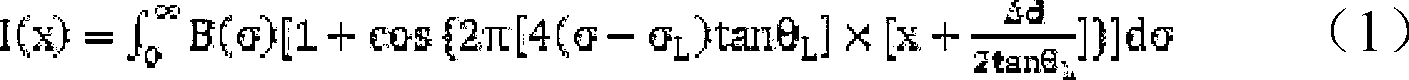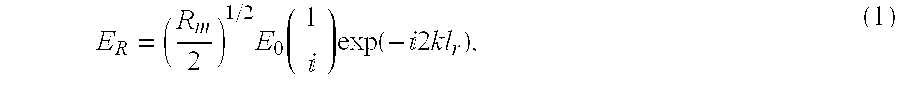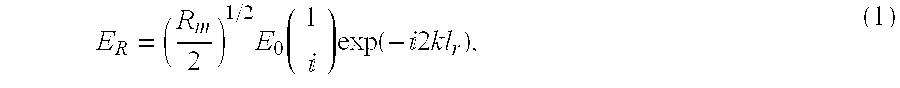Patents
Literature
113 results about "Heterodyne interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
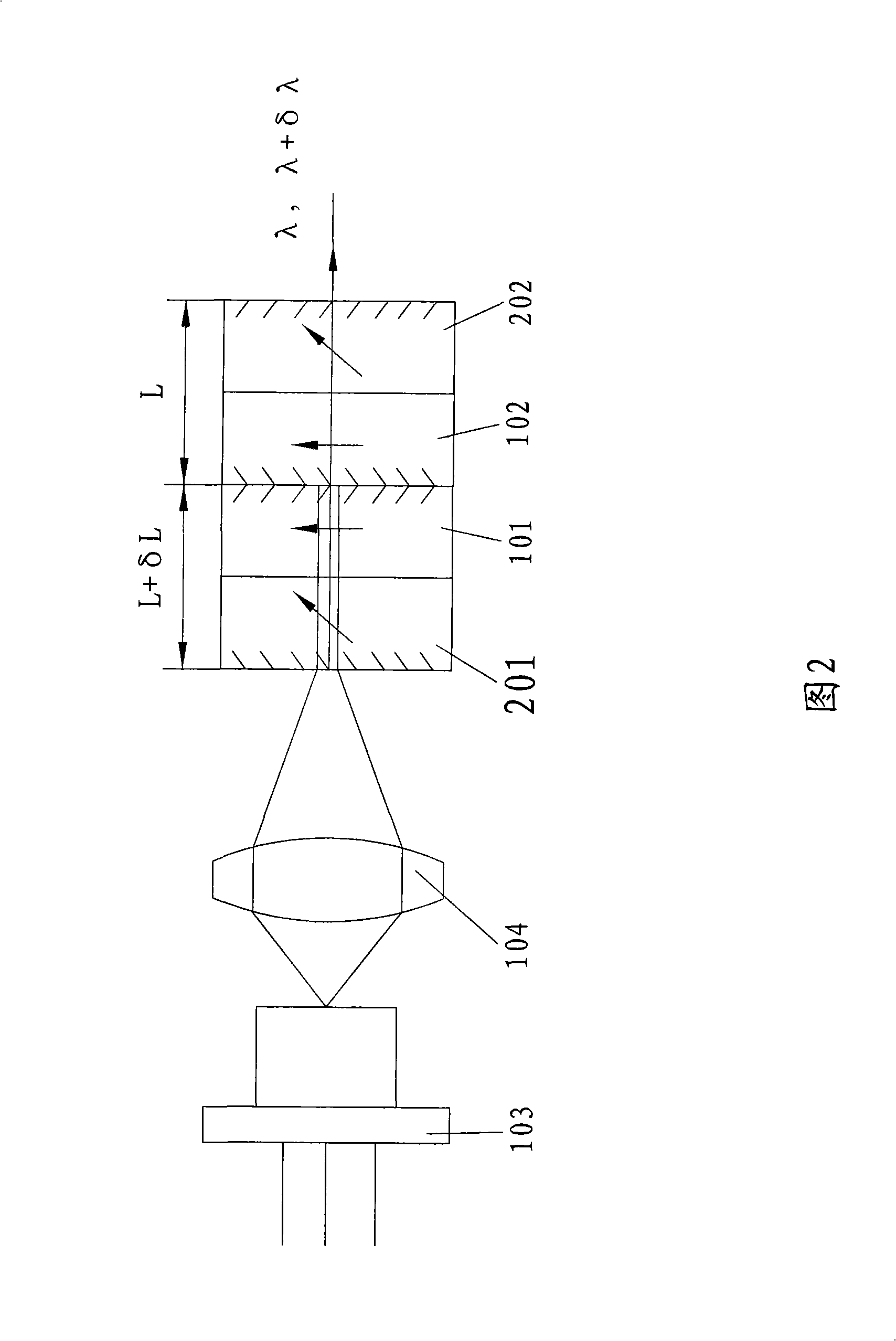
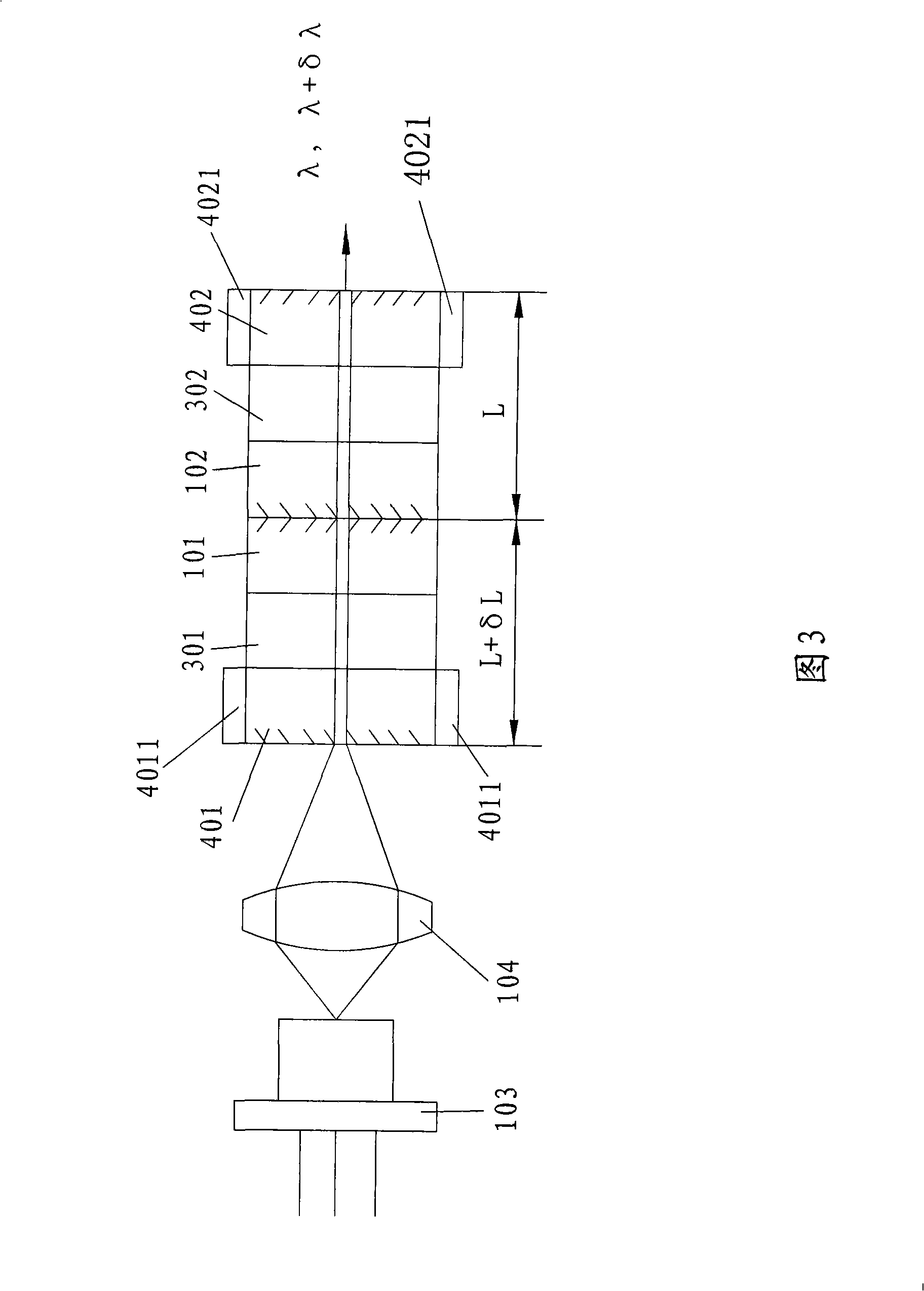
Method and device for measuring frequency scanning absolute distance based on femtosecond optical frequency comb
InactiveCN102183234AHigh precisionGood repeatabilityOptical measurementsOptical rangefindersFiberHeterodyne interferometer
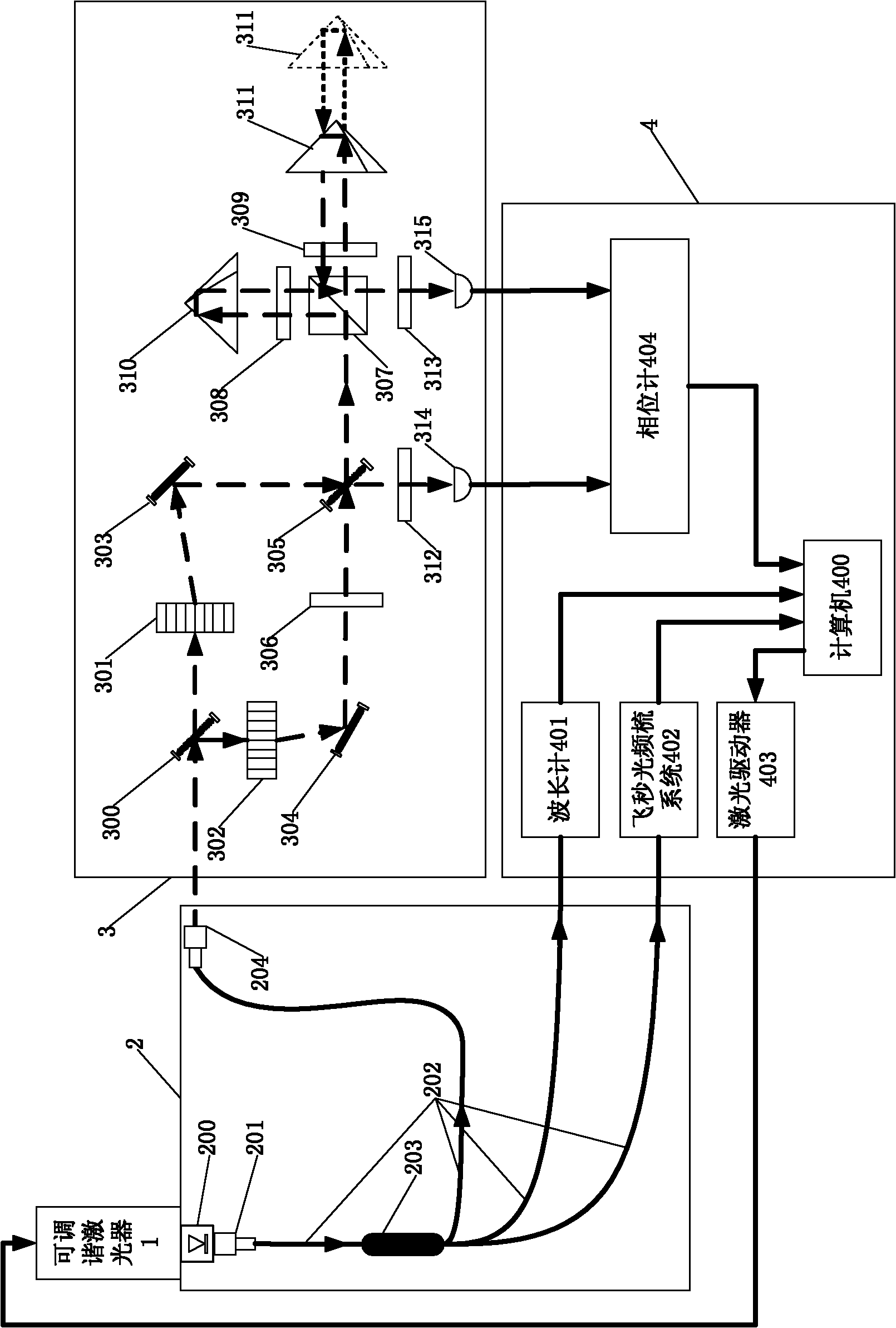
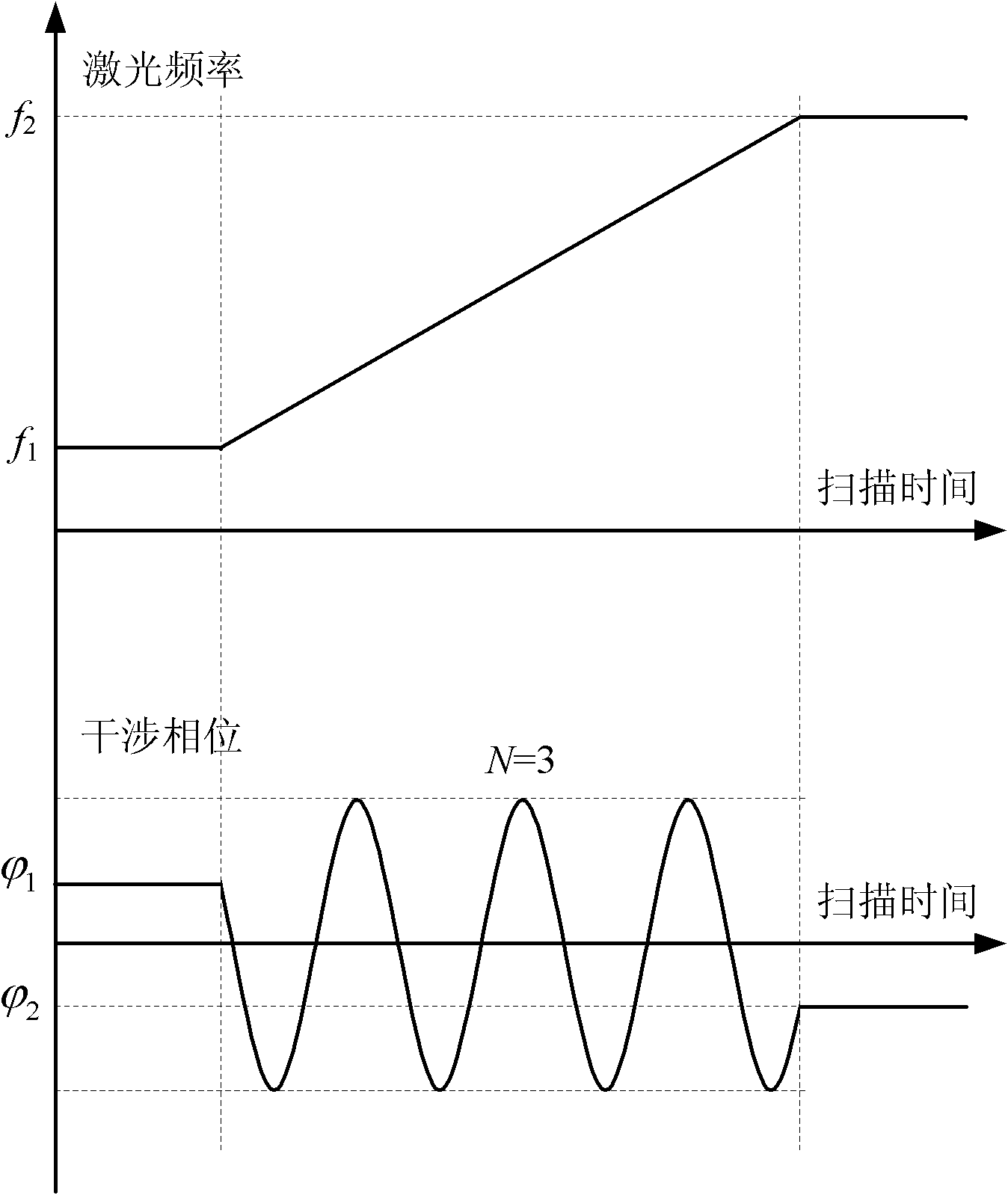
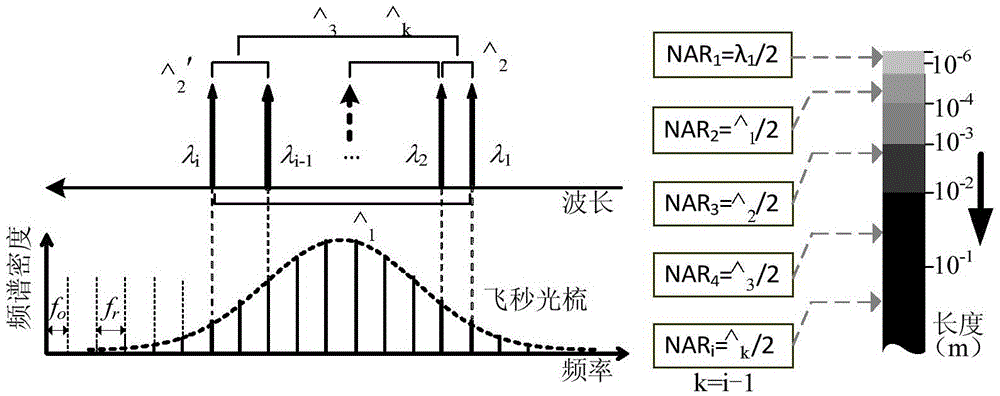
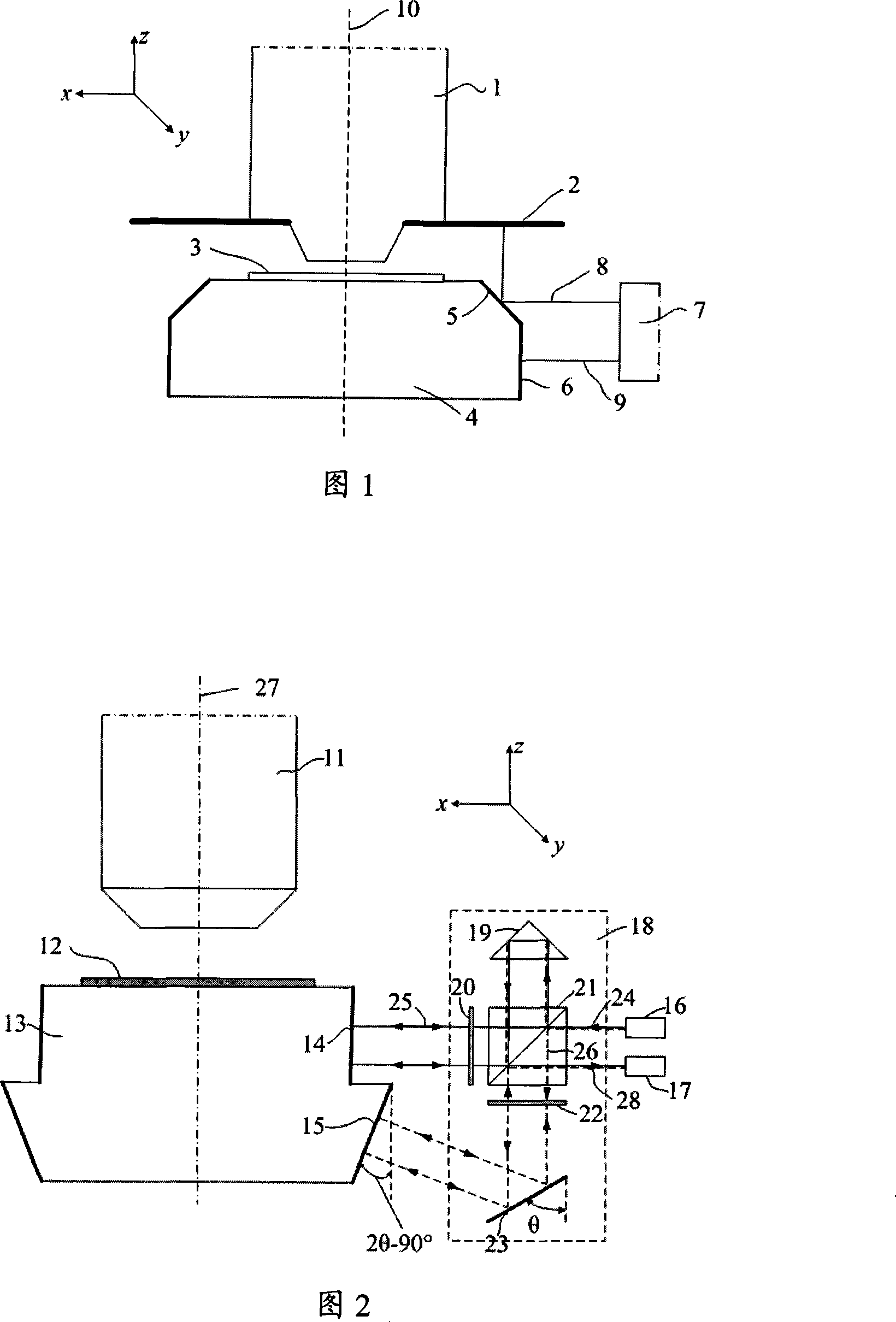
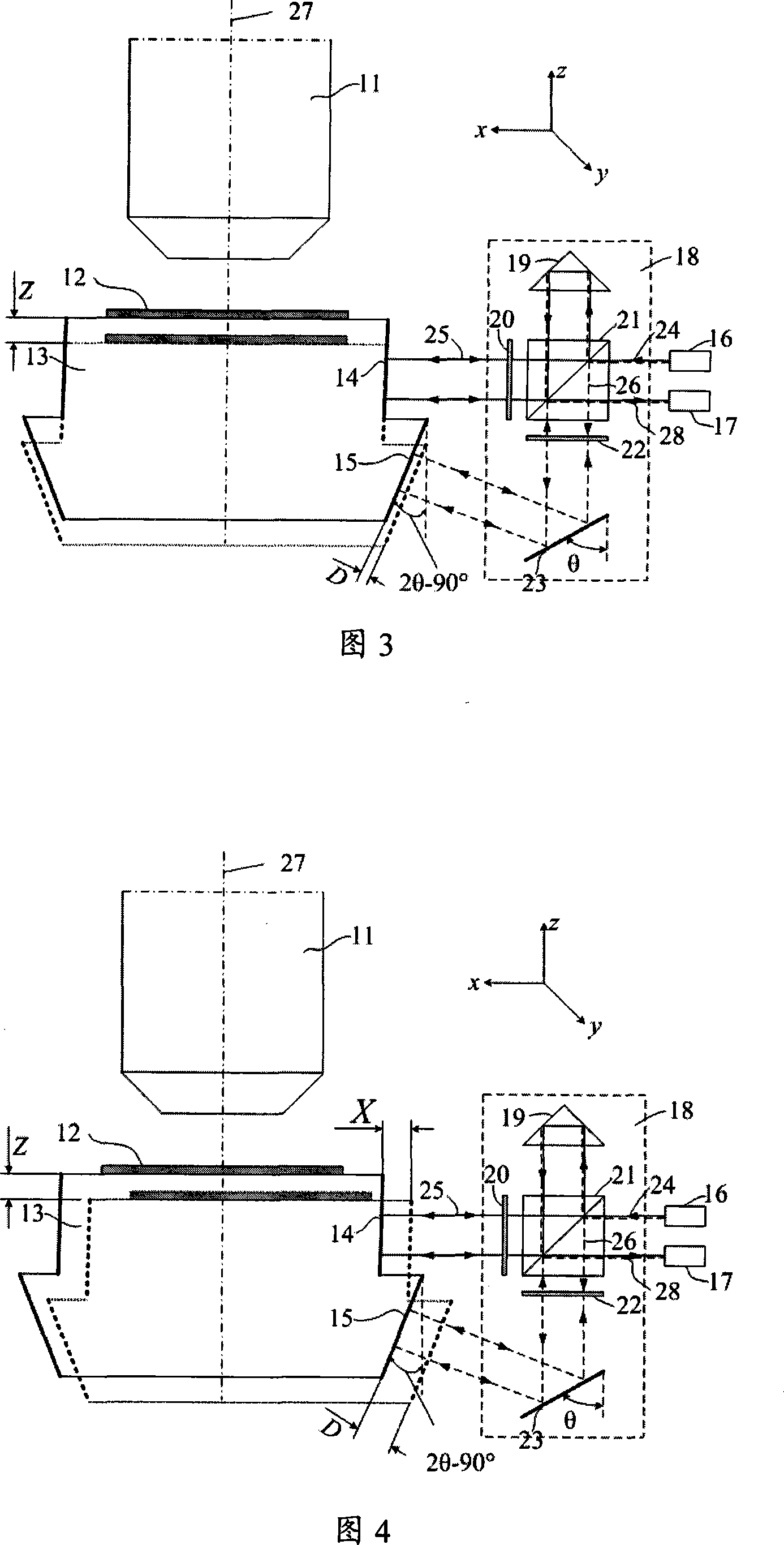
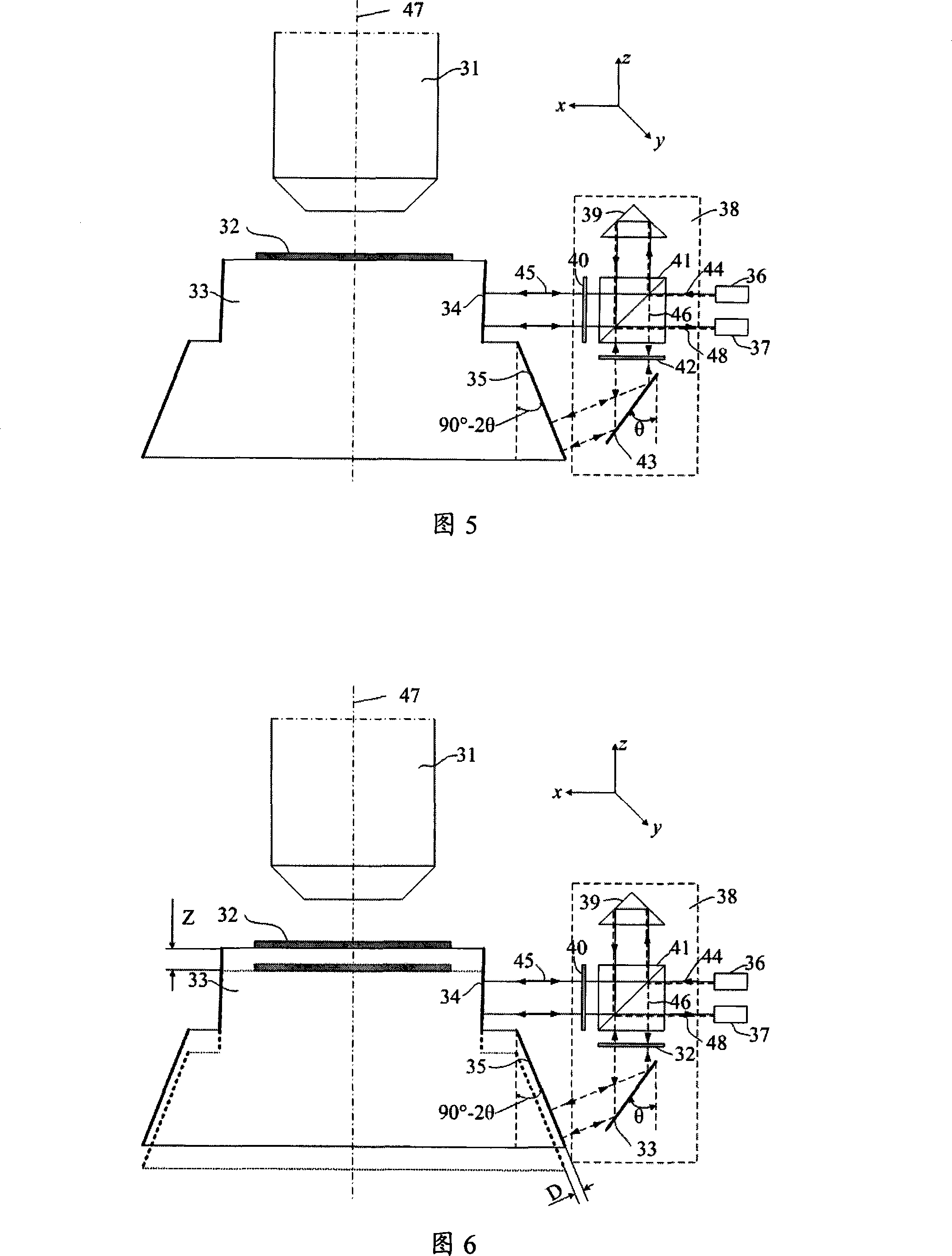
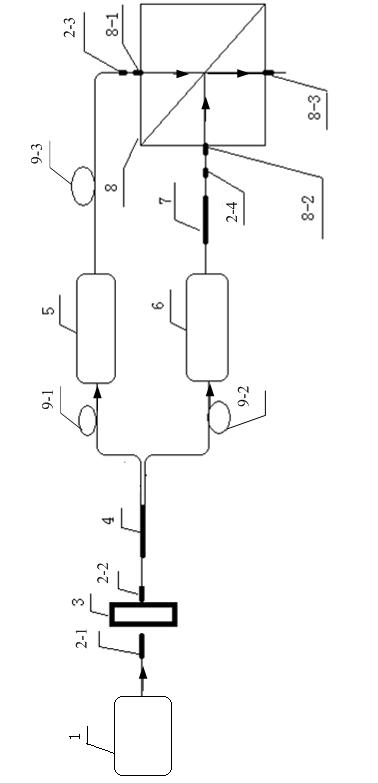
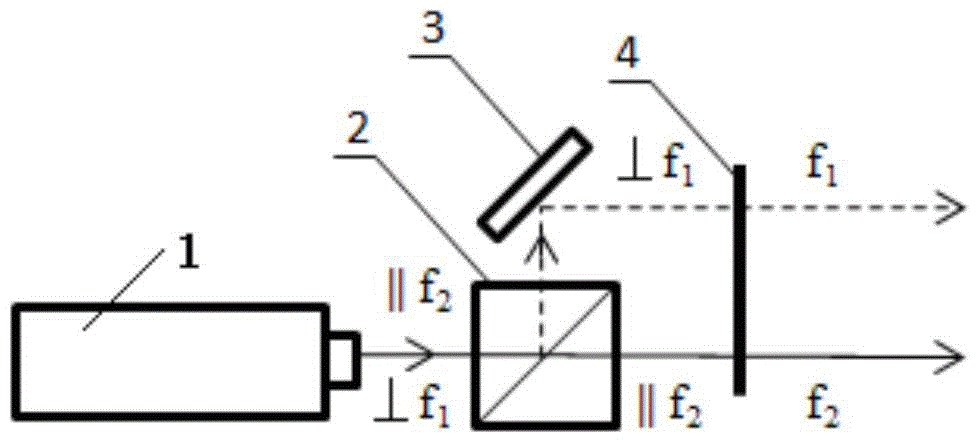
The invention relates to a device for measuring a frequency scanning absolute distance based on a femtosecond optical frequency comb and a method for measuring the absolute distance based on the device. The device comprises: a tunable laser (1), a polarization maintaining fiber system (2), a double-frequency heterodyne interferometer (3) and a system for measuring a laser frequency and an interferometric phase (4); the tunable laser (1) is used for generating single-frequency, single-line polarization laser, and an output laser frequency can be controlled by the working voltage and current ofthe tunable laser; the polarization maintaining fiber system (2) is used for coupling space laser with a polarization maintaining fiber in an unreflected way, and dividing the space laser into three paths of optical signals with equal optical intensity, and keeping an output laser polarization direction the same as an input laser polarization direction; the double-frequency heterodyne interferometer (3) is used for converting single-frequency laser into double-frequency orthogonal polarization laser, and converting distance information to be measured into phase information of a laser beat signal; and the system for measuring the laser frequency and the interferometric phase (4) is used for precisely measuring and locking and inputting the frequency of the laser, and measuring a phase different between the two paths of alternating current signals.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-wavelength interference real-time absolute distance measurement device on the basis of femtosecond optical comb synchronization frequency locking
InactiveCN105589074APreserve precisionExpanding the Unambiguous Measurement Range of RangingElectromagnetic wave reradiationHeterodyne interferometerMeasurement precision
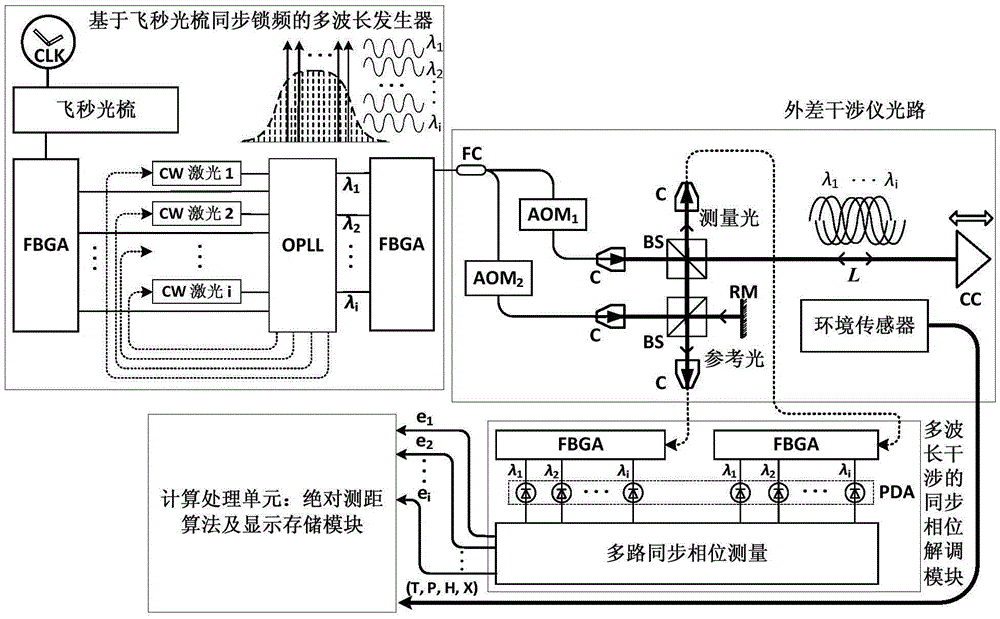
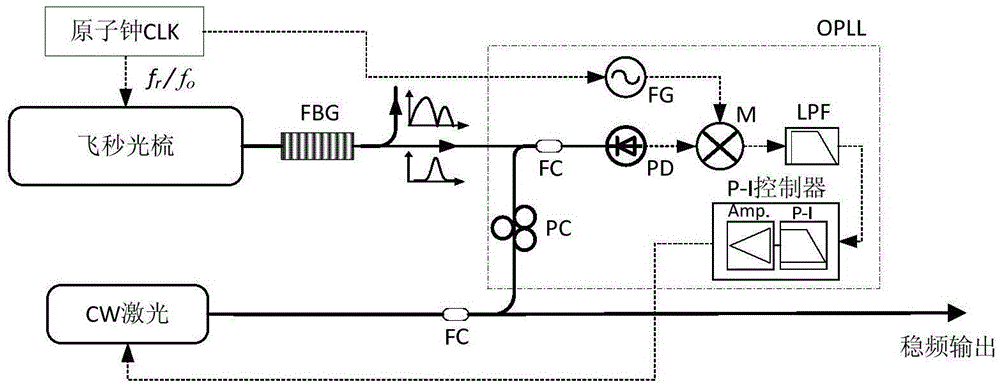
The present invention provides a multi-wavelength interference real-time absolute distance measurement device on the basis of femtosecond optical comb synchronization frequency locking. The multi-wavelength interference real-time absolute distance measurement device on the basis of femtosecond optical comb synchronization frequency locking comprises: a multi-wavelength generator on the basis of the femtosecond optical comb synchronization frequency locking configured to emit a plurality of high-frequency stable object wavelength lasers; a heterodyne interferometer configured to receive lasers outputted by the multi-wavelength generator after the femtosecond optical comb synchronization frequency locking, returning measurement light and reference light after generation of interference through the heterodyne interferometer being coupled in single mode fibers by lens focusing to form