Pulse laser apparatus
A pulsed laser and excitation light technology, applied in lasers, laser parts, phonon exciters, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining, weakening of Q-switching function, and inability to obtain laser characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
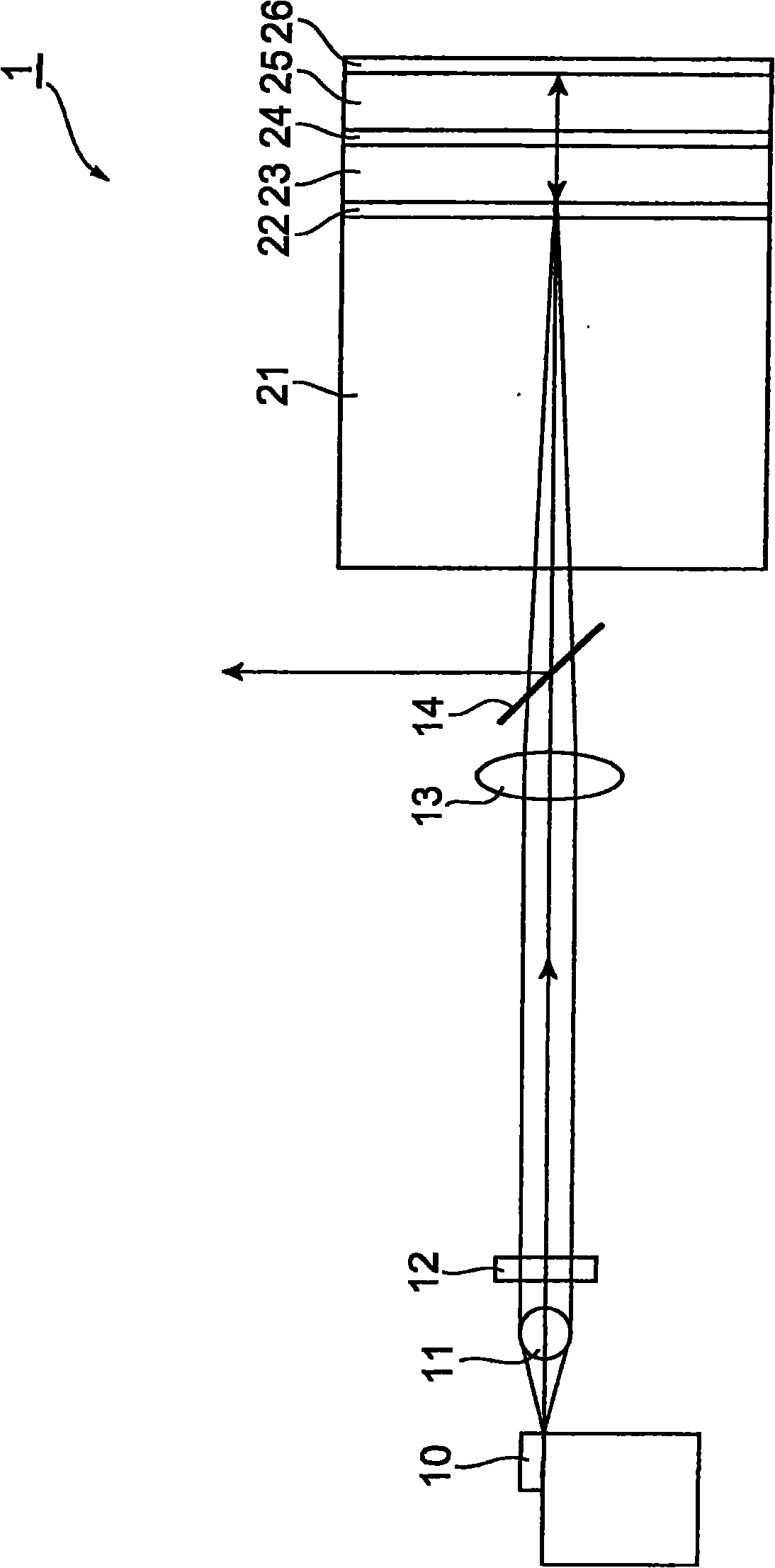
[0022] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the configuration of the pulsed laser light source 1 according to the first embodiment. The pulsed laser light source 1 shown in this figure includes an excitation light source 10, lenses 11 to 13, a dichroic mirror 14, an amplification medium 21, a first reflector 22, a laser medium 23, a third reflector 24, a saturable The absorber 25 and the second reflector 26 .
[0023] The amplifying medium 21 and the laser medium 23 each contain a photoactive material, are excited by being supplied with excitation light output from the excitation light source 10 , and emit light from the photoactive material. Preferably, the amplification medium 21 and the laser medium 23 are respectively crystals such as Nd:YAG or Yb:YAG. The thickness of the amplification medium 21 is, for example, 0.2 mm to 1.5 mm. The thickness of the laser medium 23 is, for example, 0.01 mm to 1.5 mm.
