Method for preparing corrosion-resistant sintered neodymium iron boron (NdFeB) magnet
A NdFeB, corrosion-resistant technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problem of corrosion resistance of high-performance sintered NdFeB magnets, low comprehensive performance of rare earth permanent magnets, etc. problems, to achieve the effects of reduced weight loss, satisfactory corrosion resistance, and strong electrochemical corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
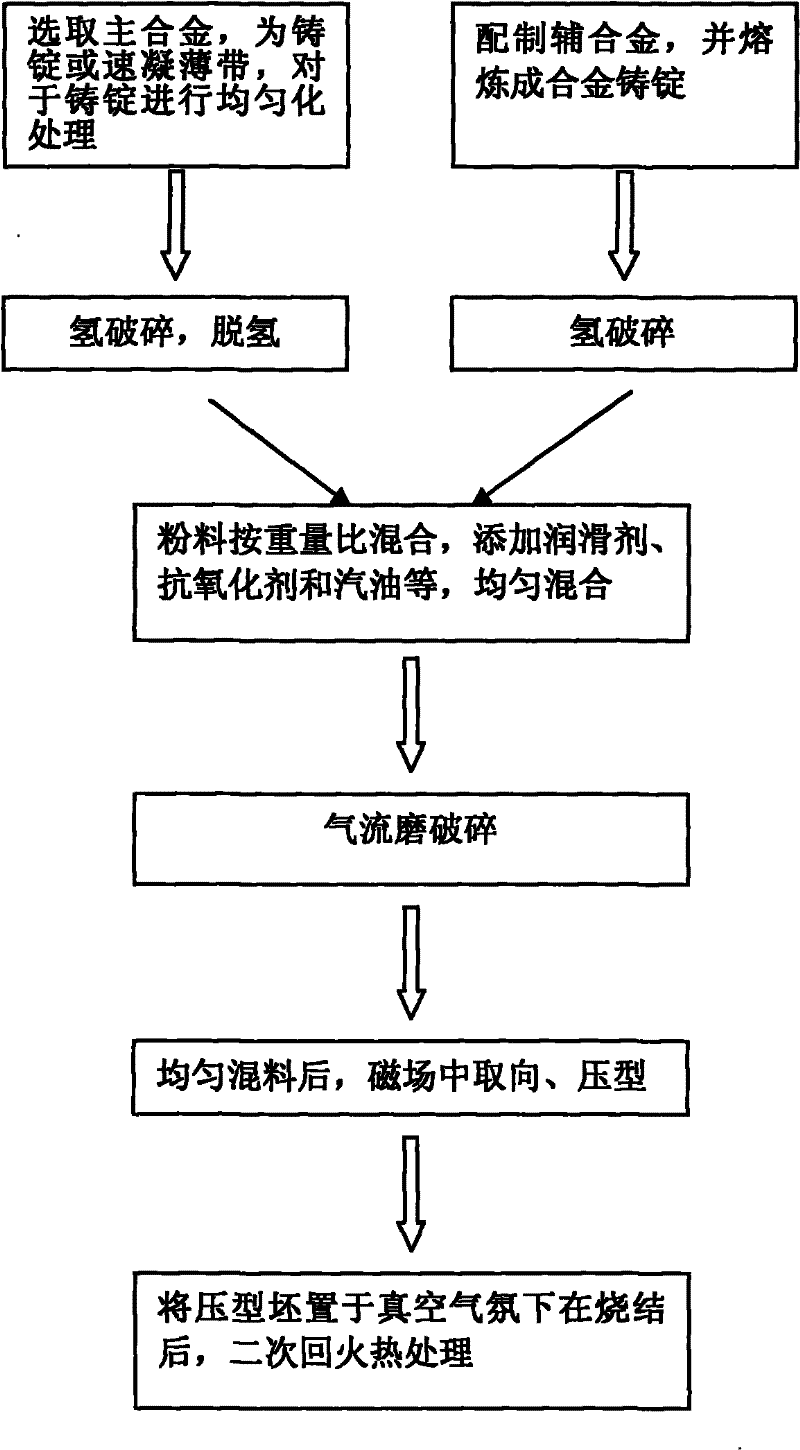
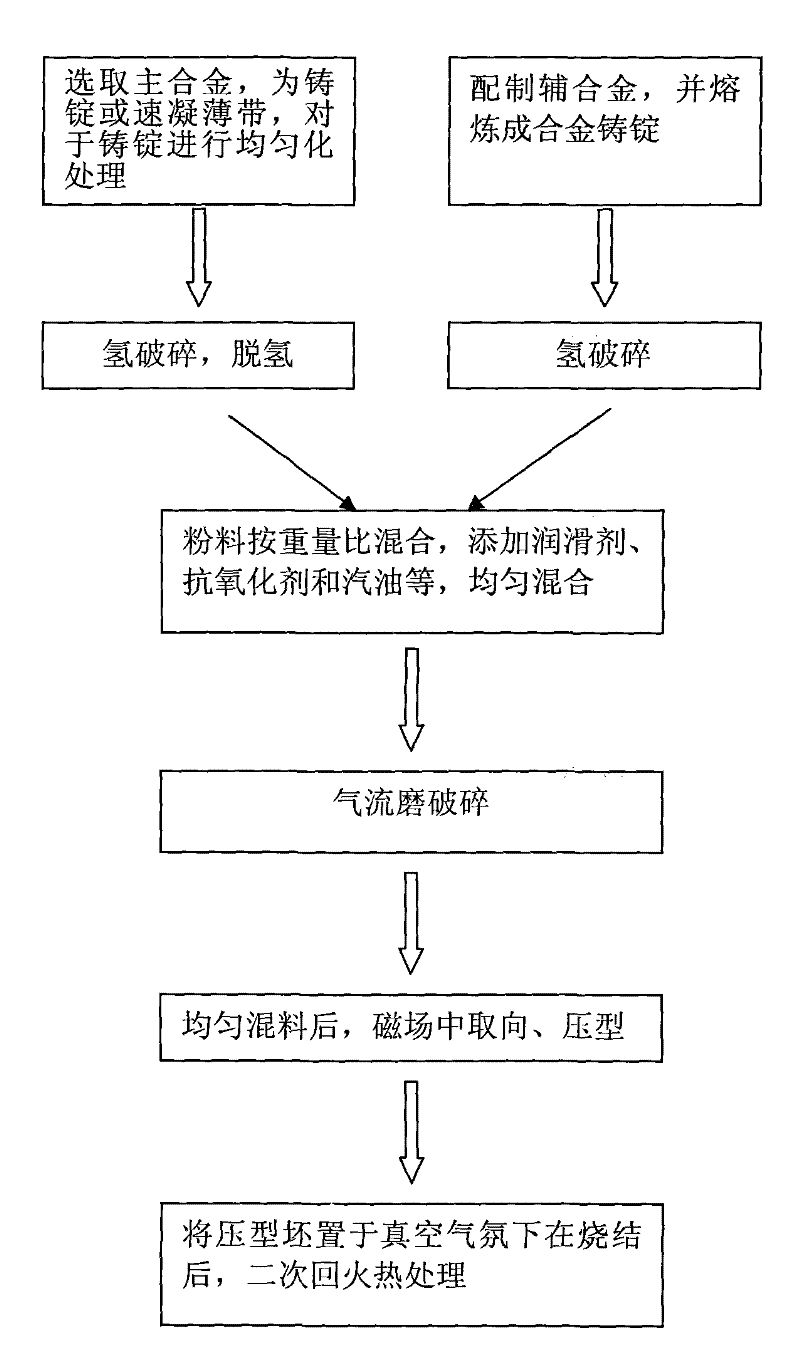
[0030] A method for preparing a corrosion-resistant sintered NdFeB magnet, comprising the following steps:
[0031] Step 1. Select the main alloy as an alloy ingot. The atomic percentage composition of the main alloy is Nd: 11.0%, Dy: 1.0%, Tb: 0.5%, Nb: 0.1%, Al: 0.2%, Cu: 0.1%, Ga: 0.1 %, Fe: 81.0%, B: 6.0%, the main alloy ingot was homogenized at 1100°C for 20h.
[0032] Step 2, preparing auxiliary alloy, the atomic percentage composition of auxiliary alloy is Nd: 40.0%, Co: 60.0%.
[0033] In step 3, the auxiliary alloy is smelted by an induction melting method to obtain an auxiliary alloy ingot.
[0034] Step 4, the main and auxiliary alloys are respectively hydrogen crushed to make powder. Dehydrogenate the crushed main alloy at 550°C for 3h.
[0035]Step 5, mixing the main and auxiliary alloys after the hydrogen crushing treatment, the weight of the auxiliary alloy powder accounts for 5% of the total weight of the two, and simultaneously adds a lubricant accounting f...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for preparing a corrosion-resistant sintered NdFeB magnet, comprising the following steps:
[0042] Step 1. Select the main alloy as quick-setting flakes, and the atomic percentage composition of the main alloy is Nd: 7.2%, Pr: 0.5%, Dy: 2.2%, Tb: 0.9%, Co: 1.5%, Nb: 0.3%, Al: 0.3 %, Fe: 80.8%, B: 6.3%.
