MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) scanning type laser heterodyne interferometer and method thereof in measuring glass stress
A laser heterodyne interference and scanning technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring, measuring devices, instruments, etc. by measuring the change of optical properties of materials when they are stressed, can solve the problems of difficult control and low detection accuracy, and achieve easy control Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
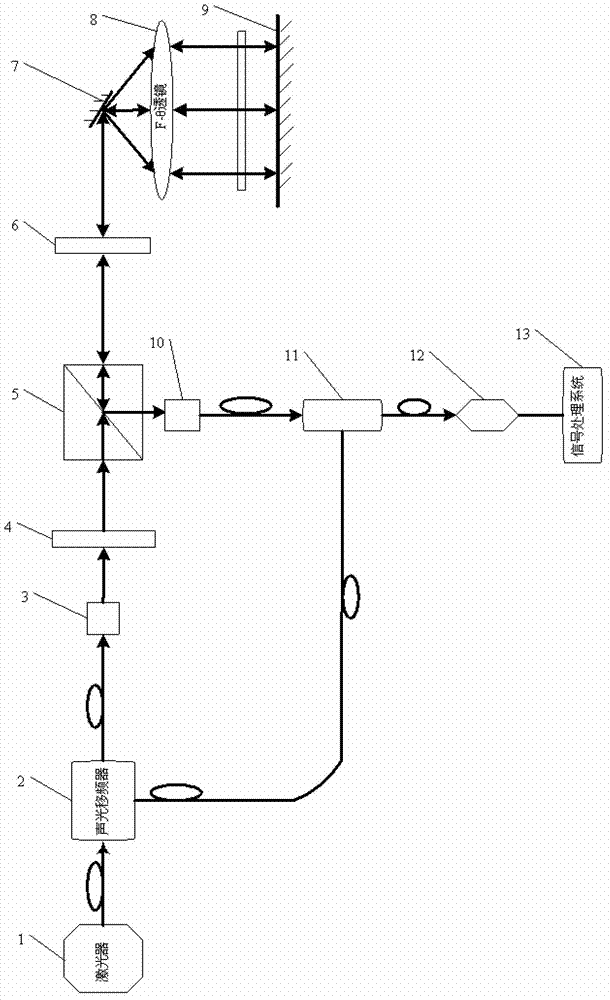
[0047] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the MEMS scanning type laser heterodyne interferometer described in this embodiment, it comprises laser 1, acousto-optic frequency shifter 2, the first fiber coupler 3, λ / 2 wave plate 4, polarization beam splitting prism 5. λ / 4 wave plate 6, MEMS vibrating mirror 7, F-θ lens 8, mirror 9, second fiber coupler 10, fiber combiner 11, detector 12 and signal processing system 13;
[0048] The light beam emitted by the laser 1 is incident on the acousto-optic frequency shifter 2, and the emitted light after passing through the acousto-optic frequency shifter 2 is the 1st-order light of frequency f and the 0-order light of frequency f', and the 0-order light of frequency f' is incident to the first fiber coupler 3,
[0049] The light beam coupled by the first fiber coupler 3 is incident on the λ / 2 wave plate 4, the light beam transmitted by the λ / 2 wave plate 4 is incident on the polarization beam sp...
specific Embodiment approach 2
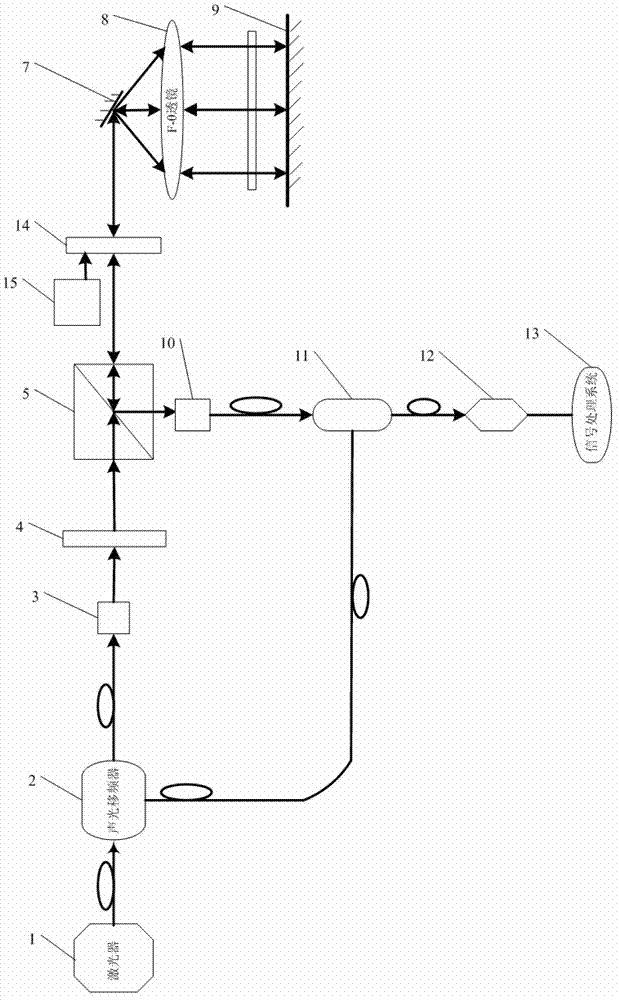
[0051] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 2 Describe this embodiment mode, this embodiment mode also provides a kind of MEMS scanning type laser heterodyne interferometer, it comprises laser device 1, acousto-optic frequency shifter 2, first fiber coupler 3, λ / 2 wave plate 4, polarization beam splitter Prism 5, MEMS vibrating mirror 7, F-θ lens 8, reflector 9, second fiber coupler 10, fiber beam combiner 11, detector 12, signal processing system 13, Kerr effect crystal 14 and electrode drive circuit 15 ;
[0052] The light beam emitted by the laser 1 is incident on the acousto-optic frequency shifter 2, and the emitted light after passing through the acousto-optic frequency shifter 2 is the 1st-order light of frequency f and the 0-order light of frequency f', and the 0-order light of frequency f' is incident to the first fiber coupler 3,
[0053] The light beam coupled by the first fiber coupler 3 is incident on the λ / 2 wave plate 4, the light beam transmi...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0056] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment is a further description of the MEMS scanning laser heterodyne interferometer described in specific embodiment two, the driving signal period of the electrode drive circuit 15 is the same as the period scanned by the MEMS vibrating mirror 7, and the electrode driving A half cycle delay is set within the cycle of the driving signal of the circuit 15 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com