[0024] The saturable absorber 25, whose light absorptivity decre...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
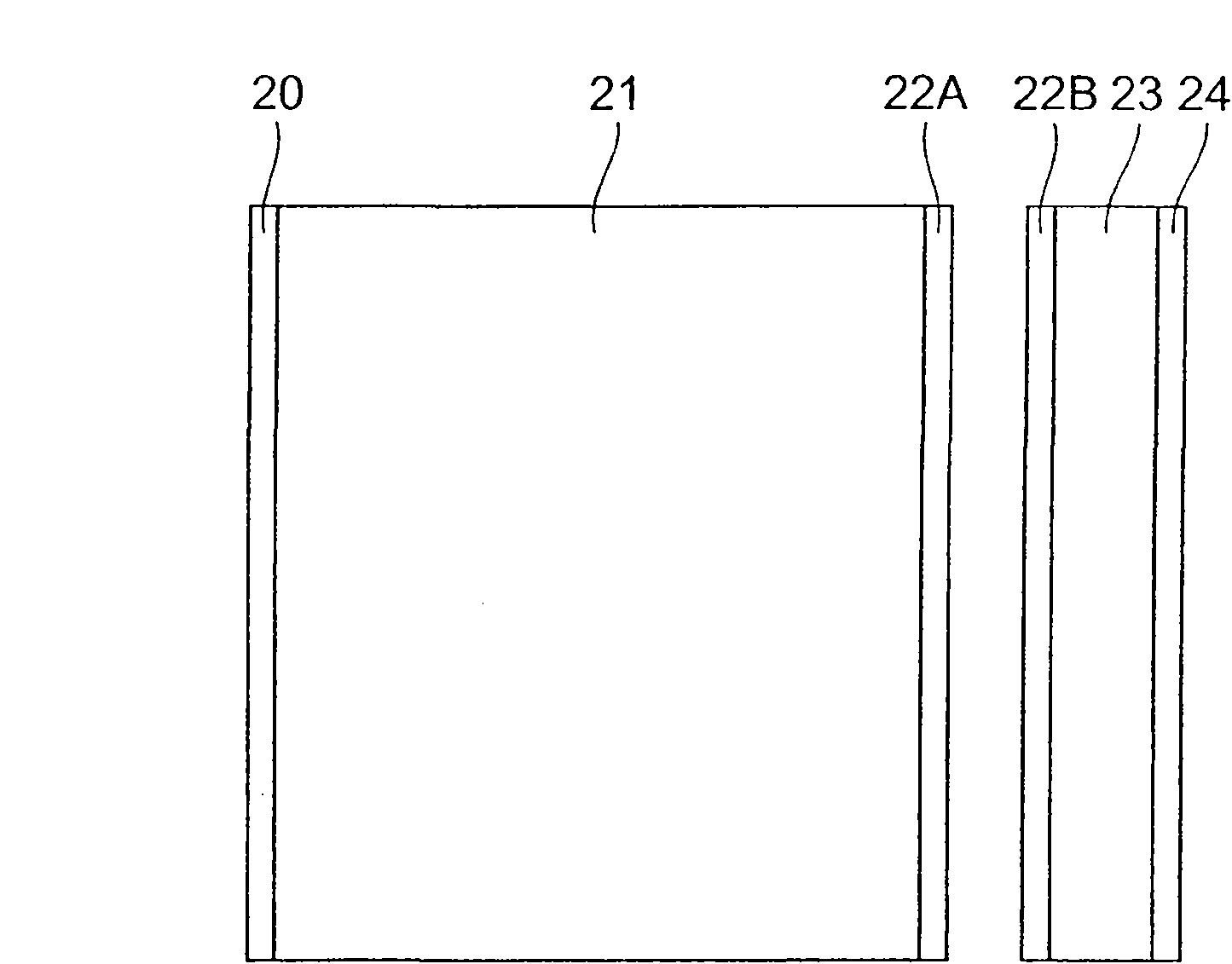
[0055] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the pulsed laser light source 2 concerning 2nd Embodiment. The pulsed laser light source 2 shown in this figure has an excitation light source 10 , lenses 11 to 13 , a dichroic mirror 14 , an amplification medium 21 , a first reflector 22 , a laser medium 23 , a saturable absorber 25 and a second reflector 26 .
[0056] and figure 1 Compared with the pulsed laser light source 1 according to the first embodiment shown, the Figure 5 The pulsed laser light source 2 according to the second embodiment shown is different in that it does not include the third reflector 24 . That is, the laser medium 23 and the saturable absorber 25 are directly bonded. In addition, in the second embodiment, the reflector 26 reflects not only emission light but also excitation light with high reflectivity.
