Detector material for a detector for use in ct systems, detector element and detector
A technology of detectors and components, applied in the direction of electrical components, electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problem of large detectable flux of direct conversion detectors, failure to prevent polarization effects of direct conversion detectors, and inability to measure, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of enhancing signal stability and measurement repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
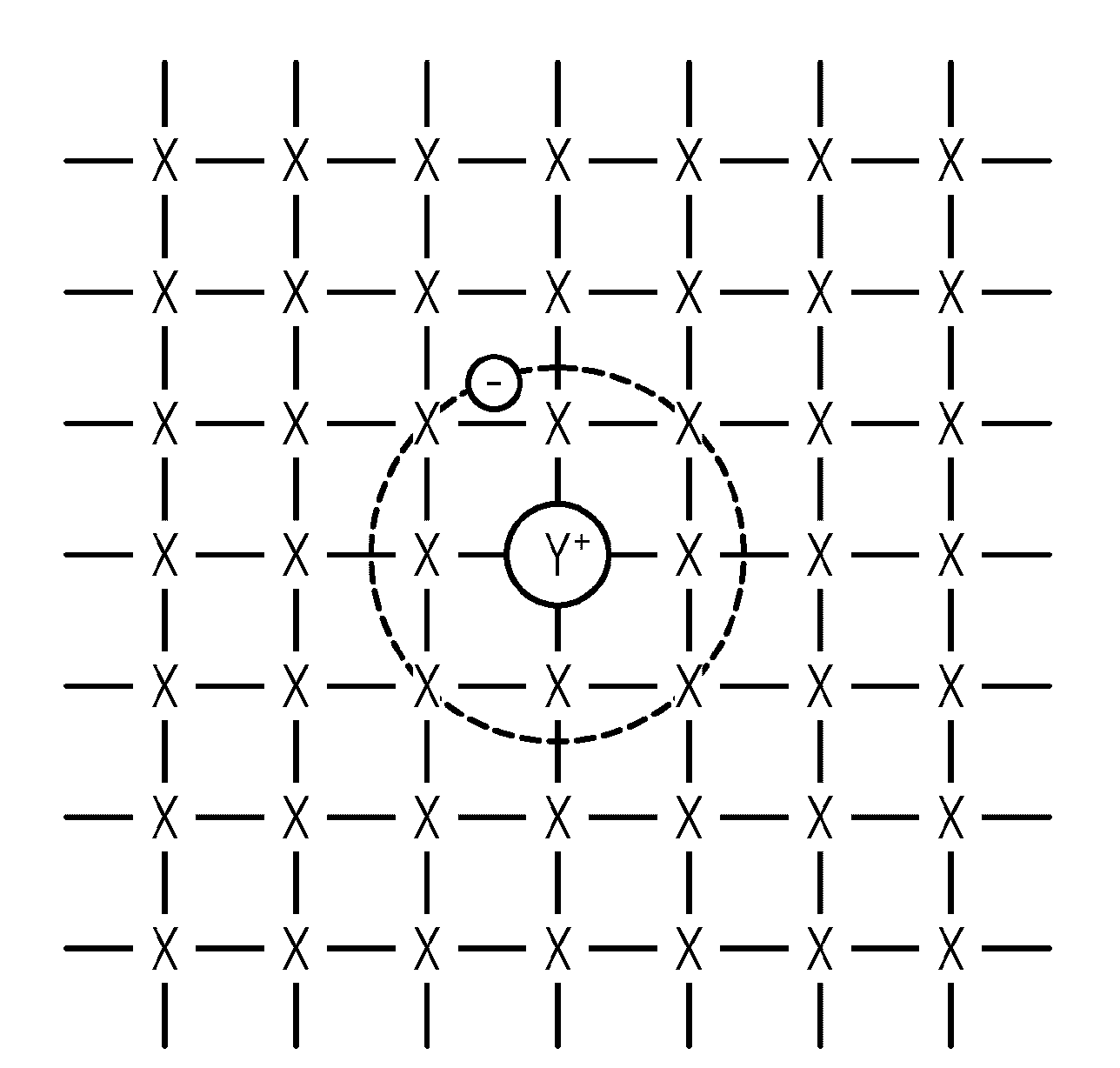
[0032] figure 1 A schematic diagram of a semiconductor doped with a donor atom. The atoms of the semiconductor crystal are marked X, and the donor atoms are marked Y. The bonds between these atoms are indicated by dashes. In this general example, the donor atom is located at the normal atomic position in the semiconductor crystal, thereby displacing a semiconductor atom. According to the relevant definition of the donor atom, the donor atom releases a weakly bound electron into the conduction band. That is, the donor atoms are ionized. Meanwhile, the donor atom's positively charged nucleus stays in place.