mixed multi-wavelength heterodyne interference signals; and a synchronization phase demodulation module configured to separate the mixed multi-wavelength heterodyne interference signals obtained by the heterodyne interferometer through wavelength demodulation to obtain interference signals corresponding to each wavelength and perform synchronization phase measurement processing of the interference signals corresponding to each wavelength to finally obtain an accurate absolute distance value. The multi-wavelength interference real-time absolute distance measurement device on the basis of femtosecond optical comb synchronization frequency locking is high in traceability of values, high in measurement precision, large in non-fuzziness measuring range, fast in update rate and easy to measurement on site in real time, and is applicable to the fields of the industrial production, the equipment manufacture and the large-size precision measurement.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
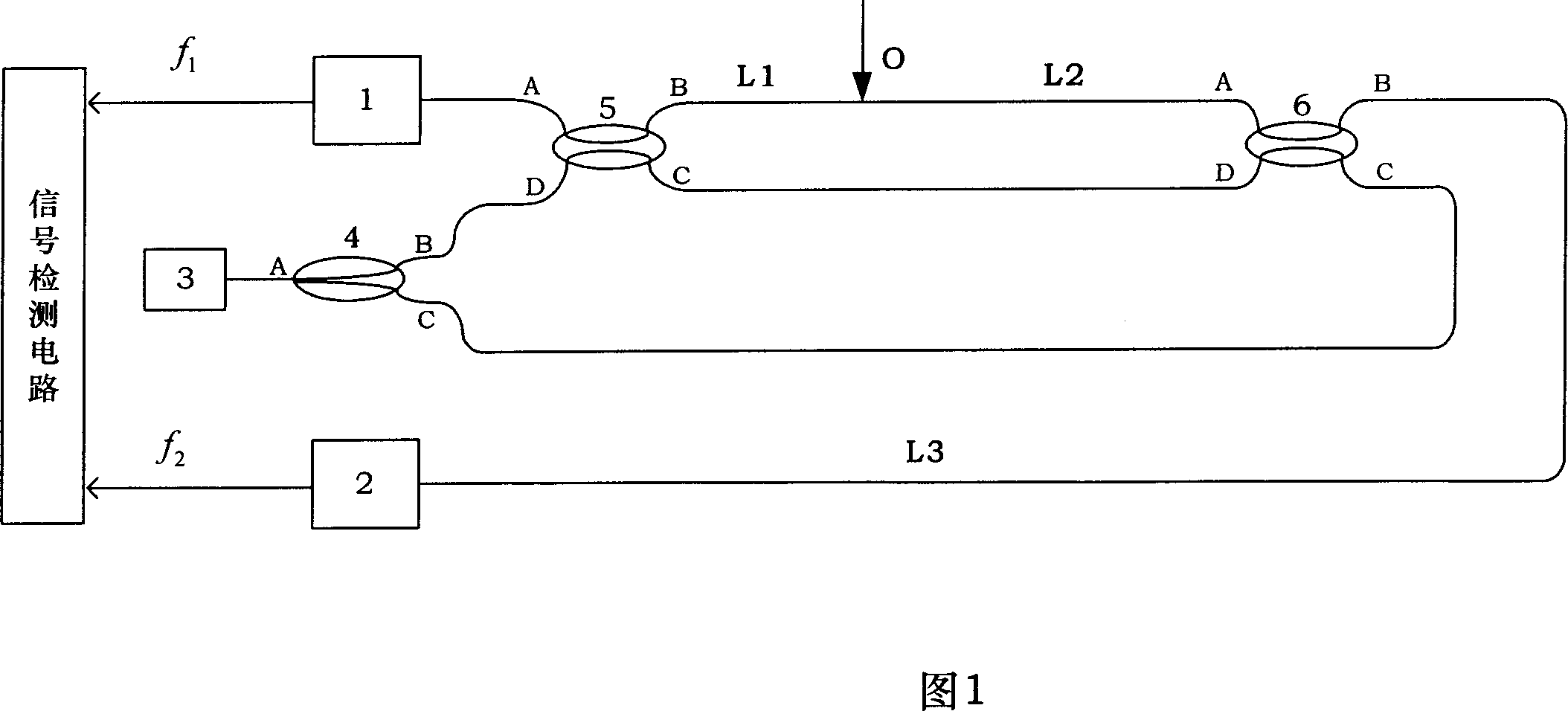
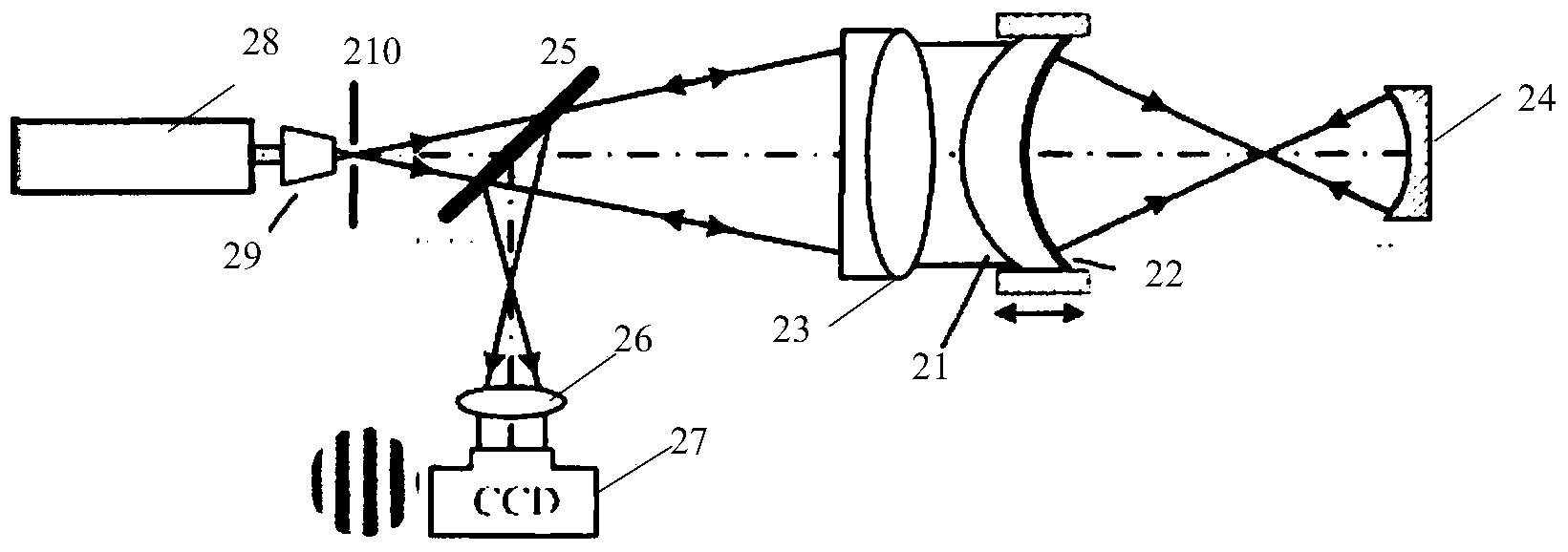
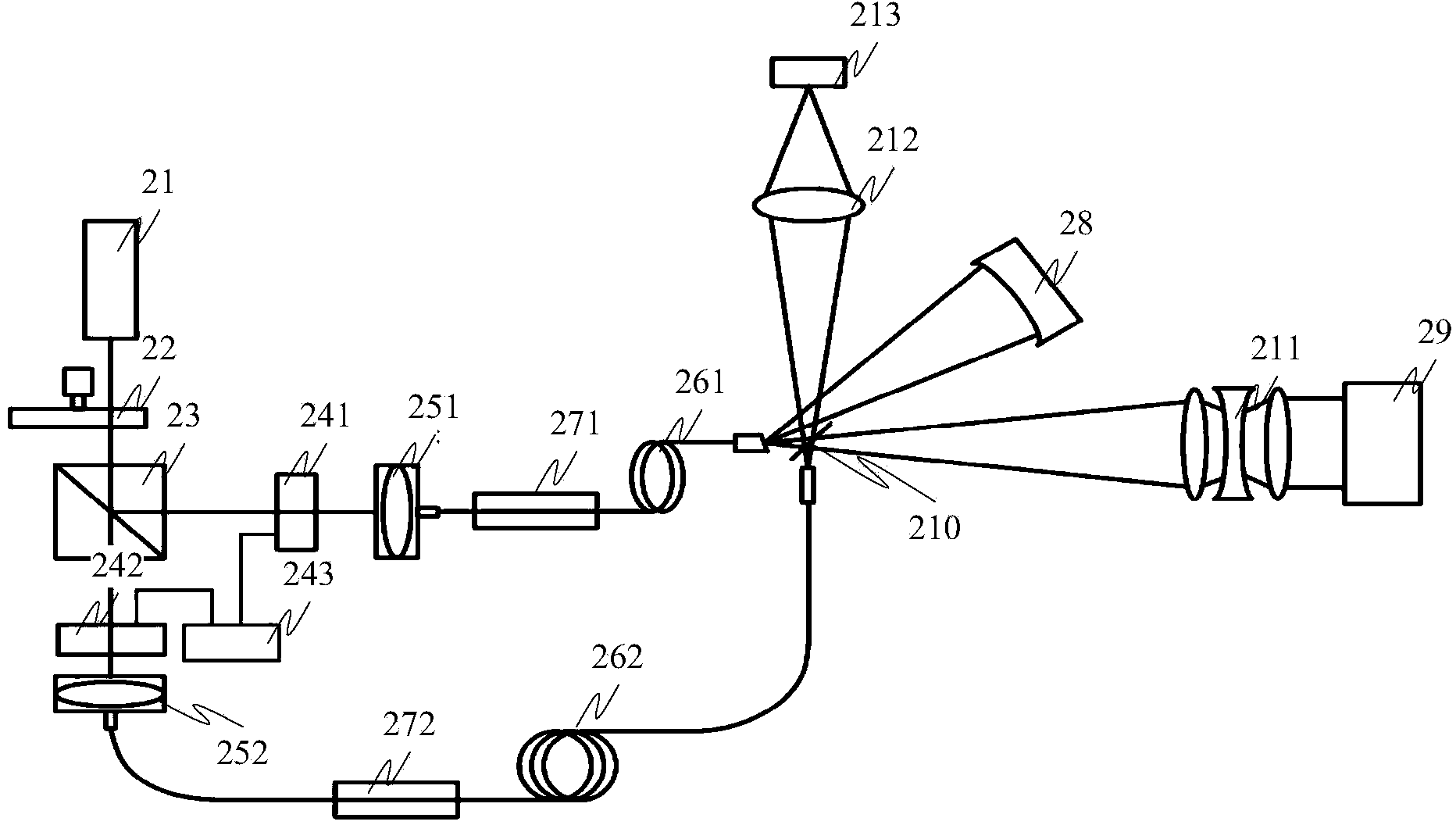
Heterodyne interferometer measuring system for measuring displacement and its measurement method
The invention relates to a heterodyne interferometer measurement system for measuring displacement and a measuring method thereof. The measurement system comprises a workbench reflector set and a laser heterodyne interferometer; the workbench reflector set comprises a first plant reflector disposed on the lateral side of the workbench and parallel with an optical axis, and a second plant reflector having certain angle with the optical axis; and the laser heterodyne interferometer comprises a polarization slitting prism, a cube corner prism, a reference plane reflector having certain angle with the optical axis, and two quarter-wave plates. The measuring method comprises the following steps of: allowing a reference beam and a measuring beam generated by a laser passing through the polarization slitting prism to respectively enter a photoelectric conversion element after multiple reflections and transmissions, processing to obtain an optical path difference (OPD), and then obtaining Z-axis displacement Z of the workbench. The invention needs not to use the plane reflectors disposed at two sides of a projection objective lens, resulting in simple structure; and needs not to increase extra size of the projection objective lens at X-axis direction. The cost of the measurement system is reduced due to less number of the used plane reflectors.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
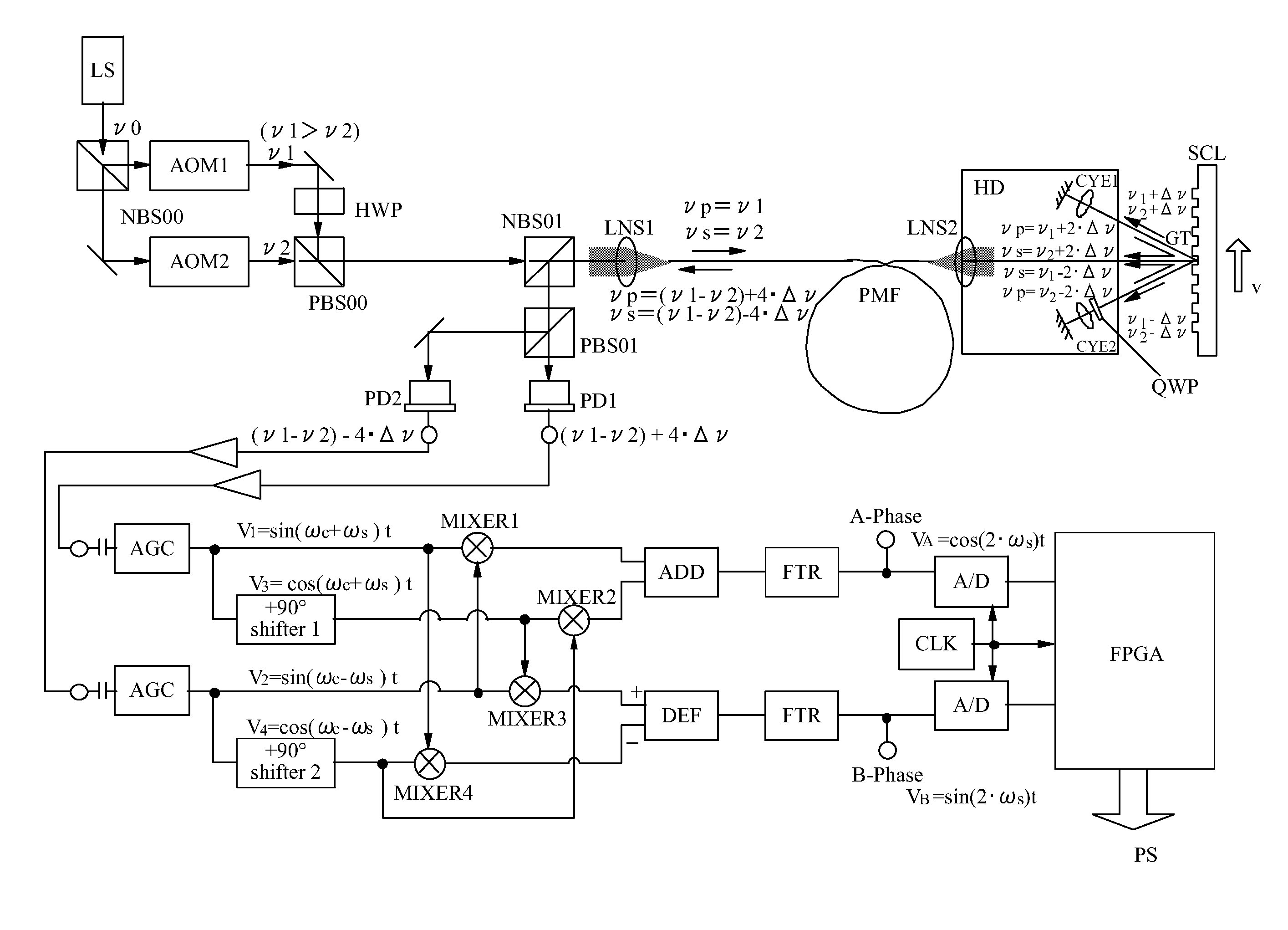
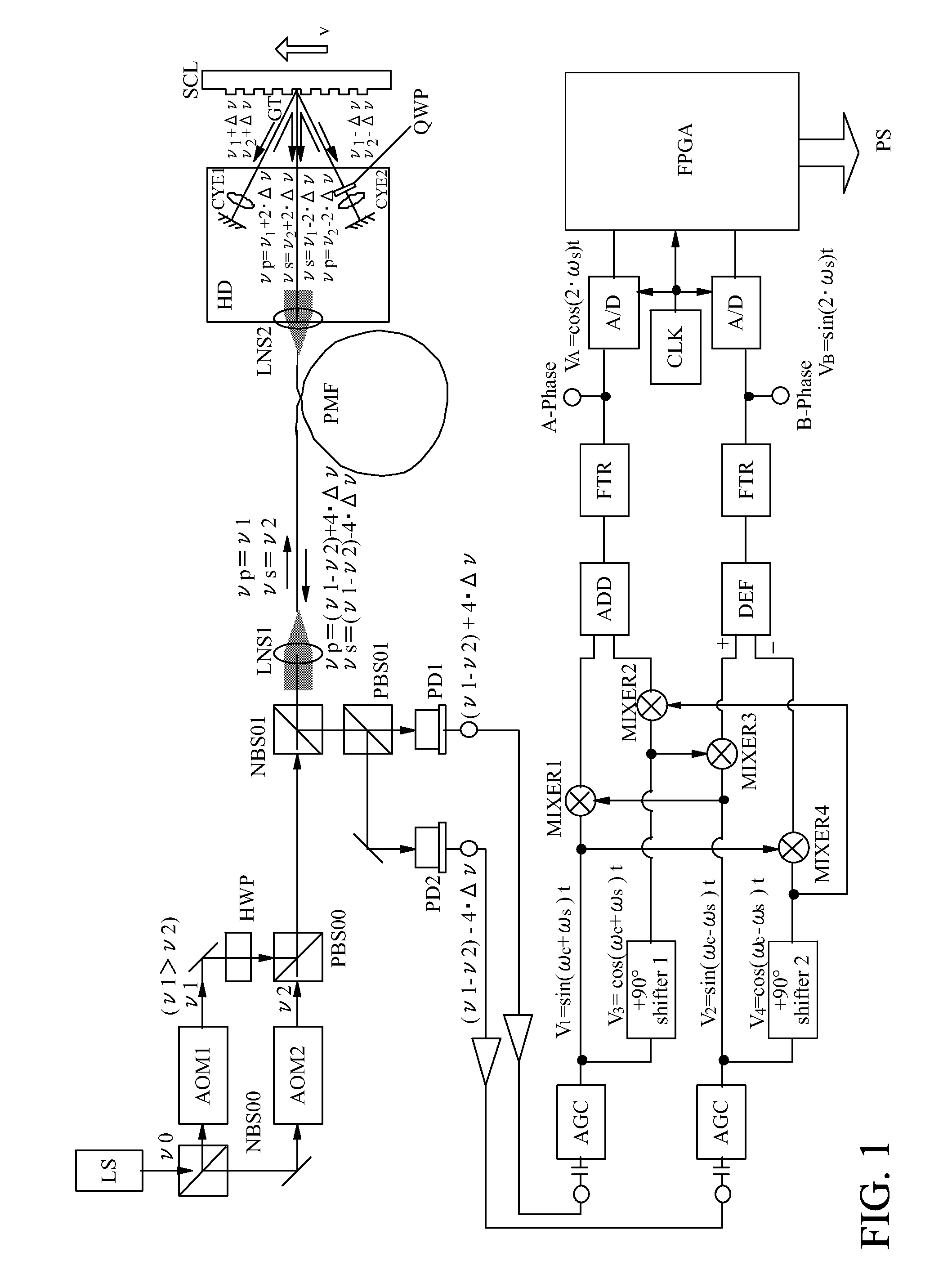
Heterodyne interferometer
InactiveUS20110096334A1Advantage in of resolutionInterferometersUsing optical meansHeterodyne interferometerSignal generator
A heterodyne interferometer includes a light source, an optical system, and a signal generator including at least two light-receiving elements that respectively output a first signal and a second signal. The signal generator generates a third signal and a fourth signal of which phases are respectively shifted by 90° from phases of the first signal and the second signal, generates a first periodic signal by adding a signal that is obtained by multiplying the first signal and the second signal to a signal that is obtained by multiplying the third signal and the fourth signal, and generates a second periodic signal by subtracting a signal that is obtained by multiplying the first signal and the fourth signal from a signal that is obtained by multiplying the second signal and the third signal.
