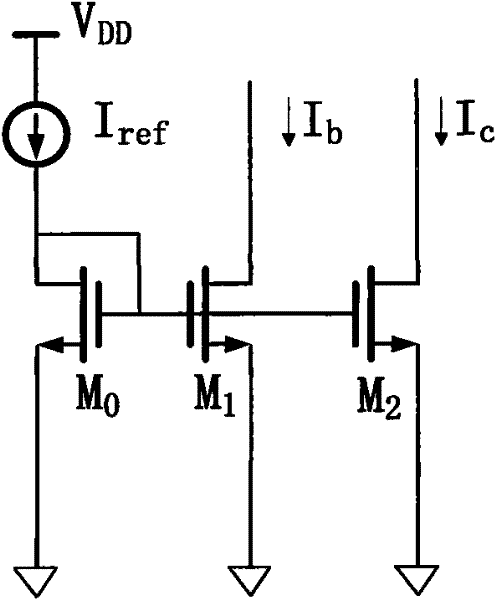
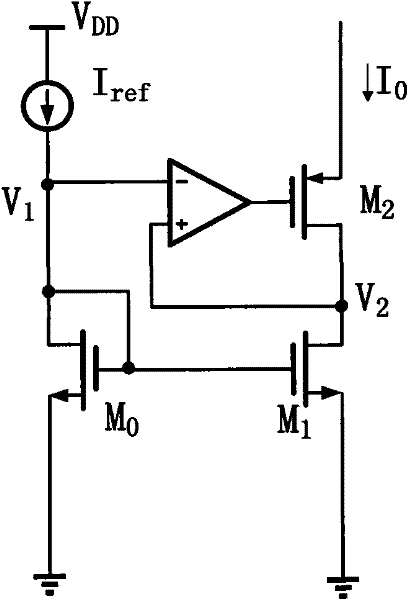
Self-adaptive current mirror
A current mirror, self-adaptive technology, applied in the direction of adjusting electrical variables, control/regulating systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of small output current range, low current accuracy, etc., to expand the current range, reduce costs, reduce chip area and The effect of complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
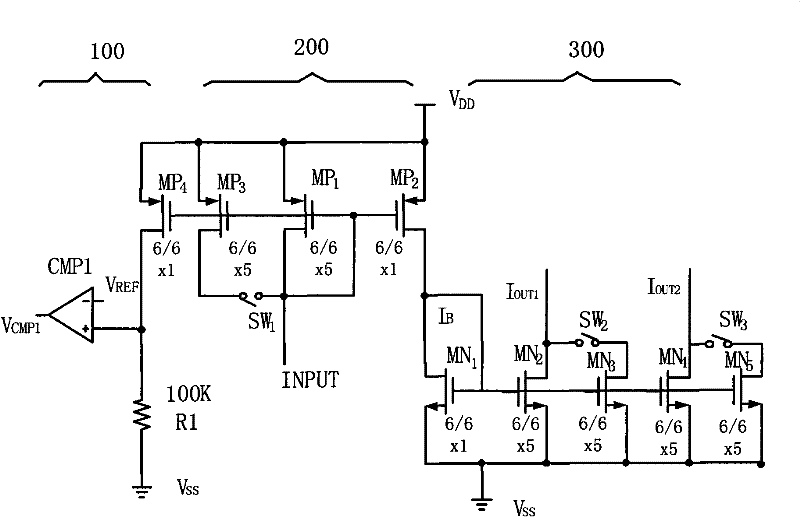
[0081] This example Figure 6 As shown, it includes an input circuit unit 11 , two output circuit units 12 , 13 , two negative feedback impedance adjustment units 14 , 15 and a voltage detection and control unit 16 .
[0082] The input circuit unit 11 is composed of four NMOS transistors M11, M12, M13, M14 and three switches SW1, SW2, SW3. The gates of the four NMOS transistors are all connected to the output terminal of the operational amplifier AMP1, and the sources are all grounded. The drain of M11 is directly connected to the positive input terminal of the operational amplifier AMP1 and the input current I ref connection, NMOS tubes M12, M13, and M14 are used as alternative tubes, and their drains are connected to the positive input terminal of the operational amplifier AMP1 and the input current I through the switches SW1, SW2, and SW3 respectively. ref Connection, the negative input terminal of the operational amplifier AMP1 is connected to the reference voltage V ref...
Embodiment 2
[0141] This example Figure 7As shown, this embodiment consists of two stages of current mirrors connected in series. Modules 100P, 200P, and 300P form a first-stage current mirror, and modules 100N, 200N, and 300N form a second-stage current mirror. The structure of the first-stage current mirror is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, but the number of alternative transistors is reduced to two, the number of NAND gates and RS flip-flops is reduced by one each, and the MOS transistors are all PMOS transistors.
[0142] In this embodiment, the input circuit unit of the first stage current mirror is composed of P5, P6 and P7, and P6 and P7 are optional tubes. The output circuit unit of the first-stage current mirror is composed of P1, P2, and P3, and P2 and P3 are optional tubes. Due to the characteristics of the PMOS tube, the input current is a pull current, and the corresponding output current is also a pull current. The output current is the drain current of the P...
Embodiment 3
[0151] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the circuit structure of this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1, but the structure is simpler, including an input circuit unit 11 , an output circuit unit 12 , a voltage detection and control unit 13 and a negative feedback impedance adjustment unit 14 . The input circuit unit 11 is composed of a basic transistor M11, an optional transistor M12 and a switch SW1 connected between the drains of the two NMOS transistors; the output circuit unit 12 is composed of a basic transistor M21, an optional transistor M22 and a connection A switch SW2 is formed between the drains of the two NMOS transistors. The structure and electrical connection of the negative feedback impedance adjustment unit 14 are the same as those in the first embodiment. Since there is only one optional tube in the input circuit unit 11 and the output circuit unit 12, correspondingly, the control of the switch is relatively simple. The state of both switches is the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com