Method for separating long terminal repeats of retrotransposons
A retrotransposon, long terminal repeat technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, microbial assay/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of high false positive rate and difficulty in isolating retrotransposons High cost and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
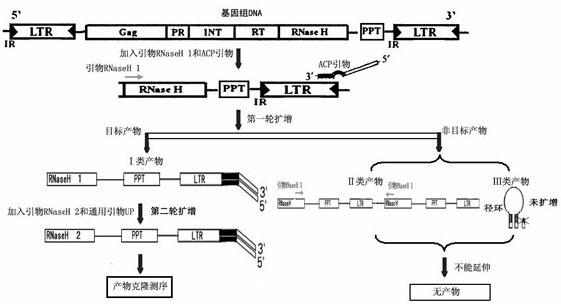
[0076] Step 1. Design primers
[0077] Design RNaseH group PCR primers, ACP group PCR primers, UP general PCR primers:
[0078] Nested primer RNaseH 1 MGNACNAARCAYATHGA
[0079] RNaseH 2 GCNGAYATNYTNACNAA
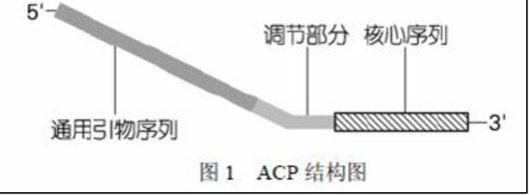
[0080] Annealing control primer (ACP)
[0081] ACP 1 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III VNVNNNGGAA
[0082] ACP 2 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA IIII BNBNNNGGTT
[0083] ACP 3 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III HNVNNNCCAC
[0084] ACP 4 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III CAATGGCTACCAC
[0085] ACP 5 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III VVNVNNNCCAA
[0086] ACP 6 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III BDNBNNNCGGT
[0087] Universal Primer UP TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA
[0088] The I represents deoxyestranine, B (CGT), D (AGT), H (ACT), V (ACG), N (AGCT)
[0089] Step 2. Peony Genome Extraction
[0090] Select the fresh leaves of the peony variety "Luoyang Red" in April, mash them, and use the DNA extraction kit to extract the genome;
[0091] Step 3, the first PCR reaction
[0092] 1) The first PCR reaction system: prepare 20 ...
Embodiment 2
[0139] Step 1. Design primers
[0140] Design RNaseH group PCR primers, ACP group PCR primers, UP general PCR primers:
[0141] Nested primer RNaseH 1 MGNACNAARCAYATHGA
[0142] RNaseH 2 GCNGAYATNYTNACNAA
[0143] Annealing control primer (ACP)
[0144] ACP 1 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III VNVNNNGGAA
[0145] ACP 2 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA IIII BNBNNNGGTT
[0146] ACP 3 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III HNVNNNCCAC
[0147] ACP 4 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III CAATGGCTACCAC
[0148] ACP 5 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III VVNVNNNCCAA
[0149] ACP 6 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III BDNBNNNCGGT
[0150] Universal Primer UP TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA
[0151] The I represents deoxyestranine, B (CGT), D (AGT), H (ACT), V (ACG), N (AGCT)
[0152] Step 2. Peony Genome Extraction
[0153] Select the fresh leaves of the peony variety "Luoyang Red" in April, mash them, and use the DNA extraction kit to extract the genome;
[0154] Step 3, the first PCR reaction
[0155] 1) The first PCR reaction system: prepare 20 ...
Embodiment 3
[0202] Step 1. Design primers
[0203] Design RNaseH group PCR primers, ACP group PCR primers, UP general PCR primers:
[0204] Nested primer RNaseH 1 MGNACNAARCAYATHGA
[0205] RNaseH 2 GCNGAYATNYTNACNAA
[0206] Annealing control primer (ACP)
[0207] ACP 1 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III VNVNNNGGAA
[0208] ACP 2 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA IIII BNBNNNGGTT
[0209] ACP 3 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III HNVNNNCCAC
[0210] ACP 4 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III CAATGGCTACCAC
[0211] ACP 5 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III VVNVNNNCCAA
[0212] ACP 6 TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA III BDNBNNNCGGT
[0213] Universal Primer UP TGTAGCGTGAAGACGACAGAA
[0214] The I represents deoxyestranine, B (CGT), D (AGT), H (ACT), V (ACG), N (AGCT)
[0215] Step 2. Peony Genome Extraction
[0216] Select the fresh leaves of the peony variety "Luoyang Red" in April, mash them, and use the DNA extraction kit to extract the genome;
[0217] Step 3, the first PCR reaction
[0218]1) The first PCR reaction system: prepare 20 μ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com