Owner:CANON KK
Acousto-optic modulation-based 2mu m polarized orthogonal laser emitting system applied to laser heterodyne interferometer
InactiveCN101916957AImprove transmission efficiencyAvoid lostLaser detailsUsing optical meansBeam splitterHeterodyne interferometer
The invention discloses an acousto-optic modulation-based 2mu m polarized orthogonal laser emitting system applied to a laser heterodyne interferometer, which relates to a polarized orthogonal laser source emitting system. The system solves the problem of low measurement precision of the laser heterodyne interferometer due to polarized mixing error of the conventional orthogonal polarized light source emitting system. The system comprises a 2mu m laser device, a plurality of fiber collimators, a polarization sheet, a fiber beam splitter, two acousto-optic frequency shifters, a polarization controller, a polarized beam splitter prism and a plurality of fibers, wherein the laser of the 2mu m laser device passes through the fiber collimators and the polarization sheet and then enters the fiber beam splitter, the input laser is split into two beams of P laser by the fiber beam splitter, one beam of P laser enters one acousto-optic frequency shifter through the fibers to perform frequency shift and then enters the polarized beam splitter prism, the other beam of P laser is subjected to frequency shift and then enters the polarization controller, the polarization controller converts the P laser into S laser and outputs the S laser to the polarized beam splitter prism, and the P laser and the S laser form an orthogonal polarized beam for emission at an emission port of the polarized beam splitter prism. The system is suitable for a light source system of the laser heterodyne interferometer.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
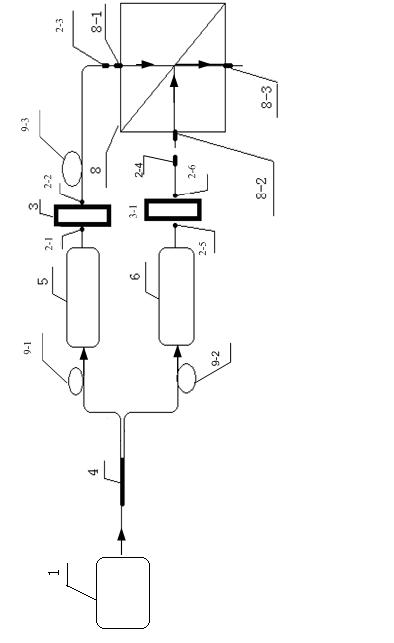
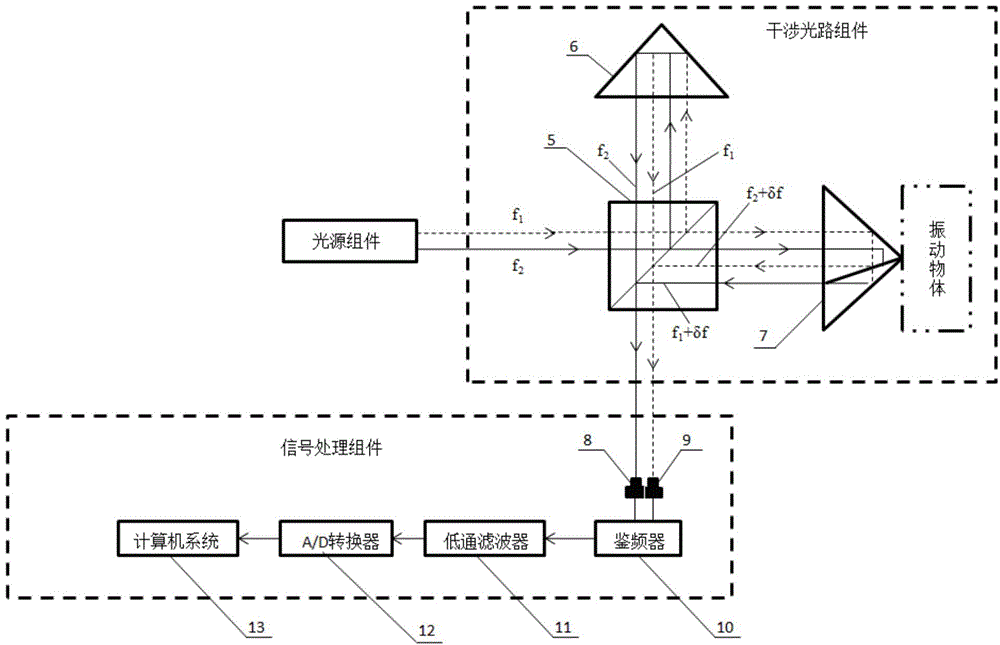
Heterodyne interferometer vibration measurer based on laser doppler effect
InactiveCN104316158AAvoid errorsImprove Vibration Measurement AccuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansHeterodyne interferometerLaser light
Disclosed is a heterodyne interferometer vibration measurer based on a laser doppler effect. The heterodyne interferometer vibration measurer based on the laser doppler effect comprises a light source component, an interference light path component and a signal processing component. The light source component comprises a double frequency laser light source, a polarization splitting prism, a reflecting mirror and a polarizer; the interference light path component comprises an unpolarized splitting prism, a rectangular prism and a curved-surface prism which is mounted on a to-be-measured vibration object; the signal processing component is used for receiving two beams of interference light that is emitted by the unpolarized splitting prism in the interference light path component, an interference light signal is converted to an electric signal to be processed, and vibration information of the to-be-measured vibration object is obtained. By means of the heterodyne interferometer vibration measurer based on the laser doppler effect, the vibration measuring accuracy can be improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Pound-Drever-Hall frequency stabilizing system of dual-cavity dual-frequency solid laser device
ActiveCN102916335AExcellent laser frequency stabilityActive medium materialDual frequencyResonant cavity
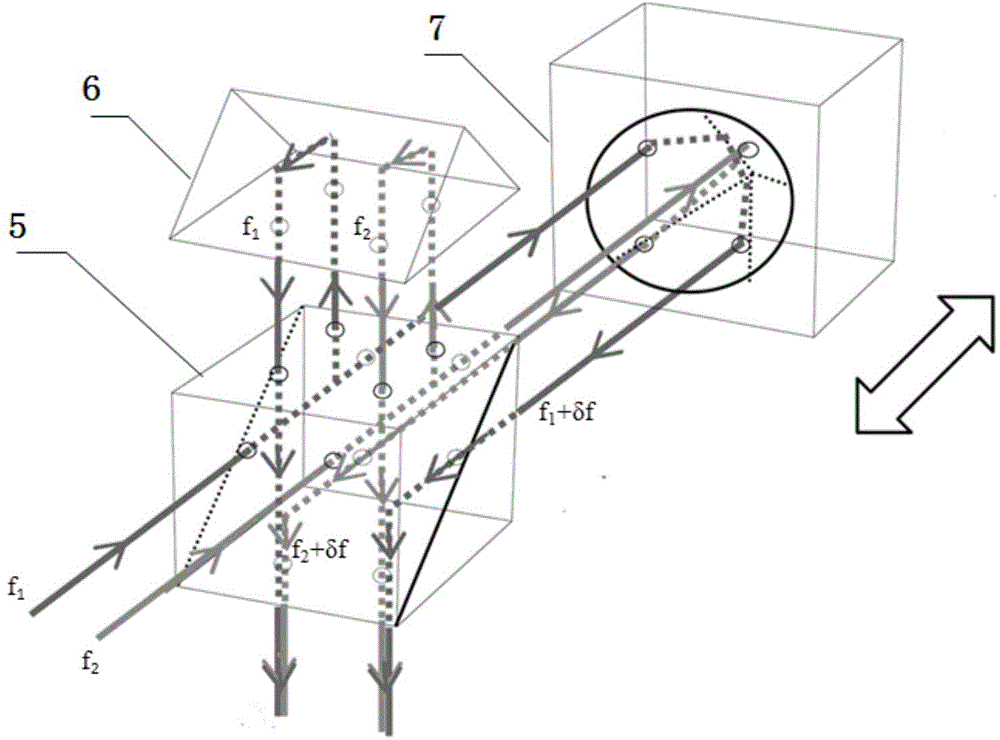
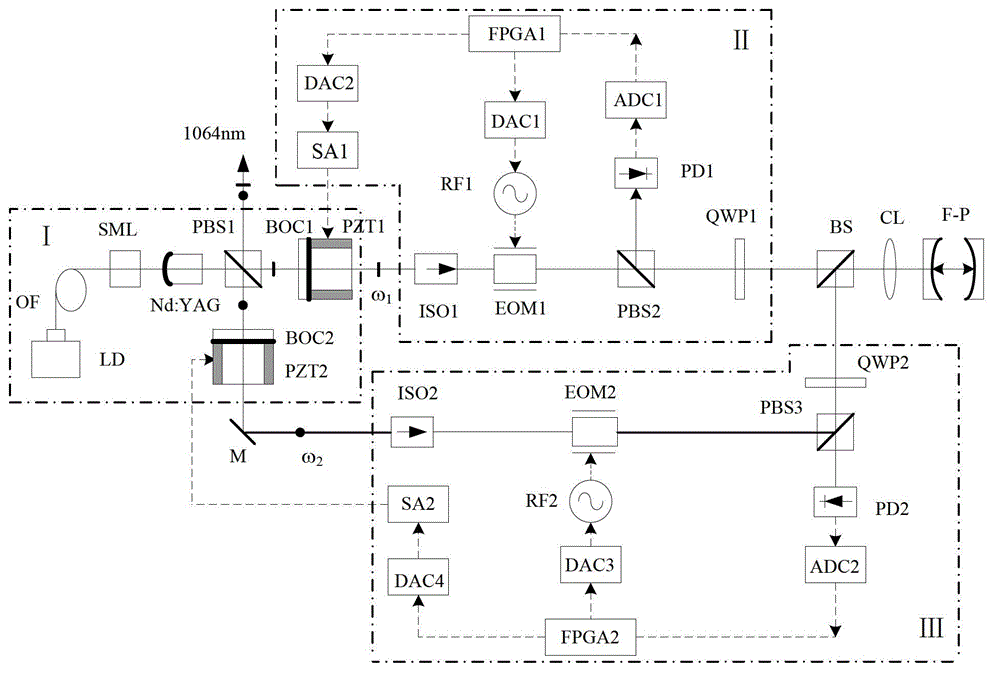
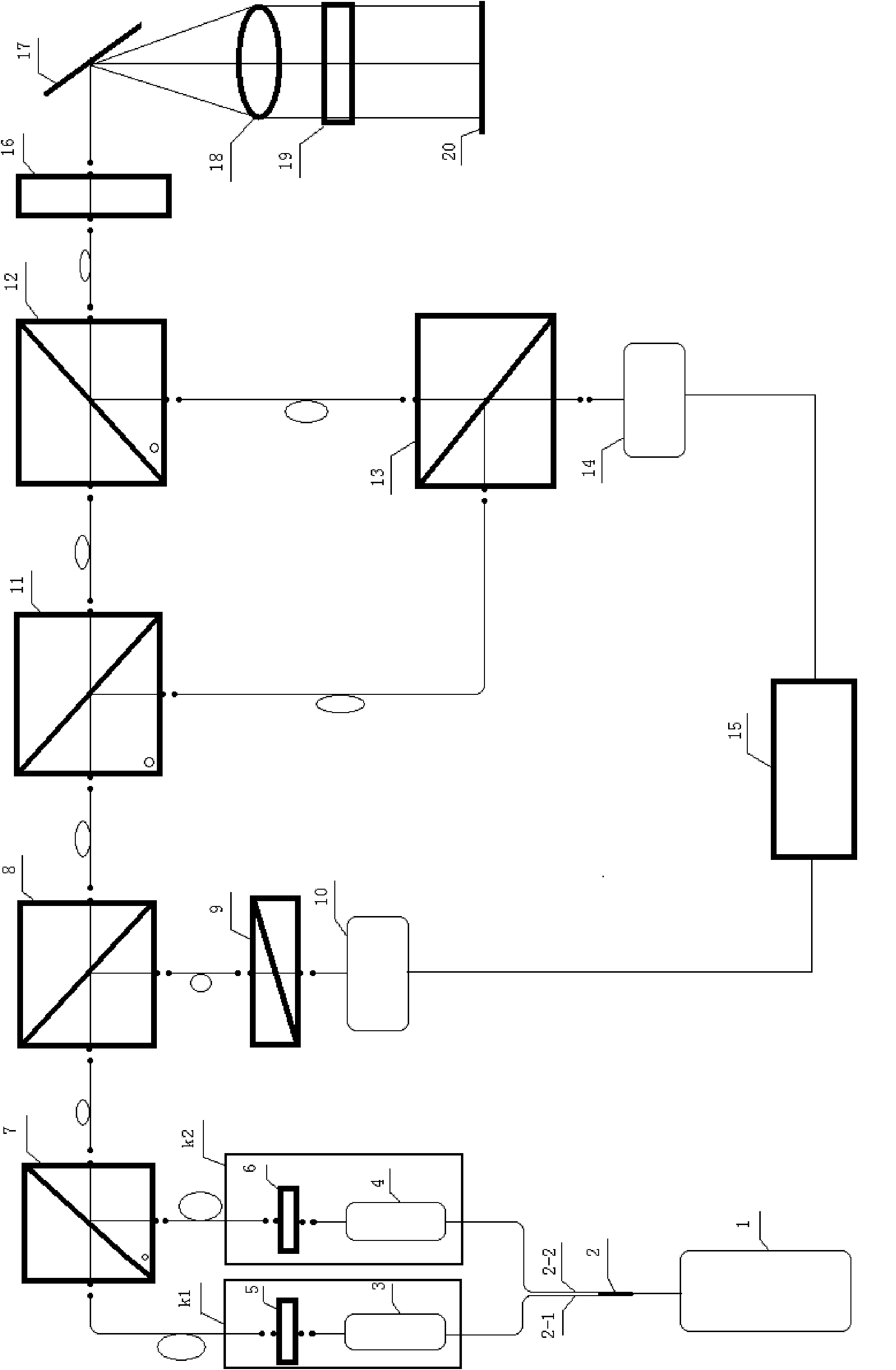
A Pound-Drever-Hall frequency stabilizing system of a dual-cavity dual-frequency solid laser device comprises the dual-cavity dual-frequency solid laser device, two independent heterodyne interferometer systems, two frequency regulators and an F-P (Fabry-Perot) optical resonant cavity. The optical resonant cavity is used as frequency stabilizing reference, the two independent heterodyne interferometer systems are used for detection to obtain two channels of error signals, the two frequency regulators are driven, and two working frequencies of the dual-cavity dual-frequency solid laser device are simultaneously locked at two resonance frequencies of the F-P optical resonant cavity. The F-P optical resonant cavity is used as the frequency stabilizing reference, the two working frequencies of the dual-cavity dual-frequency solid laser device are stabilized simultaneously, the laser frequency stability is higher than 10<-10>, and the Pound-Drever-Hall frequency stabilizing system can be widely applied to fields of interferometry for absolute distances of synthesis waves, generation of THz waves and the like.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Double-shaft MEMS scanning-based heterodyne interference system and method
InactiveCN102022977AFor scanning purposePhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansBeam splitterHeterodyne interferometer
The invention discloses a double-shaft micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) scanning-based heterodyne interference system and a double-shaft MEMS scanning-based method, relates to a quick scanning-based laser heterodyne interferometer system and a quick scanning-based laser heterodyne interferometer method, and solves the problems that the operation wavelength of the conventional cross-polarization heterodyne interferometer technology is a visible light wave band and shaking errors are large. The scheme is that: 2 mu m polarization orthogonal laser is subjected to beam splitting by a beam splitter prism to form a transmitted beam and a reflected beam, wherein the reflected beam serving as a reference intermediate frequency signal is transmitted to a computer, S light in the transmission beam is reflected, P light is transmitted, passes through a one fourth wave plate, an MEMS oscillating mirror and an F-theta lens, passes through a to-be-tested sample cell, returns according to the original optical path and is mixed with the P light; and a mixed beam serving as a measurement intermediate frequency signal is sent to the computer, and is processed by the computer so as to obtain the physical quantity information of a to-be-tested sample. The system and the method are suitable for the detection field of infrared optical materials.
Owner:THE 3RD ACAD 8358TH RES INST OF CASC +1
Disturbing signal detecting system based on bidirectional Mach Zehnder heterodyne interferometer
InactiveCN101008583AReduce the impactSuppress interferenceSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansTime lagHeterodyne interferometer
This invention discloses one interference signal test system based on double direction Mach interometer, which comprises distribution fiber sensor and signal test circuit, wherein, the sensor comprises first detector, second detector, light source and three couplers; the said interference signalphi(t) to first detector time t1 difference from second detector time t2+t3 to get vibration point O real position according to the time lag.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Nonlinear-error-free laser heterodyne interferometer system for angle measurement
InactiveCN105571529ASuitable for precision measurementAvoid Periodic Nonlinear ErrorsUsing optical meansNumerical controlPhase difference
The invention discloses a nonlinear-error-free laser heterodyne interferometer system for angle measurement, wherein the nonlinear-error-free laser heterodyne interferometer system comprises a single-frequency laser source, an acousto-optical frequency shift unit, an optical interference device, a planar mirror which moves along with the movement of a measured member, and a phase detecting device, wherein the single-frequency laser source and the acousto-optical frequency shift unit can operate for generating an incident light beam which has no frequency aliasing and has certain frequency difference and is spatially separated. Under the function of the optical interference device, the incident light beam is reflected twice by the planar mirror. Finally the reflected incident light beam is input to the phase detecting device. The yaw angle of the measured member is determined by means of change amount of the phase difference. Between generation of a measuring light beam with certain frequency difference from the acousto-optical frequency shift unit and interference, the transmission paths are separated and are spatially independent. The nonlinear-error-free laser heterodyne interferometer system prevents a periodical nonlinear error which is caused by polarized light with two frequencies in the interference optical path, thereby effectively improving measurement accuracy. The nonlinear-error-free laser heterodyne interferometer system can be widely used for geometric quantity precise measurement in the fields of numerical control machine tools, military industry, spaceflight, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Biaxial MEMS reflective galvanometer and F-Theta lens-based linear scanning system used for laser heterodyne interferometer
InactiveCN101915542ASimple structureCompact structurePhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansPhotovoltaic detectors2 μm laser
