Detection method of nucleotide mutation points of KRAS gene and/or BRAF gene
A mutation site and detection method technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency and high cost of detection methods, and improve accuracy and detection efficiency , save time and cost, and simplify operating procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
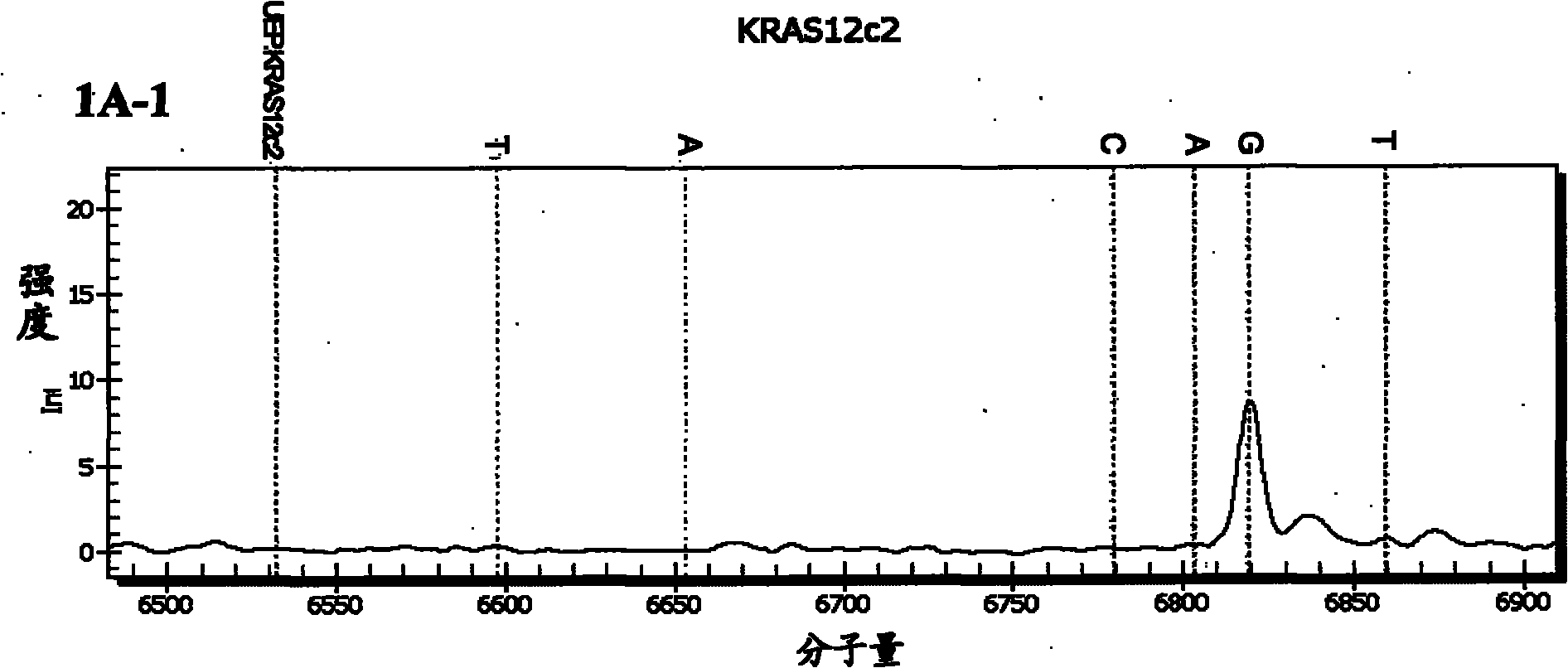
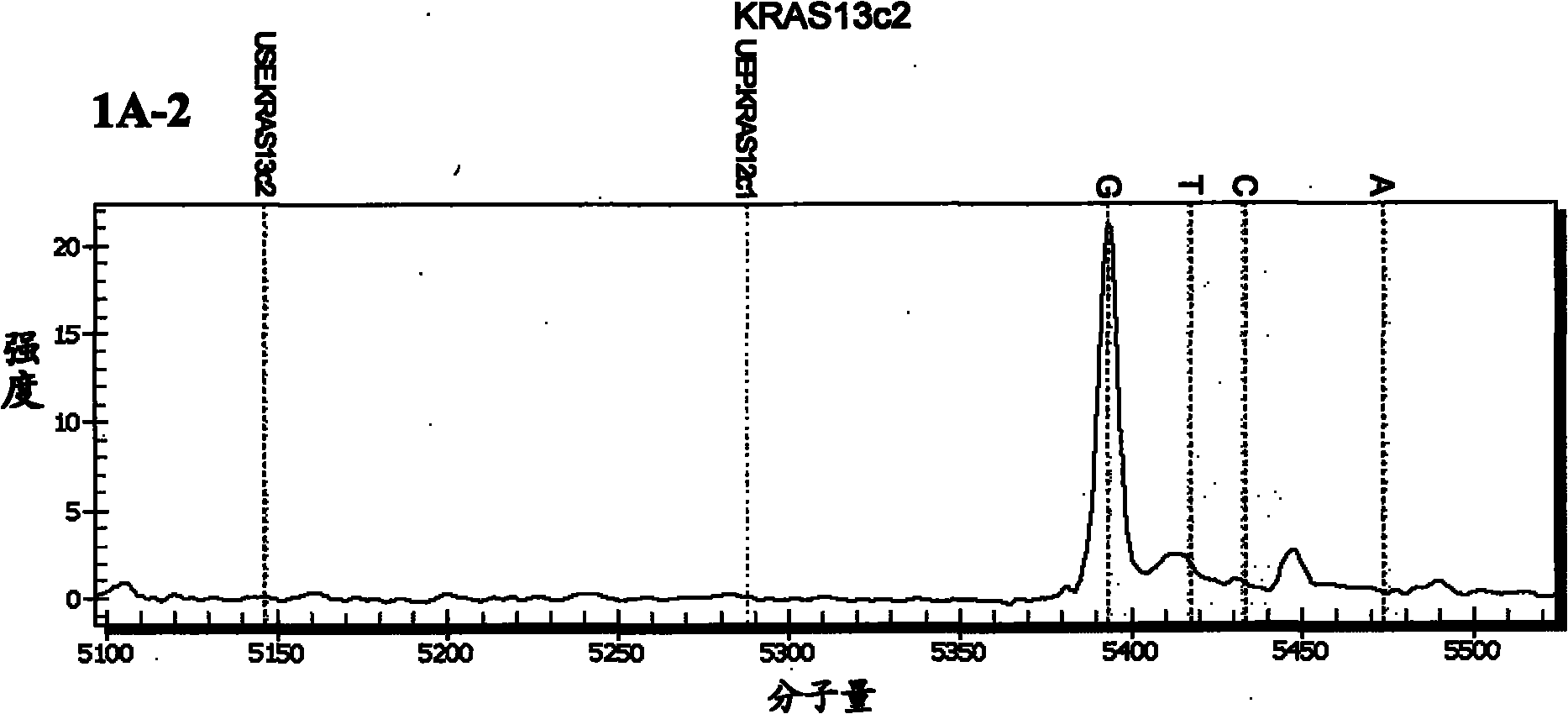
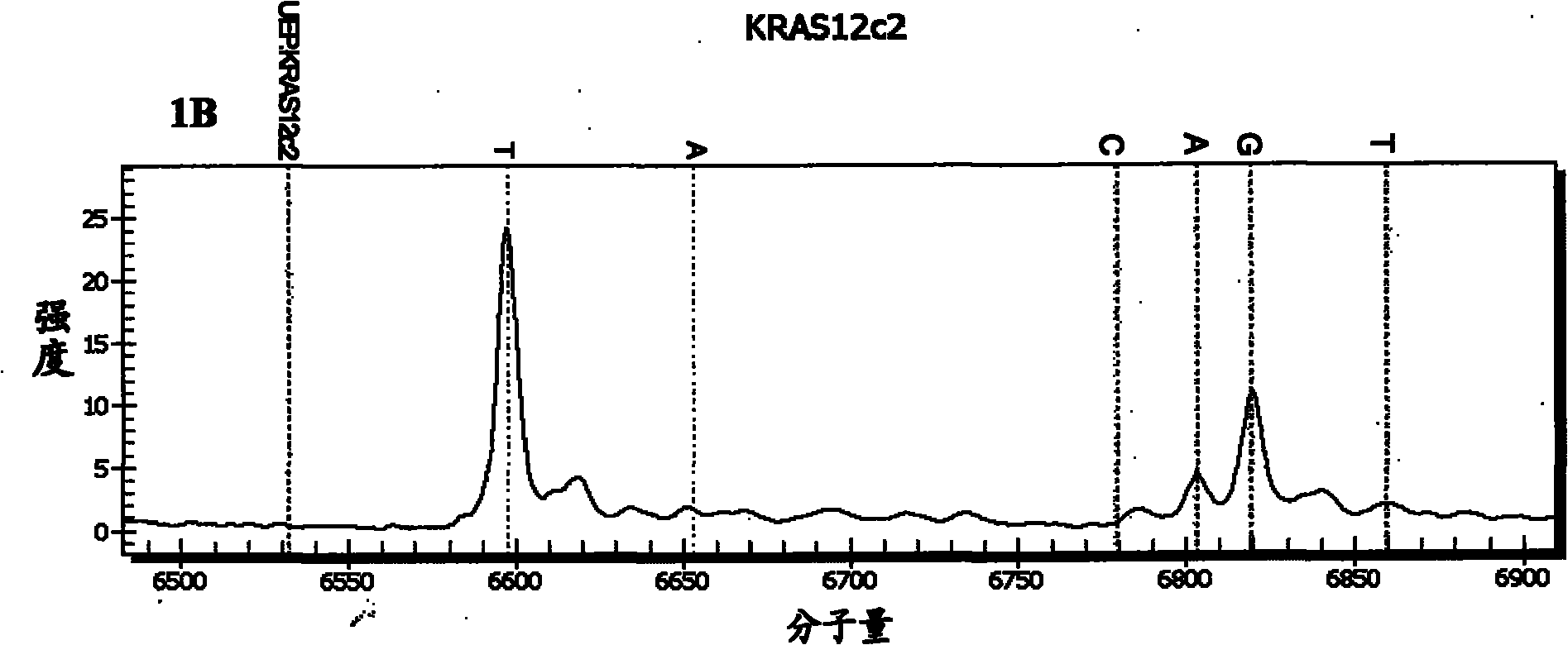
[0092] Embodiment 1: Detection of the nucleotide mutation site of the KRAS gene
[0093] (1) Design amplification primers for amplifying codons 12, 13, 61 and 146 of the KRAS gene and extension primers for detecting nucleotide mutations at each site