[0043] Step 2, preparing auxiliary alloy, the atomic percentage composition of auxiliary alloy is Nd: 30%, Pr: 25%, Dy: 1%, Co: 40%, Cu: 2%, Ga: 2%.
[0044] In step 3, the auxiliary alloy is smelted by an induction melting method to obtain an auxiliary alloy ingot.
[0045] Step 4, the main and auxiliary alloys are hydrogen crushed to make powder respectively, and the crushed main alloy is dehydrogenated at 500° C. for 4 hours.
[0046] Step 5, mixing the main and auxiliary alloys after the hydrogen crushing treatment, the weight of the auxiliary alloy powder accounts for 7% of the total weight of the two, and simultaneously adds 0.1% of the lubricant by we...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A method for preparing a corrosion-resistant sintered NdFeB magnet, comprising the following steps:
[0053] Step 1. Select the main alloy as an alloy ingot, and the atomic percentage composition of the main alloy is Nd: 7.2%, Pr: 0.5%, Dy: 2.0%, Tb: 0.5%, Co: 2.0%, Nb: 0.3%, Al: 0.5 %, Cu: 0.4%, Nb: 0.4%, Ga: 0.5%, Fe: 80.0%, B: 6.0%, the main alloy ingot was homogenized at 1050°C for 10h.
[0054] Step 2, preparation of auxiliary alloy, the atomic percentage composition of auxiliary alloy is Nd: 40%, Pr: 15%, Dy: 5%, Tb: 5%, Co: 25%, Al: 4%, Cu: 2%, Nb: 1%, Ga: 3%.
[0055] Step 3, using an arc melting method to melt the auxiliary alloy to obtain an auxiliary alloy ingot.
[0056] Step 4, the main and auxiliary alloys are hydrogen crushed to make powder respectively, and the crushed main alloy is dehydrogenated at 550° C. for 4 hours.
[0057] Step 5, mixing the main and auxiliary alloys after the hydrogen crushing treatment, the weight of the auxiliary alloy powde...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com