Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Improve grain boundary strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
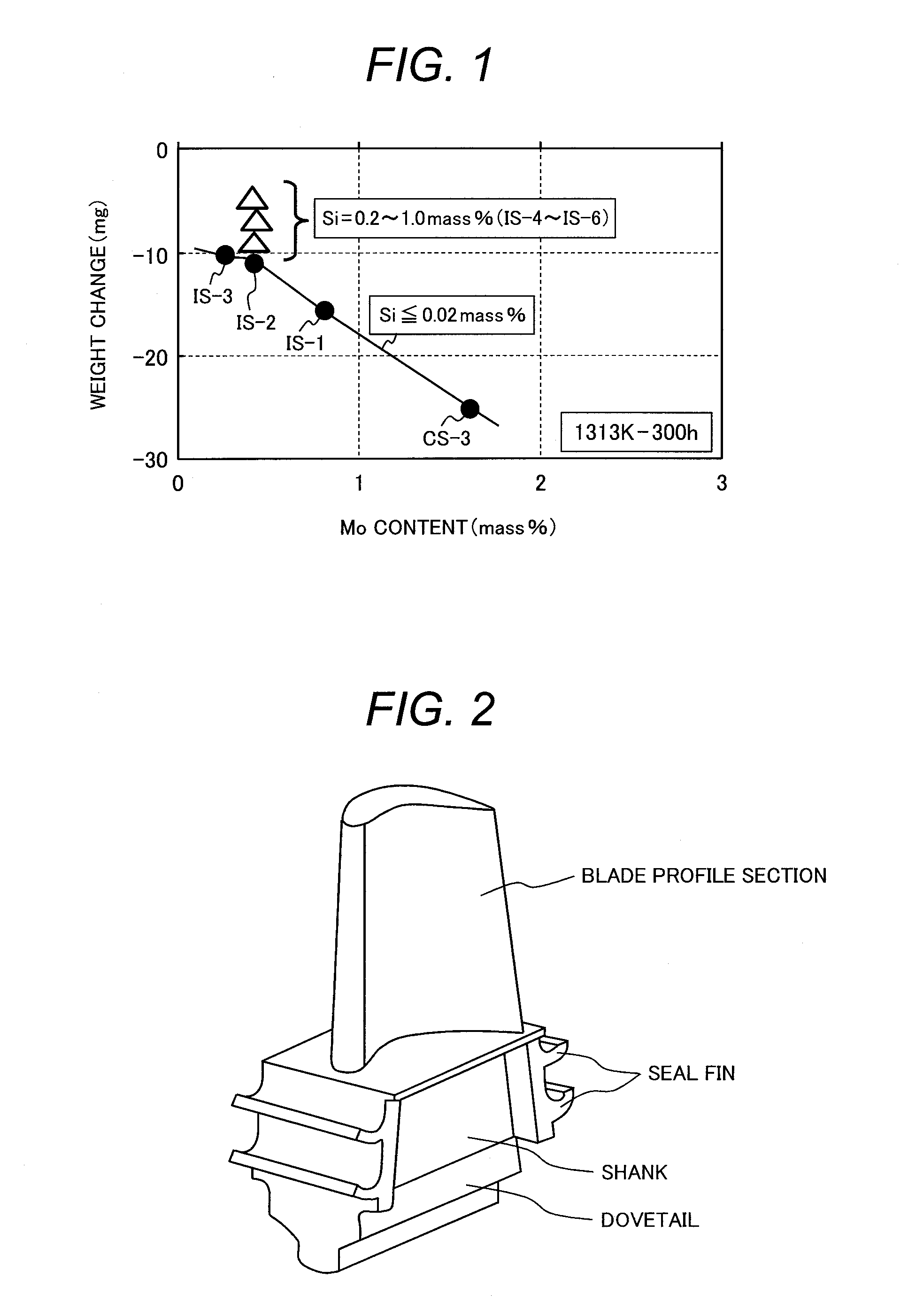
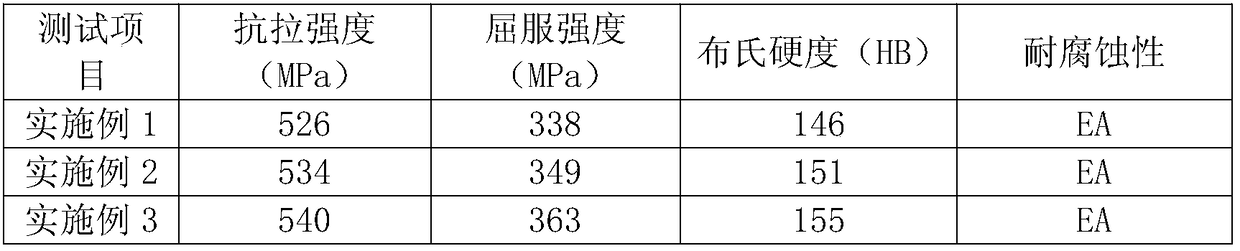
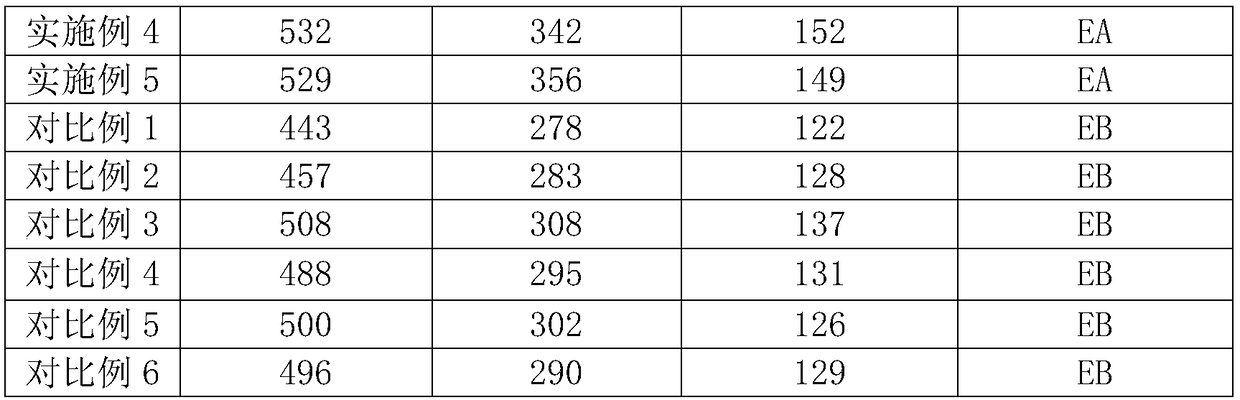
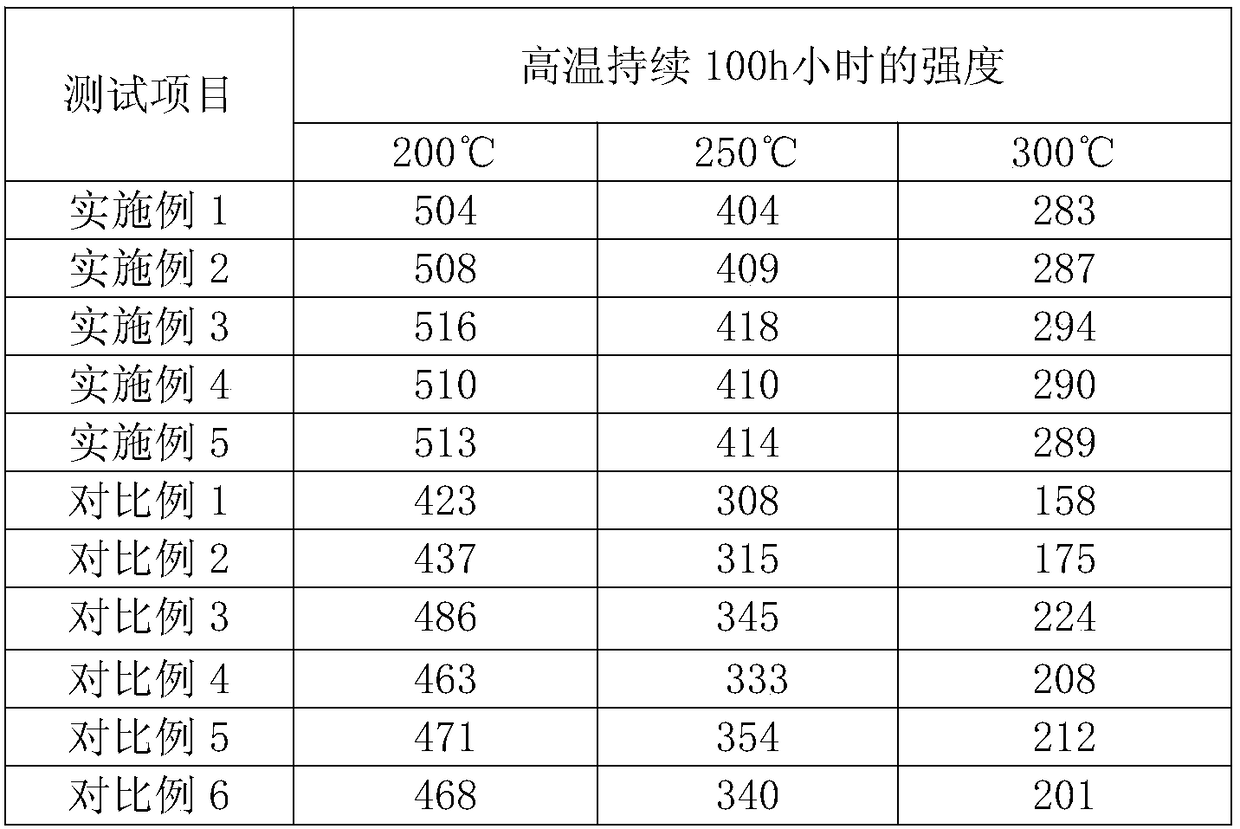
Production method of high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistant copper alloy
ActiveCN108526422AGuaranteed lubrication effectImprove thermal conductivityCarbon compositesShielding gas
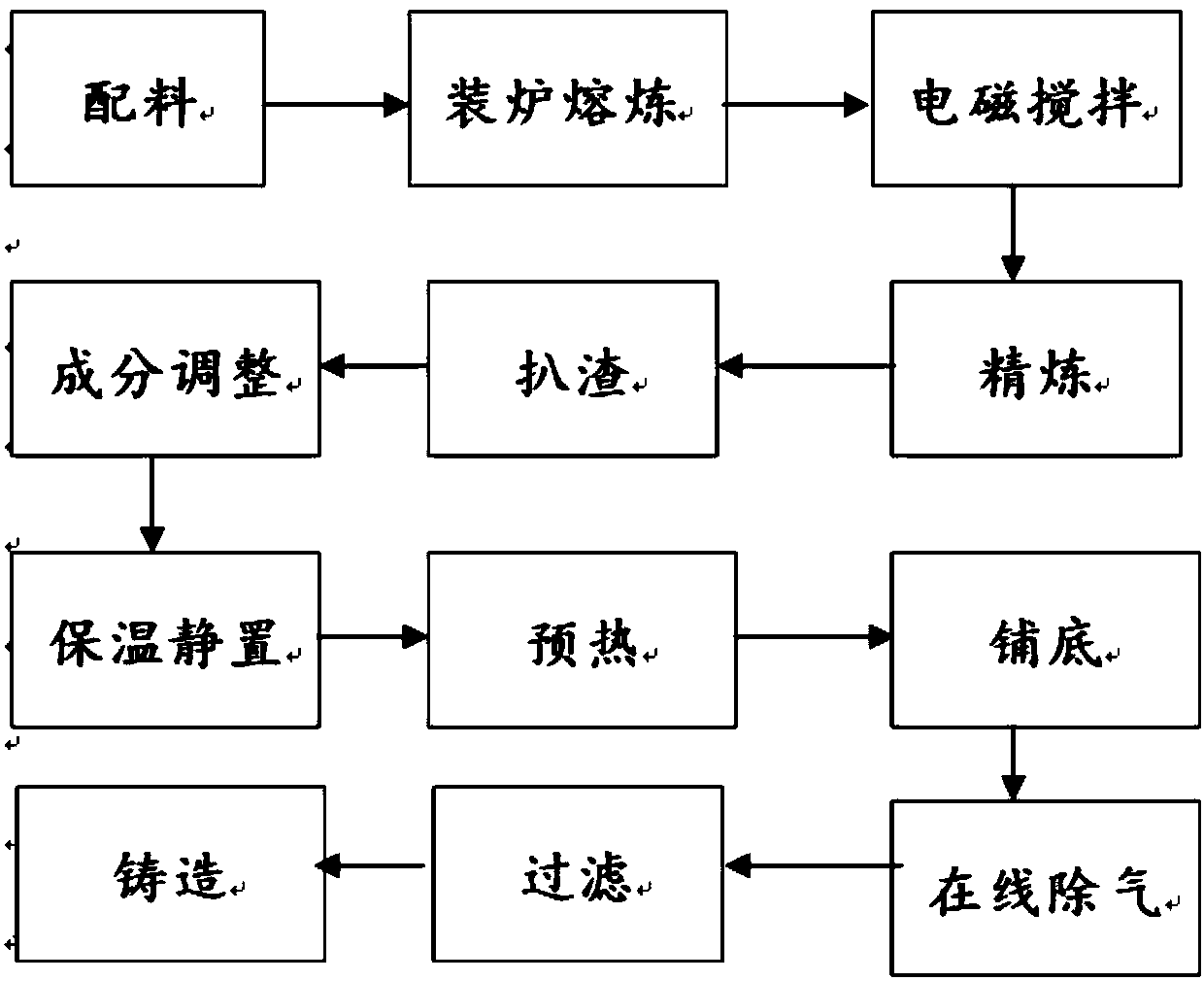
The invention discloses a production method of a high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistant copper alloy, and belongs to the technical field of copper alloy machining. Accoding to the production method of high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistant copper alloy, the inner liner of a crystallizer adopted in the upper-induced continuous casting process is a carbon-carbon composite material so as to ensure the lubrication, high heat conduction and high temperature resistance properties; the temperature of the upper-induced