Method and device for carbonizing and curing soil
A solidification method and soil technology, applied in soil protection, infrastructure testing, construction, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing carbon dioxide emissions, reducing carbon dioxide emissions and energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
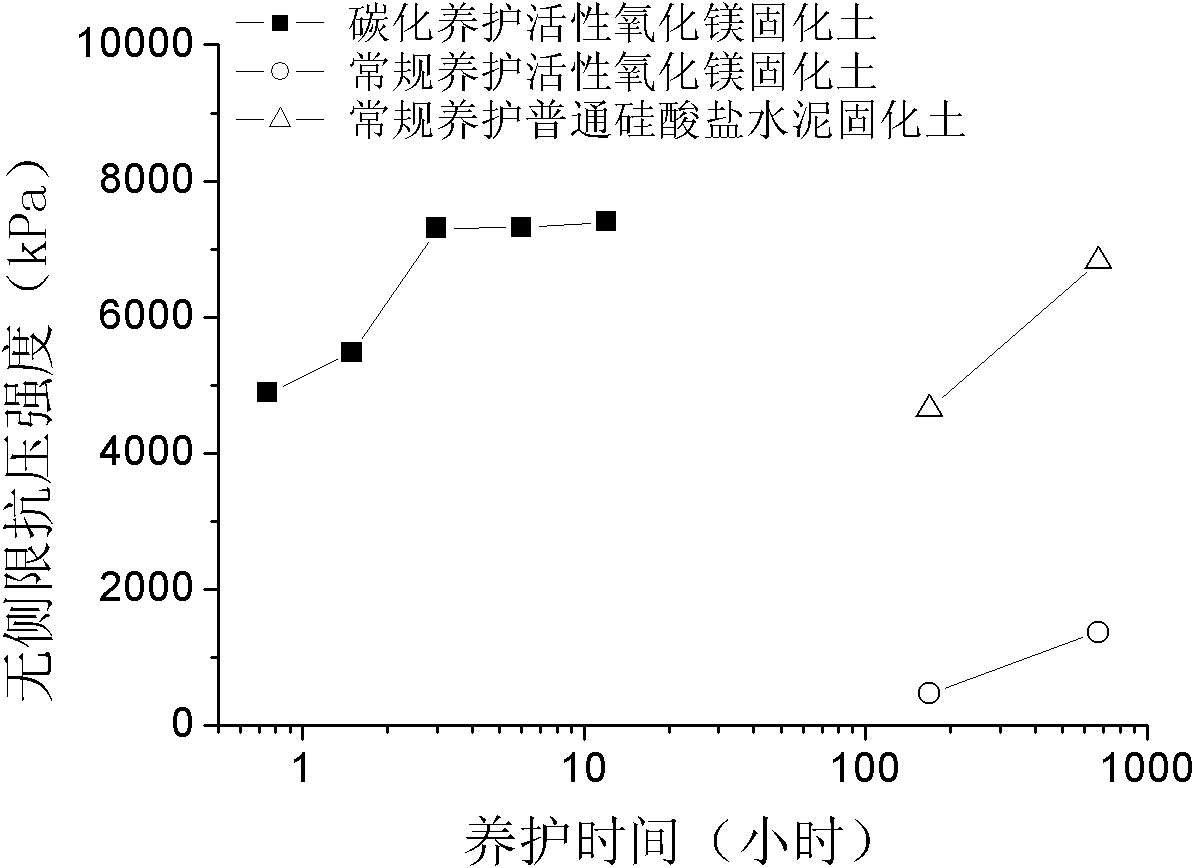
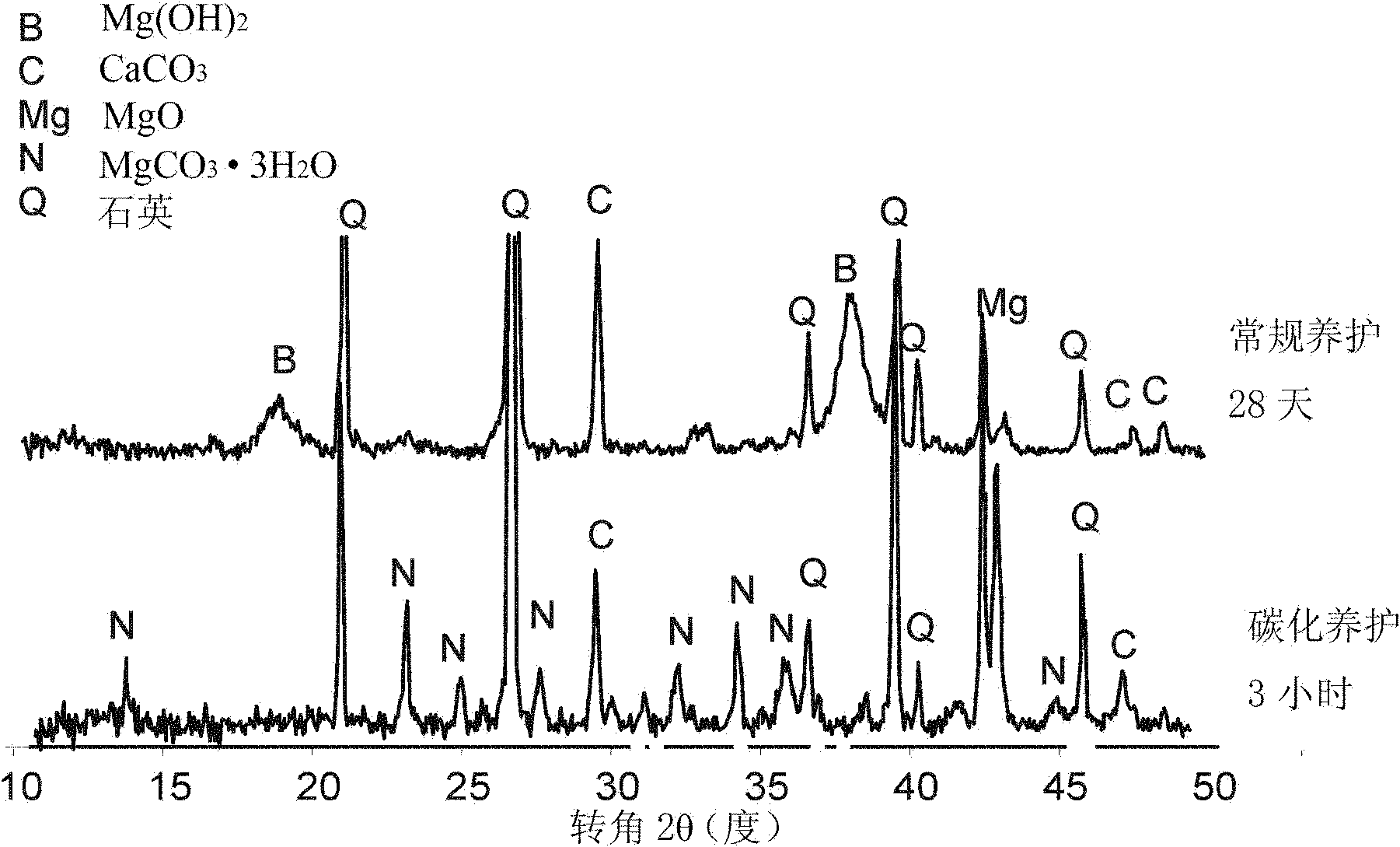
[0023] In this embodiment, it is an indoor test, mainly analyzing the feasibility of carbonization and solidification method and the influence of different carbonization time on the strength of carbonized soil. The soil to be solidified is sandy soil with a water content of 10%, the curing agent is active magnesium oxide, and the active magnesium oxide content (the ratio of active magnesium oxide to the total mass of the soil body and active magnesium oxide) is 10%. First mix the active magnesium oxide and the soil according to the design ratio, stir evenly, pour it into a standard mold with a diameter of 5 cm and a height of 10 cm, vibrate and compact it, and demould it after about half an hour, and install the sample on the On the three-axis permeameter, a confining pressure of 400kPa is applied, and then 200kPa of carbon dioxide gas is injected into the sample from the bottom for carbonization curing. The curing time is 45 minutes, 1.5 hours, 3 hours, 6 hours and 12 hours re...
