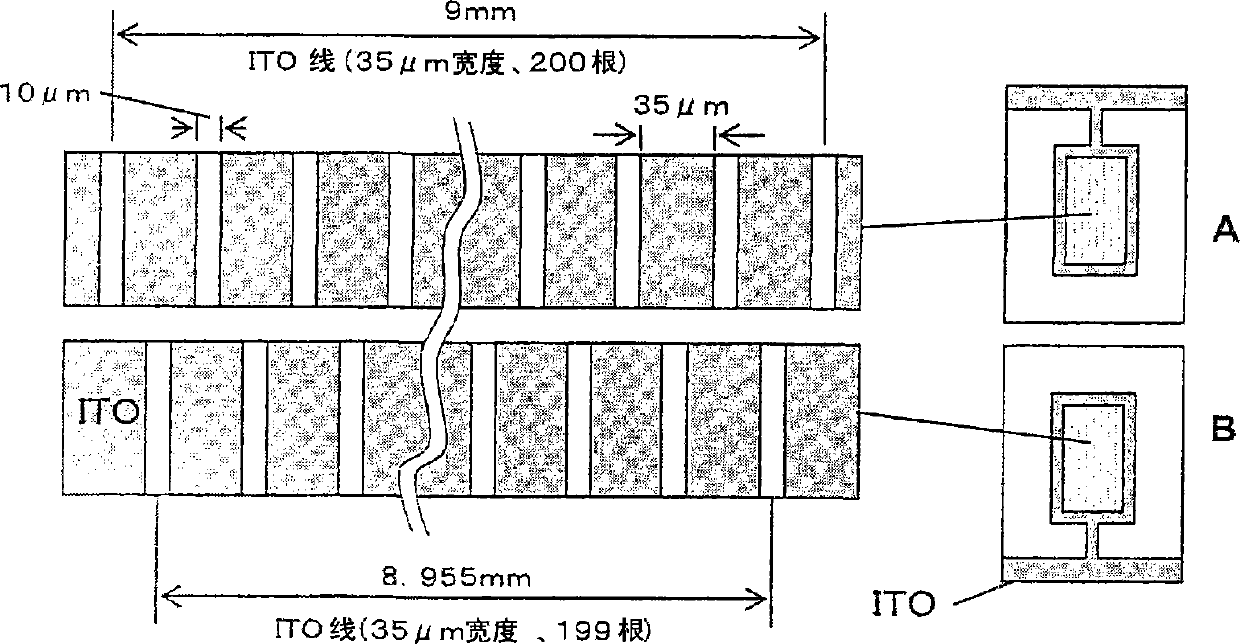
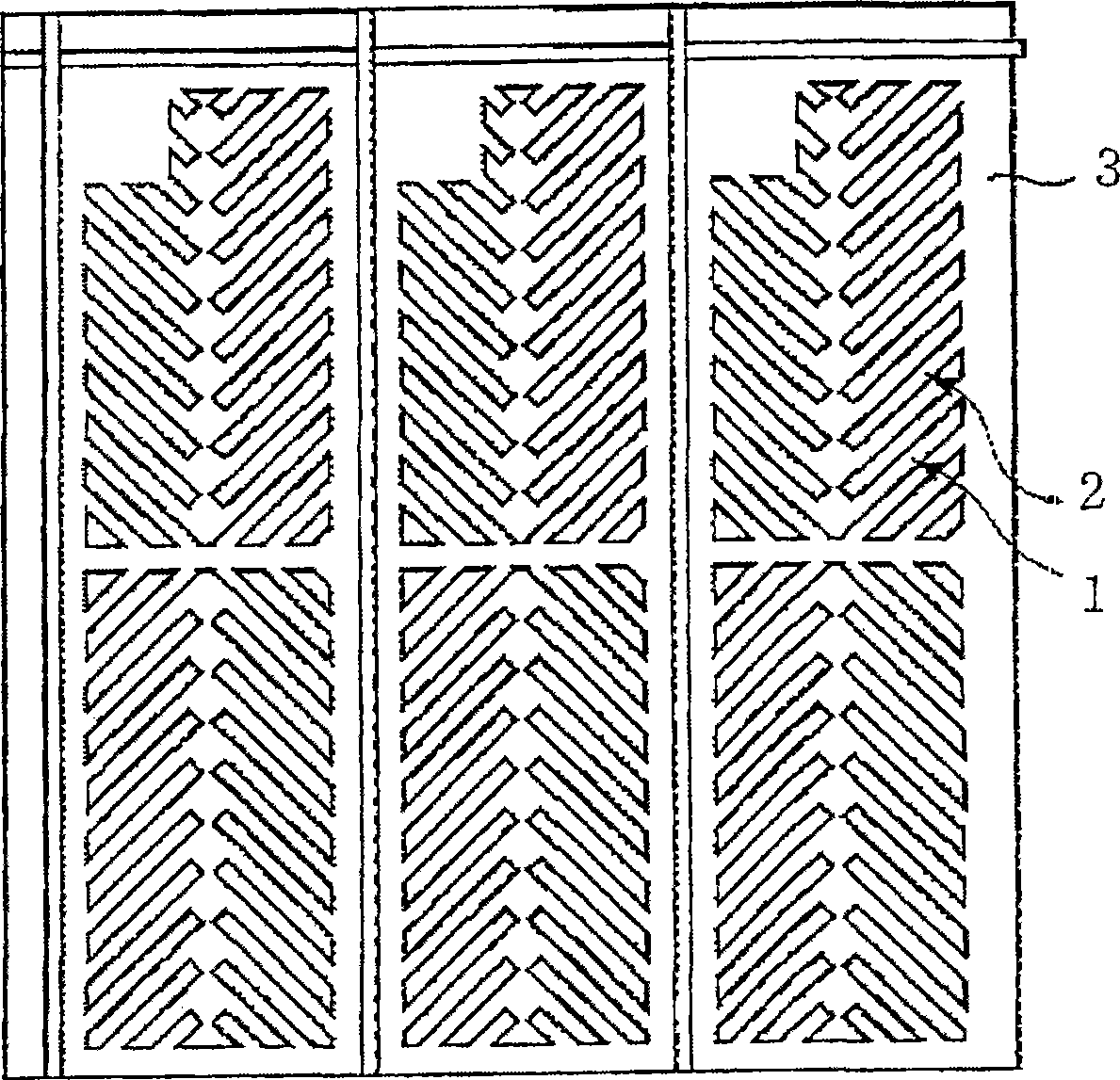
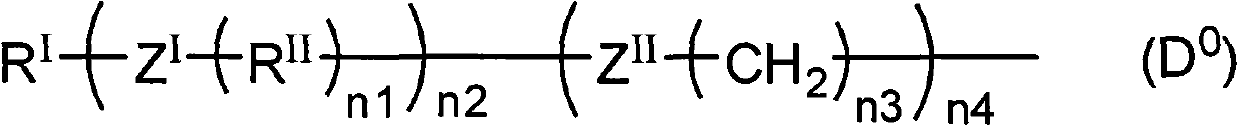Liquid crystal display element manufacturing method , polymer composition and liquid crystal display element
A technology for liquid crystal display elements and manufacturing methods, applied in liquid crystal materials, chemical instruments and methods, instruments, etc., which can solve the problems of high ultraviolet irradiation, failure to eliminate display properties, voltage retention properties, etc., and achieve non-destructive display properties and excellent display properties , the effect of wide viewing angle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Synthetic example S-1
[0305] [Hydrolysis and condensation reaction]
[0306] In a reaction vessel with a stirrer, a thermometer, a dropping funnel and a reflux condenser, 73.9 g of 2-(3,4-epoxycyclohexyl)ethyltrimethoxysilane (ECETS ) and 24.8g of γ-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (GMPTS) (ECETS:GMPTS=75:25 (molar ratio)) and 500g of methyl isobutyl ketone as a solvent and as a catalyst 10.0 g triethylamine, mixed at room temperature. Next, after adding 100 g of deionized water dropwise from the dropping funnel over 30 minutes, it was reacted at 80° C. for 6 hours while stirring under reflux. After the reaction, the organic layer was taken out, washed by 0.2% by weight of ammonium nitrate aqueous solution until the washed water was neutral, and the solvent and water were distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain a hydrolysis condensate with epoxy groups, which was viscous transparent liquid.