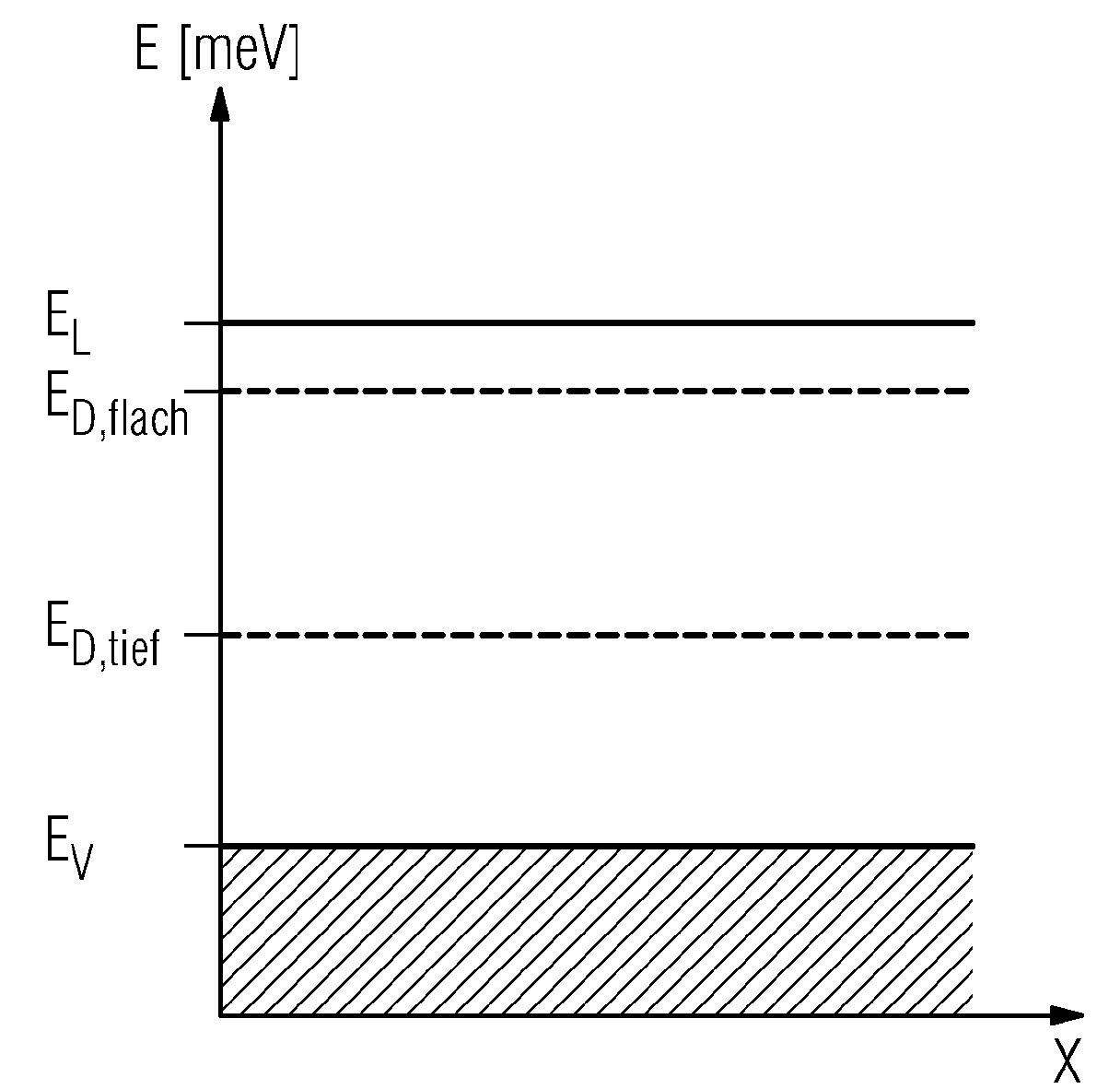
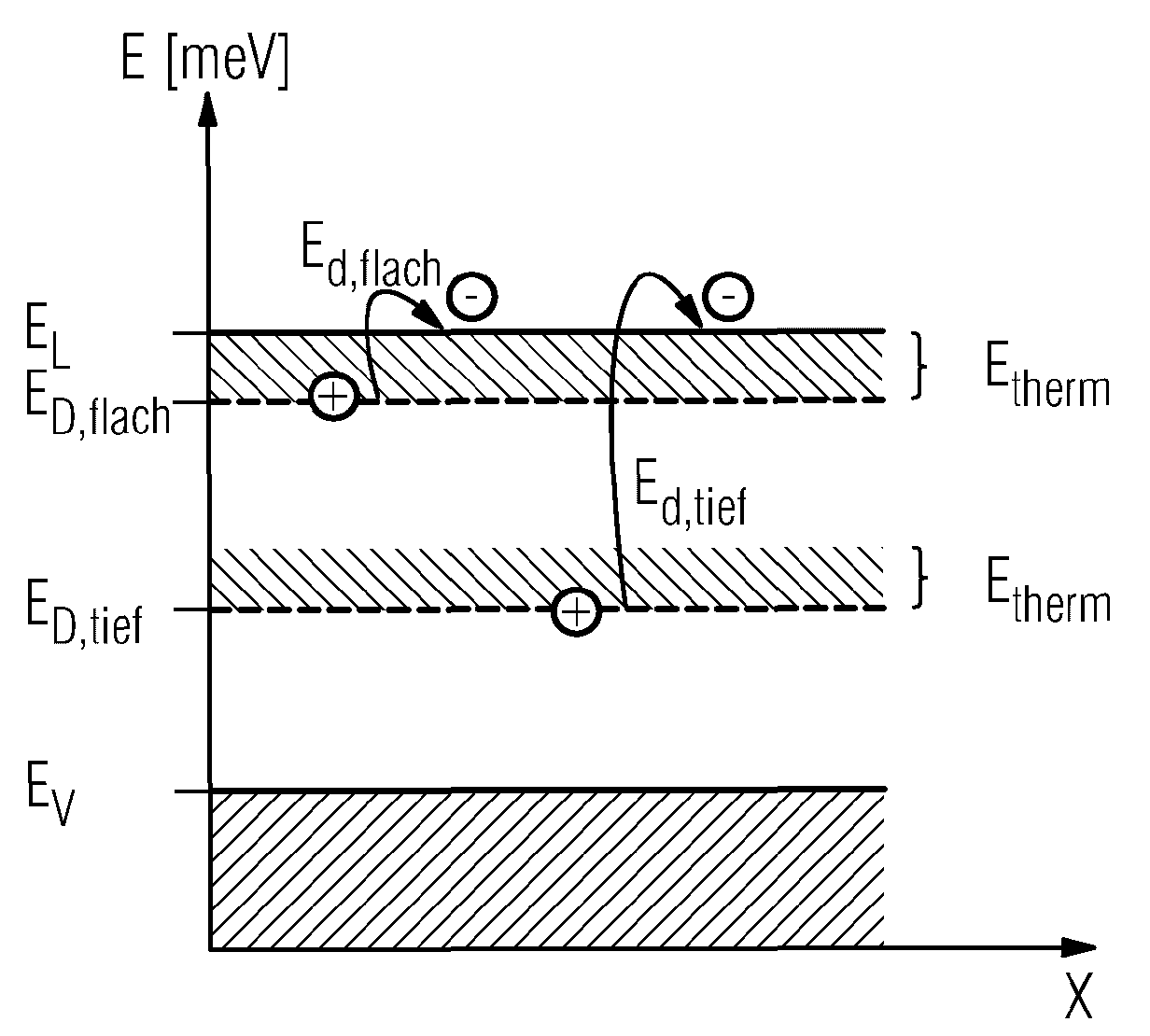
[0033] As a specific example of semiconductor doping in the present invention, CdTe semiconductor is doped with chlorine. The Cl concentration of conventional CdTe:Cl detectors for detecting gamma radiation and X-ray radiation is about 1*10 17 / cm 3 up to 2*10 17 / cm 3 . Such detectors are not suitable for high-throughput applications due to the strong polarizatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com