Implanted passive wireless acoustic surface wave sensor detection device
A surface acoustic wave, passive wireless technology, applied in sensors, diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of application limitations, short measurement distance, different electromagnetic wave attenuation, etc., and achieve continuous and uninterrupted measurement of physiological parameters, improve Energy efficiency, effects of real-time physiological parameter measurements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The invention combines surface acoustic wave sensor technology, implantable antenna technology, wireless energy supply technology, and has the advantages of passive wireless, simple structure, high precision, long measurement distance and the like.
[0021] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings:
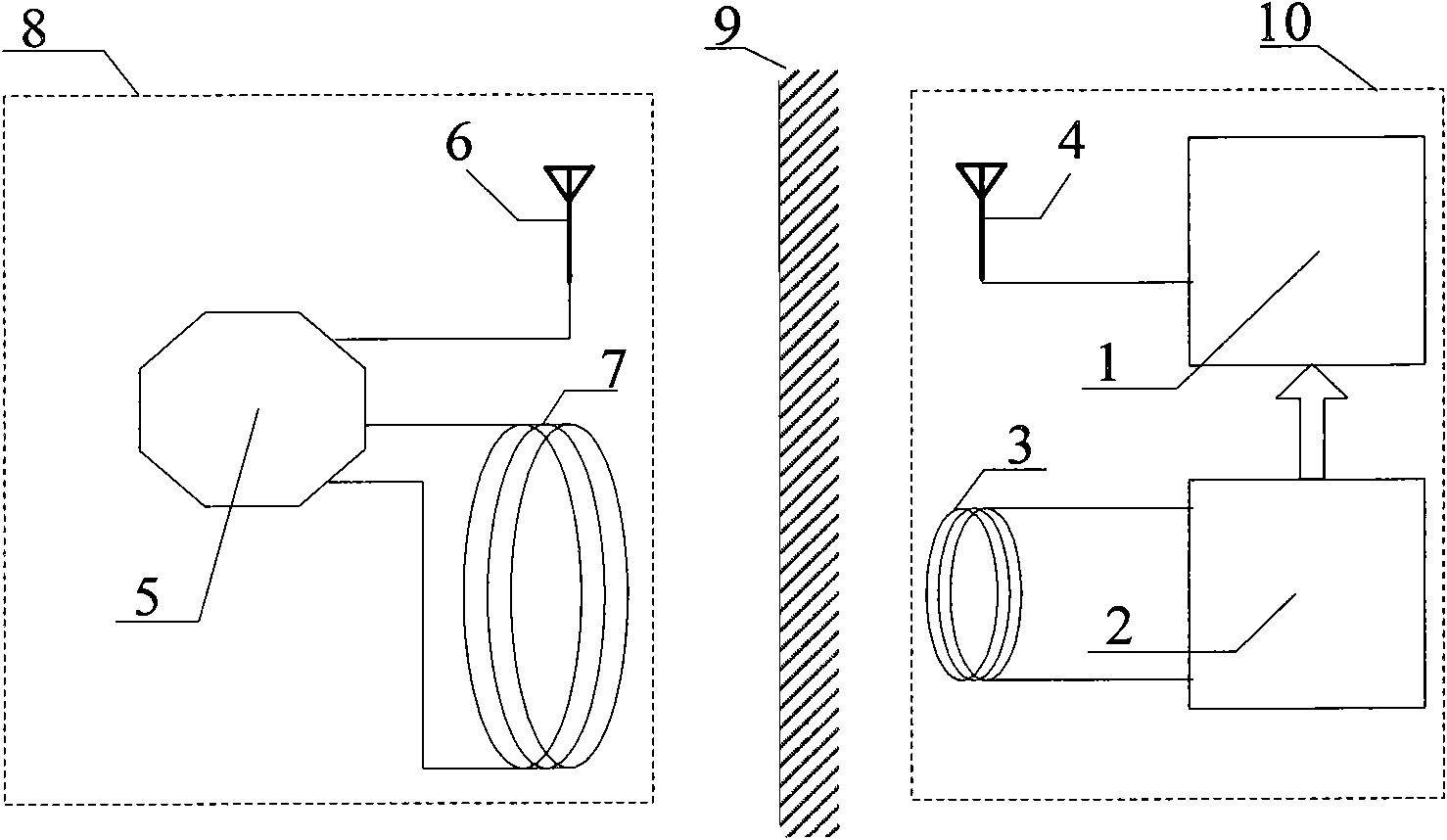
[0022] in figure 1 Among them, the implanted passive wireless surface acoustic wave sensing detection device of the present invention includes an external part 8 and an internal part 10. Among them, the extracorporeal part 8 is placed outside of the organism and consists of an extracorporeal processing module 5, an extracorporeal receiving antenna 6 and an extracorporeal transmitting antenna 7. The intracorporeal part 10 is implanted in the organism and consists of a surface acoustic wave sensing detection module 1, a wireless The energy supply module 2, the internal receiving antenna 3 and the internal transmitting antenna 4 are c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com