The invention discloses a biaxial MEMS reflective galvanometer and F-Theta lens-based linear scanning system used for a laser heterodyne interferometer, which relates to a scanning system using an optical lens and solves the problems that the conventional optical scanning system has single applicable wavelength and cannot realize linear and uniform-speed scanning. The linear scanning system comprises a laser, a polarization beam splitter prism, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a biaxial MEMS reflective galvanometer, a triplet F-Theta lens set, a high reflection mirror and a photoelectric detector, wherein the biaxial MEMS reflective galvanometer is positioned at the position of a system focal length of the triplet F-Theta lens set. The biaxial MEMS reflective galvanometer and F-Theta lens-based linear scanning system used for the laser heterodyne interferometer is suitable for the scanning system of the laser heterodyne interferometer.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) scanning type laser heterodyne interferometer and method thereof in measuring glass stress
InactiveCN102829903AEasy to measureGood effectForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansHeterodyne interferometerOptoelectronics
The invention relates to an MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) scanning type laser heterodyne interferometer and a method thereof in measuring glass stress, relating to an interferometer and a method thereof in measuring the glass stress and aiming at solving the problem of limitation of the measurement of the glass stress on infrared materials. Light emitted by a laser passes through an acoustooptic frequency shifter to become 1-grade light with the frequency of f and 0-grade light with the frequency of f', the 1-grade light is signal light, the 0-grade light is local oscillating light, the 1-grade light passes through a lambda / 2 wave plate to enter a polarization beam splitter prism and then transmitted through a part, scans a sample through an MEMS vibrating mirror 7 and then reflected by a reflecting mirror to return according to an original optical path; light beams pass through the part again and then reflected into horizontal components by the polarization beam splitter prism, carry out frequency beat with the 0-grade light and respectively form the angles of 0 degree and 45 degrees with the polarization direction of incident light through a changed part; a signal processing system processes two currents detected by a detector to obtain the glass stress of the sample; and the part is a lambda / 4 wave plate or a Kerr effect crystal adding an electrode in a direction at 45 degrees. The MEMS scanning type laser heterodyne interferometer disclosed by the invention is used for measuring the glass stress.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
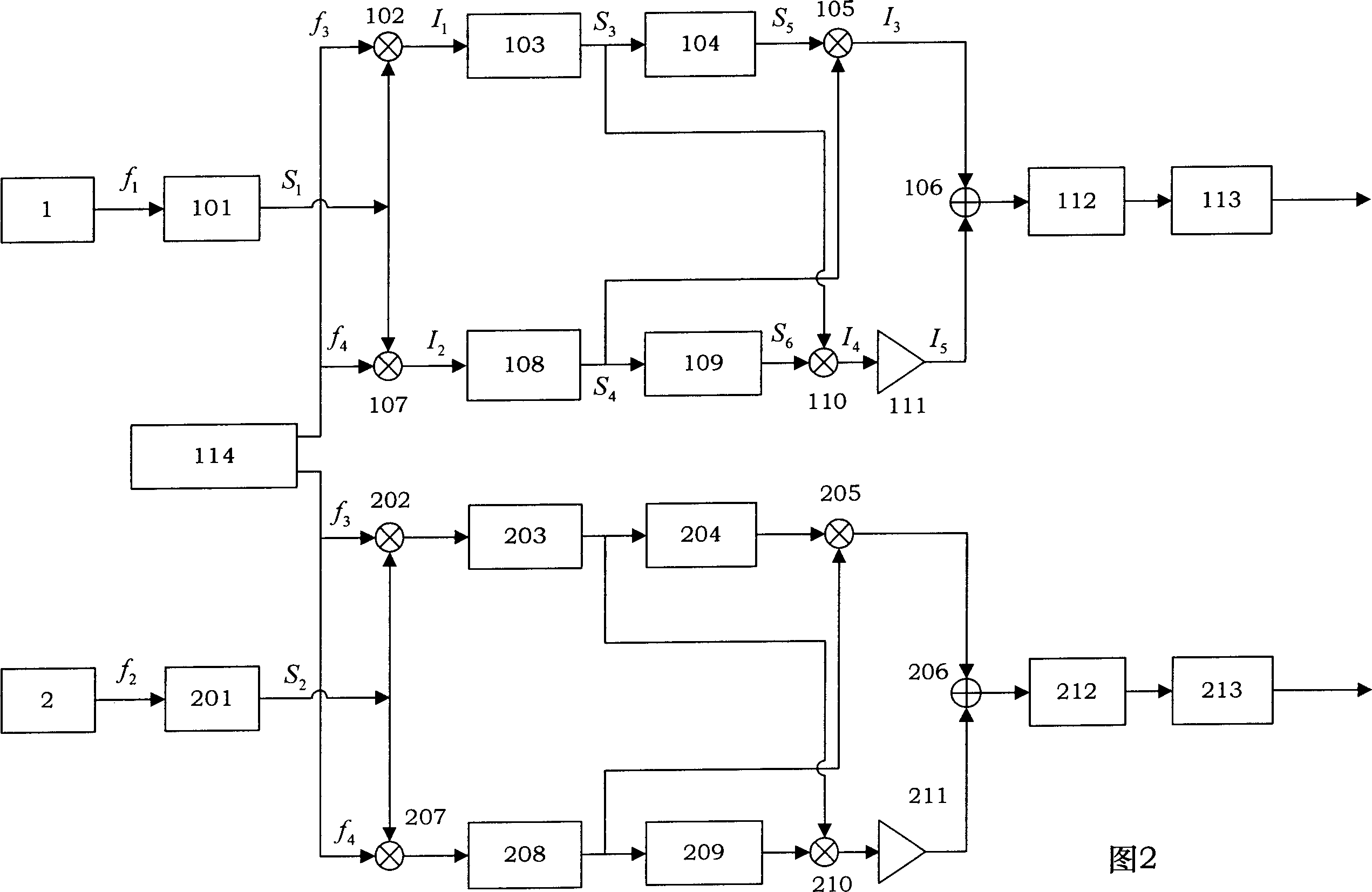
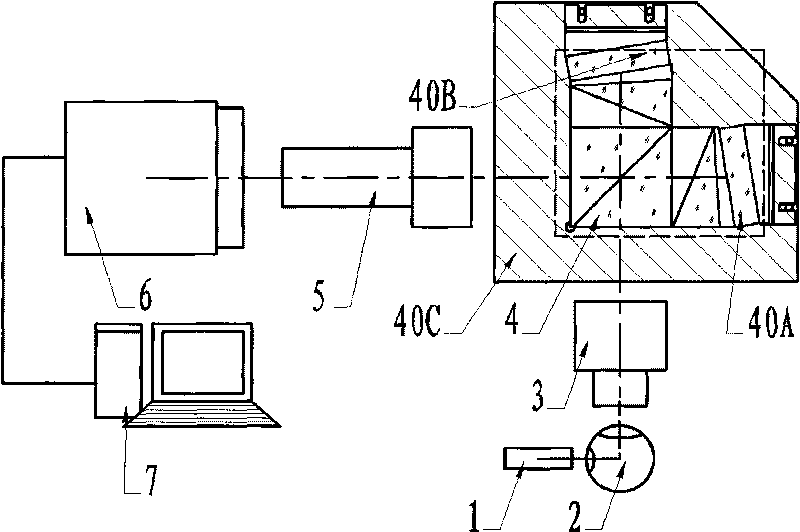
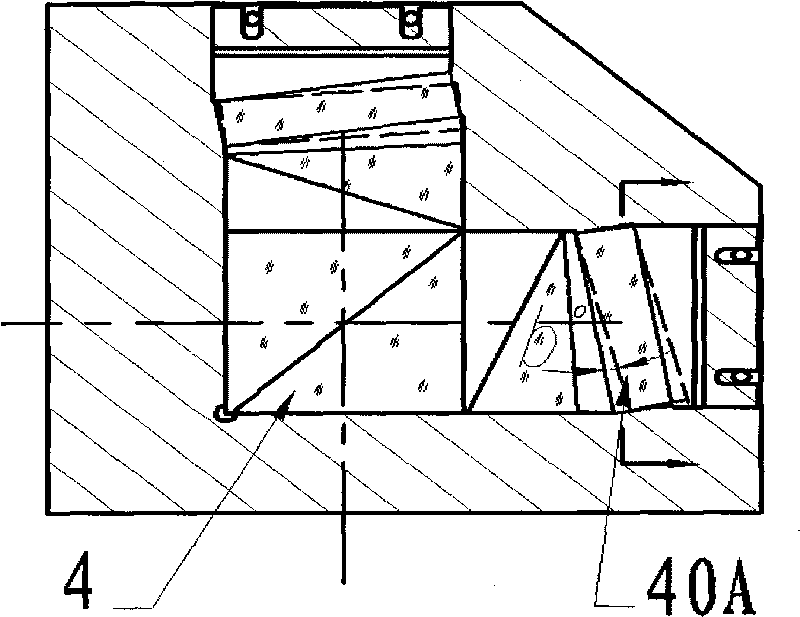
Absolute distance measurement system based on interferometric phase comparison method
InactiveCN101825458AAvoid scan rangeSimple structureOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansExternal cavity laserHeterodyne interferometer
The invention discloses a high-precision absolute distance measurement system based on an interferometric phase comparison method, belonging to the technical field of precision measurement. The system equals to the improvement on an absolute distance measurement system based on a traditional frequency scanning interferometry method, and comprises a single frequency tunable external cavity laser, a three-way optical heterodyne interferometer and a phase measurement comparison system. The single frequency tunable external cavity laser is used for laser frequency scanning, the three-way optical heterodyne interferometer is adopted for obtaining heterodyne interference signals of a reference interference arm, a measurement interference arm and a calibration interference arm in the process of laser frequency scanning, then the phase measurement comparison system is used for extracting interference phase drift distances of the calibration interference arm and the measurement interference arm in the frequency scanning process, the interference phase drift distances are in direct proportion with optical path differences of the interference arms, and therefore, the absolute distance can be measured by comparing the interference phase drift distances of the two paths of the interference arms. By adopting the three-way optical heterodyne interferometer and the phase measurement comparison system, the system does not need to measure an air refractive index when compared with the traditional frequency scanning absolute distance measurement systems, the system can overcome frequency drift and avoids the scanned range for measuring laser frequency, and therefore, frequency calibration devices, such as a Fabry-Perot cavity, and the like, are not needed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
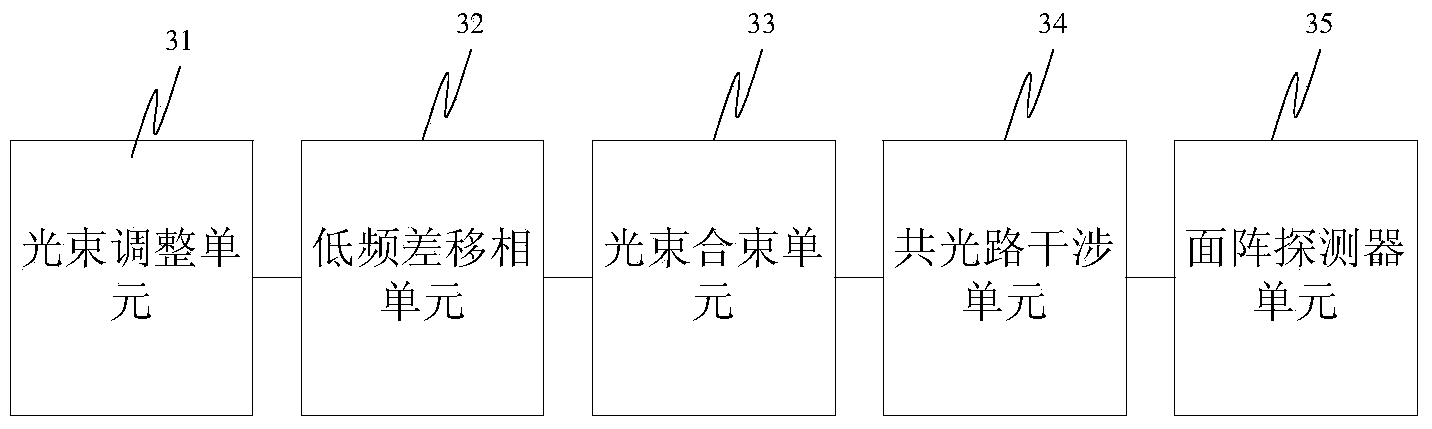
Common-path heterodyne interferometer based on phase shift of low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter
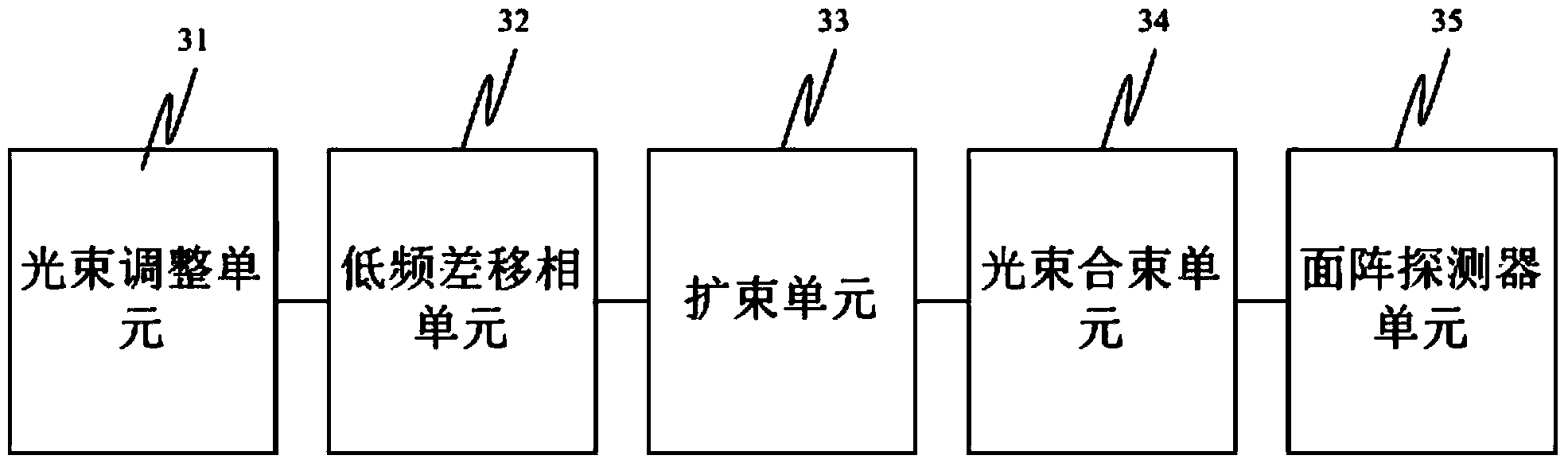
ActiveCN104296677AAvoid problemsReduce the impact of your own errorsUsing optical meansHeterodyne interferometerOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a common-path heterodyne interferometer based on the phase shift of a low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter. The common-path heterodyne interferometer based on the phase shift of the low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter comprises a light beam adjusting unit, a low-frequency-difference phase shifting unit, a light beam combining unit, a common-path interference unit and an area array detector unit. The light beam adjusting unit is used for adjusting output lasers of a laser device into two laser beams with identical powers. The low-frequency-difference phase shifting unit is used for adjusting the frequencies of the two laser beams obtained by the light beam adjusting unit to obtain two laser beams with the output difference frequency being a low difference frequency lower than 100 Hz. The light beam combining unit is used for carrying out beam combination on the two laser beams output by the low-frequency-difference phase shifting unit. The common-path interference unit is used for dividing the lasers combined by the light beam combining unit into common-path measuring light and reference light so as to generate interference. The area array detector unit is used for collecting the interference. According to the common-path heterodyne interferometer based on the phase shift of the low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter, heterodyne interference phase shift of the acousto-optic frequency shifter is adopted to avoid that moving parts exist in the interferometer, the measurement accuracy is improved, the anti-interference performance is good, the anti-interference capacity is improved through the common path and the influences of the self-errors of a system light path are lowered through the common path.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
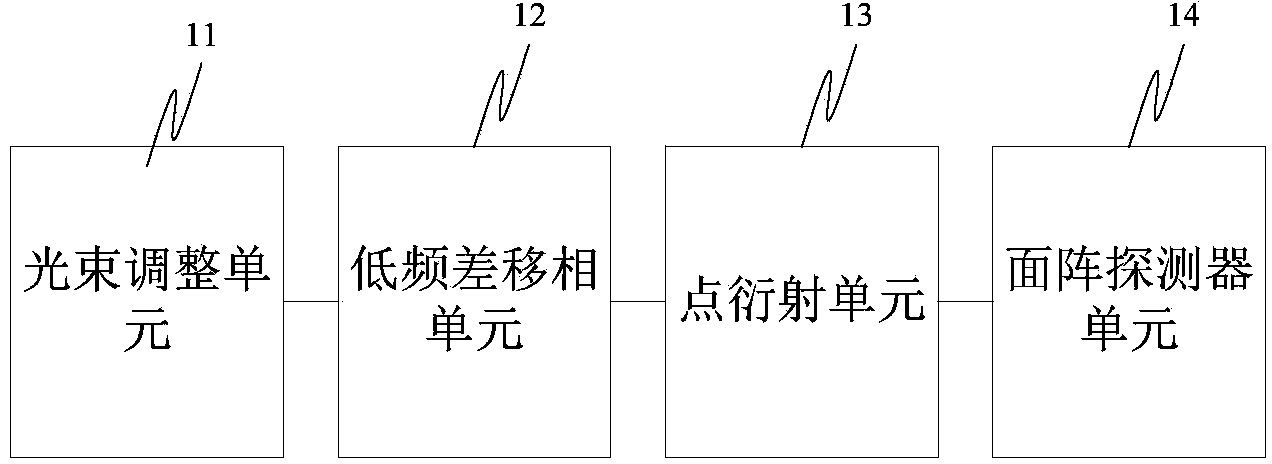
Heterodyne point diffraction interferometer based on phase shift of low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter
ActiveCN104296676AAvoid problemsHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerPhase shifted
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Frequency multiplexed, multiple channel heterodyne interferometer
ActiveUS20080144041A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansMeasurement testWavefront
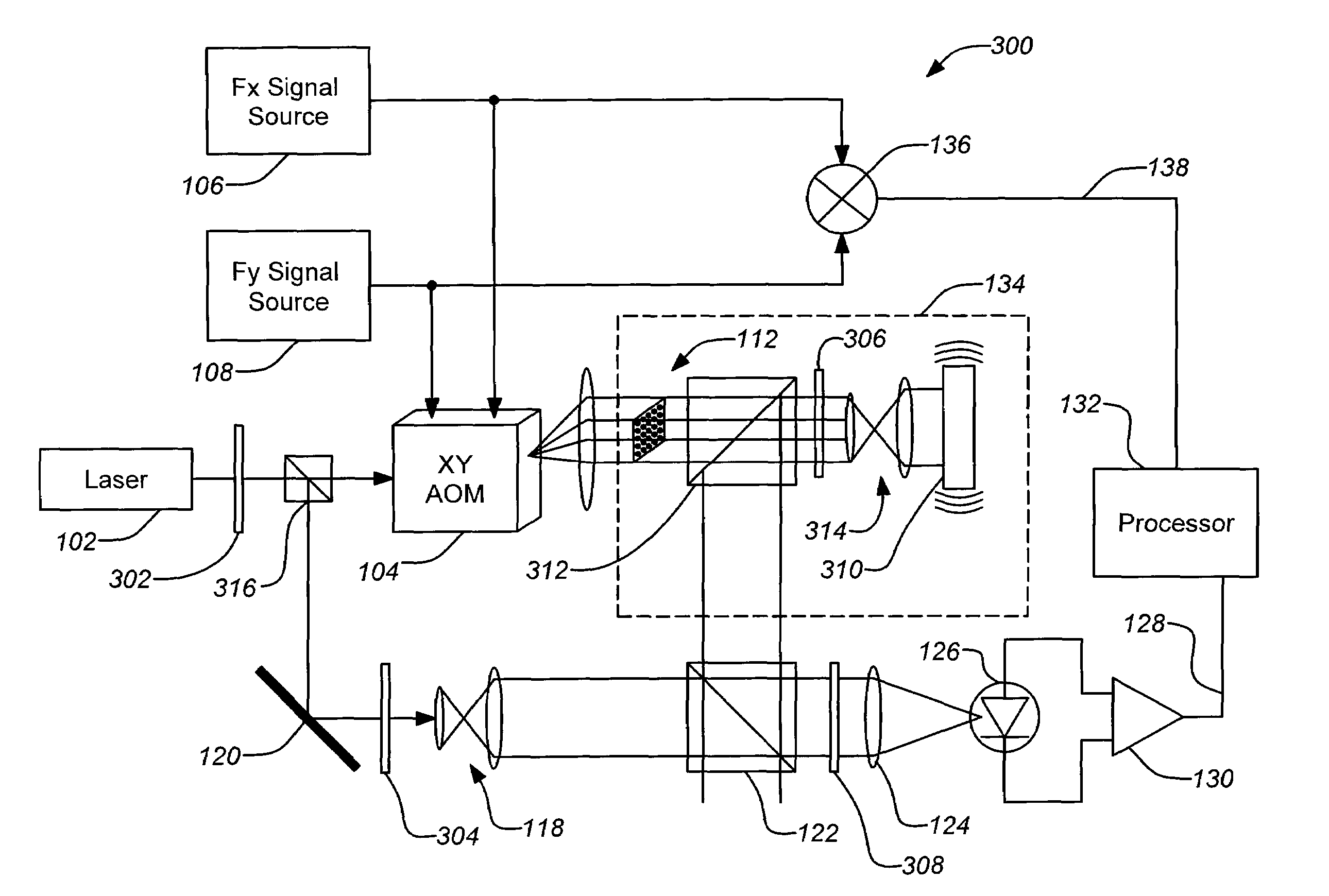
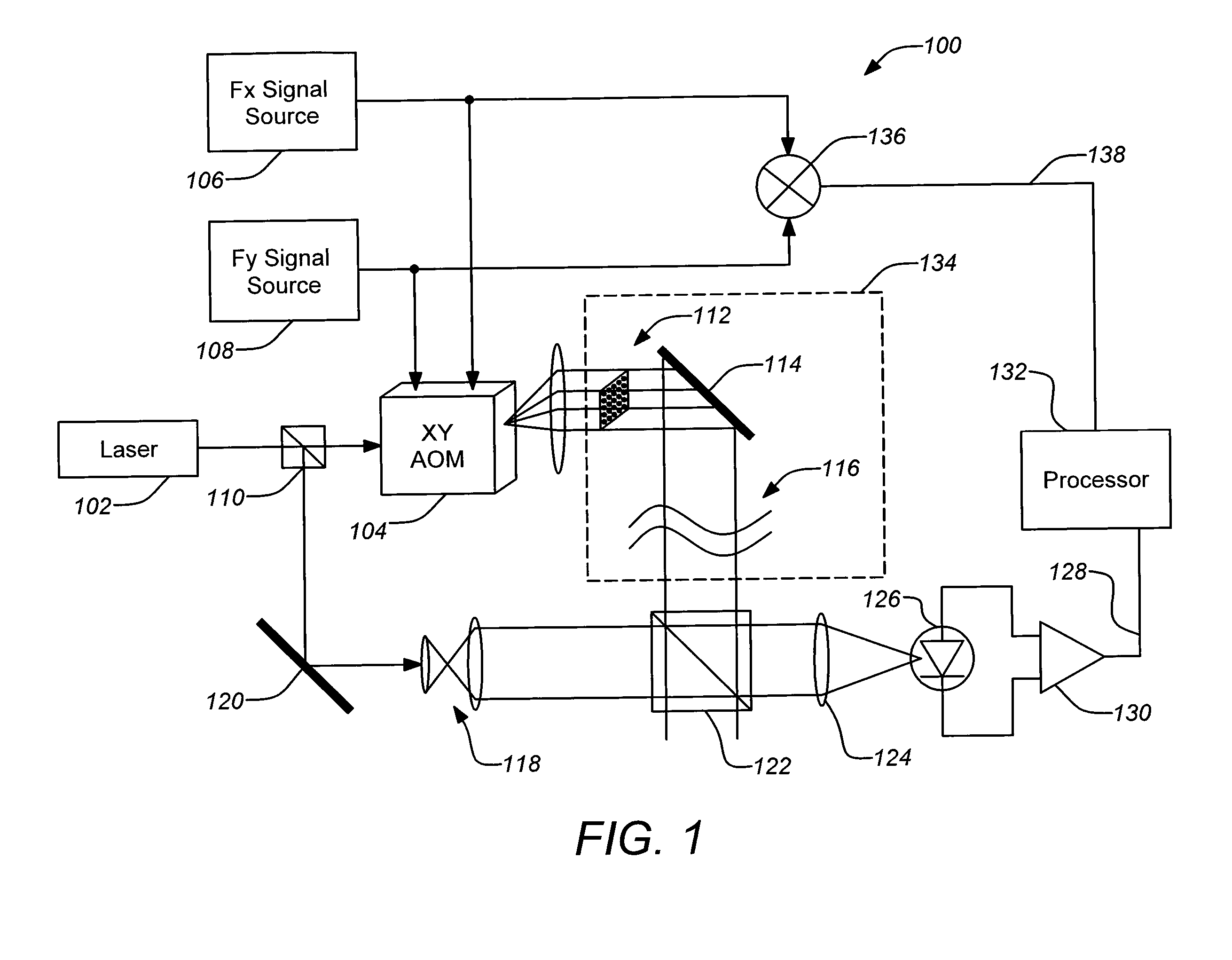
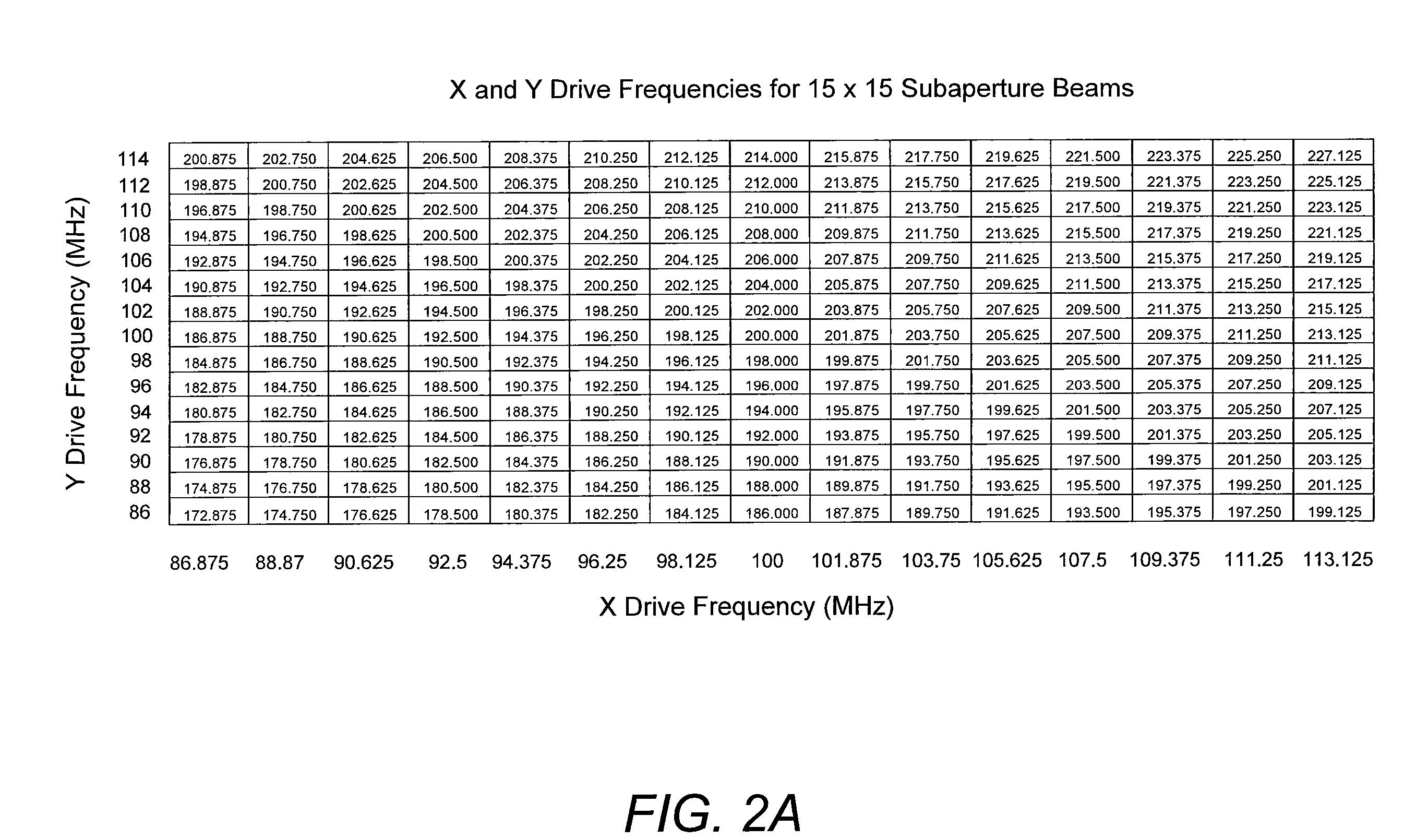
A novel technique using an acousto-optic modulator (AOM) as part of a heterodyne interferometer which measures optical path differences between a test signal and a reference signal is disclosed. An array of distinct frequencies are used to drive the AOM, yielding a spatially dispersed array of frequency-shifted subaperture beams of the test signal which are interfered with the wavefront to be measured and then combined with the dispersed reference signal. The frequency shifting of the AOM allows a single detector to collect the beams for signal processing to determine a measurement of the wavefront.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
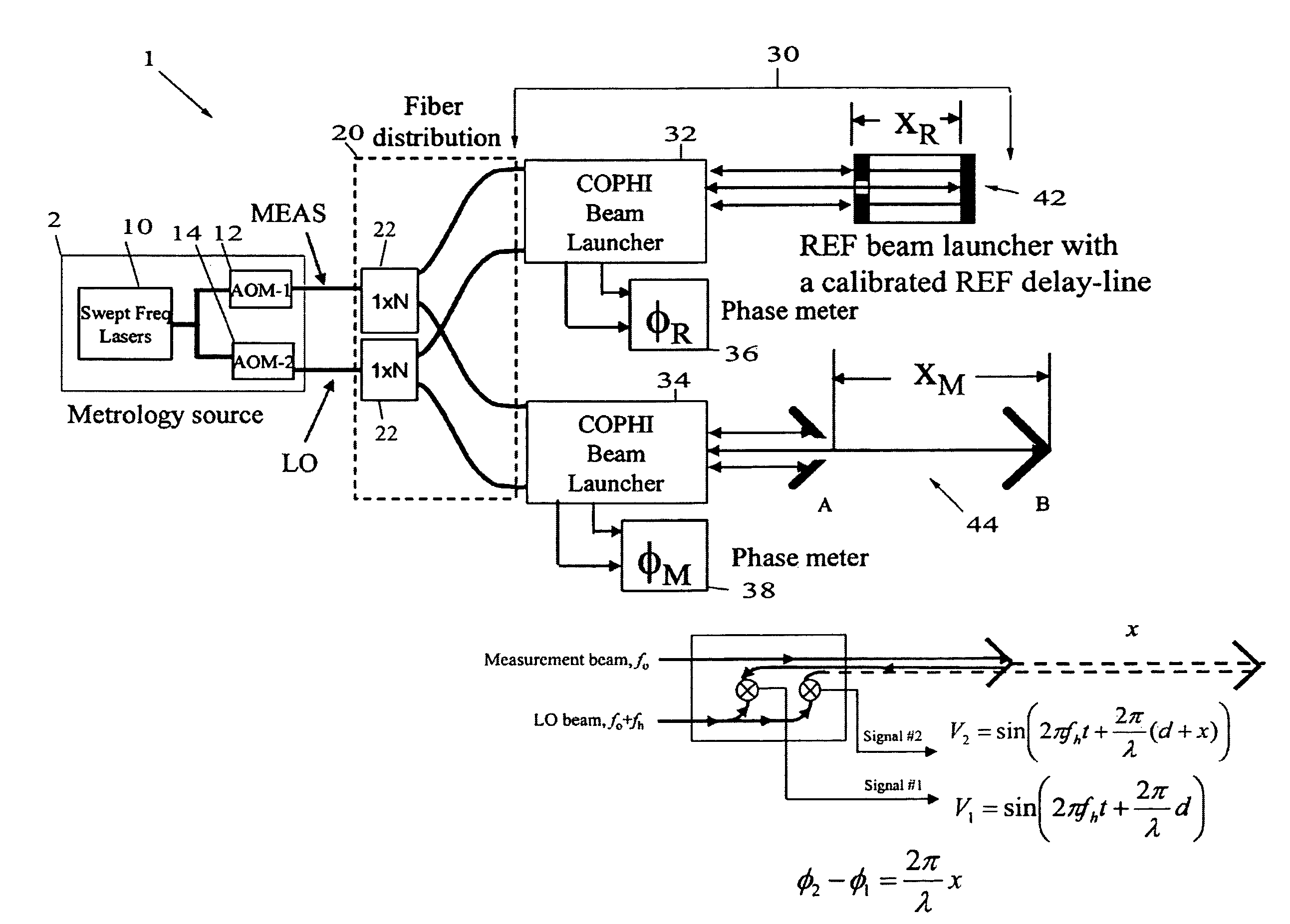
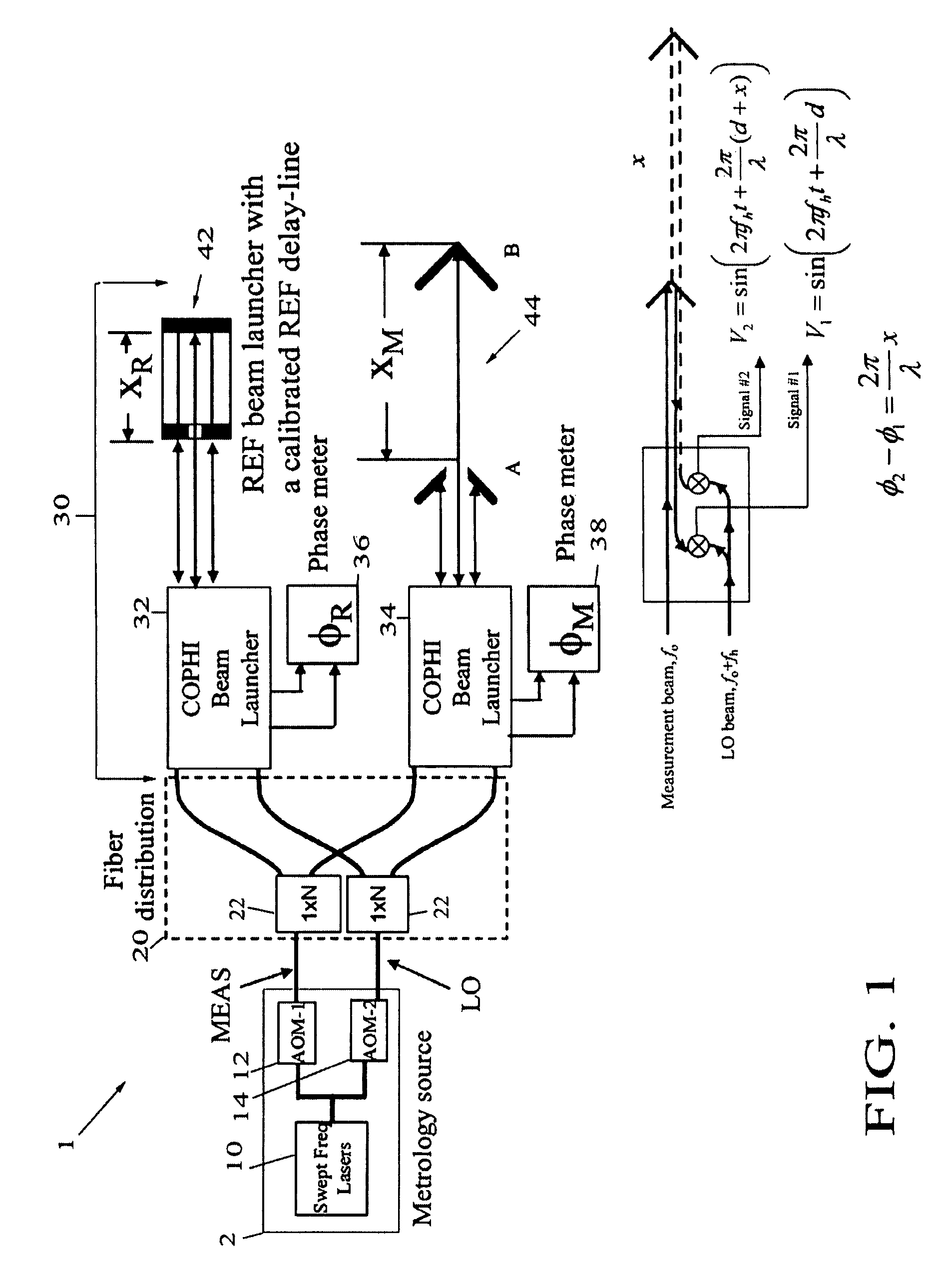
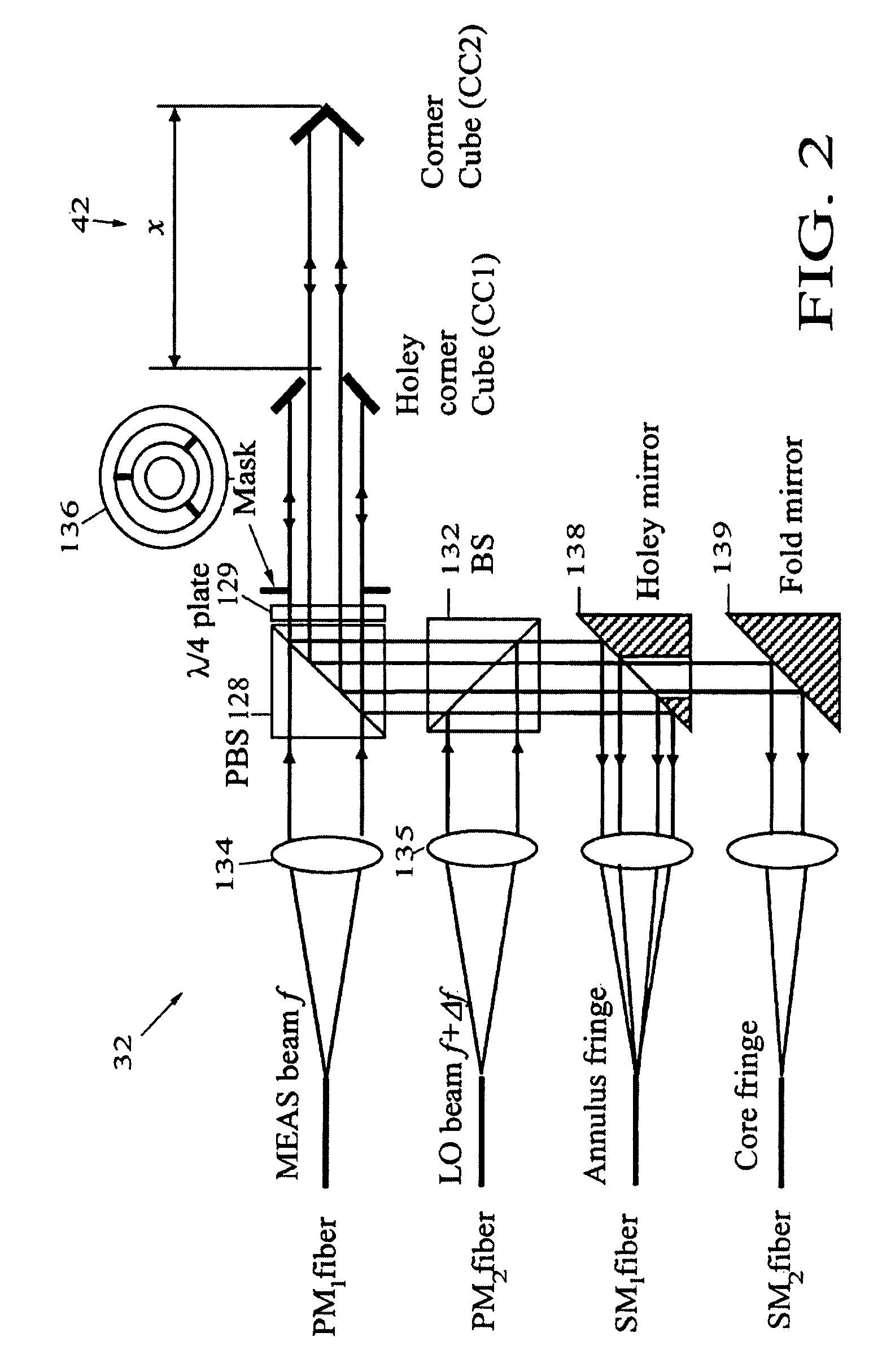
Swept frequency laser metrology system
InactiveUS7764384B1Improve immunitySimplify the metrology systemUsing optical meansLaser rangingMetrology
A swept frequency laser ranging system having sub-micron accuracy that employs multiple common-path heterodyne interferometers, one coupled to a calibrated delay-line for use as an absolute reference for the ranging system. An exemplary embodiment uses two laser heterodyne interferometers to create two laser beams at two different frequencies to measure distance and motions of target(s). Heterodyne fringes generated from reflections off a reference fiducial XR and measurement (or target) fiducial XM are reflected back and are then detected by photodiodes. The measured phase changes ΔφR and Δφm resulting from the laser frequency swept gives target position. The reference delay-line is the only absolute reference needed in the metrology system and this provides an ultra-stable reference and simple / economical system.