continuous casting is 1180-1230 DEG C, the casting temperature is low so that the problem that molten liquid in the crystallizer is difficult to solidify and the crystallizer inner liner is worn during casting can be effectively avoided; the pressure of protective gas nitrogen in the liquid surface of an upper-induced furnace is controlled to be 0.2-0.7 atmosphere, so that the phenomenon of solid-liquid interface separation in the crystallizer is avoided, and a copper-chromium alloy product with larger weight and length is produced; according to the production method of the high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistant copper alloy, the cheapelement (Mg) is used for replacing the rare noble metal, and the mechanical property and the softening resistance property of the copper-chromium alloy are improved; and the production method is a non-vacuum and short-process preparation technology, the cost is low, and the production method is suitable for large-scale industrial production and has important economic and social significances.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Iron-based sintered alloy with dispersed hard particles
An iron-based sintered alloy having improved thermal and mechanical strength is provided. The iron-based sintered alloy with dispersed hard particles comprises: a matrix comprising, by weight, 0.4 to 2% silicon (Si), 2 to 12% nickel (Ni), 3 to 12% molybdenum (Mo), 0.5 to 5% chromium (Cr), 0.6 to 4% vanadium (V), 0.1 to 3% niobium (Nb), 0.5 to 2% carbon (C), and the reminder of iron (Fe); and hard particles comprising 60 to 70% molybdenum (Mo), 0.3 to 1% boron (B), 0.1% or less carbon (C), and the reminder of iron (Fe). The hard particles are dispersed in the matrix in an amount in the range of 3 to 20% based on the entire alloy. They are sintered to produce the iron-based sintered alloy. Addition of boron into the ferromolybdenum hard particles enhances the wettability of the ferromolybdenum hard particles to prevent the hard particles from falling off the matrix. Thus, the adhesive property between the matrix and the hard particles is improved, thereby enhancing the thermal and mechanical strength of the iron-based sintered alloy.
