Noise shaping time to digital converter
A technology of digital converter and time, applied in the direction of time-to-digital converter, analog/digital conversion, code conversion, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the performance of TDC noise shaping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
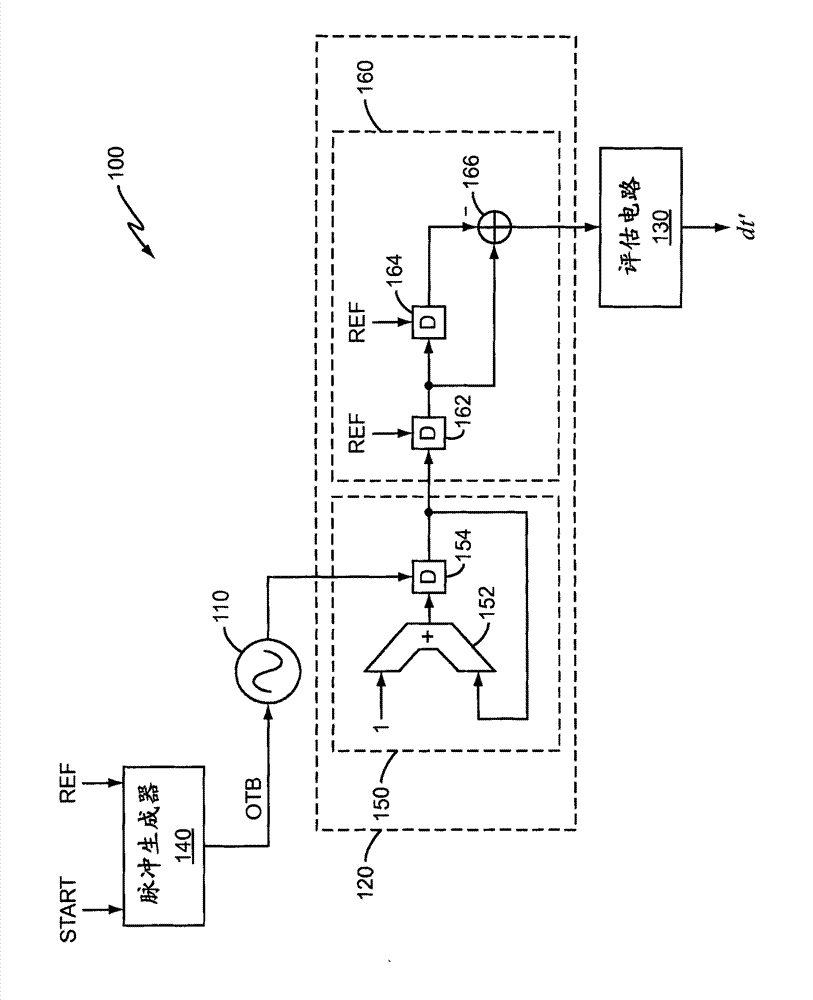
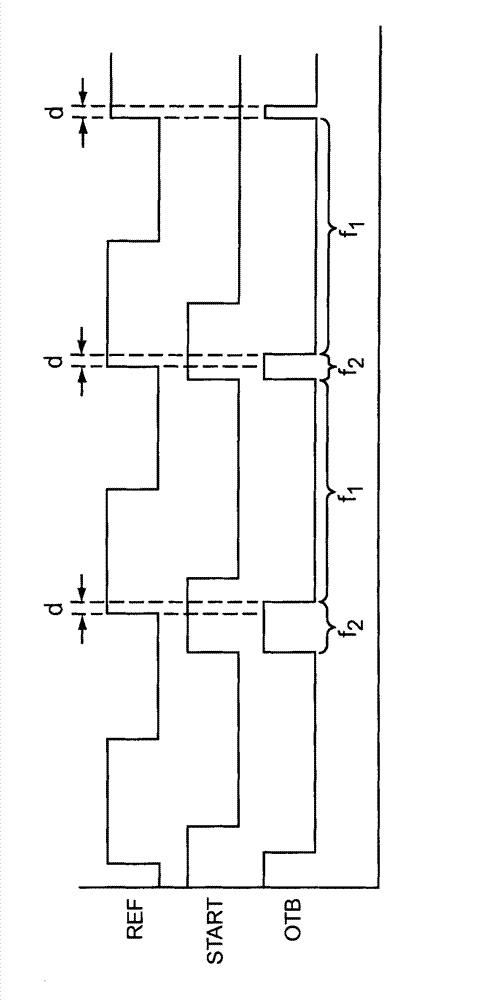
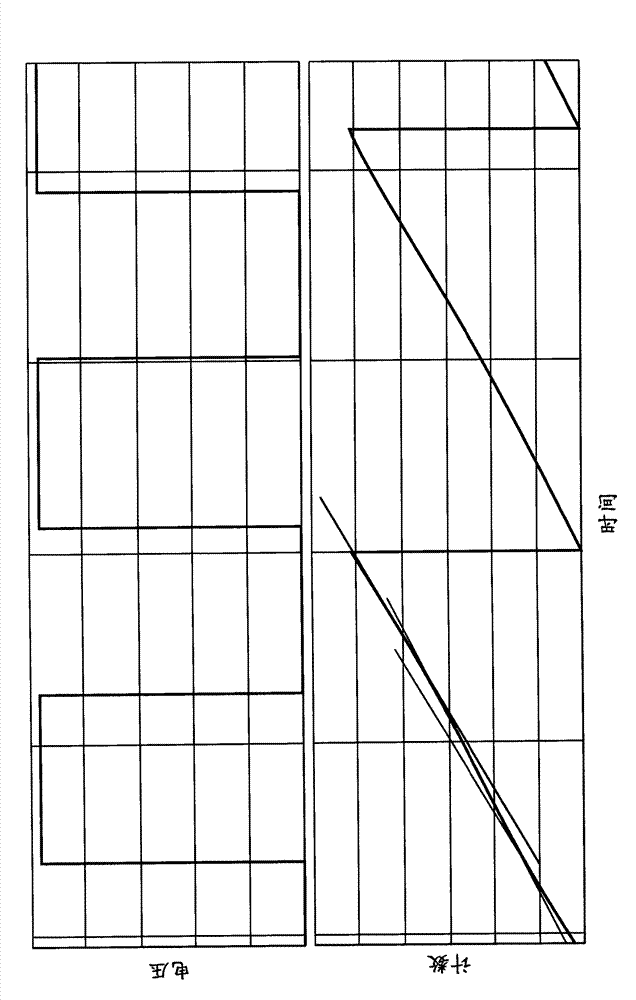
[0015] figure 1 An embodiment of a time-to-digital converter (TDC) 100 is illustrated. TDC 100 includes digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) 110 , counter circuit 120 , evaluation circuit 130 and pulse generator 140 . The TDC 100 utilizes noise shaping to provide very high resolution time measurements. When TDC 100 operates at a frequency (REF) that is multiple times higher than the bandwidth of the signal of interest (START), TDC 100 has a relatively high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) compared to conventional non-noise-shaping TDCs. In addition, the TDC 100 performs quantization noise shaping by shifting the quantization noise towards higher frequencies. Optionally high frequency noise can be filtered, which results in a significant increase in SNR depending on the oversampling ratio employed by the TDC 100 .
[0016] The shaped quantization noise can be modeled as white noise filtered by a difference filter. In a sampled system, the transfer function of the differential f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com