Owner:AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE NAT
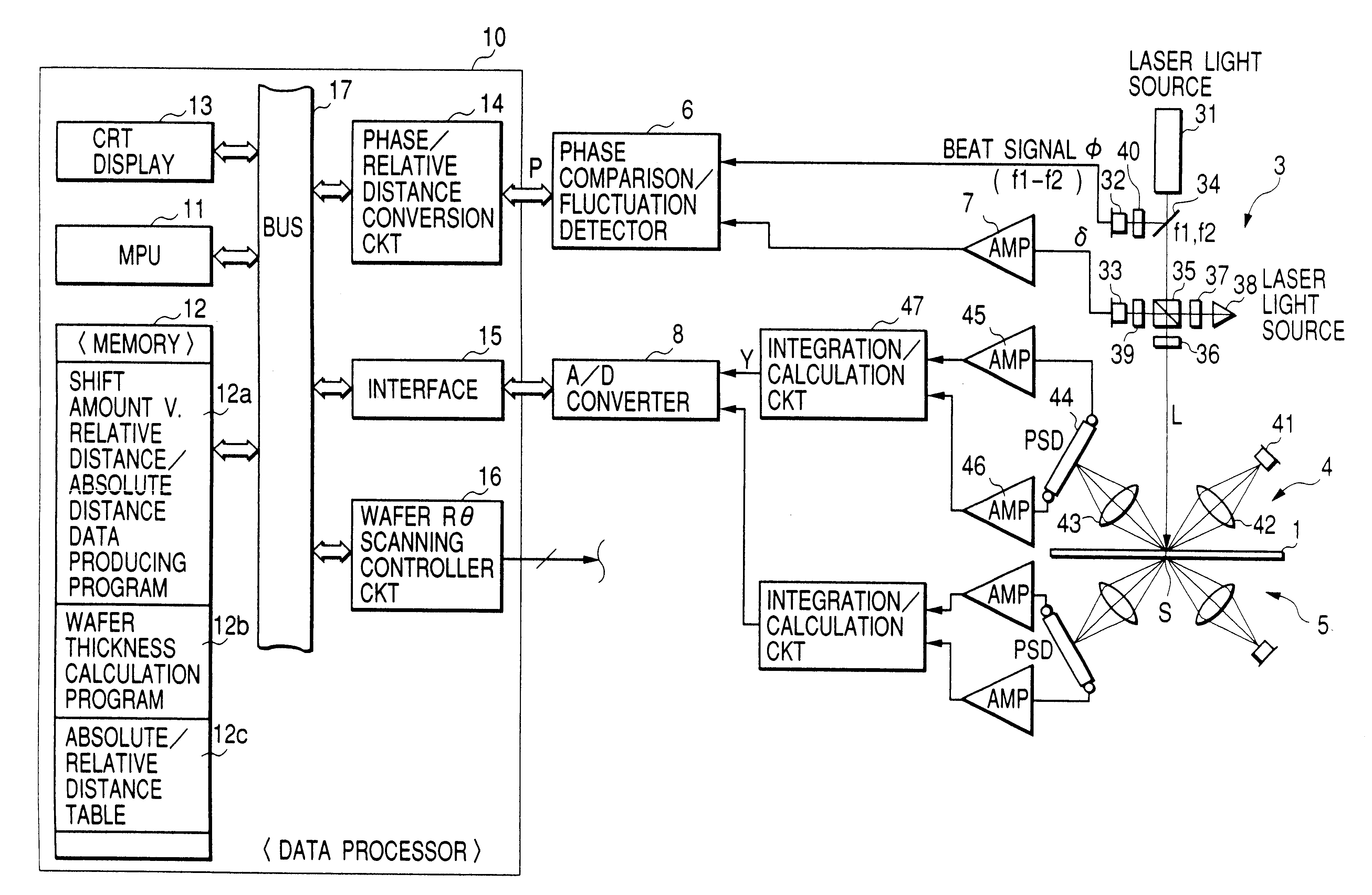
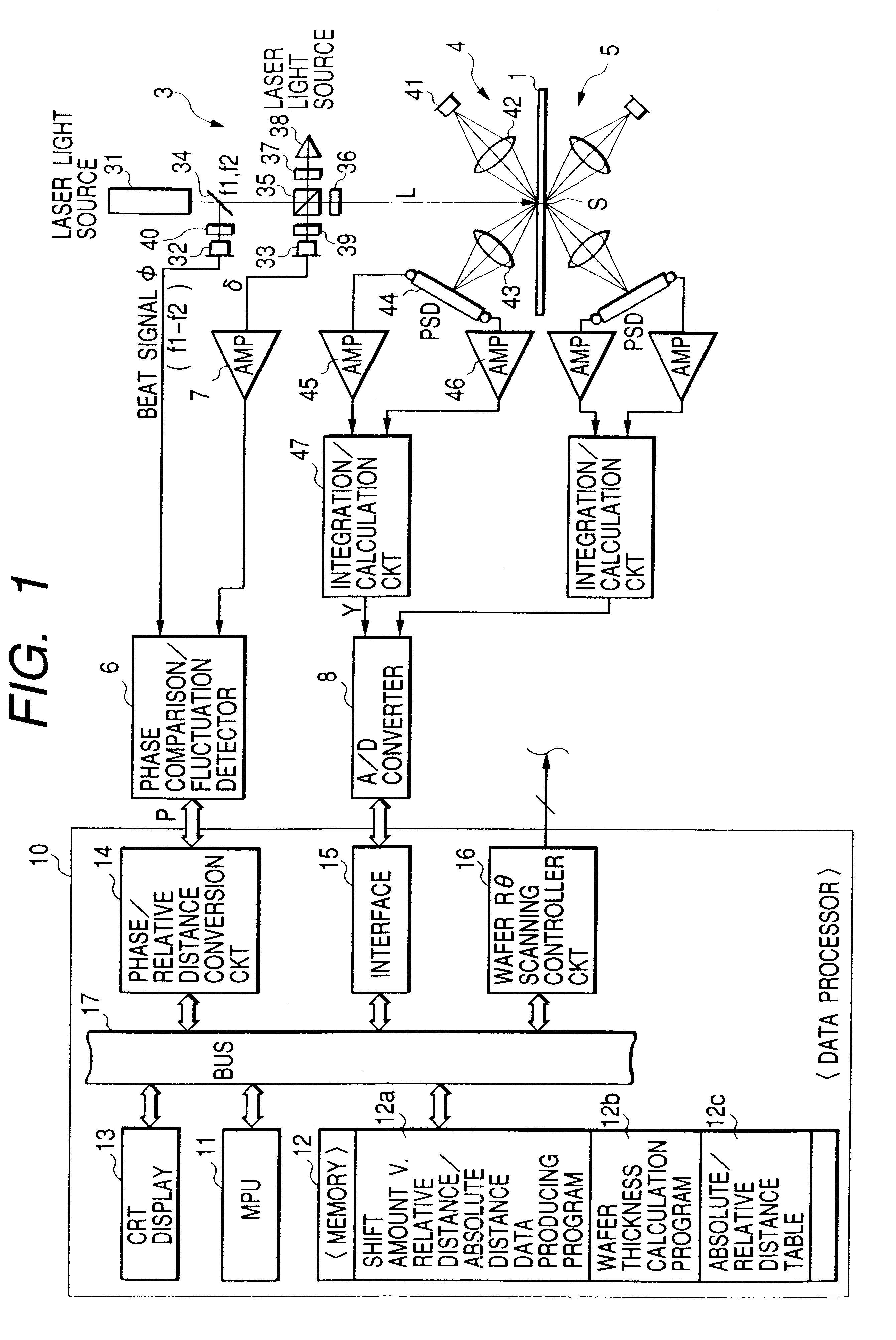
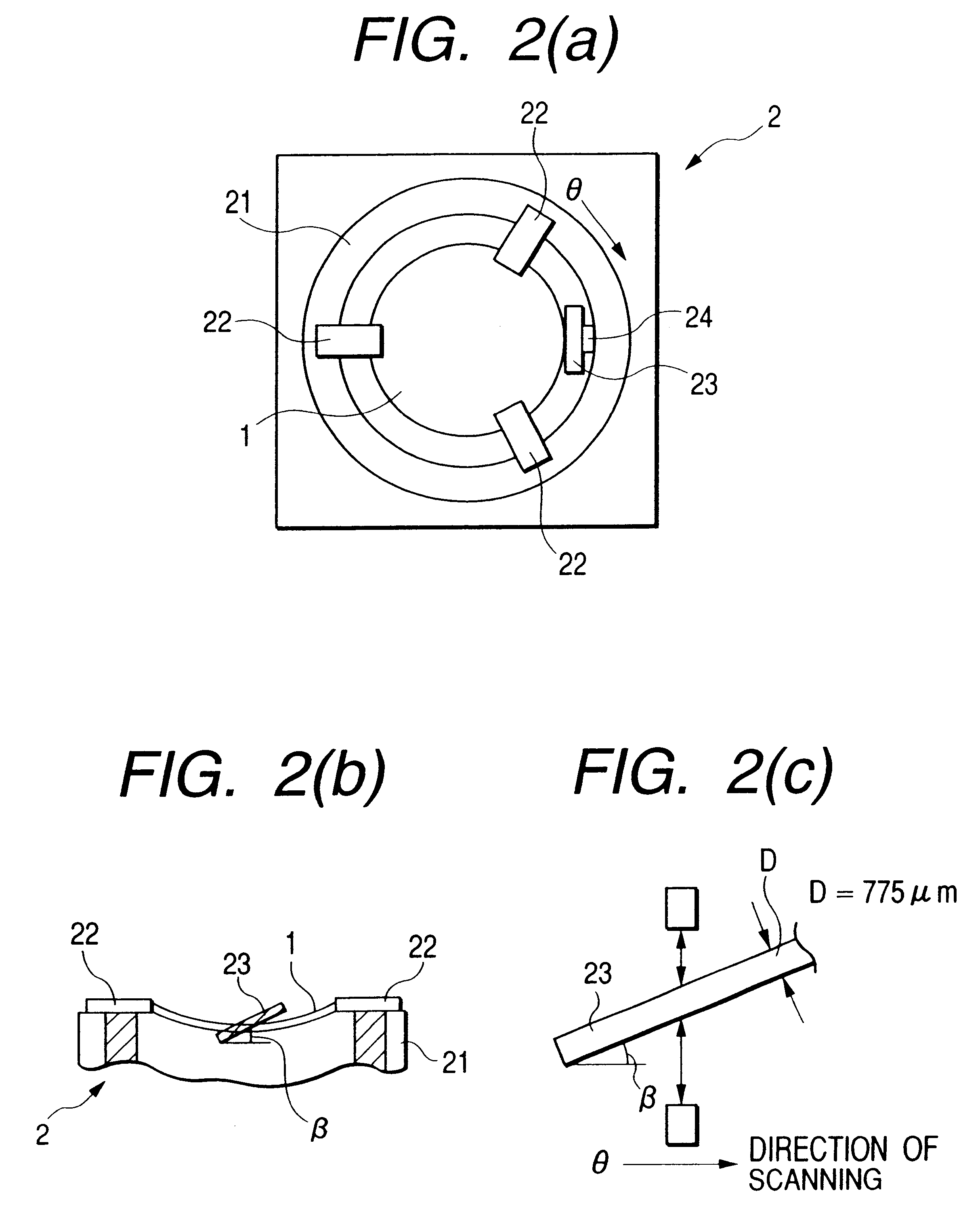
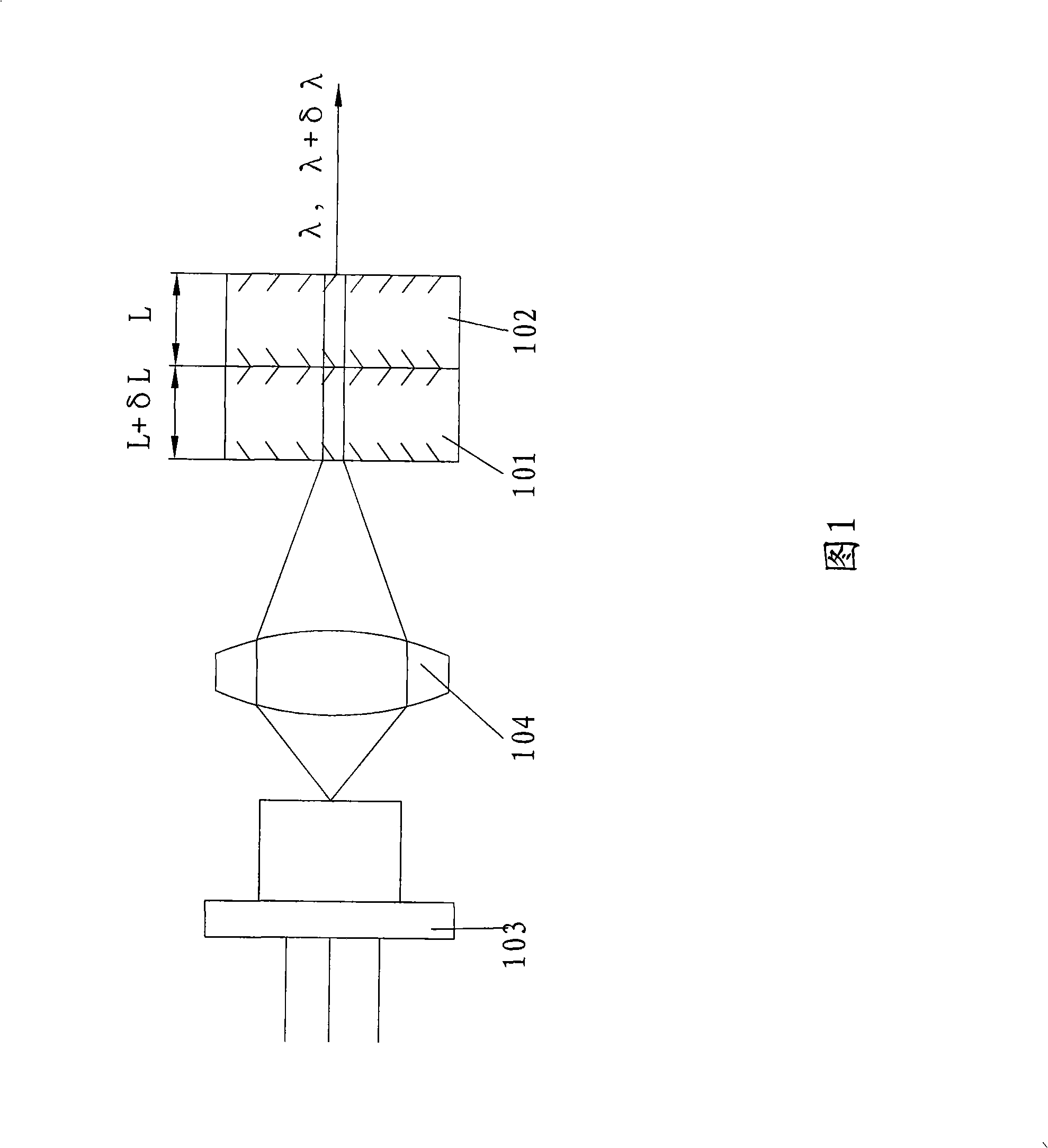
Wafer thickness measuring apparatus and detection method thereof
InactiveUS6353473B1Electric devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMeasurement deviceMeasurement point
Owner:HITACHI ELECTRONICS ENG CO LTD
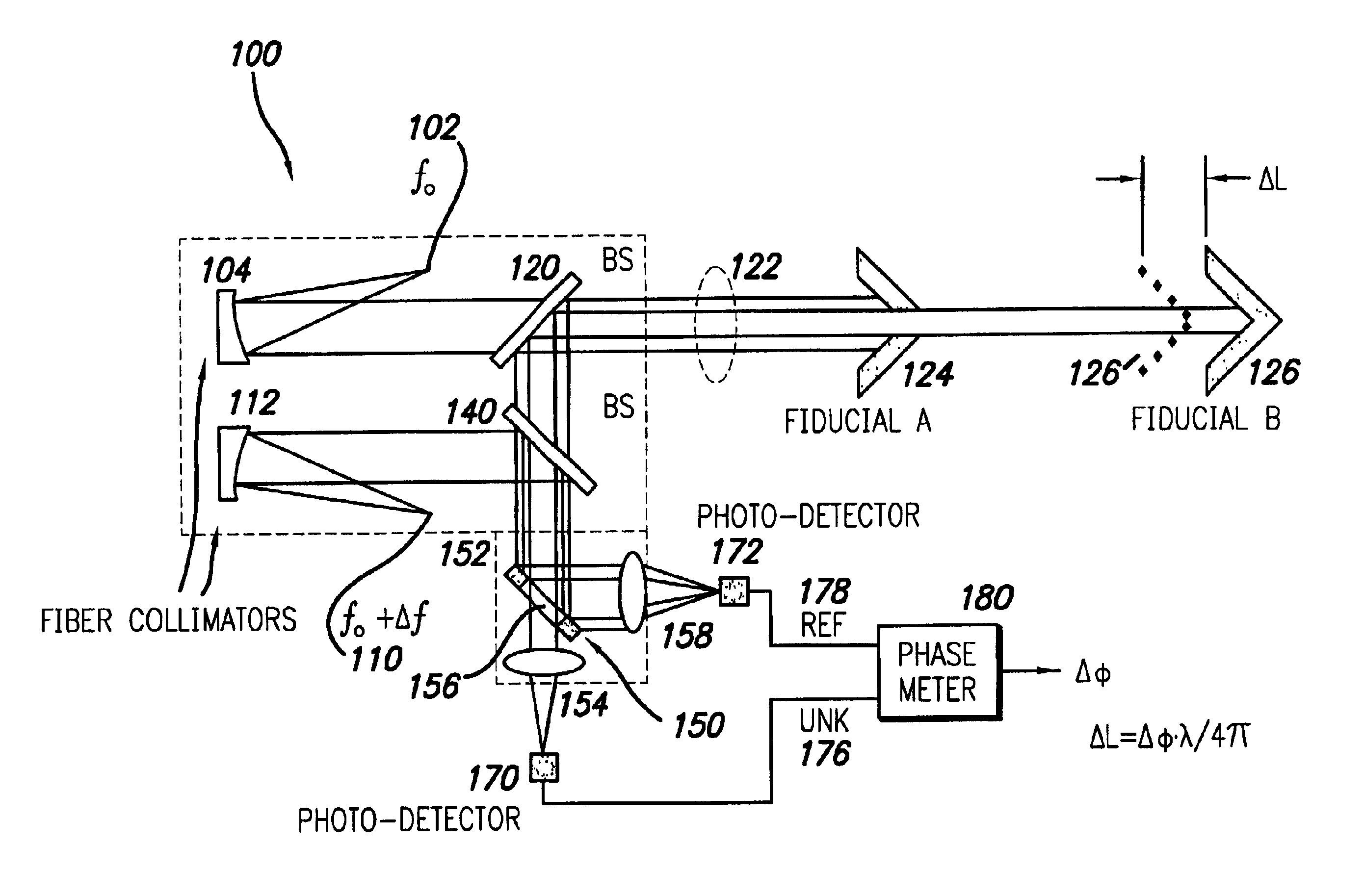
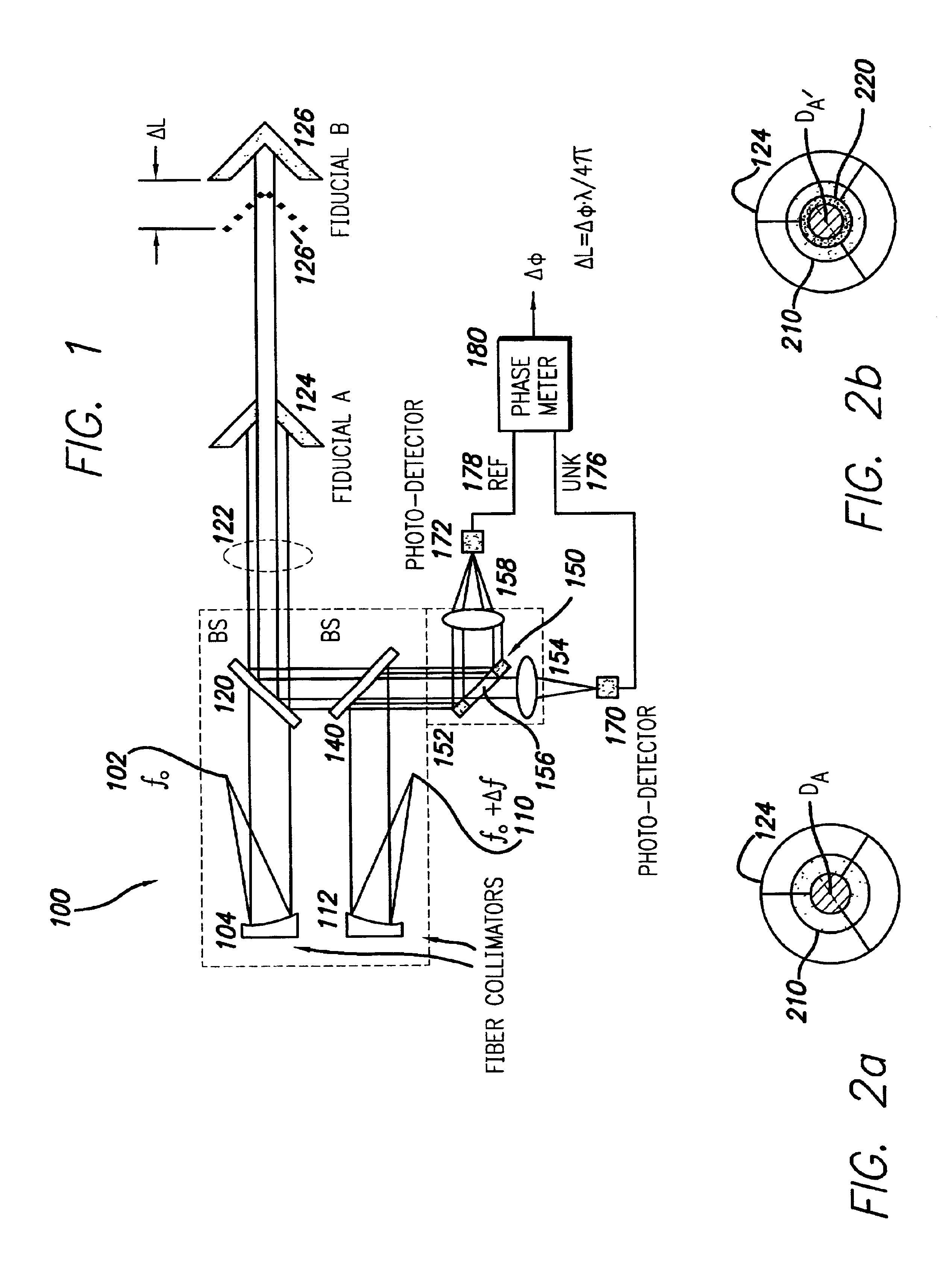
Interferometric apparatus for ultra-high precision displacement measurement
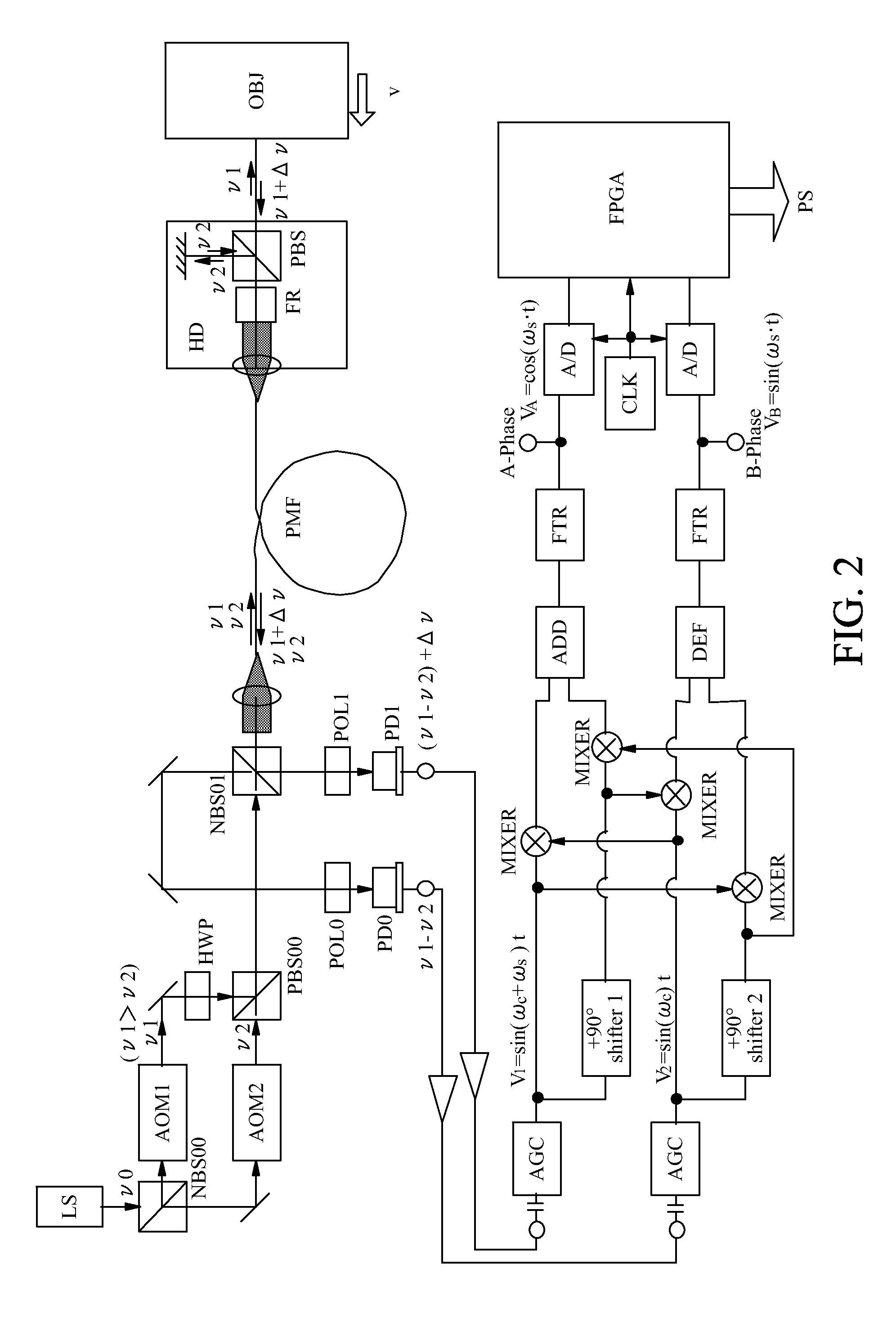
InactiveUS6710880B1Accurate measurementEasy to measureInterferometersUsing optical meansRelative displacementHeterodyne interferometer
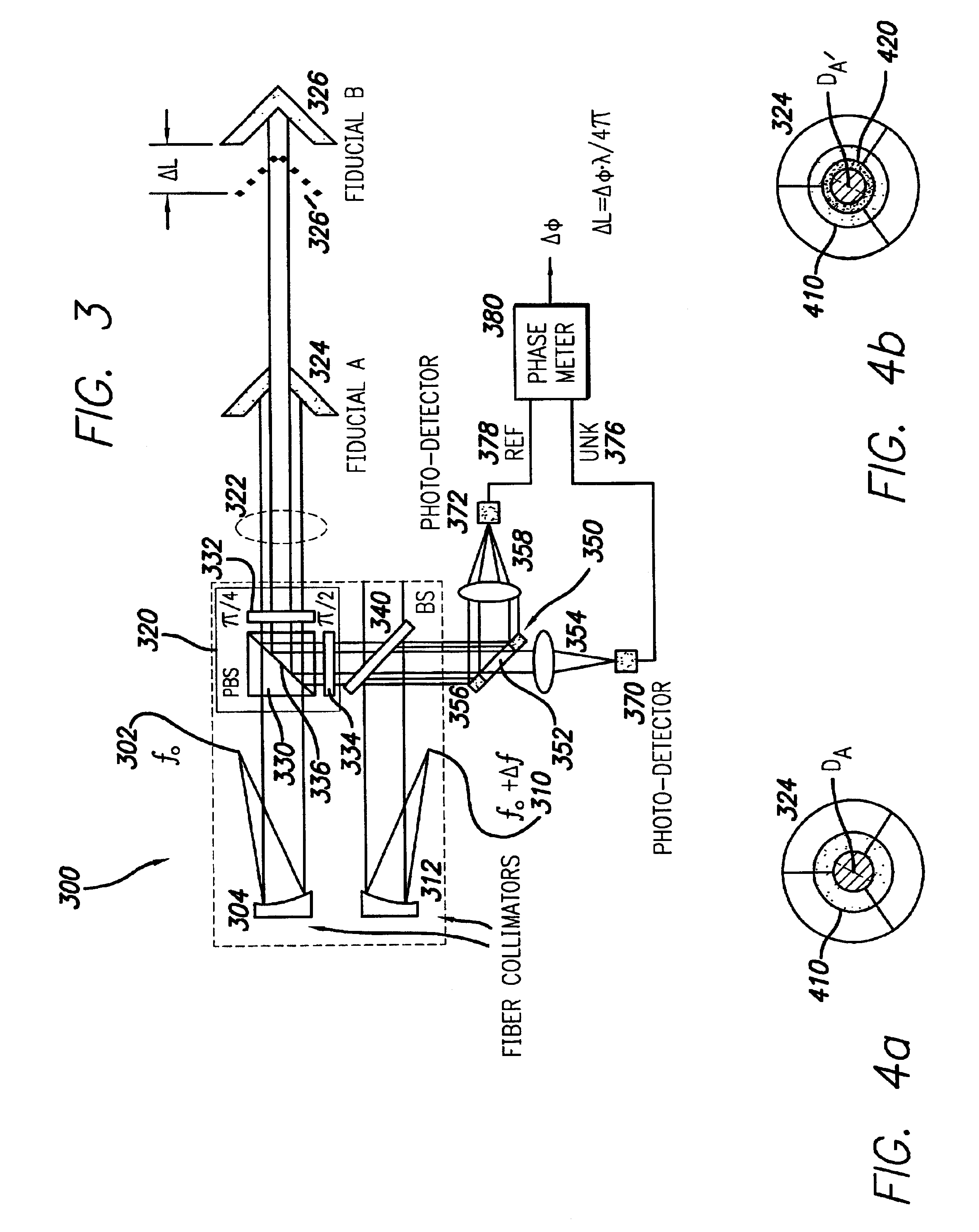
A high-precision heterodyne interferometer measures relative displacement by creating a thermally-insensitive system generally not subject to polarization leakage. By using first and second light beams separated by a small frequency difference (Deltaf), beams of light at the first frequency (f0) are reflected by co-axial mirrors, the first mirror of which has a central aperture through which the light is transmitted to and reflected by the second mirror. Prior to detection, the light beams from the two mirrors are combined with light of the second and slightly different frequency. The combined light beams are separated according to the light from the mirrors. The change in phase (Deltaphi) with respect to the two signals is proportional to the change in distance of Fiducial B by a factor of wavelength (lambda) divided by 4pi (DeltaL=lambdaDeltaphi1 / (4pi)). In a second embodiment, a polarizing beam splitting system can be used.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Heterodyne interferometer based on phase shift of low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter
ActiveCN104296678AAvoid problemsHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansPhase shiftedHeterodyne interferometer
The invention discloses a heterodyne interferometer based on the phase shift of a low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter. The heterodyne interferometer based on the phase shift of the low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter comprises a light beam adjusting unit, a low-frequency-difference phase shifting unit, a beam expanding unit, a light beam combining unit and an area array detector unit. The light beam adjusting unit is used for adjusting output lasers of a laser device into two laser beams. The low-frequency-difference phase shifting unit is used for adjusting the frequencies of the two laser beams obtained by the light beam adjusting unit to obtain two laser beams with the output difference frequency being a low difference frequency lower than 100 Hz. The beam expanding unit is used for expanding the diameters of the two laser beams output by the low-frequency-difference phase shifting unit to be equal to the size of a surface to be measured and using the expanded two laser beams as reference light and measuring light respectively. The light beam combining unit is used for enabling the measuring light returned from the surface to be measured and the reference light to be combined to generate interference. The area array detector unit is used for collecting the interference. According to the heterodyne interferometer based on the phase shift of the low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter, heterodyne interference phase shift of the acousto-optic frequency shifter is adopted to effectively avoid that moving parts exist in the interferometer, the measurement accuracy is further improved, and the anti-interference performance is good.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-channel Doppler heterodyne interferometer