[0307] The hydrolyzed condensate 1 In H-NMR analysis, a peak due to the epoxy group of theoret...
Synthetic example S-2~S
[0310] Synthesis Examples S-2~S-6, S-10, S-11 and S-16
[0311] [Hydrolytic Condensation Reaction] and [Reaction of Hydrolytic Condensate with Epoxy Group and Carboxylic Acid]
[0312] In the above-mentioned Synthesis Example S-1, the hydrolyzable silane compound and carboxylic acid of the kind and amount described in Table 1 were respectively used, and the hydrolytic condensation reaction and the hydrolytic condensation product and carboxylic acid were carried out in the same manner as Synthesis Example S-1. After the reaction, polyorganosiloxanes (PS-2) to (PS-6), (PS-10), (PS-11) and (PS-16) as (A) the first polymer were obtained respectively. The yields and Mw of these polyorganosiloxanes are combined in Table 1 and shown. In addition, in Synthesis Examples S-3 to S-5 and S-16, two kinds of carboxylic acids were used for each. Synthesis Example S-6 is a comparative synthesis example.
Synthetic example S-7~S-9
[0314] [Hydrolysis and condensation reaction]
[0315] In the above-mentioned Synthesis Example S-1, except that the type and amount of hydrolyzable silane compounds described in Table 1 were used, the hydrolytic condensation reaction was carried out in the same manner as in Synthesis Example S-1, and the first polymers (A) were obtained, respectively. polyorganosiloxane (PS-7) ~ (PS-9). The yields and Mw of these polyorganosiloxanes are combined in Table 1 and shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com