Owner:RIKEN CO LTD
Heat treatment technology for improving high-temperature tensile ductility of Ni-Fe-Cr based deformation high-temperature alloy
ActiveCN106834990AImprove grain boundary strengthImprove tensile plasticitySolution treatmentCarbide
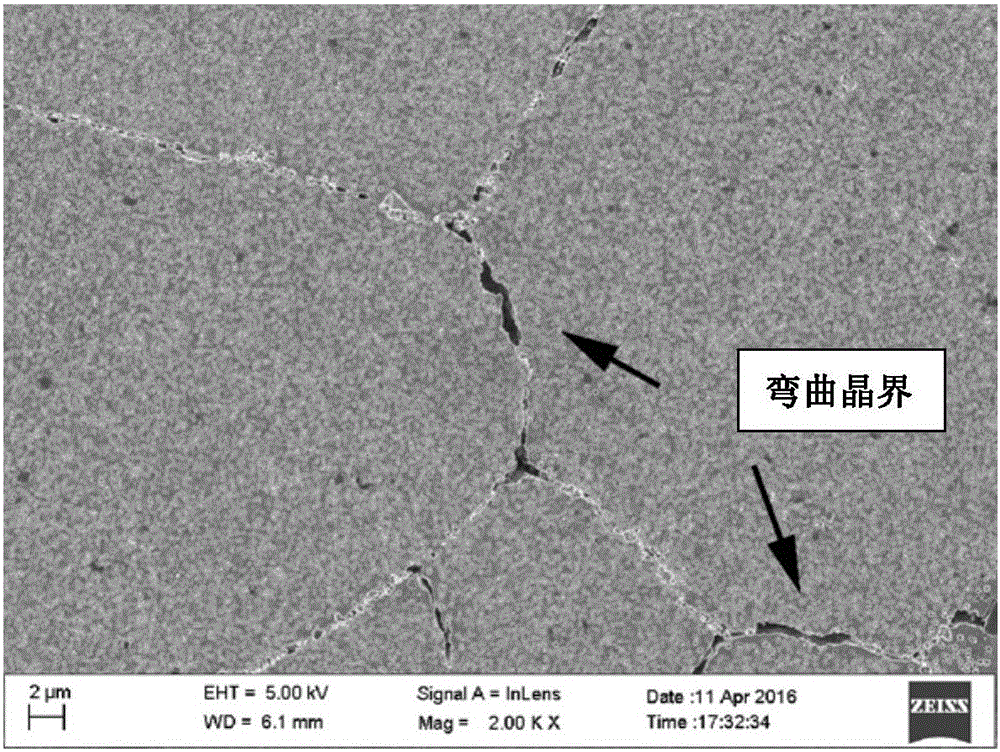
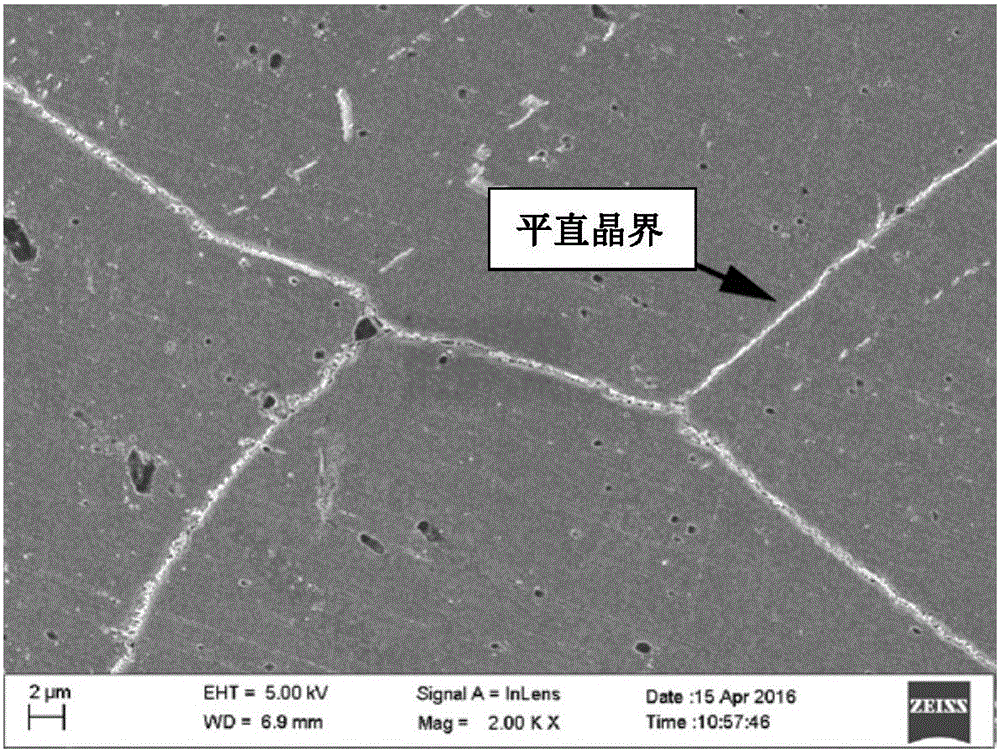
The invention discloses a heat treatment technology for improving high-temperature tensile ductility of Ni-Fe-Cr based deformation high-temperature alloy. The technology includes the steps that heat preservation lasts for 0.5-2h within the temperature range of 1050-1200 DEG C for performing solution treatment; the temperature