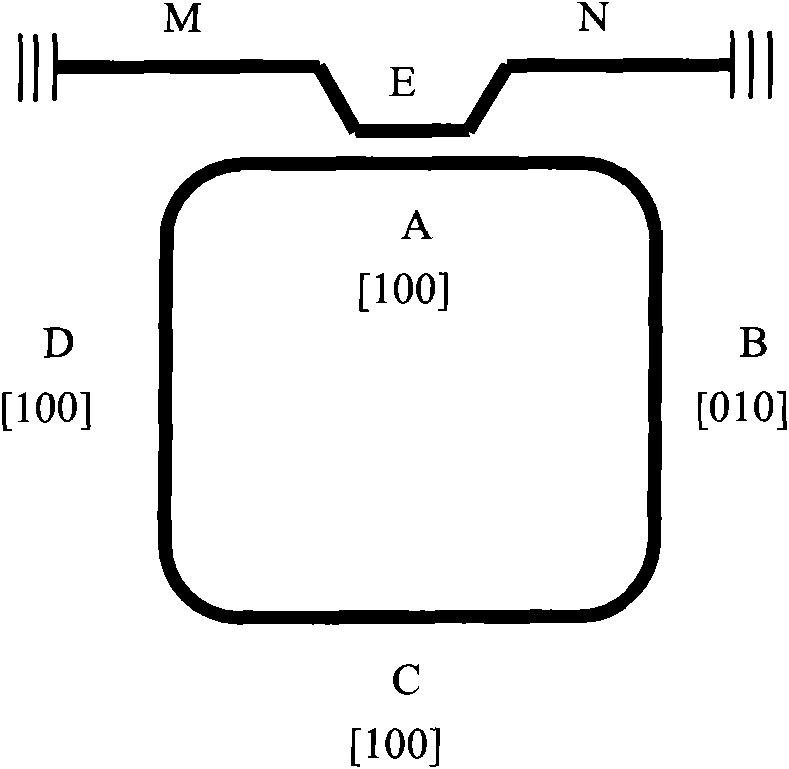
[0010] The specific implementation of the present invention will be described below by taking a GaP-based waveguide stimulated Raman scattering laser gyroscope as an example.
[0011] The schematic diagram of the principle of the all-solid-state laser gyroscope of the present invention is shown in the accompanying drawings. The laser gyroscope is composed of an input and output optical waveguide, a directional coupler and a ring optical resonant cavity, wherein the ring cavity optical waveguide is along the [100] or [010] direction. Assuming that the pump light is input from the X end of the optical waveguide, and the pump light is polarized along the [001] direction of the crystal, the pump light enters the A arm of the ring cavity waveguide through the directional coupler, and still maintains the polarization in the [001] direction, according to The selection rule of Raman scattering in the crystal, at this time, the polarization directions of Raman scattered light and optica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com