Active constituent extracted from plant of altingia yunnanensis and application thereof
An active ingredient and plant technology, applied in the directions of plant/algae/fungus/moss ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, plant raw materials, etc., can solve the problem of no anti-Bacillus cereus activity, etc., and achieve a strong inhibitory effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
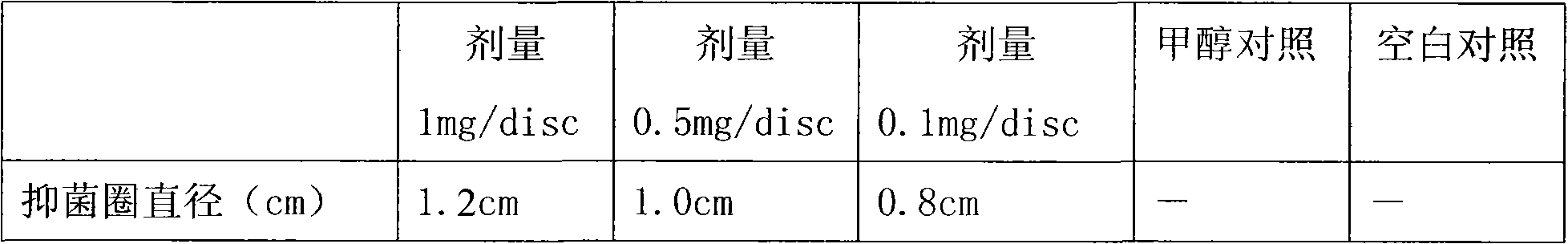
[0020] The branches of the Mengzi mushroom tree were washed with water, put into an oven, and baked at 60°C for 12 hours. 10 grams of dried branches were chopped, put into a conical flask, soaked in 100ml of 100% methanol, and extracted on a water bath at 40°C. The time for soaking and extracting for the first time is 2 hours, and the time for soaking and extracting for the second time and the second time is 4 hours and 8 hours respectively. The extracts from the three extractions were combined and concentrated at 60°C to obtain the extract. The extract was dissolved in methanol and prepared to a concentration of 10 mg / ml for activity determination. At the same time as a comparison, the results are shown in Table 1.
[0021] Table 1 The antibacterial effect of the extract of Mushroom branch on Bacillus cereus
[0022]
[0023] - No zone of inhibition appears
[0024] The result shows: the active ingredient that the present invention extracts has obvious antibacterial ac...
Embodiment 2
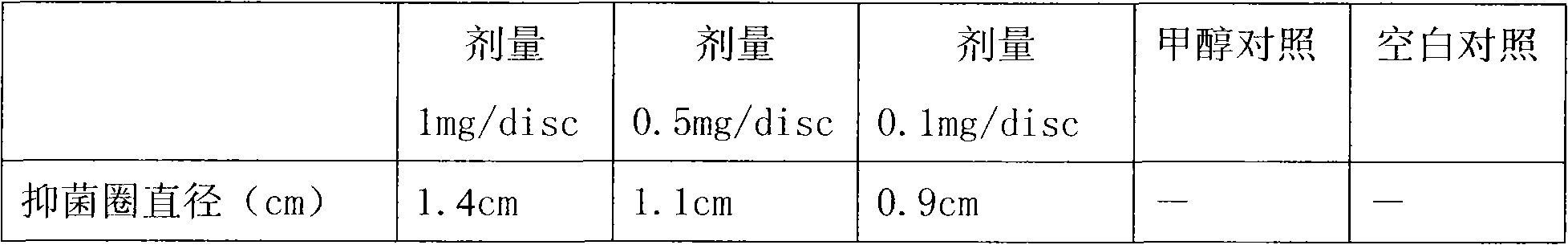
[0026] Basically the same as embodiment one, the difference is that the material used is the leaves of the Mengzi mushroom tree. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0027] Table 2 The antibacterial effect of the extract of Mushroom leaves on Bacillus cereus
[0028]
[0029] - No zone of inhibition appears
[0030] Compared with branch extracts, leaf extracts have relatively stronger antibacterial activity. When the extract is at 1mg, the size of the bacteriostatic zone is 1.4cm, and when 0.1mg, the antibacterial activity also occurs, the activity is relatively weak, and the size of the bacteriostatic zone is 0.9cm.
Embodiment 3
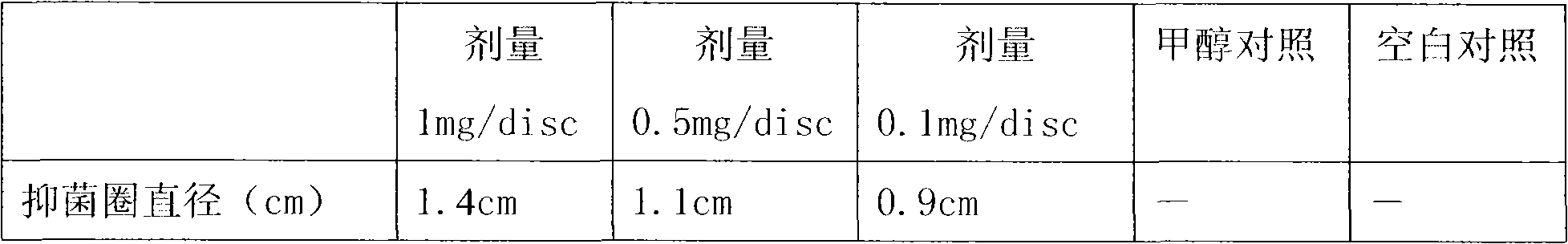
[0032] Basically the same as Example 2, the difference is that the extracted extract is heated in boiling water at 100°C for 30 minutes, then dissolved in methanol, and prepared at a concentration of 10 mg / ml for activity. At the same time as a comparison, the results are shown in Table 3.
[0033] Table 3 The antibacterial effect of the extract of Mushroom leaves on Bacillus cereus after high temperature treatment
[0034]
[0035] - No zone of inhibition appears
[0036] The results showed that the samples after high temperature treatment had the same antibacterial activity as the samples without high temperature treatment, indicating that the active ingredient was stable to heat.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com