Radiating fin of magnetron
A heat sink and magnetron technology, which is applied in the field of magnetron, can solve the problems that the heat sink blades reduce the air circulation space of the heat sink, the overall heat dissipation capacity of the heat sink cannot reach, and the motherboard increases the thickness of the heat sink blades, etc., so as to reduce the temperature, Improved heat conduction efficiency and improved performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
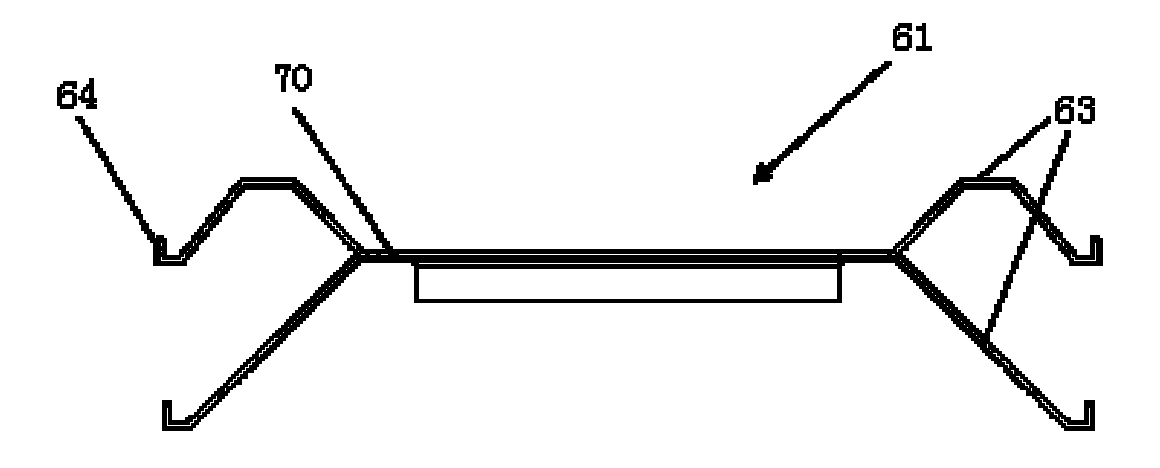
[0027] Figure 4 It is a side view of the heat sink of the magnetron of the present invention.
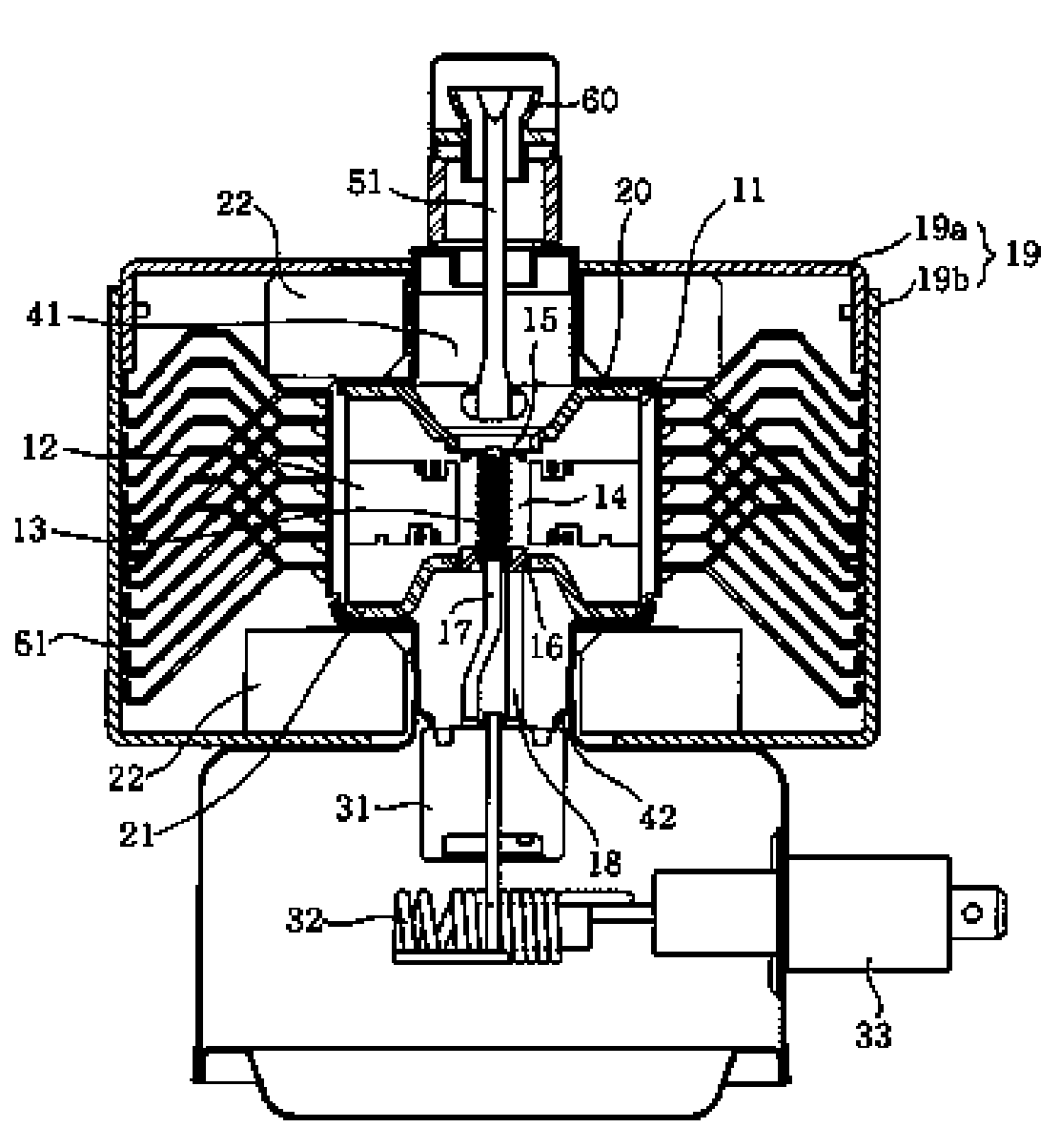
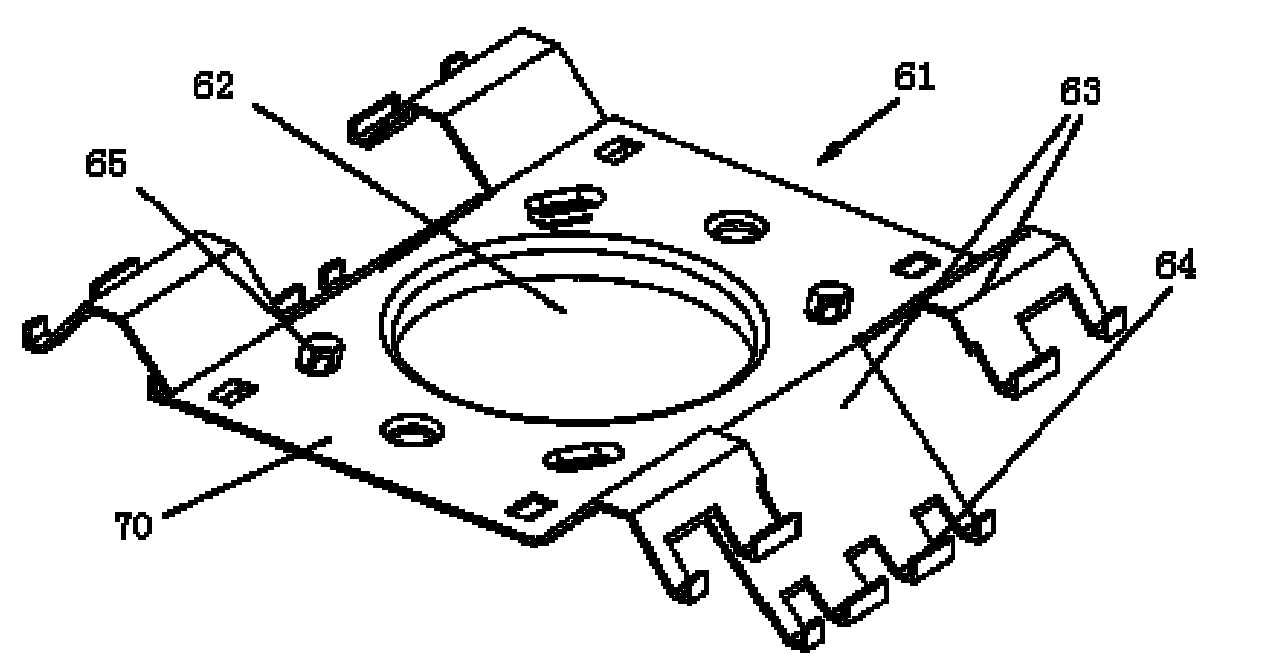
[0028] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the heat sink 61 of the magnetron of the present invention is integrally formed and stamped from an aluminum metal plate, and is divided into a main board 70 and cooling fins 63 arranged on both sides of the main board according to the position. An anode hole for assembling the magnetron anode shell 11 is left on the main board 70 in the middle of the heat sink. When the heat sink is installed, match the anode hole with the anode shell and press down into the heat sink. Repeat this step several times. A group of heat sinks of the same model can be stacked and installed on the same anode shell, and each heat sink is provided with a plurality of limiting protrusions (not shown). When installing, press each heat sink until...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com