Influenza vaccines
A flu vaccine, influenza technology, applied in vaccines, multivalent vaccines, immunoglobulins, etc., can solve problems such as damage to antigenic proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0239] Example 1: Intravenous administration of BALB / c mice with gamma-irradiated influenza A virus inoculation
[0240] (i) Materials and methods
[0241] animal
[0242] BALB / c mice of the same sex and in a similar age group (8-12 weeks old) were used in each experiment.
[0243] virus and immunity
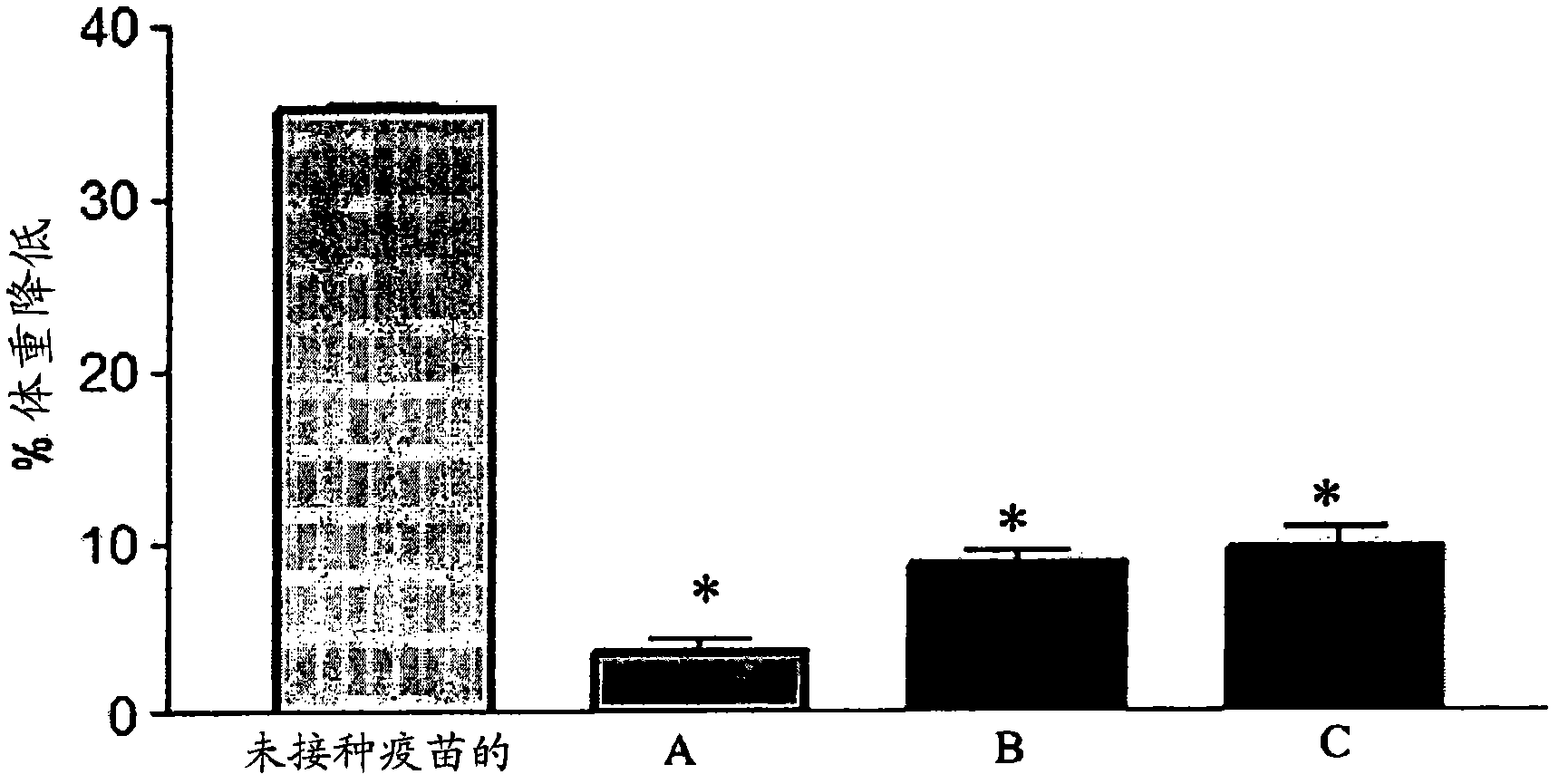
[0244] As described by Yap et al., 1977, "Cytotoxic T cells specific for influenza virus-infected target cells", Immunology, 32: 151, for influenza virus strains A / WSN (H1N1), A / JAP (H2N2) and A / PC(H3N2) for incubation and titration. Virus titers were expressed as hemagglutination units (HAU). By exposing crude allantoic fluid to Co 60 Source 1.26X 10 6 rads (12.6 KGy) (60 h exposure at 350 rads / min), or by exposing dialyzed infectious allantoic fluid to UV radiation (320 μW / cm 2 ) for 10 minutes to inactivate the A / JAP influenza virus. Exposure to gamma or UV irradiation for these periods completely abolished infectivity as tested in embryonated eggs. By a single ...
Embodiment 2
[0274] Example 2: Intravenous inoculation of gamma-irradiated influenza A strains A / WSN [H1N1], A / PR8 [H1N1], A / JAP [H2N2] and A / PC [H3 / N2]
[0275] (i) Materials and methods
[0276] animals and viruses
[0277] Stocks of influenza A virus (strain A / WSN, A / Pr8[H1N1]; A / JAP[H2N2]; A / PC[H3N2]) were prepared in 10-day-old embryonated eggs. Viral stocks were prepared from allantoic fluid and stored in aliquots at -70°C. Initially, BALB / c and C57B1 / 6 mice were infected intranasally and the severity of influenza virus infection was evaluated in terms of mortality, body weight loss, lung histology and lung infiltration.
[0278] Gamma-irradiation of influenza virus strains
[0279] Gamma-ray dose-response studies of frozen and room temperature-maintained virus stocks were performed at NSTO / Lucas Heights / NSW to determine conditions that yielded inactivated virus preparations with optimal immunogenicity. 5x10 5 An irradiation dose of rads (5 KGy) was sufficient to induce inactiva...
Embodiment 3
[0302] Example 3: Intranasal vaccination with gamma-irradiated influenza A virus protects against H5N1 (avian influenza).
[0303] (i) Materials and methods
[0304] animal
[0305] Ten-week-old BALB / c mice were used in this experiment.
[0306] Virus
[0307] Virus stocks of two influenza A strains (A / PR8[H1N1] and A / PC[H3N2]) were grown in embryonated chicken eggs and purified by temperature-dependent adsorption to chicken erythrocytes, and passage through Madin Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells were assessed for viral titers using standard plaque assays and titers were expressed as pfu / mls.
[0308] Gamma-irradiation of influenza strains
[0309] Expose purified stock to 1x10 6 rad (10 kGy) gamma-rays (ANSTO, Lucas Height, Australia) as described in Example 2 above. Residual virus infectivity in irradiated stocks was detected by using embryonated chicken eggs. Viral stocks are inactivated, but phantom hemagglutination activity is maintained after irradiation.
[0310] ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com