is lowered to 20-150 DEG C below a gamma' phase precipitation temperature from the solution temperature at the speed of 0.1-20 DEG C / min, and air cooling is conducted to an indoor temperature after heat preservation lasts for 0.5-4h; and heat preservation is performed for 4-30h at the temperature 150-350 DEG C below the gamma' phase precipitation temperature, and air cooling is conducted again to the indoor temperature. According to the heat treatment technology, the method with high-temperature solution, slow cooling and low-temperature aging combined is adopted, the grain size of an obtained alloy structure is moderate, a bent sawtooth crystal boundary is formed among grains, and M23C6-type carbide is evenly distributed on the crystal boundary; and the crystal boundary has a good reinforcement effect under the high-temperature condition, and the high-temperature tensile ductility of the alloy is high.
Owner:HUANENG POWER INT INC +1
Non-oriented electrical steel sheet and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130306200A1Low maneuverabilityLow costInorganic material magnetismHeat treatment process controlChemical compositionElectrical steel
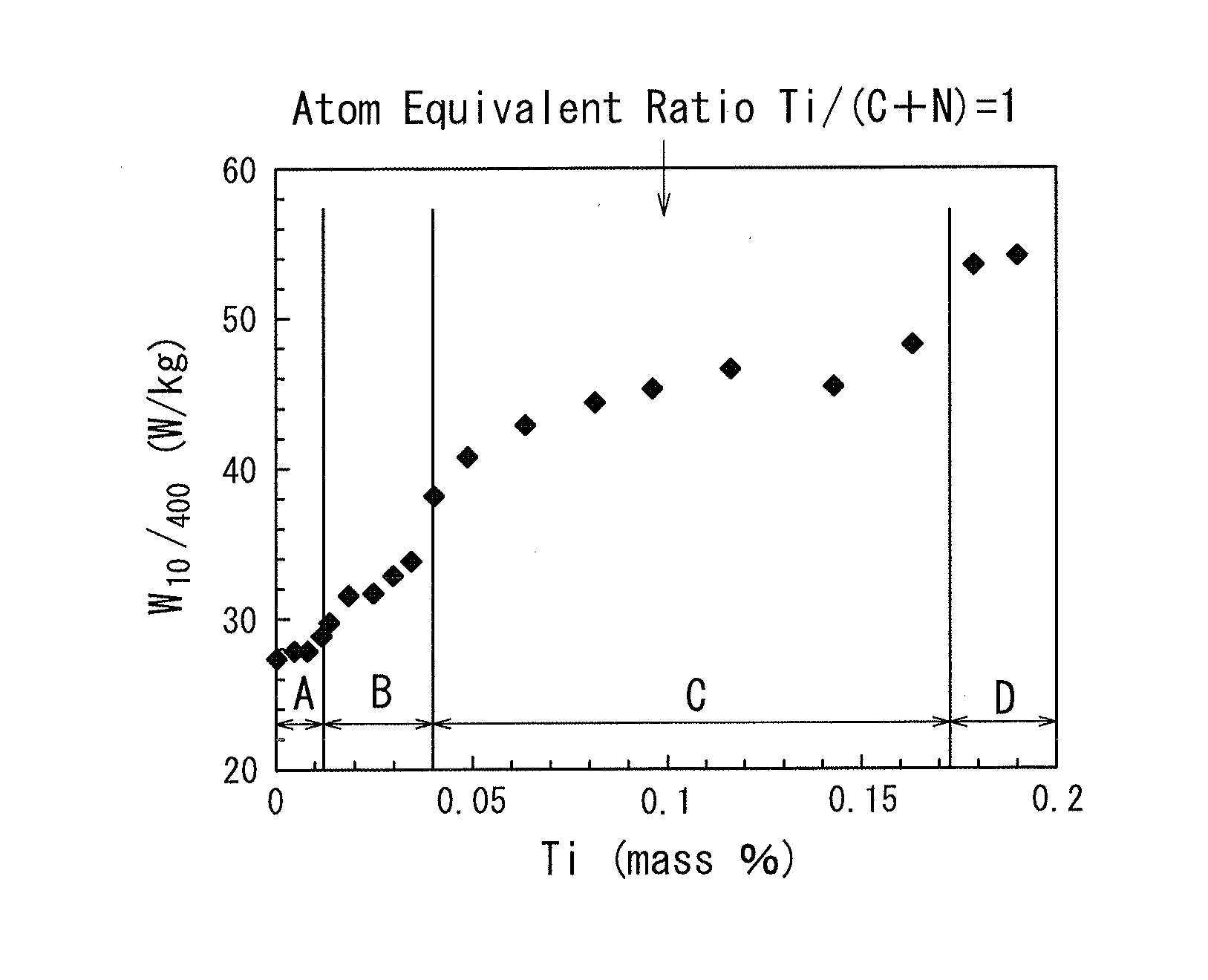
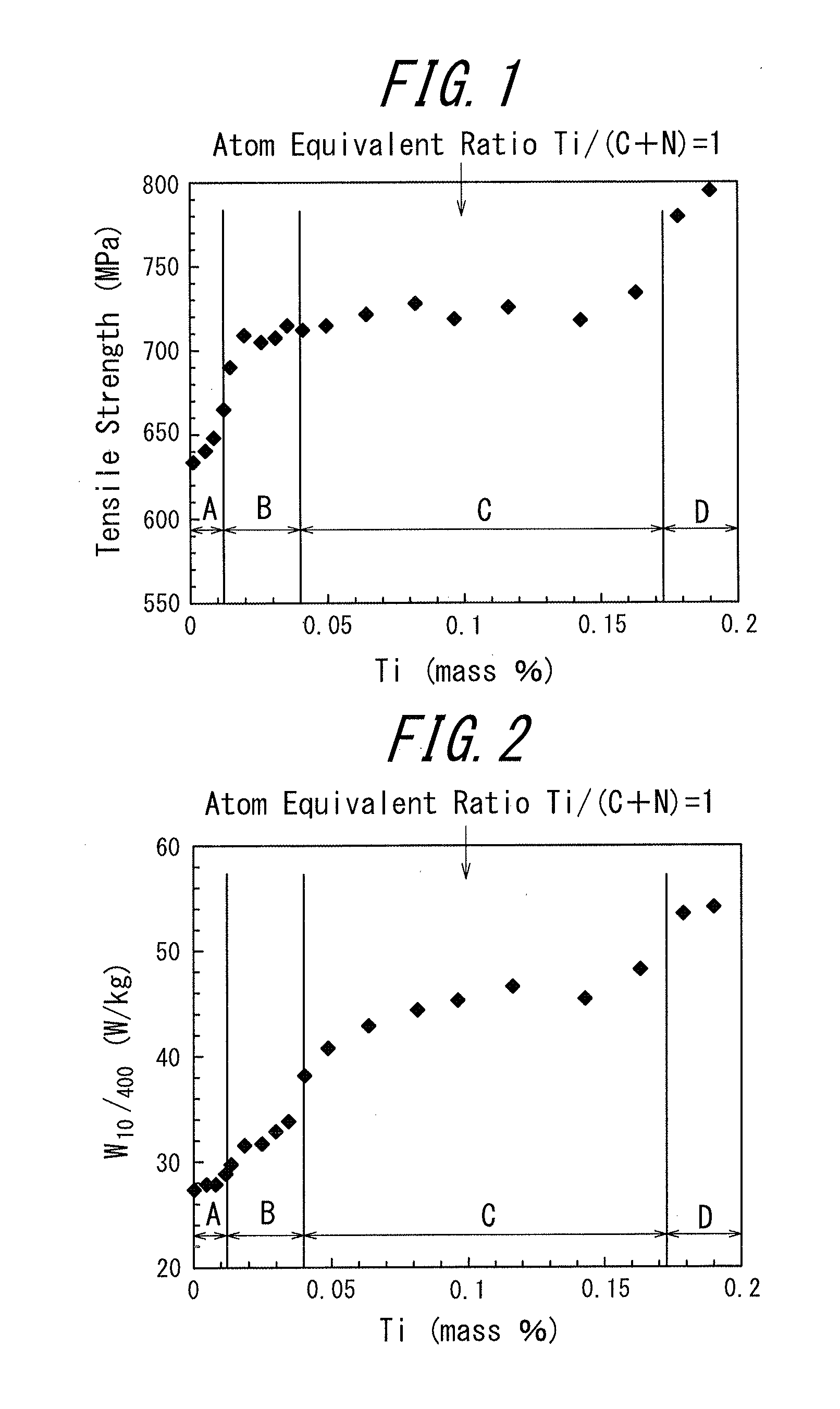
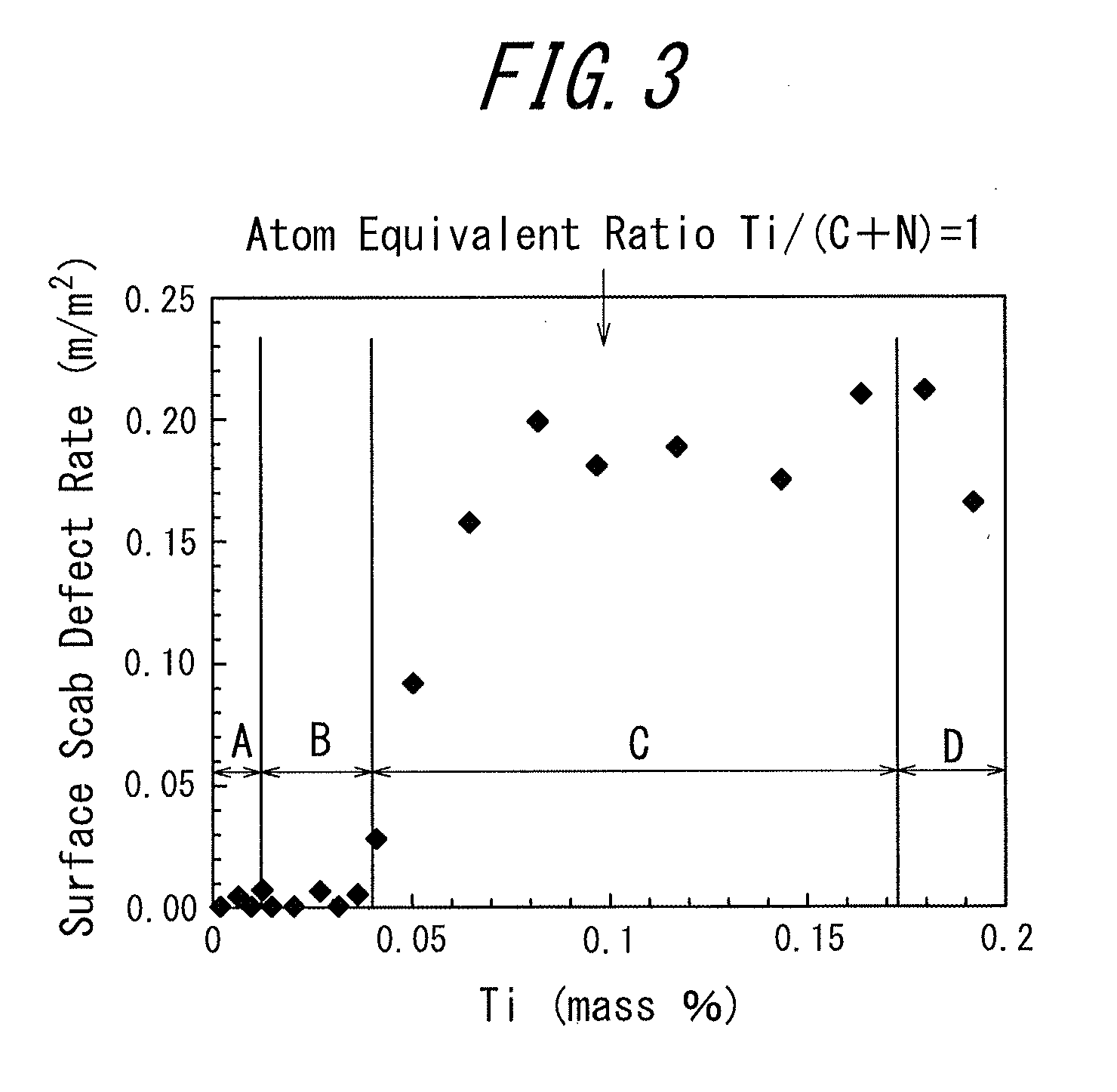
The present invention provides a non-oriented electrical steel sheet at low cost that has excellent magnetic properties and mechanical properties as well as excellent quality of steel sheet. The non-oriented electrical steel sheet has a chemical composition containing, by mass %, Si: 5.0% or less, Mn: 2.0% or less, Al: 2.0% or less, and P: 0.05% or less, in a range satisfying formula (1), and furthermore, C: 0.008% or more and 0.040% or less; N: 0.003% or less, and Ti: 0.04% or less, in a range satisfying formula (2), with the balance composed of Fe and incidental impurities:300≦85[Si %]+16[Mn %]+40[Al %]+490[P %]≦430 (1)0.008≦Ti*<1.2[C %] (2),where Ti*=Ti−3.4[N %].