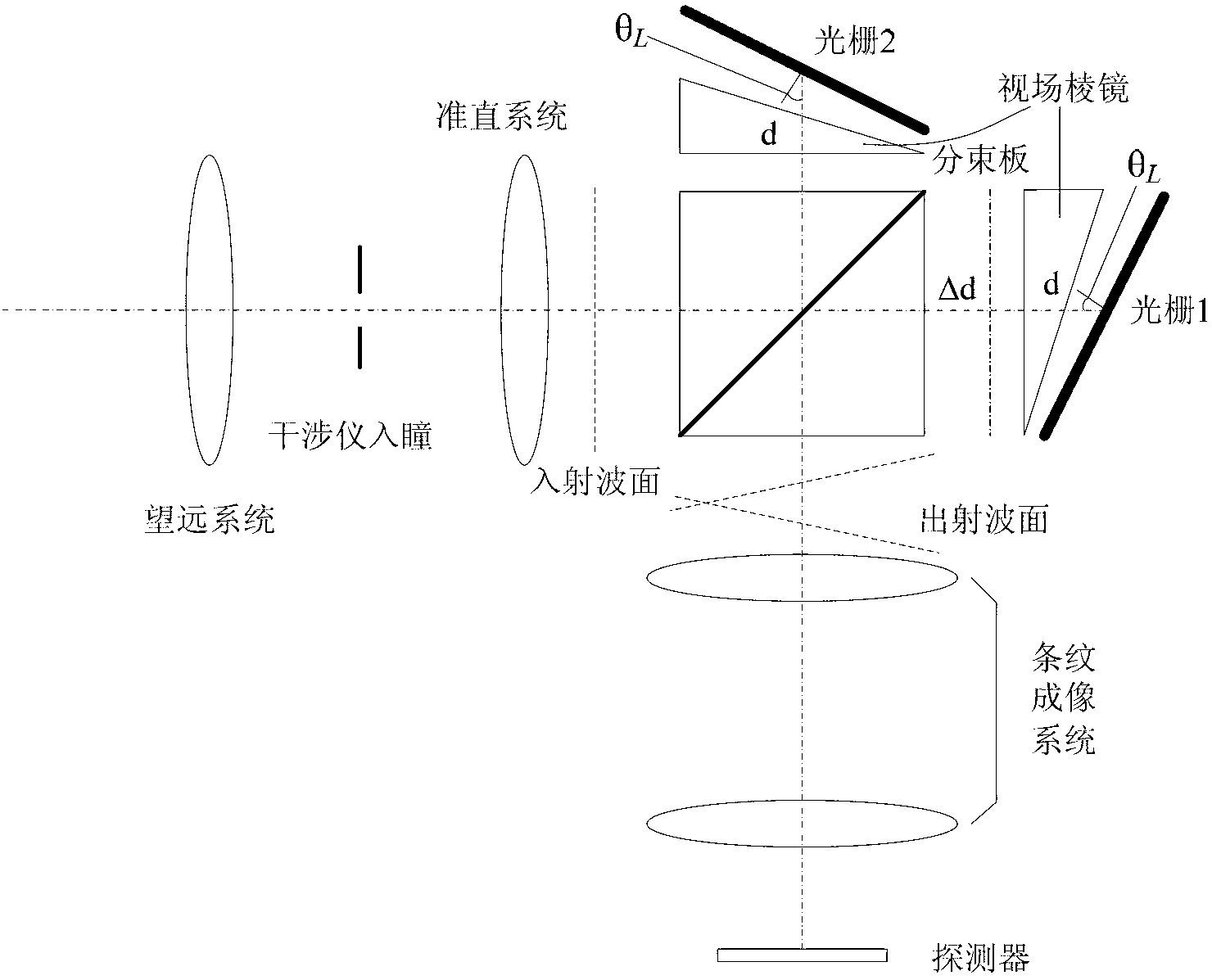
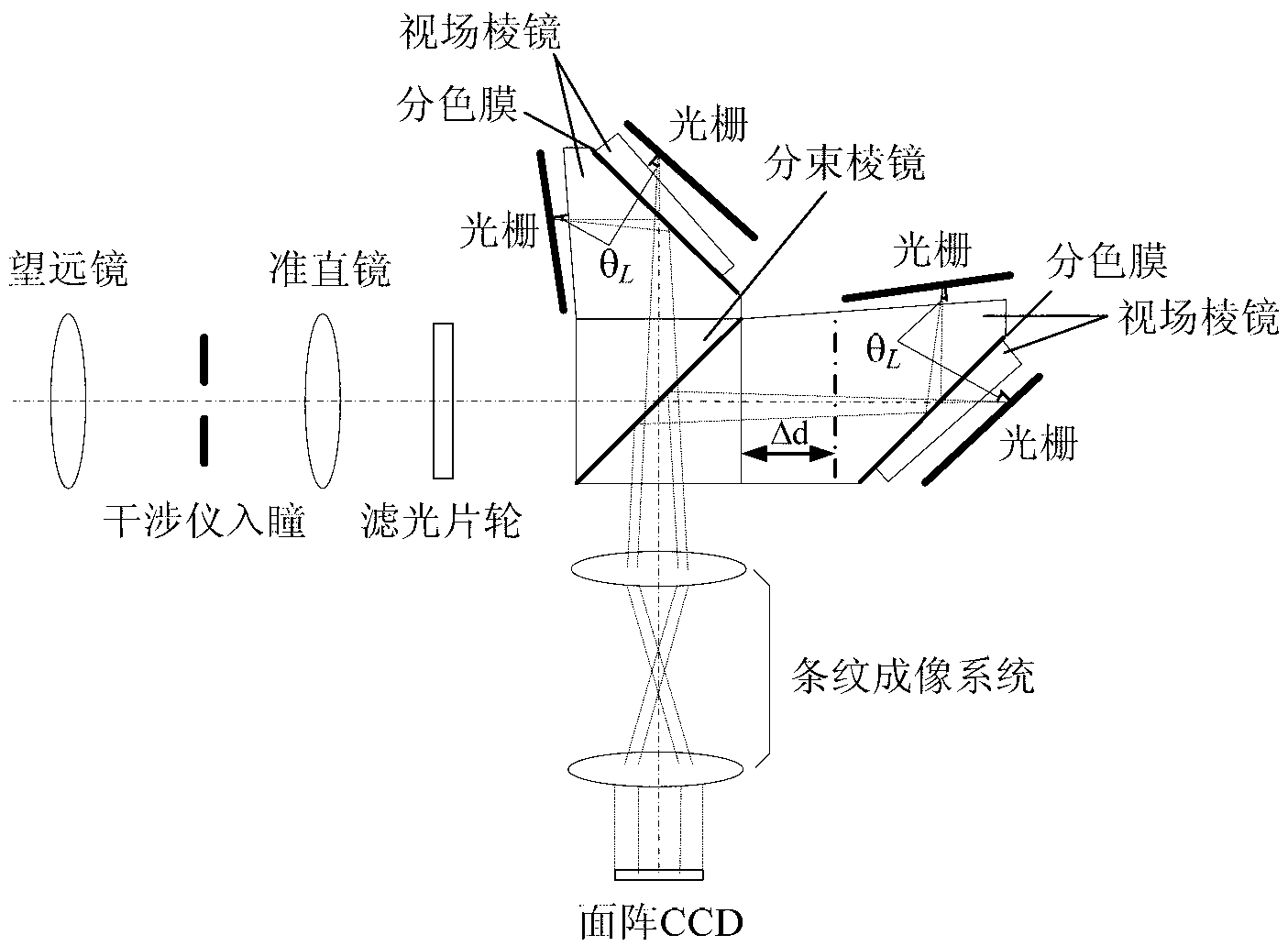
ActiveCN103063305ARealize measurementReduce processing requirementsInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterGrating
The invention provides a two-channel Doppler heterodyne interferometer. The Doppler heterodyne interferometer aims at achieving the measurement of two central wavelength target spectral lines. The interferometer comprises an interferometer entrance pupil, a collimating system, a beam splitter prism, a blazed grating component, a stripe imaging system and a detector array. The core component of the beam splitter prism is a depolarization beam splitting film in a 50-to-50 half-reflective and half-transparent mode. The stripe imaging system comprises a front lens group and a back lens group, and a narrow-band filter switching device is arranged between the collimating system and the beam splitter prism. The blazed grating component includes that a first blazed grating, a second blazed grating, a third blazed grating and a fourth blazed grating are respectively arranged on a reflected light way. A Littrow angle is formed by the working face normals of the four blazed gratings and the corresponding incident optical axis, wherein, a working grating is formed by the first blazed grating and the third blazed grating, and another working grating is formed by the second blazed grating and the fourth blazed grating so that the interference of individual wavelength is achieved. The corresponding grating working surface center of the working grating forms an optical path difference of the interferometer along the difference between the distances of the center of the beam splitter prism.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
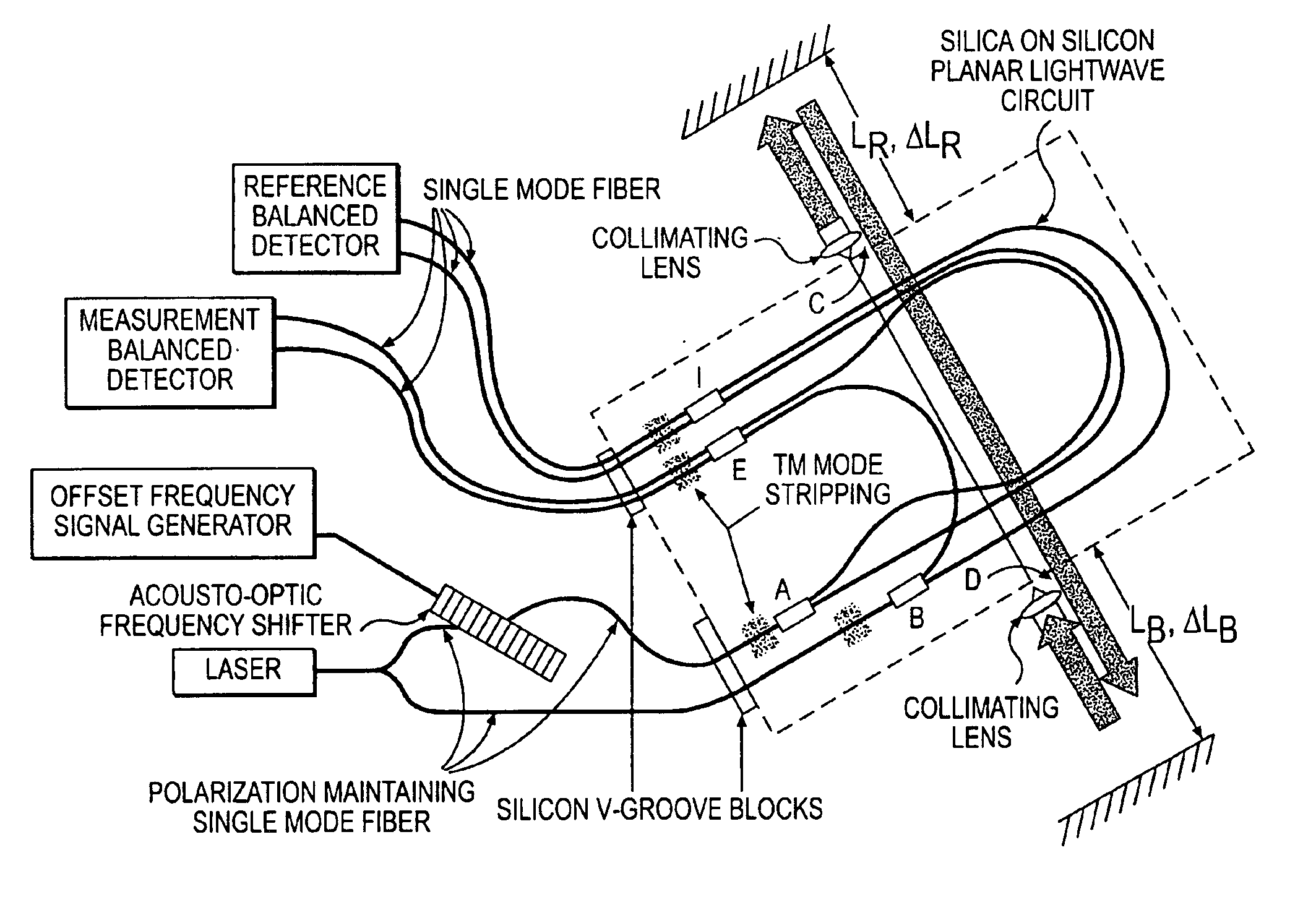
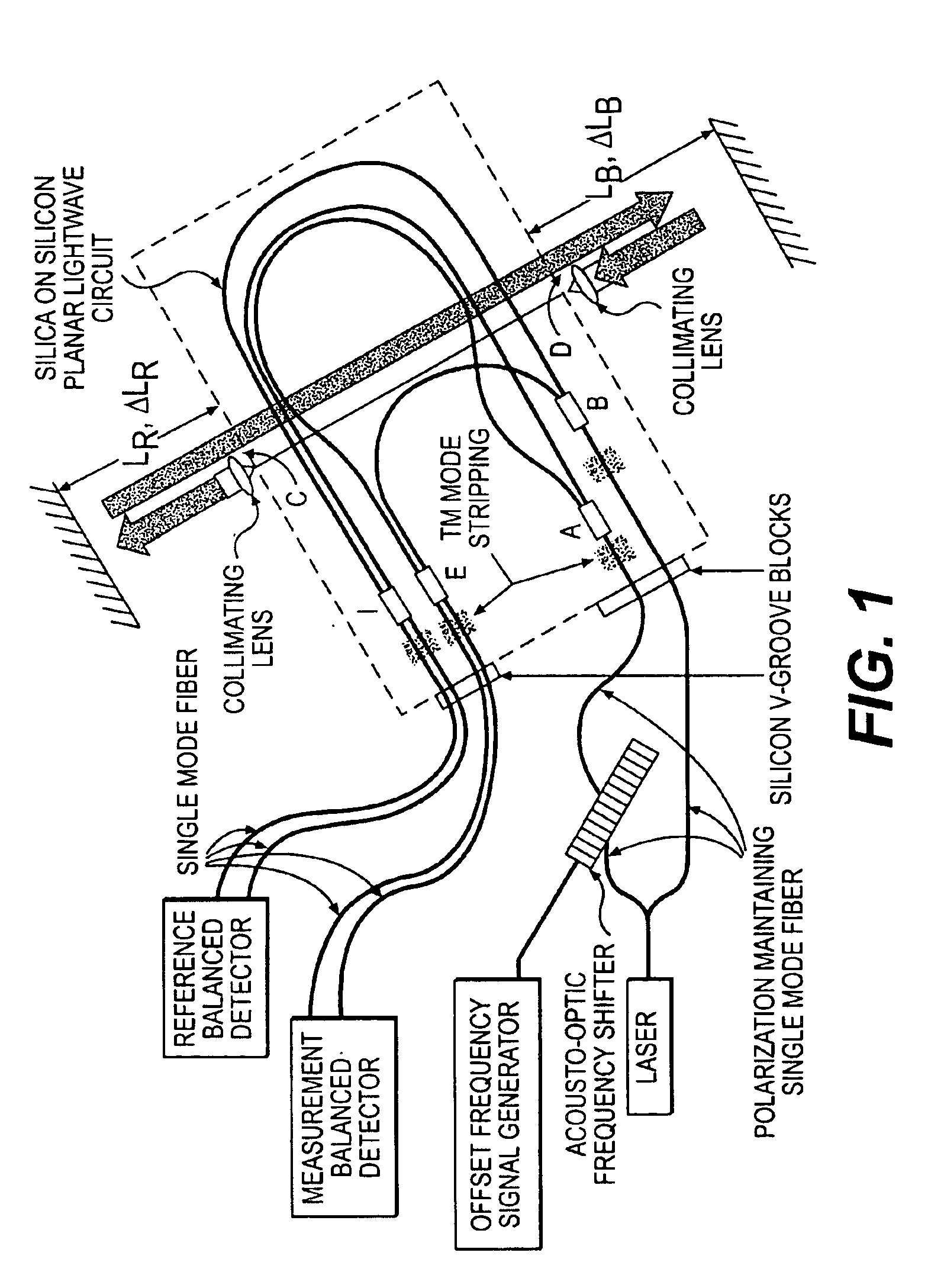
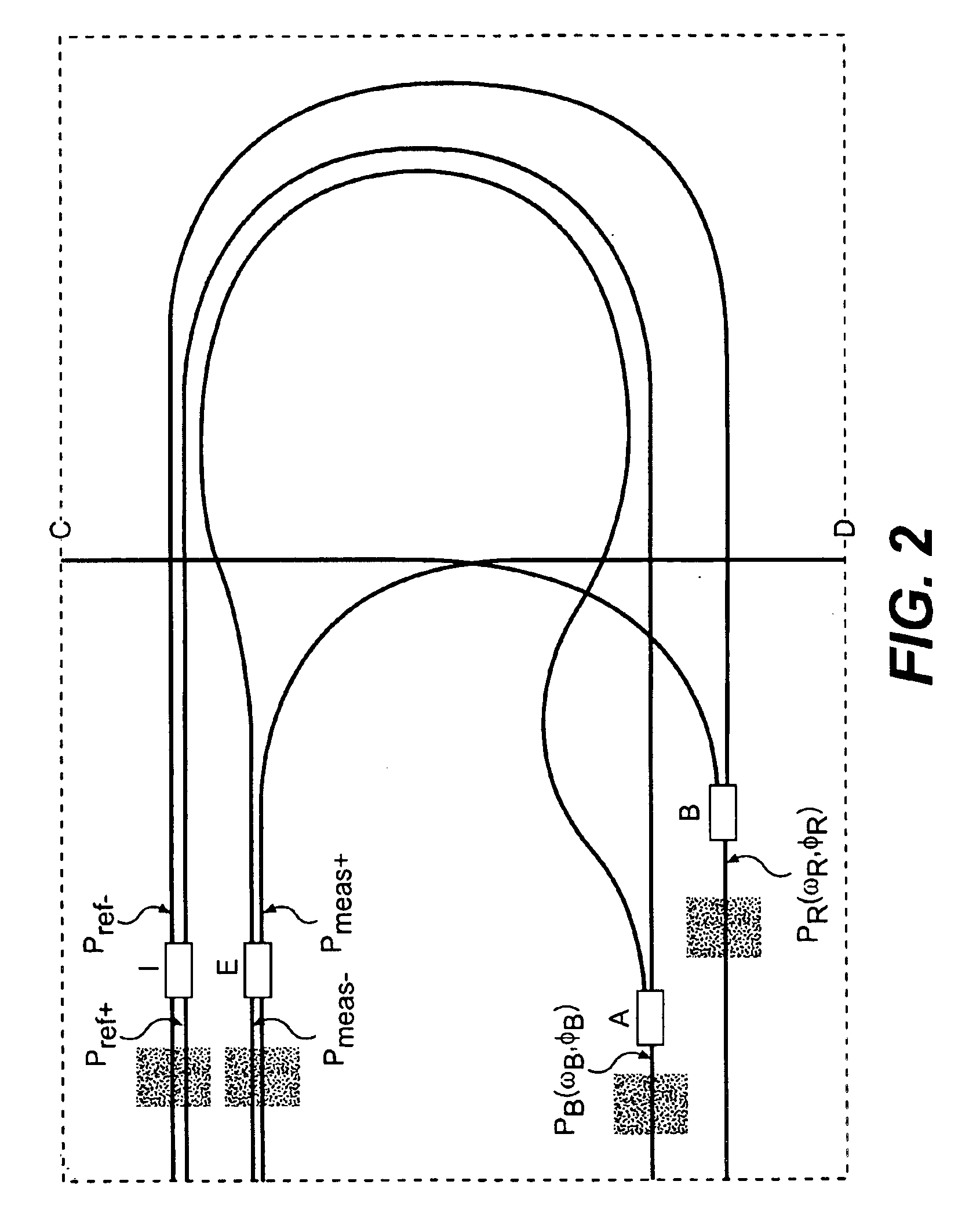
Robust heterodyne interferometer optical gauge
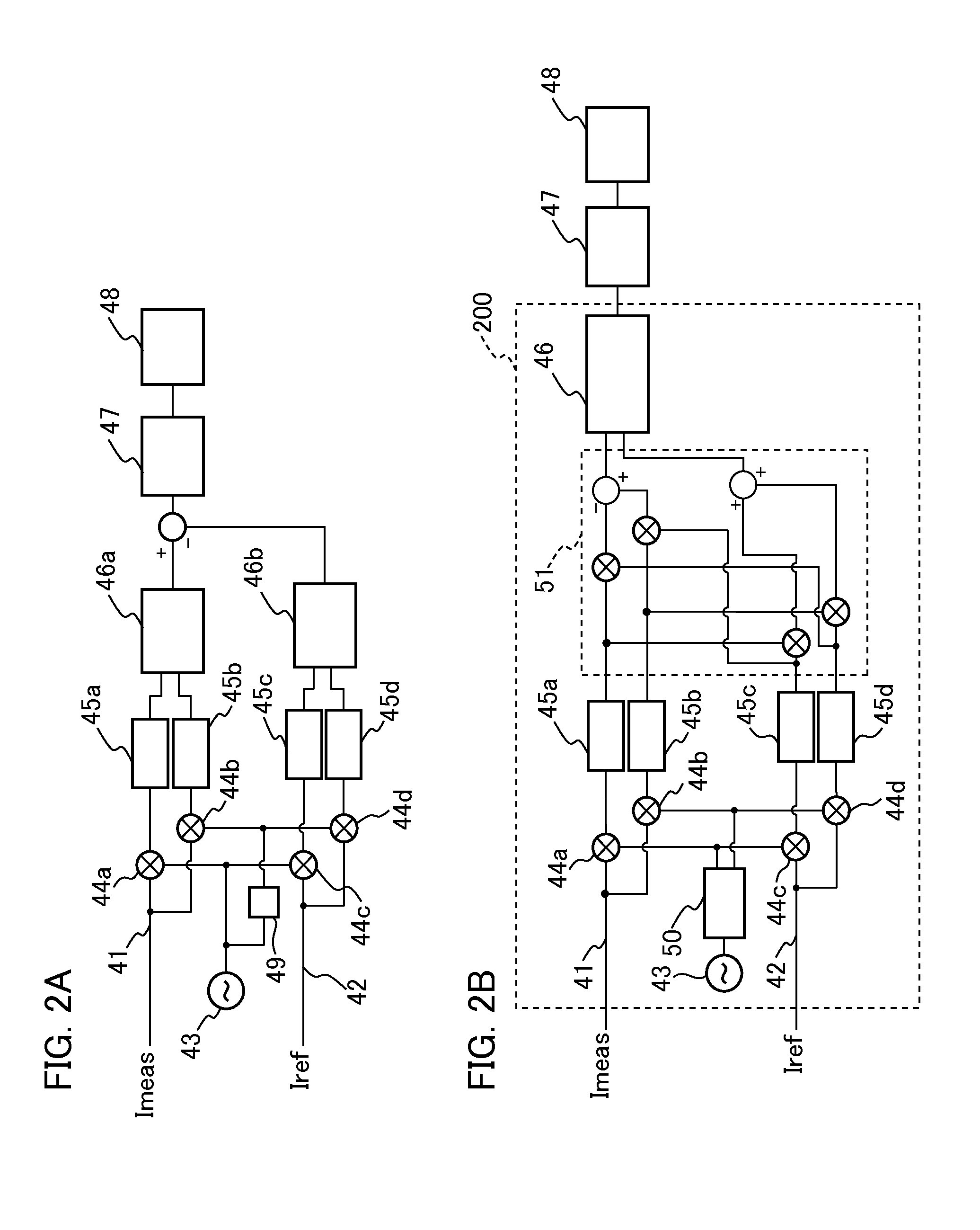
A method for performing optical signal and beam distribution in a heterodyne interferometer. A planar lightwave circuit is provided including a plurality of waveguide optical transmission elements and an input coupler and an output coupler arranged along the optical transmission elements. Optical pathlengths of the transmission elements are matched between the input coupler and the output coupler to compensate for thermal effects. Reference and measurement optical phases are determined employing the input coupler and the output coupler.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Absolute distance dynamic measurement system based on swept-frequency interferometer, and measurement method of absolute distance dynamic measurement system
ActiveCN106226775AEliminate the effects ofHigh measurement accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationHeterodyne interferometerAcousto-optics