[0094] The wild type of codon 12 of KRAS gene is GGT, and its common mutation types include CGT, AGT, TGT and GCT, GAT, GTT; the wild type of KRAS gene codon 13 is GGC, and its common mutation types include CGC, AGC, TGC and GCC, GAC, GTC; the wild-type codon 61 of the KRAS gene is CAA, and its common mutation types include AAA, GAA, CCA, CGA, CTA, CAC, and CAT; the wild-type codon 146 of the KRAS gene is GCA, and its common mutations Types include ACA, CCA, GTA.
[0095] For the mass spectrometry detection of the above mutation sites, according to the KRAS gene sequence (NCBI accession number: EU332849), design each amplification primer and extension primer, each amplification primer has a tag sequence of 10 bases acgttggatg at...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2: Simultaneous detection of each mutation site of the KRAS and BRAF genes.
[0114] In this embodiment, the 12th, 13th, 61st and 146th codons of the KRAS gene and the 600th codon of the BRAF gene were detected simultaneously.
[0115] (1) Design the amplification primer used to amplify the 600th codon of the BRAF gene and the extension primer used to detect the nucleotide mutation of this codon
[0116] The wild type of the 600th codon of the BRAE gene is GTG, and its common mutation types include GAG and GCG. According to the BRAF gene sequence (NCBI accession number: NG_007873), each amplification primer and extension primer were designed, and each amplification primer had a tag sequence of 10 bases acgttggatg at the 5' end. The amplification primers used to amplify each codon of the KRAS gene are the same as in Example 1. The sequences and sequence numbers of the various amplification primers and extension primers are shown in Table 1 above.
[0117] (2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com