Heat process capable of lowering ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades
A technology of ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture, applied in heat treatment furnaces, heat treatment equipment, heat treatment process control, etc. The temperature and intergranular fracture ratio are high, and the process effect is easily affected by the chemical composition of the raw material of the blade.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0008] (1) Choose X20Cr13 material blades, put the blades evenly into the general quenching basket according to the process plan, and then put the quenching basket into the heat treatment quenching furnace;
[0009] (2) The first quenching: the quenching temperature is 980°C, the heat preservation is 3 hours, the cooling rate is 30°C / min, and the quenching cooling medium is air;
[0010] (3) Second quenching: quenching temperature 960°C, heat preservation for 100 minutes, cooling rate 40°C / min, and oil as quenching medium;
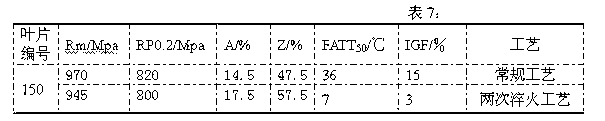
[0011] Compared with the conventional process, the ductile-brittle transition temperature (FATT 50 ) and intergranular fracture ratio are shown in Table 1.
[0012]
Embodiment 2
[0014] (1) Choose blades made of X20Cr13 material, put the blades evenly into the general quenching basket according to the process plan, and then put the quenching basket into the heat treatment quenching furnace;
[0015] (2) The first quenching: the quenching temperature is 1020°C, heat preservation is 2 hours, the cooling rate is 50°C / min, and the quenching cooling medium is water;
[0016] (3) Second quenching: quenching temperature 980°C, heat preservation for 15 minutes, cooling rate 40°C / min, and oil as quenching medium;
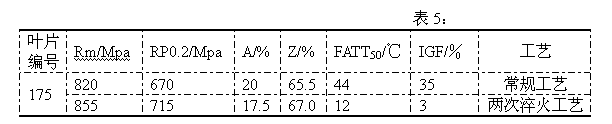
[0017] Compared with the conventional process, the ductile-brittle transition temperature (FATT 50 ) and intergranular fracture ratio are shown in Table 2.
[0018]
Embodiment 3
[0020] (1) Choose blades made of X20Cr13 material, put the blades evenly into the general quenching basket according to the process plan, and then put the quenching basket into the heat treatment quenching furnace;
[0021] (2) The first quenching: the quenching temperature is 1030°C, the heat preservation is 1 hour, the cooling rate is 30°C / min, and the quenching cooling medium is air;
[0022] (3) The second quenching: the quenching temperature is 950°C, the heat preservation is 30 minutes, the cooling rate is 50°C / min, and the quenching cooling medium is water;
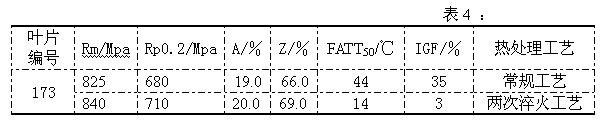
[0023] Compared with the conventional process, the ductile-brittle transition temperature (FATT 50 ) and intergranular fracture ratio are shown in Table 3.
[0024]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com