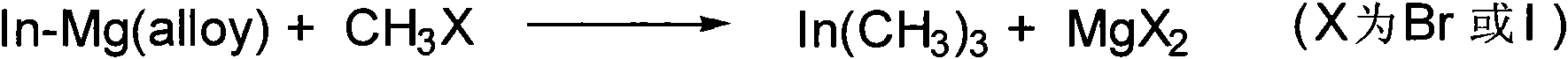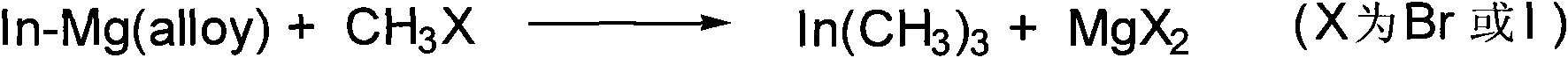Method for industrially preparing trimethyl indium
A technology of trimethylindium and haloalkane, which is applied in the field of preparation of trimethylindium, can solve the problems of low reaction conversion efficiency, expensive indium trichloride, and high cost of raw materials, and achieves a simple and stable reaction suitable for large-scale industrial production. The effect of high reaction yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] In a reactor filled with nitrogen, put 800g of indium-magnesium alloy into it, add 2150g of anhydrous ether, and gradually add methyl iodide (CH 3 I) 2420g, by controlling iodomethane (CH 3 The addition speed of 1) controls the solvent reflux speed, after the reaction is completed, continue to keep reflux for 4 hours, then the solvent is steamed, and then under reduced pressure (vacuum degree is between 1~70mmgH) to obtain trimethyl indium and ether The complex was finally decomposed (the decomposed temperature was between 80°C and 160° C.) to obtain 492 g of trimethylindium, with a yield of 87% (calculated as metal indium).
Embodiment 2
[0017] In a reactor filled with nitrogen, put 800 g of indium-magnesium alloy into it, add 1600 g of anhydrous ether, and gradually add methyl iodide (CH 3 I) 2420g, by controlling iodomethane (CH 3 The addition speed of 1) controls the solvent reflux speed, after the reaction is completed, continue to keep reflux for 4 hours, then the solvent is steamed, and then under reduced pressure (vacuum degree is between 1~70mmgH) to obtain trimethyl indium and ether The complex was finally decomposed (the decomposed temperature was between 80°C and 160° C.) to obtain 475 g of trimethylindium, with a yield of 84% (calculated as metal indium).
Embodiment 3
[0019] In a reactor filled with nitrogen, put 800g of indium-magnesium alloy into it, add 2150g of anhydrous ether, and gradually add methyl iodide (CH 3 I) 2050g, by controlling iodomethane (CH 3 The addition speed of 1) controls the solvent reflux speed, after the reaction is completed, continue to keep reflux for 4 hours, then the solvent is steamed, and then under reduced pressure (vacuum degree is between 1~70mmgH) to obtain trimethyl indium and ether The complex was finally decomposed (the decomposed temperature was between 80°C and 160° C.) to obtain 458 g of trimethylindium, with a yield of 81% (calculated as metal indium).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com