The invention discloses an absolute distance dynamic measurement system based on a swept-frequency interferometer, and a measurement method of the absolute distance dynamic measurement system, and belongs to the field of absolute distance dynamic measurement. The invention aims at solving a problem that a conventional measurement system is low in measurement precision under the impact of vibration. The system comprises two parts, wherein one part is used for carrying out the FSI absolute distance measurement, and the other part is used for carrying out the real-time monitoring of a target displacement through employing an additional heterodyne interferometer which consists of a single frequency laser and an acoustic optical modulator, thereby eliminating the impact from a Doppler effect introduced by the change of an optical path of a measurement path. The method comprises the step: obtaining an absolute distance (shown in the description) through employing the signals detected by a first detector, a second detector and a balance detector in the measurement system. A signal obtained by the second detector is used for correcting an error caused by the instable modulation frequency of the acoustic optical modulator.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Idle running error automatic compensation apparatus for laser heterodyne interferometer
InactiveCN101493311AGood effectEliminate Gap Length ErrorsUsing optical meansHeterodyne interferometerMeasuring instrument
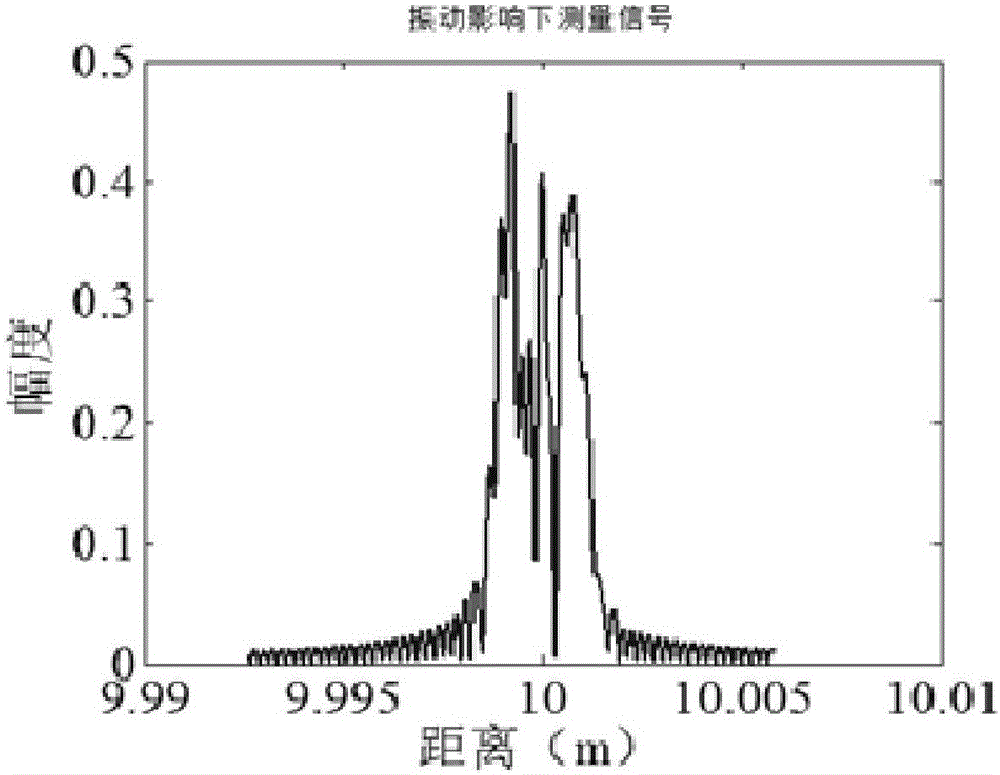
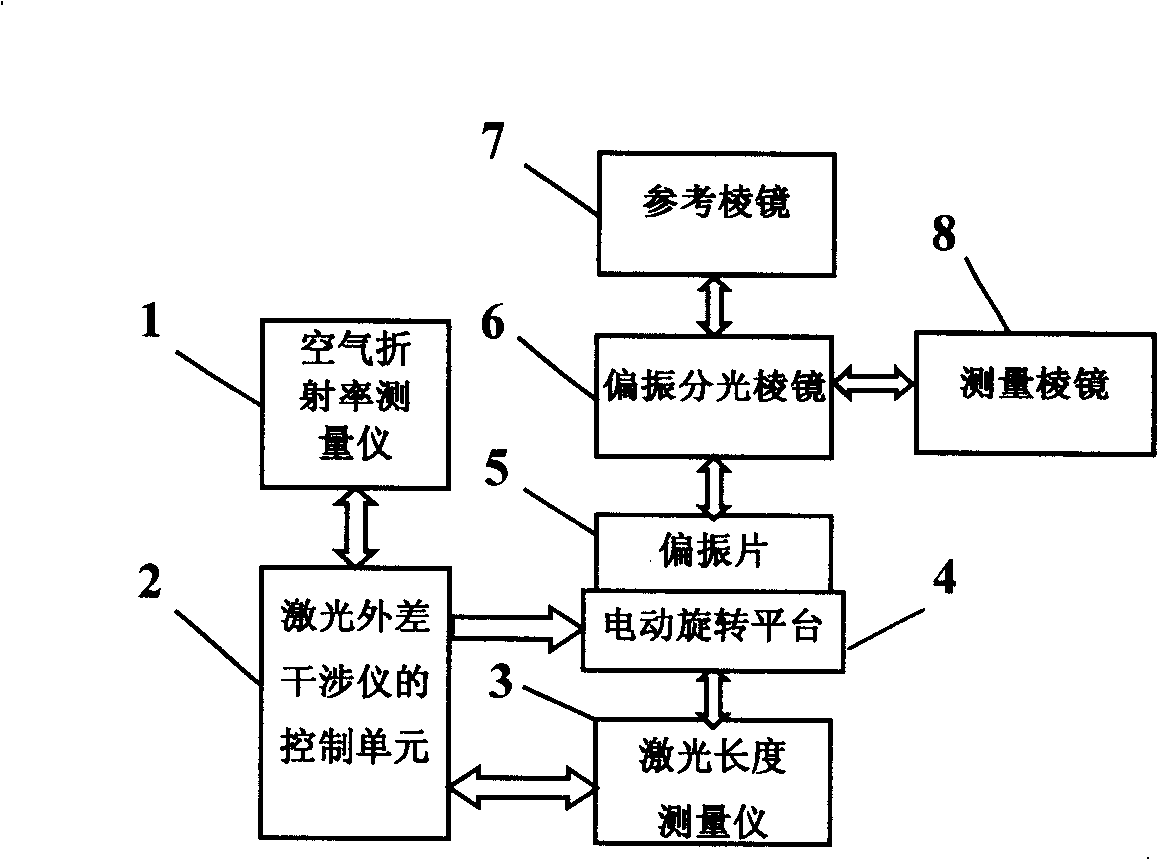
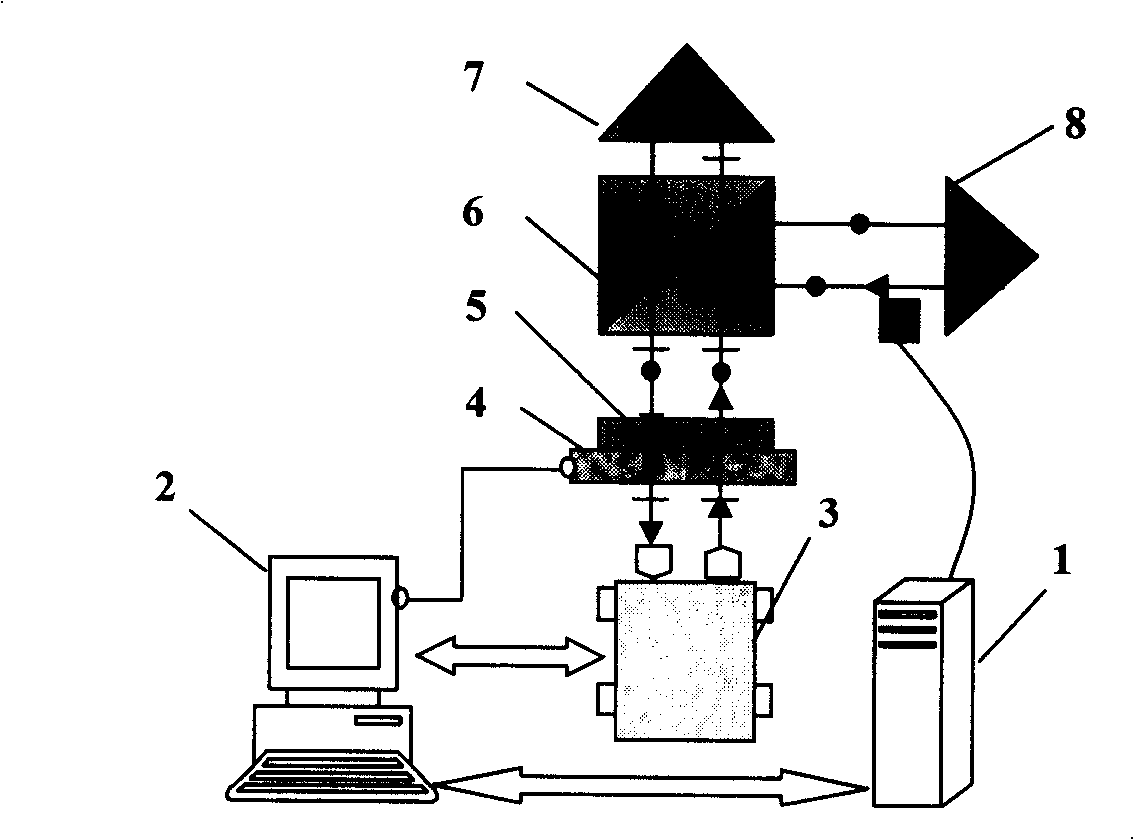
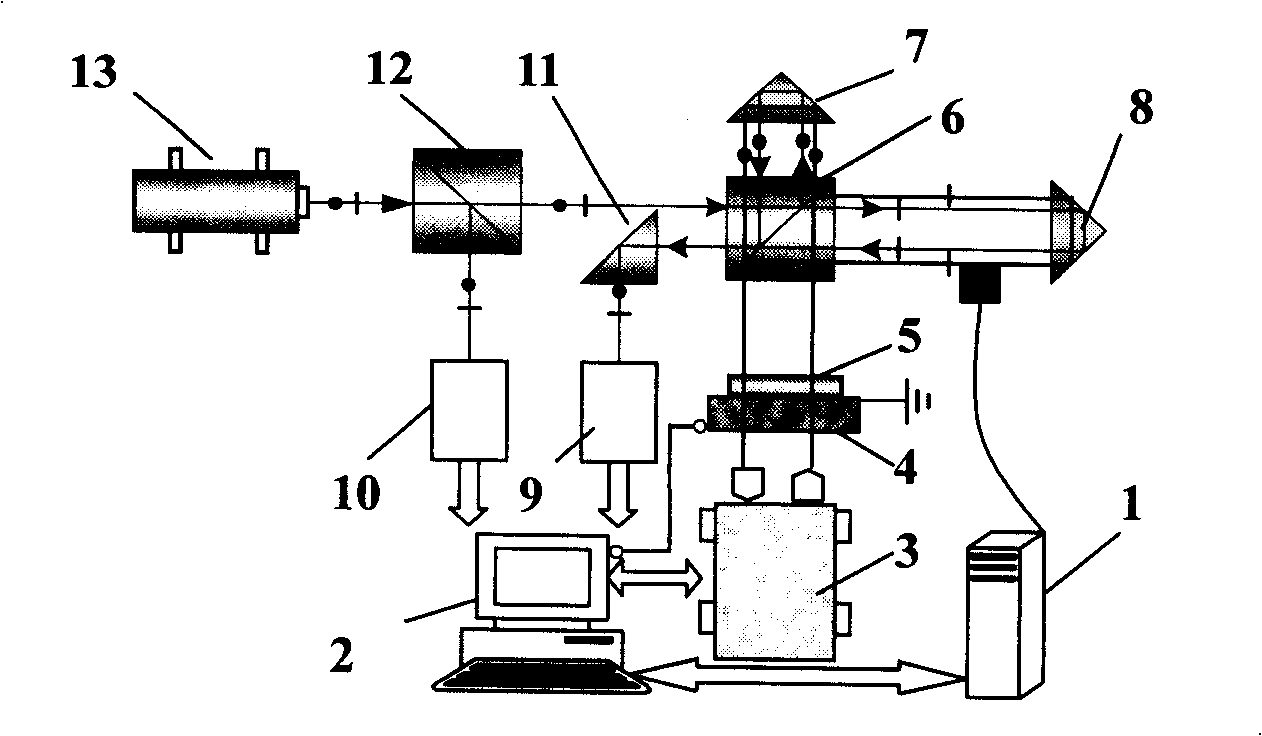
A laser heterodyne interferometer idle stroke error automatic compensator belongs to the technical field of laser measurement. A polaroid sheet and a laser length measuring instrument are arranged in sequence at a co-optical axis at one side of a polarization splitting prism opposite to a reference prism; the polaroid sheet is fixed at an electric rotary platform; the electric rotary platform, the laser length measuring instrument and an air refracting index measuring instrument are respectively connected with a control unit of the laser heterodyne interferometer by a control bus; a probe sensor of the air refracting index measuring instrument is arranged between the polarization splitting prism and a measurement prism. The compensator can effectively reduce effects by the idle stroke error on measurement results during real-time measurement.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
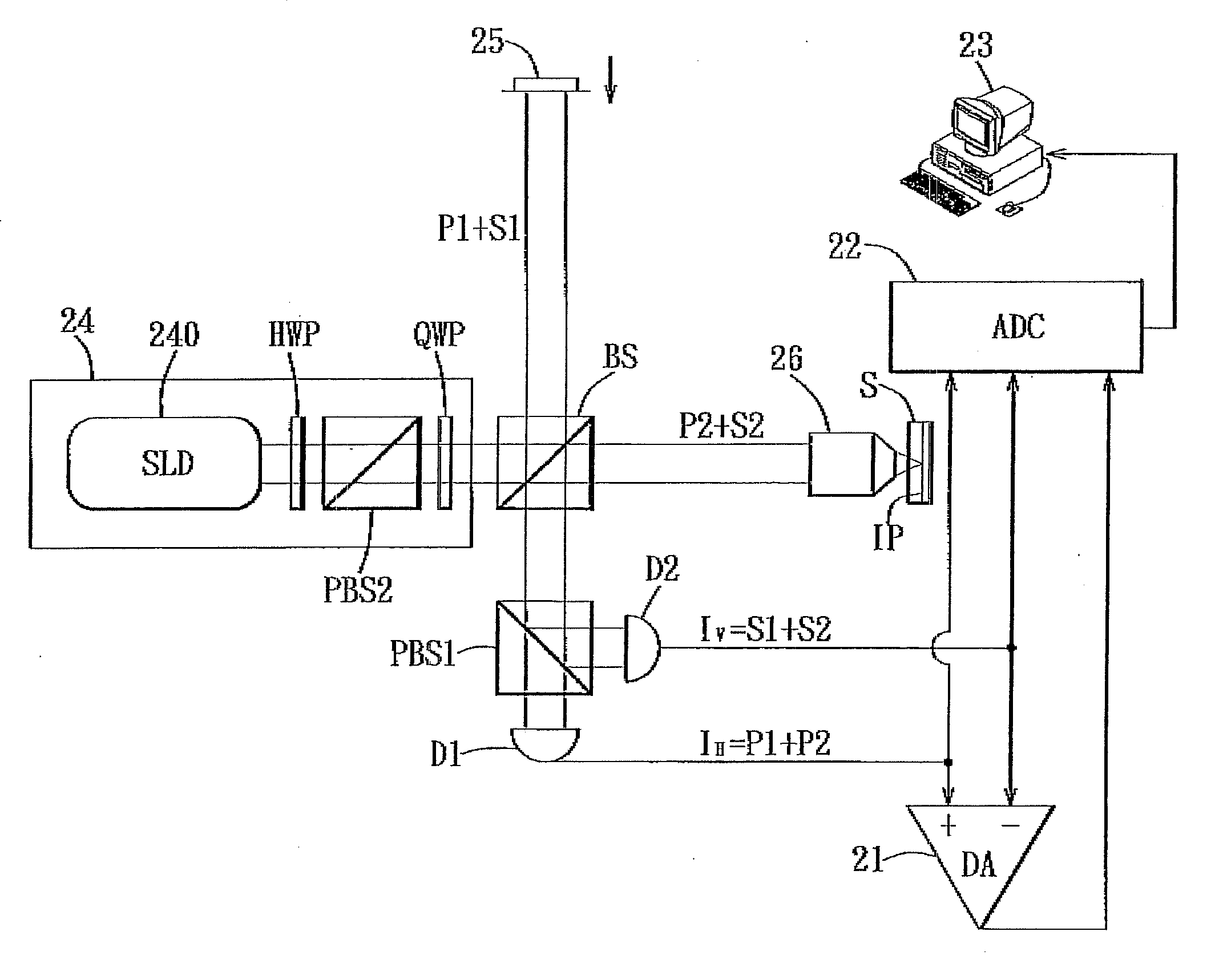
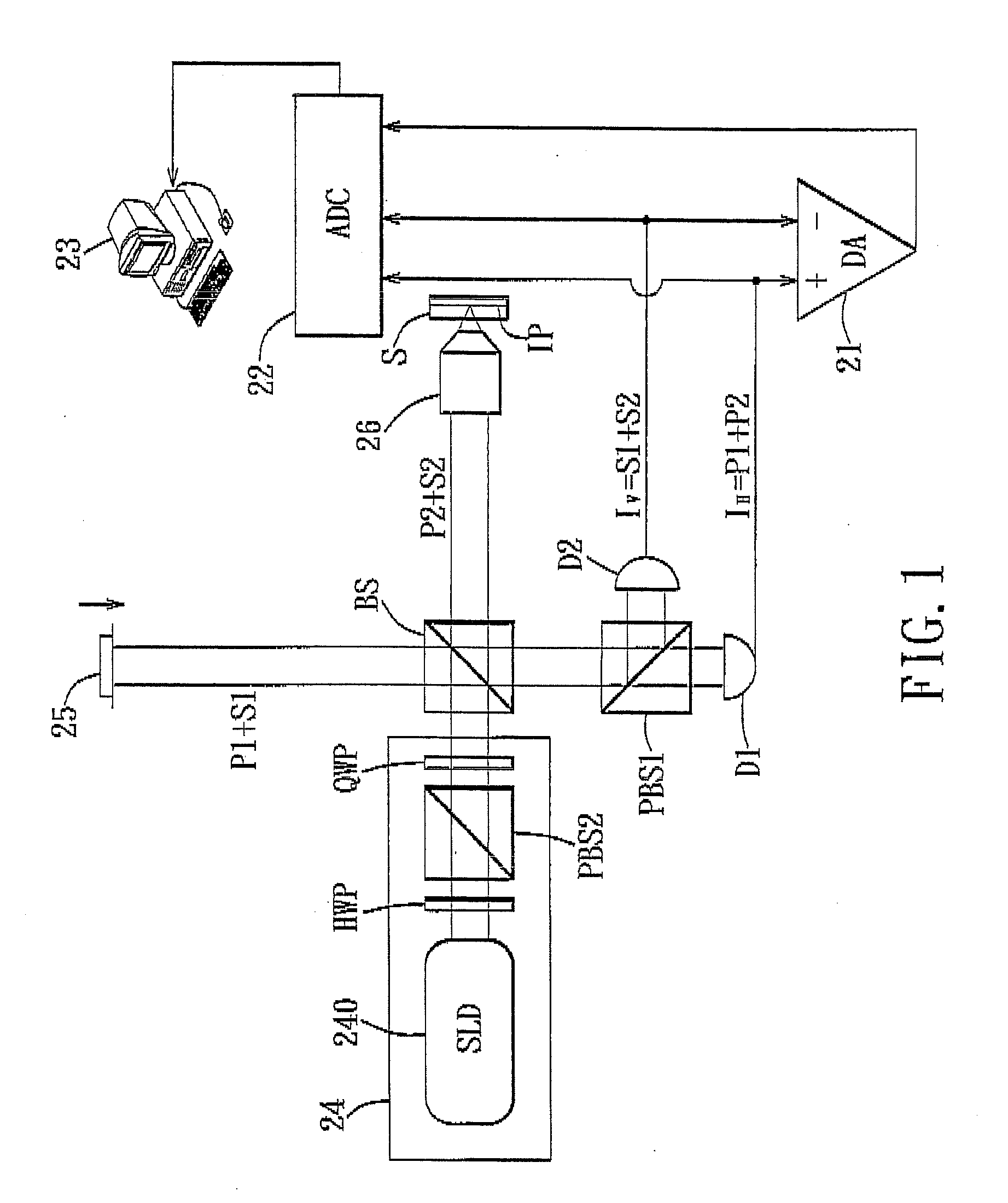
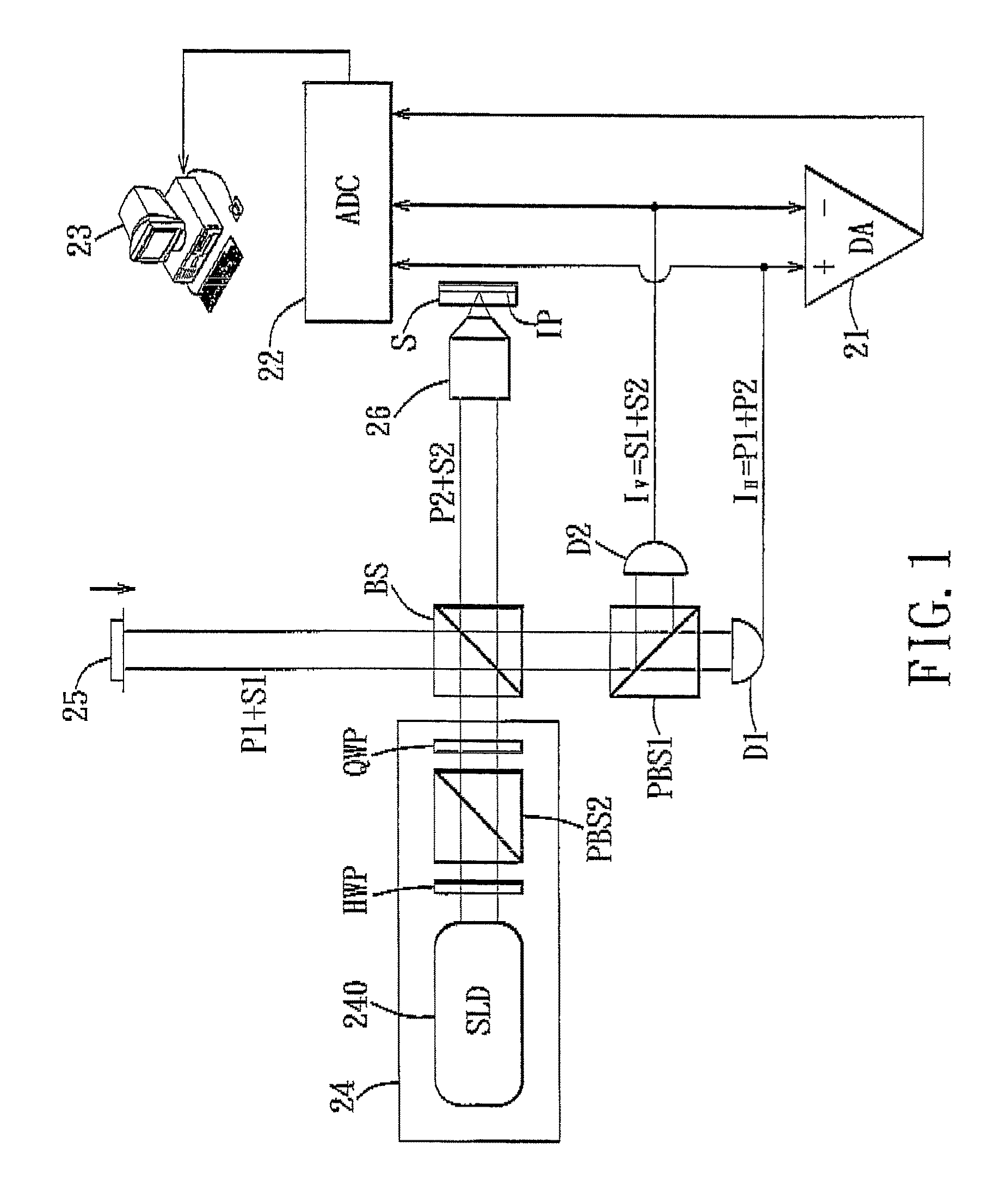
Differential-Phase Polarization-Sensitive Optical Coherence Tomography System
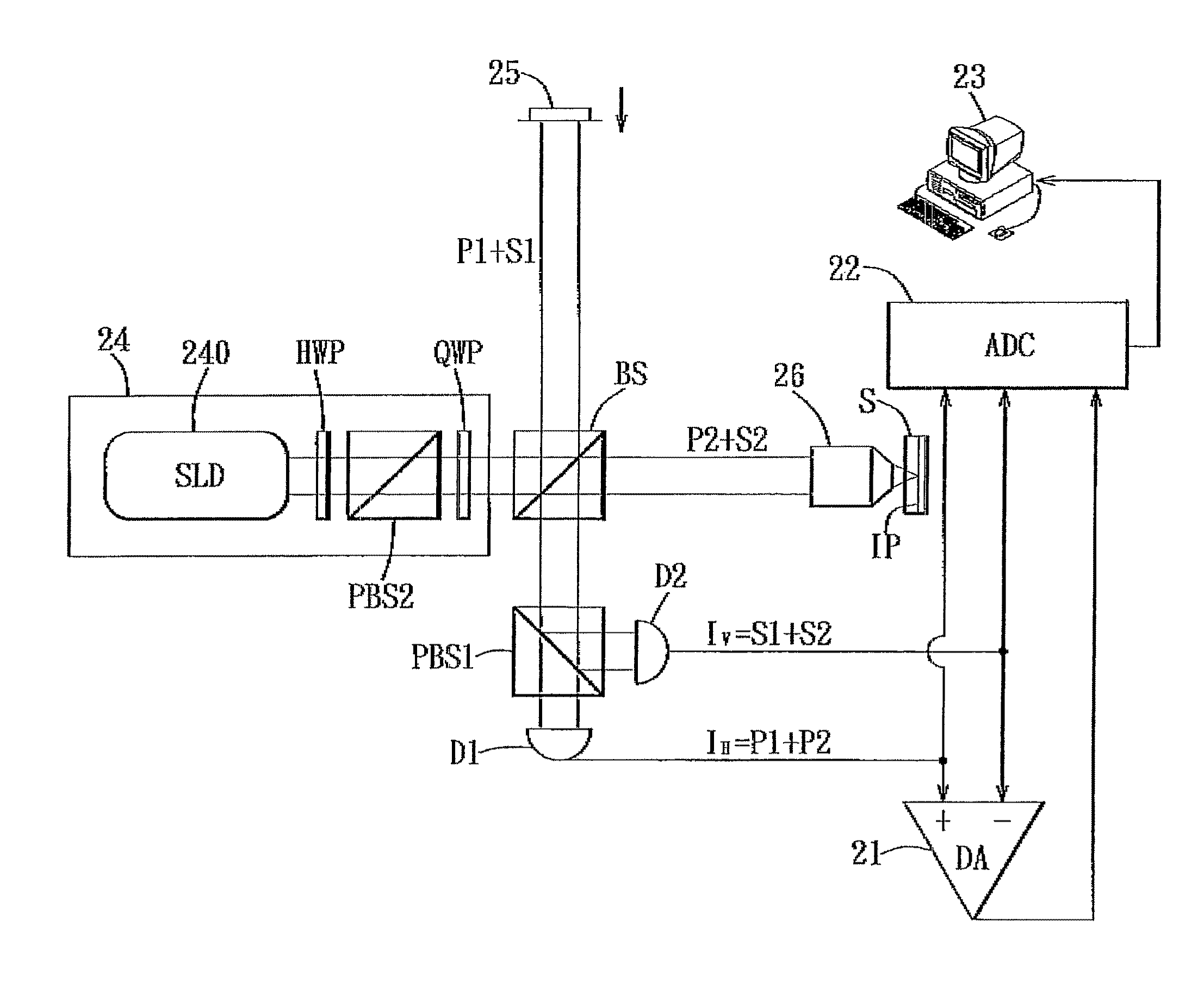
InactiveUS20100067019A1Increase speedHigh detection sensitivityInterferometersUsing optical meansHeterodyne interferometerDifferential signaling
A differential-phase polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography system includes a polarized heterodyne interferometer for generating a reference beam to be reflected by a movable mirror unit, and a signal beam to be reflected by an imaging plane in a specimen. The interferometer further generates a first electrical signal output corresponding to first linear polarized waves of the reference and signal beams, and a second electrical signal output corresponding to second linear polarized waves of the reference and signal beams. A differential amplifier receives the first and second electrical signal outputs, and generates a differential signal output therefrom. A data acquisition unit is used to measure amplitudes of the first and second electrical signal outputs and the differential signal output. A computing unit computes the amplitudes measured by the data acquisition unit to determine a reflectivity, a phase retardation, and a fast axis angle of the imaging plane in the specimen.