[0057] The pulsed laser light source 2 according to the second embodiment operates as follows. The excitation light output from...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
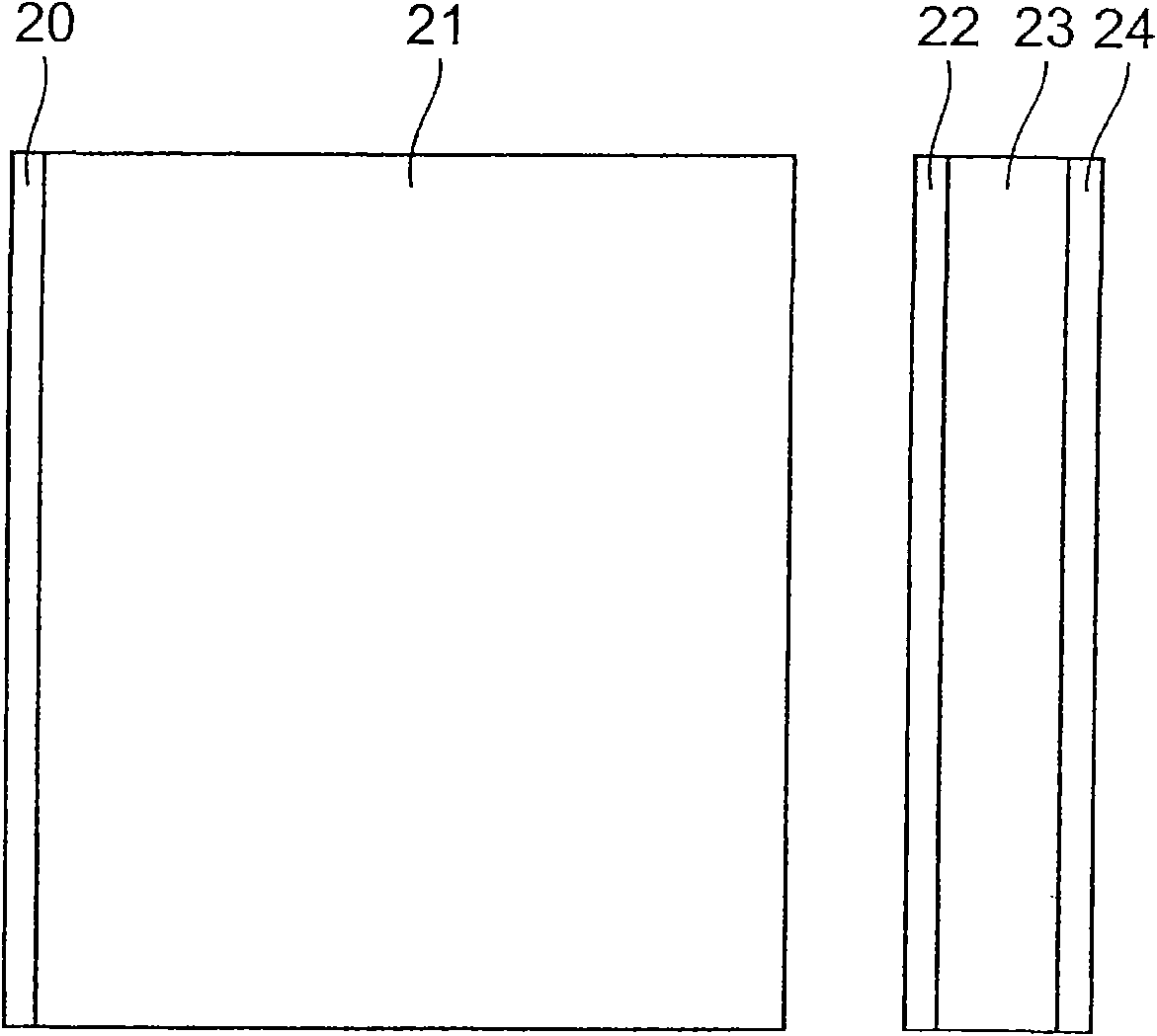
[0062] Image 6 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the pulsed laser light source 3 which concerns on 3rd Embodiment. The pulsed laser light source 3 shown in this figure has an excitation light source 10, lenses 11 to 13, a dichroic mirror 14, a 1 / 4 wavelength plate 15, an amplification medium 21, a first reflection part 22, a laser medium 23, and a saturable absorber 25. , the second reflection part 26 and the thermal diffusion parts 27-29.
[0063] and Figure 5 Compared with the structure of the pulsed laser light source 2 according to the second embodiment shown, the Image 6 The pulsed laser light source 3 according to the third embodiment shown is different in that it further includes a 1 / 4 wavelength plate 15 and thermal diffusion parts 27 to 29 .
[0064] The thermal diffusion parts 27 to 29 diffuse heat generated by light absorption in the laser medium 21 or the saturable absorber 23 . The thermal diffusion parts 27 to 29 are crystals not containing a pho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com