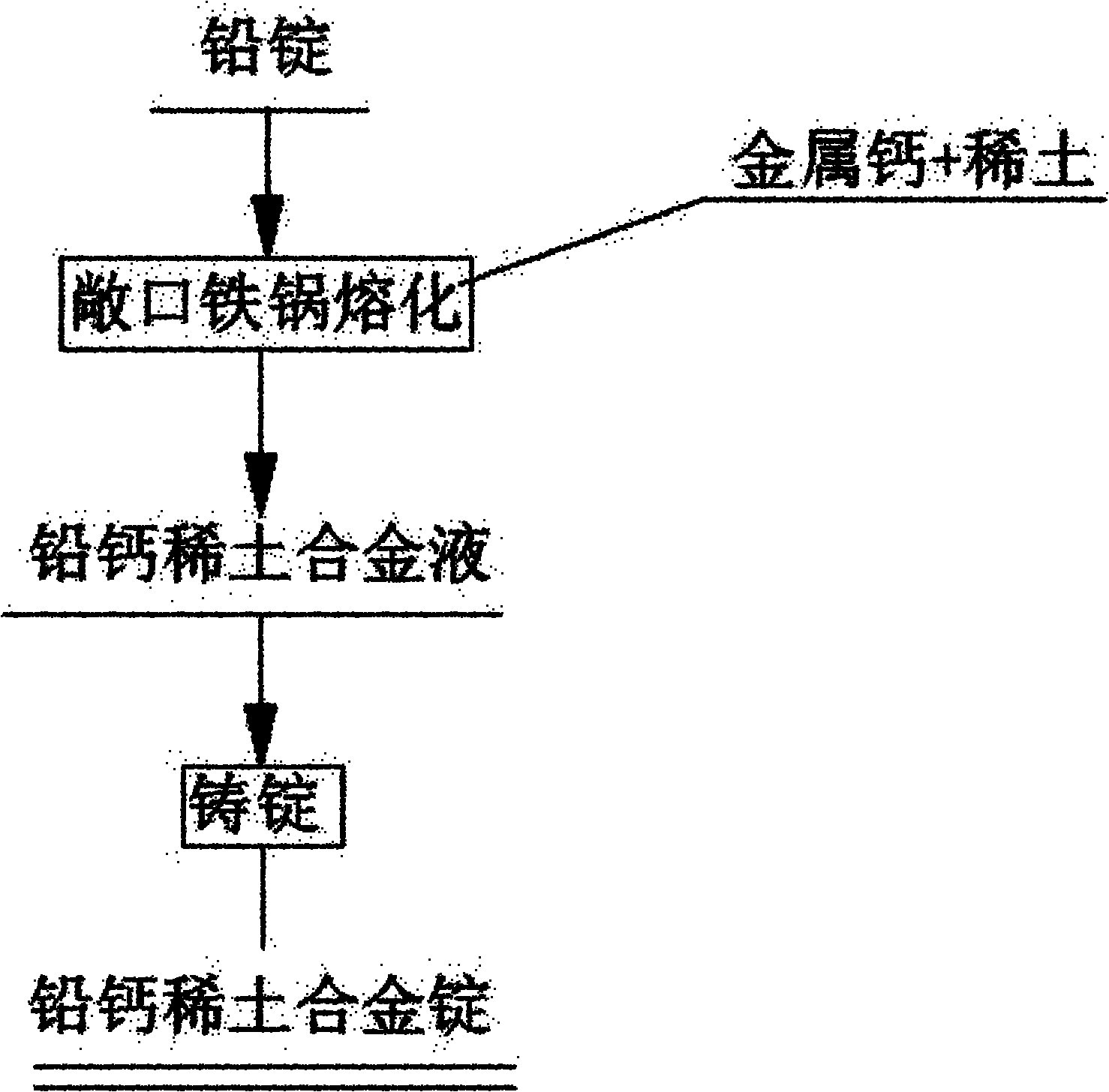
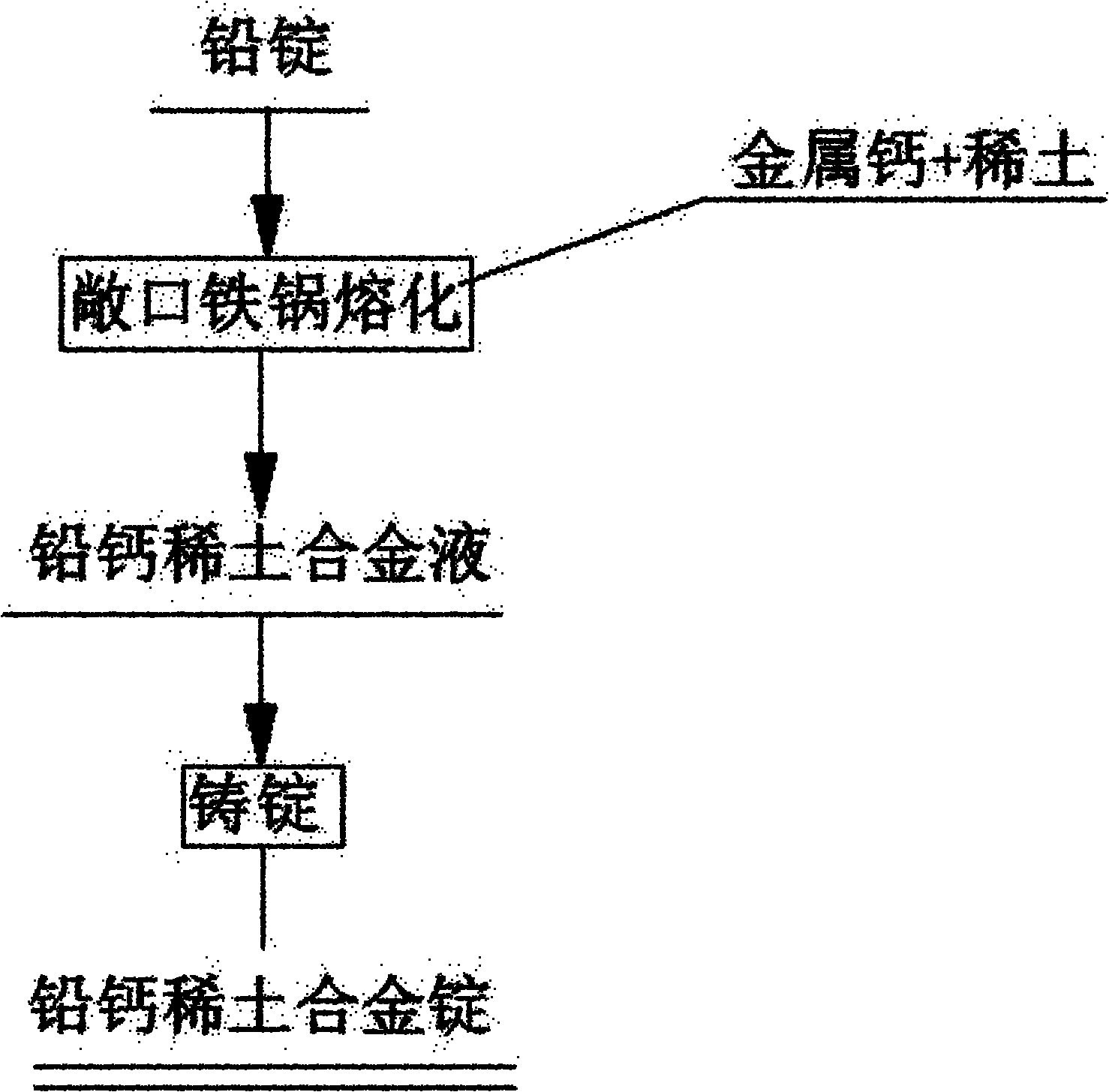
Direct production method for lead calcium rare earth alloy
A rare earth alloy and production method technology, which is applied in the field of direct production method of lead-calcium rare earth alloy, can solve the problems of troublesome batching calculation, complicated production process and high production cost, and achieves reduced production cost, low slag content and uniform structure distribution. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Ingredients: electric lead 1260kg, metallic calcium chips 1.65kg, rare earth (RE) 0.14kg, put electric lead into an iron pot, heat and melt to 600°C, press calcium and rare earth and stir for 12min, cast ingot out of furnace, mechanical stirring speed 120r .p.m, sampling test results (wt%): Ca: 0.119%, RE: 0.01%, utilization rates of Ca and RE: 91%, 90%, respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Ingredients: 1250kg electric lead, 1.65kg metal calcium scraps, 1.565kg rare earth protective agent (aluminum alloy) 1.3kg, put electric lead into an iron pot, heat and melt to 650°C, stir lead liquid, add protective agent (Al alloy ) was melted, pressed calcium and rare earth were stirred for 15 minutes, and the ingot was cast out of the furnace, the mechanical stirring speed was 120r.pm, the sampling test results (wt%): Ca: 0.121%, RE: 0.1%, Al: 0.036%, the utilization of Ca, RE and Al Rates were 93%, 80%, 40%.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Ingredients: electric lead 1261kg, metal calcium scraps 1.8kg, metal tin 8kg, rare earth 2.967kg, put the electric lead into an iron pot, heat and melt to 580°C, stir the lead liquid, add metal tin, add calcium, rare earth and stir The ingot was cast in 10 minutes, the mechanical stirring speed was 120r.pm, the sampling test results (wt%): Ca: 0.128%, Sn: 0.6%, RE: 0.2%, the utilization rate of Ca, Sn and RE were 89%, 95% respectively , 85%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com