Owner:CHOU CHIEN
Method for implementing dual-frequency output laser
The invention relates to the laser field, in particular to a method for realizing double-frequency output lasers. The method for realizing double-frequency output lasers comprises the following steps that: a first microchip laser and a second microchip laser are pumped by a pump light source, so as to ensure that the first microchip laser and the second microchip laser have optical thickness difference in cavity length, and furthermore, the range of the optical thickness difference is between 0 and 0.1 mm. The first microchip laser and the second microchip laser are a single whole through optical cement, gluing or deepened optical cement. Two single-longitudinal-mode output fundamental wave or frequency doubled laser output lasers with little difference in wavelength are formed through the pumping of the same pumping source, so as to obtain a microchip-type double-frequency laser which is used for double-frequency laser heterodyne interferometers and replaces the common double-frequency He-Ne laser. As the invention puts forward a novel method for realizing double-frequency output lasers, the double-frequency laser in small size can be obtained.
Owner:FUZHOU PHOTOP QPTICS CO LTD
Method for detecting adhesion between spatial heterodyne interferometer gratings
InactiveCN101762323AImprove control accuracyWavelength stableRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsGratingHeterodyne interferometer
The invention discloses a method for detecting adhesion between spatial heterodyne interferometer gratings, which relates to the field of optical instruments. The method comprises the steps that: a heterodyne interferometer to be adhered is vertically placed on a transparent platform of an adhesion regulation mechanism; laser lights output by a laser are subjected to diffuse reflection of an integrating sphere to form a uniform surface light source and are incident to an alignment system to form parallel lights which are incident on the heterodyne interferometer to be adhered; interference fringes are formed on an exit end of the heterodyne interferometer to be adhered, wherein the interference fringes are received by a CCD after passing through an image system and are displayed on a computer in real time; fx interference fringes formed on the whole image surface width w1 of the CCD by a special wavelength light source lambda 0 after the special wavelength light source lambda 0 passes through an interference system are calculated; a photosensitive adhesive is uniformly coated on the heterodyne interferometer to be adhered, micro-adjustment is performed on oblique angles of alpha and beta of two arm gratings, and the interference fringes on the whole image surface of the CCD are read till f changes to fx to enable the two gratings to be positioned; and two adhered gratings are cured. The method for detecting adhesion between the spatial heterodyne interferometer gratings solves the technical problem of difficult accurate control over the grating oblique angle in the adhesion process of the spatial heterodyne interferometer. The error of the oblique angels of the two arm gratings can be controlled in 2.5 seconds.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Scanning microscope using heterodyne interferometer
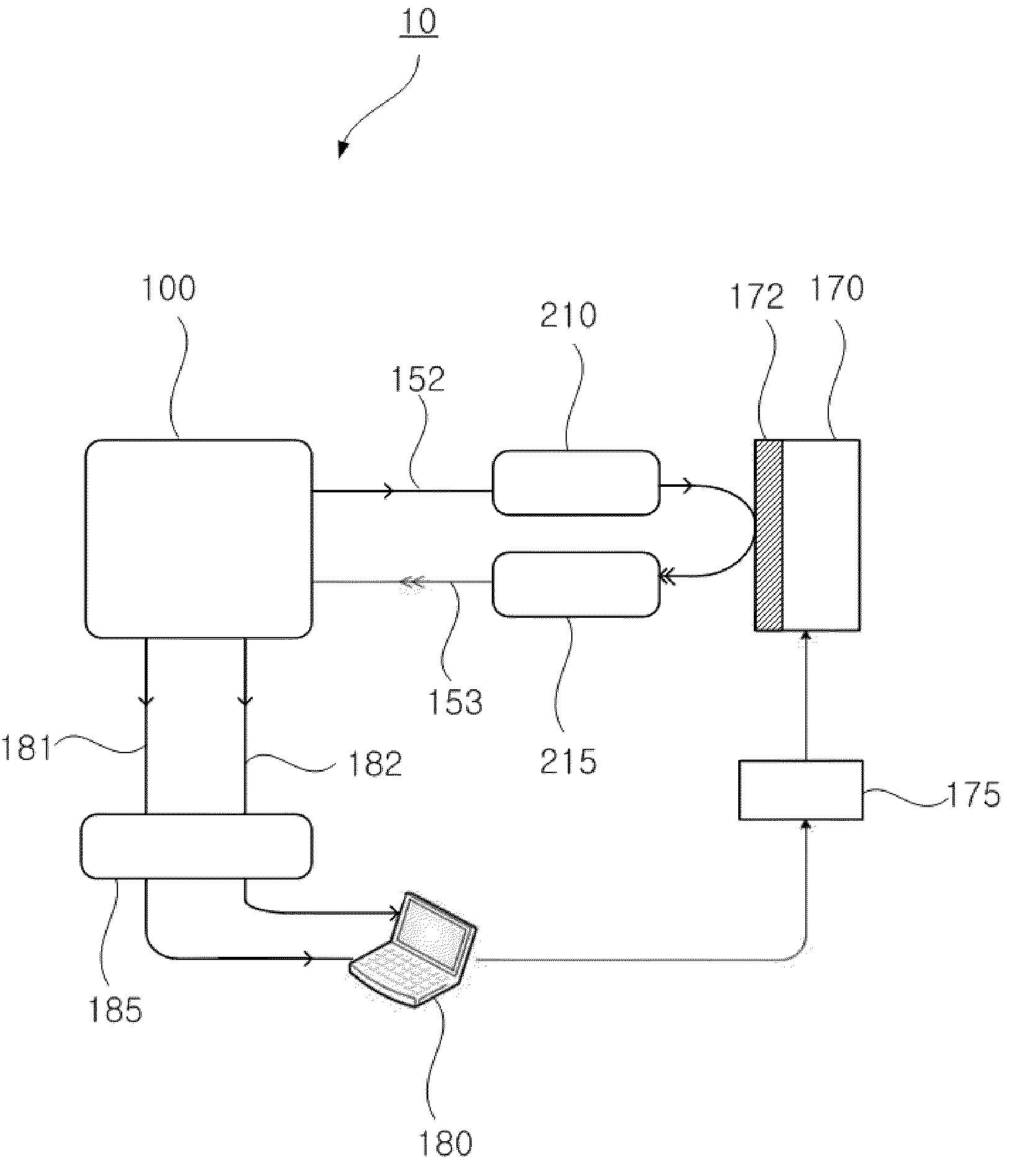
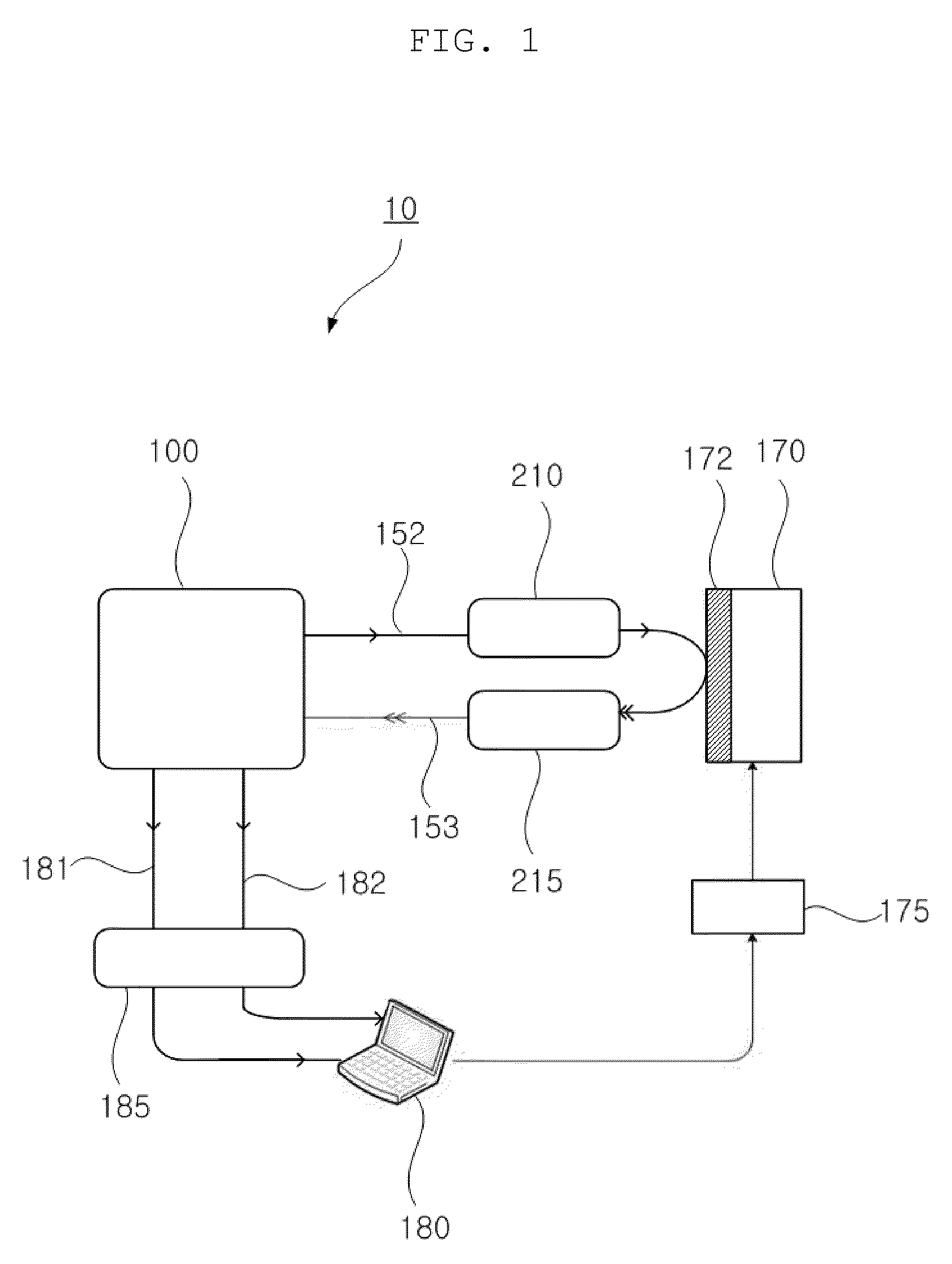
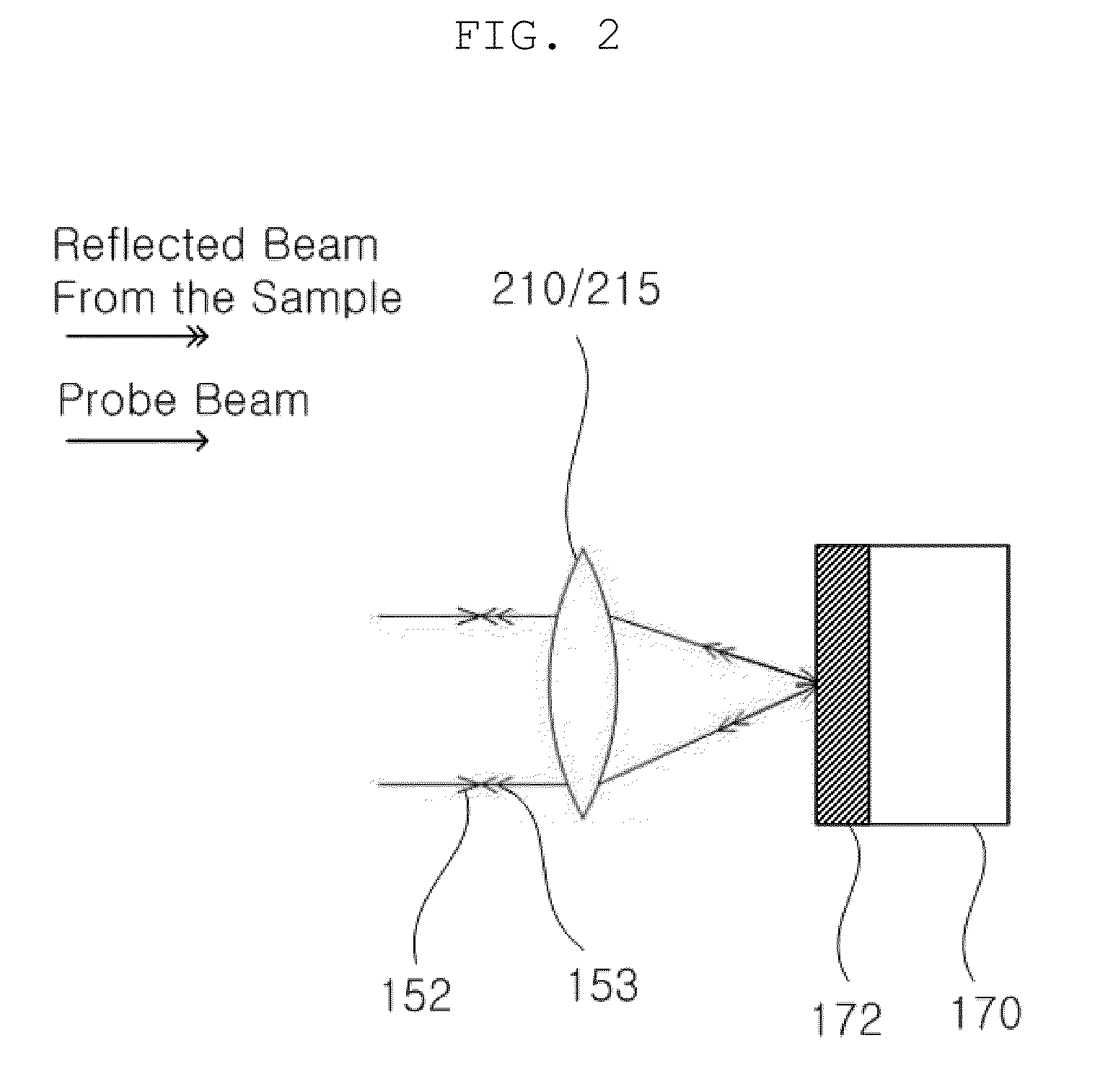
InactiveUS20100128279A1More informationImprove shortcomingsElectric discharge tubesInterferometersHeterodyne interferometerLight beam
The present invention relates to a scanning microscope using a heterodyne interferometer, which can be used for mapping or imaging complex optical parameters such as physical structures and material properties of a sample under test. The heterodyne interferometer is designed to provide in- and quadrature-phase interference signal which can be used for extracting the phase and amplitude change induced on the probe beam. The phase and the amplitude of the probe beam, which is reflected from or transmitted through the sample, are modified by the physical structures and material properties of the sample. Therefore, by scanning the probe beam, local variations of the phase and amplitude can be mapped, and, thereby, three-dimensional microscopic physical structures and material properties can be imaged by processing the phase and amplitude values.
Owner:IND UNIV COOP FOUND SOGANG UNIV
Measuring apparatus and article manufacturing method
InactiveUS20140307263A1High precision measurementReduce the impactInterferometersUsing optical meansObject basedMeasurement device
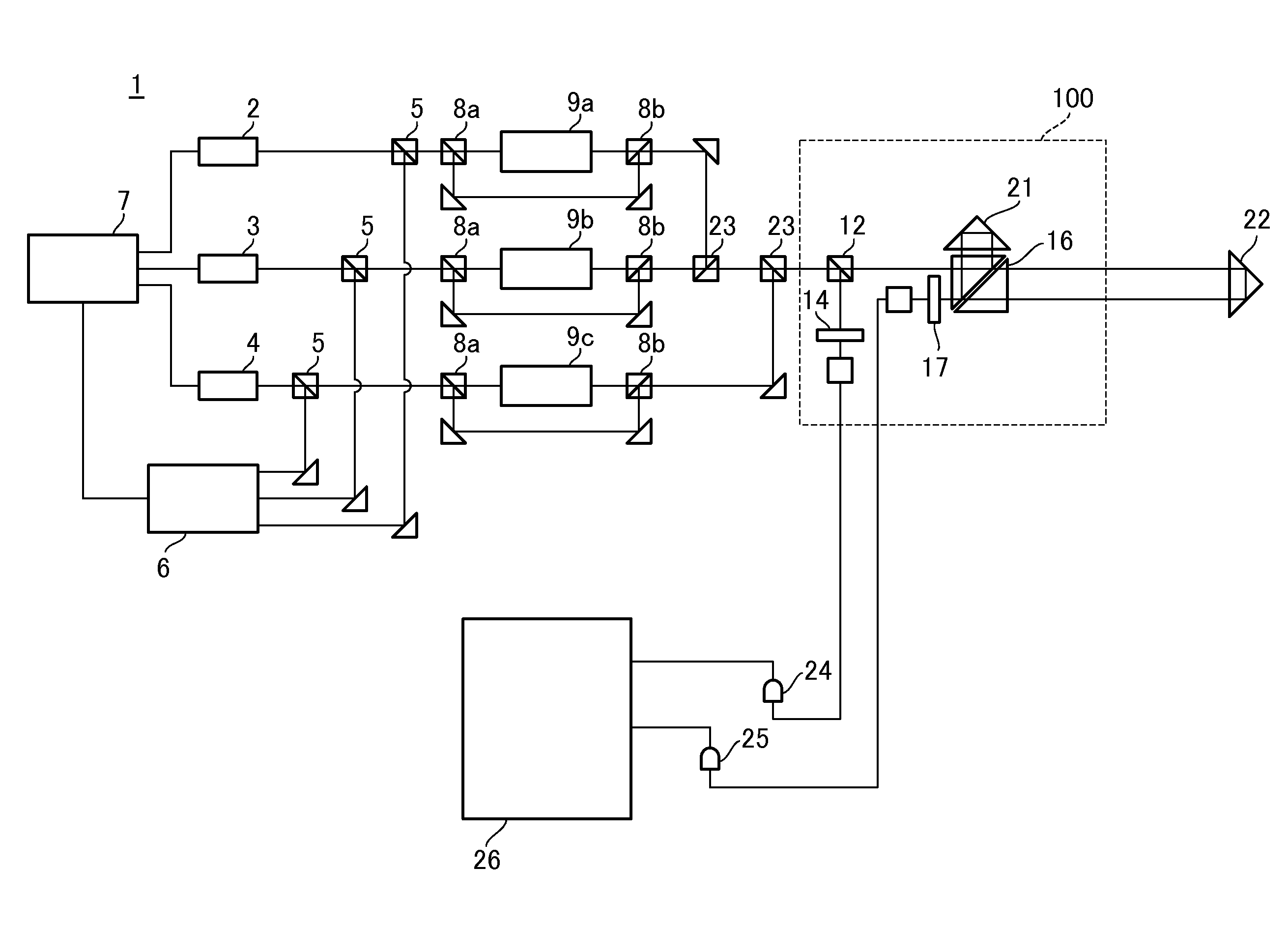
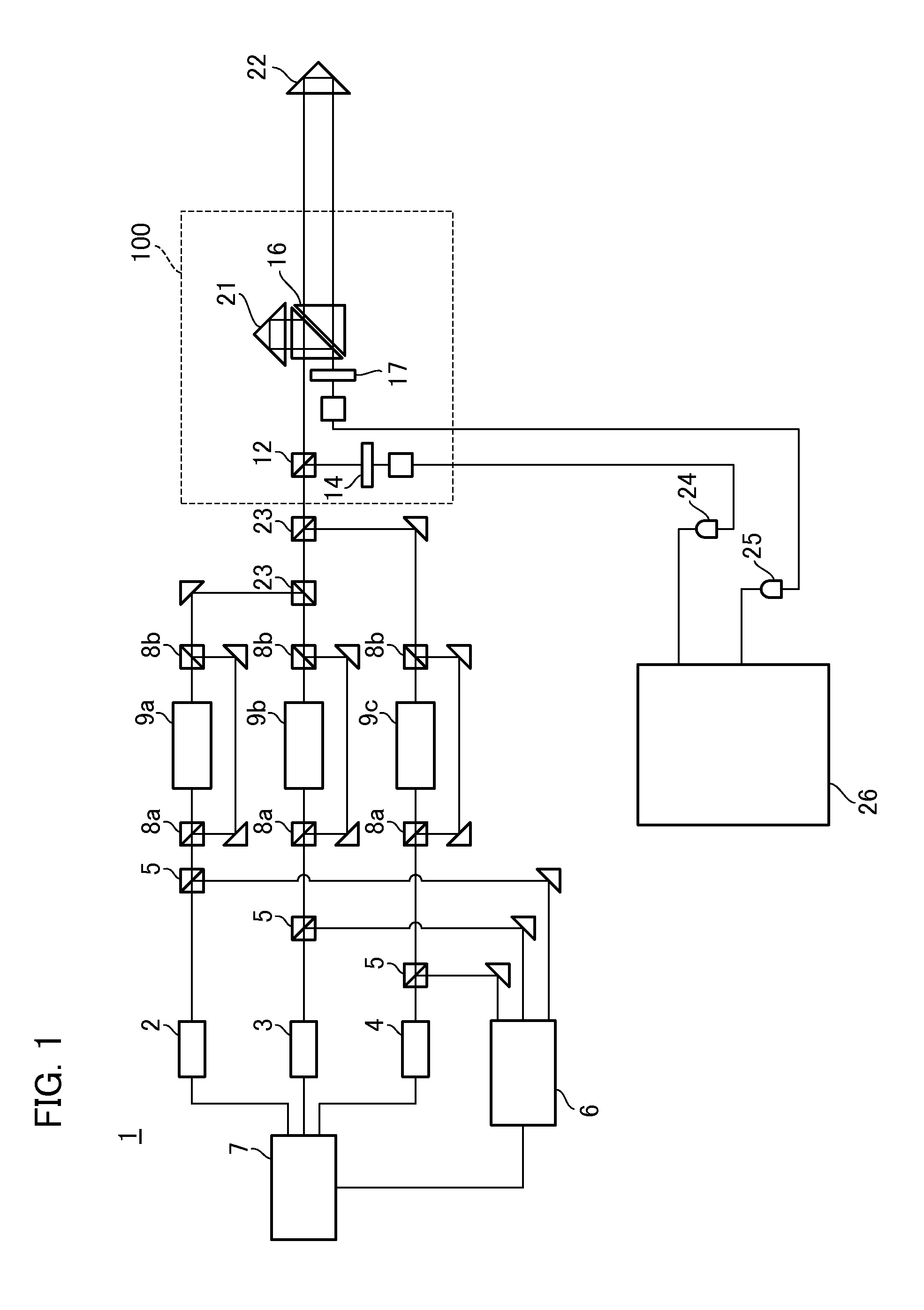
Provided is a measuring apparatus that includes a heterodyne interferometer; a first detector configured to detect interference light between reference light and light to be detected, and output a measured signal; a second detector configured to detect interference light between the first and the second light, and output a reference signal; an oscillator configured to generate a standard signal having a frequency corresponding to a frequency shift amount; a first synchronization detector configured to perform synchronous detection of the measured signal and the standard signal; a second synchronization detector configured to perform synchronous detection of the reference signal and the standard signal; a first processing unit that determines a phase difference between the measured signal and the reference signal based on the outputs of the first synchronization detector and the second synchronization detector; and a second processing unit that determines the position of the object based on the phase difference.
Owner:CANON KK
Differential-phase polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography system
InactiveUS7973939B2Increase speedHigh detection sensitivityInterferometersUsing optical meansDifferential phasePhase retardation
A differential-phase polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography system includes a polarized heterodyne interferometer for generating a reference beam to be reflected by a movable mirror unit, and a signal beam to be reflected by an imaging plane in a specimen. The interferometer further generates a first electrical signal output corresponding to first linear polarized waves of the reference and signal beams, and a second electrical signal output corresponding to second linear polarized waves of the reference and signal beams. A differential amplifier receives the first and second electrical signal outputs, and generates a differential signal output therefrom. A data acquisition unit is used to measure amplitudes of the first and second electrical signal outputs and the differential signal output. A computing unit computes the amplitudes measured by the data acquisition unit to determine a reflectivity, a phase retardation, and a fast axis angle of the imaging plane in the specimen.
Owner:CHOU CHIEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com