Embodiment 2
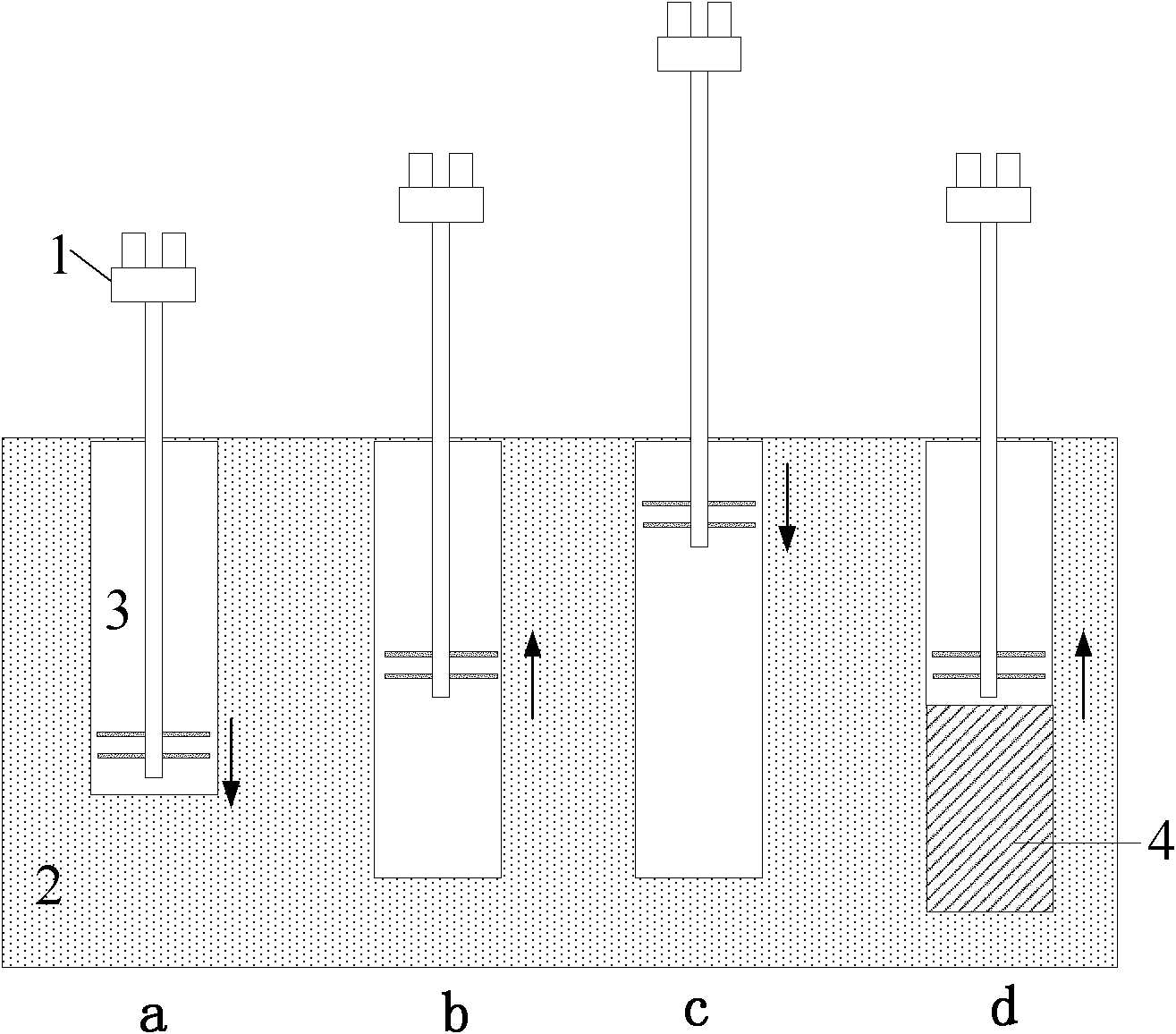
[0027] In this embodiment, it is a carbonized stirring pile test, the soil to be reinforced is dry sandy soil, the curing agent is activated magnesium oxide, and the mass ratio of activated magnesium oxide to dry soil is 10%. First use a small stirring pile machine 1 to stir in the soil and spray active magnesia slurry to form uncarbonized active magnesia solidified soil 3, and then use the stirring pile machine 1 to introduce carbon dioxide gas while stirring for carbonization. The specific construction see process image 3 , and introduced as follows:
[0028] (a) Arrange the stirring pile 1 above the natural soil body 2 to be solidified, start the stirring pile 1, the stirring pile 1 sinks, stir and spray active magnesium oxide slurry at the same time, until the stirring blade reaches the design elevation of the bottom surface;
[0029] (b) Stirring pile driver 1 promotes, simultaneously stirs and sprays activated magnesium oxide slurry, until stirring blade reaches the gr...
Embodiment 3
[0034] This embodiment is a carbonized stirring pile test, the soil to be reinforced is dry sandy soil, the curing agent is activated magnesia, and the mass ratio of activated magnesia to dry soil is 10%. First use a small-scale stirring pile machine 1 to stir in the soil, spray active magnesium oxide slurry to form uncarbonized active magnesium oxide to stir and solidify the soil 3, and then deploy a carbonization device to carry out carbonization through the carbonization device.
[0035] Carbonization device comprises carbon dioxide generator 7 and outer sleeve 5, is provided with the through hole 12 as carbon dioxide outlet on the tube wall of outer sleeve 5, is connected with carbon dioxide import pipe 6 on carbon dioxide generator 7 and the carbon dioxide on carbon dioxide generator 7 The gas outlet is connected with one end of the carbon dioxide introduction pipe 6, and the other end of the carbon dioxide introduction pipe 6 is located at the end of the outer sleeve 5. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com