Preparation method of metal-base superhydrophobic material
A technology based on hydrophobic materials and ultra-based materials, which is applied in electrolysis process, electroforming, etc., can solve the problems of lack of mechanical, electrical, and mechanical properties, and limit the application range of materials, and achieve the effects of low price, good portability, and safe operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
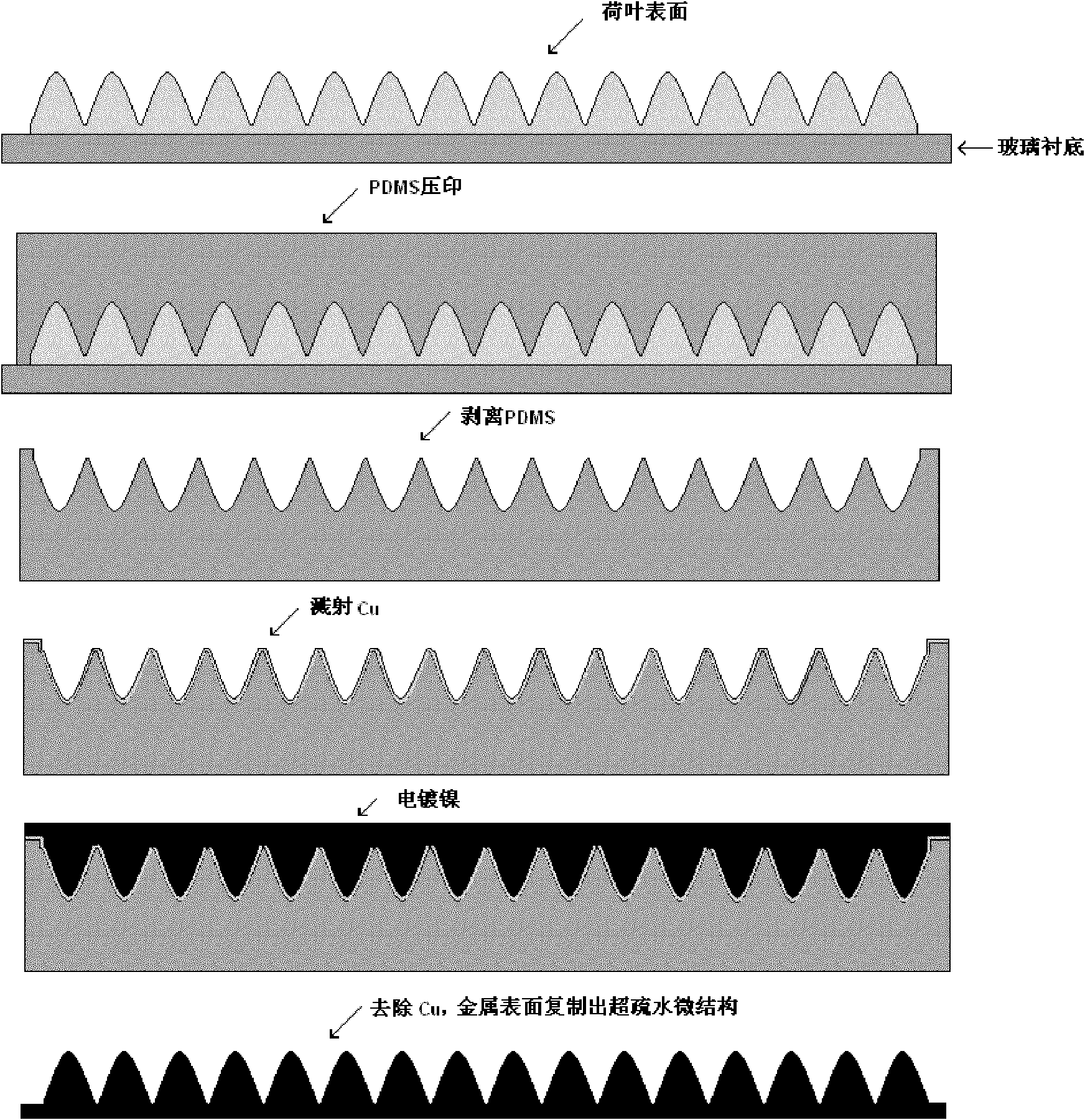
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0026] Step 1: Collect pigeon feathers, wash them with deionized water, and dry them at room temperature. Paste the feather flat on a clean glass slide.
[0027] Step 2: Coat the configured PDMS (polydimethylsilane) evenly on the feather surface, and then cure.
[0028] The PDMS is formulated according to the ratio of main agent:curing agent=10:1, and is viscous liquid at normal temperature. The curing temperature is 40° C., and the curing time is 120 minutes.
[0029] Step 3: The cured PDMS was peeled off from the glass slide, and the micro / nano array structure was successfully replicated on the PDMS surface. The PDMS surface is evenly distributed with micron-scale strip structures with a height of 2 μm, a length of 5 μm, and a spacing of 15 μm.
[0030] Step 4: sputtering a Cu seed layer on the PDMS surface with micro / nanostructures replicated.
[0031] The sputtering seed layer refers to...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0041] Step 1: Clean the surface of the lotus leaf with deionized water and dry it at room temperature. Paste the lotus leaves flat on a clean glass slide.
[0042] Step 2: Coating the prepared PDMS (polydimethylsilane) evenly on the surface of the lotus leaf, and then curing.
[0043] The PDMS is formulated according to the ratio of main agent:curing agent=10:1, and is viscous liquid at normal temperature. The curing temperature is 50° C., and the curing time is 60 minutes.
[0044] Step 3: The cured PDMS was peeled off from the glass slide, and the micro / nano array structure on the surface of the lotus leaf was successfully replicated on the PDMS surface. The PDMS surface is uniformly distributed with a cone-shaped array structure with a height of 2 μm, a diameter of 2 μm, and a pitch of 5 μm.
[0045]Step 4: sputtering a Cu seed layer on the PDMS surface with the micro / nano structure repl...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0056] Step 1: Clean the surface of the bamboo leaves with deionized water and dry them at room temperature. Stick the bamboo leaves flat on the clean glass.
[0057] Step 2: Coating the configured PDMS (polydimethylsilane) evenly on the surface of bamboo leaves, and then curing.
[0058] The PDMS is formulated according to the ratio of main agent:curing agent=10:1, and is viscous liquid at normal temperature. The curing temperature is 60°C, and the curing time is 60 minutes.
[0059] Step 3: The cured PDMS was peeled off from the glass slide, and the micro / nano array structure of the bamboo leaf surface was successfully replicated on the PDMS surface. The uniform distribution on the surface of PDMS has a cluster array structure with a height of 3 μm, a diameter of 2 μm, and a pitch of 8 μm.
[0060] Step 4: sputtering a Cu seed layer on the PDMS surface with the micro / nano structure replica...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com