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Method for preparing composite material of silicon nitride-titanium carbide
A process for preparing the nano-class composite silicon nitride-titanium carbide ceramic in which the granularities of silicon nitride are distributed by dual peaks includes such steps as mixing Si3N4 nanoparticles and TiC nanoparticles with Si3N4 micron-particles, and sintering by segmentally raising temp and pressurizing. Its advantages are high strength, toughness, heat shock resistance and antioxidizing performance.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Austenitic stainless steel plate and manufacture method thereof
The invention provides an austenitic stainless steel plate which is composed of the following chemical compositions in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 0.03% of C, 0.3-1.0 % of Si, 0.8-2.0% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.003% of S, less than or equal to 0.03 % of P, 16.0-20.0% of Cr, 10.0-14.0% of Ni, 1.0-3.0% of Mo, less than or equal to 0.08% of N, less than or equal to 0.004% of O, 0.005-0.01% of optional Ca and / or 0.001-0.003 % of optional B and the balance of Fe and other inevitable impurities, wherein the weight percentage of Ni, Mn, N, C, Cr, Mo and Si also satisfies that the content of ferrite delta in the steel plate is less than 3%. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a manufacture method of the austenitic stainless steel plate. By the technical scheme, the austenitic stainless steel plate of the invention has good surface quality and does not have the surface defects, such as liner scale, inclusion, peeling, crazes and the like.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for preparing tungsten carbide-zirconium oxide-aluminum oxide composite knife material
The invention belongs to the technical field of material science and relates to a preparation method of a tungsten carbide-zirconia-alumina composite cutting tool material. In the invention, submicron-scale ZrO2 particles and nano-scale Al2O3 powder are added to the sub-micron-scale WC matrix, and the micro-scale VC and TaC particles are used as inhibitors. A new type of composite tool material with ZrO2 and Al2O3 as the matrix as the matrix. By adding submicron ZrO2 particles and nano-Al2O3, the high temperature stability and oxidation resistance of the WC matrix are improved. The composite tool material has high comprehensive mechanical properties, and its hardness, flexural strength, and fracture toughness can reach: 18GPa , 880MPa and 13MPa.m1 / 2.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Surface coated cutting tool made of cermet having property-modified α type Al2O3 layer of hard coating layer
ActiveUS7763346B2High hardnessImprove the heating effectPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesScanning electron microscopeTitanium
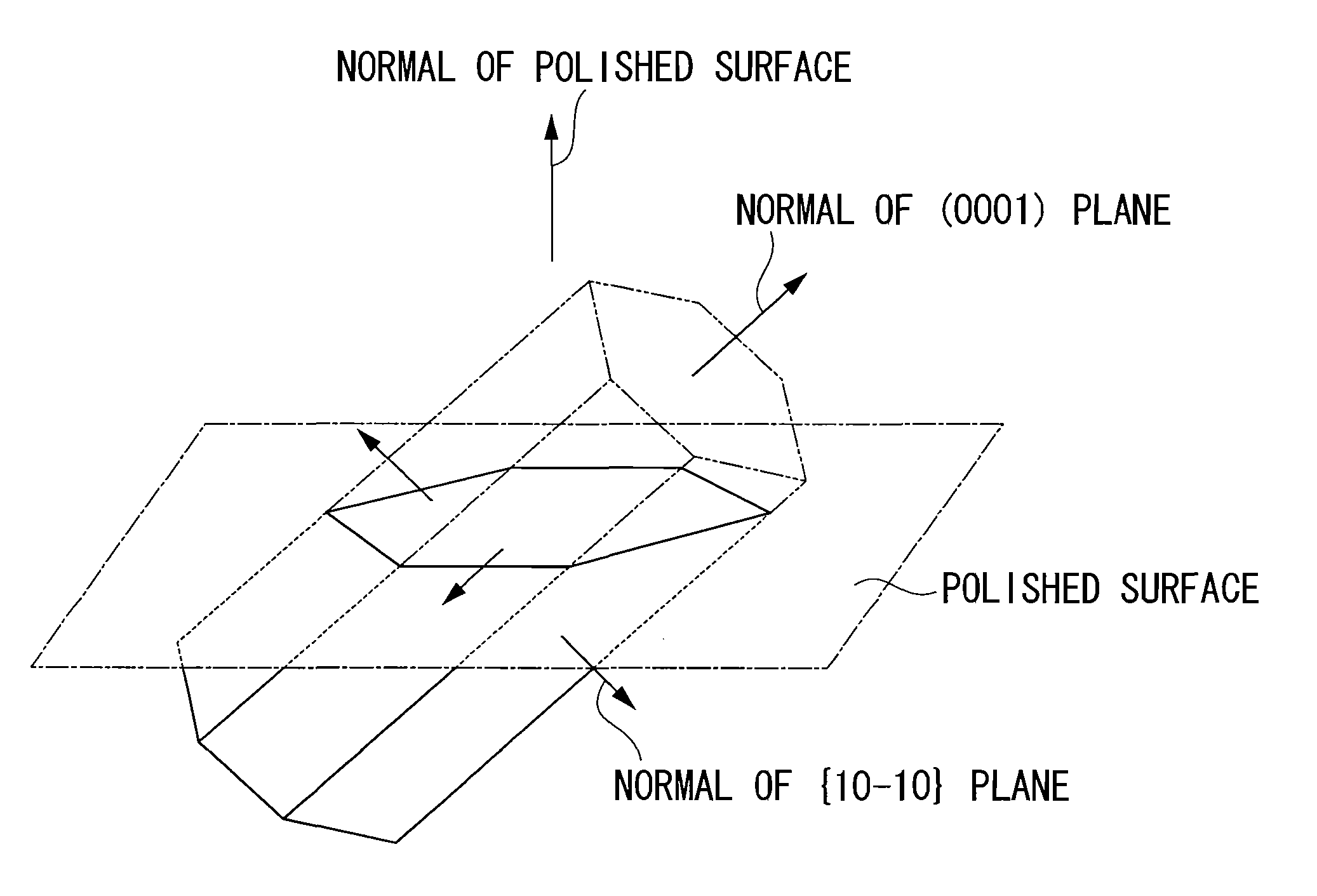
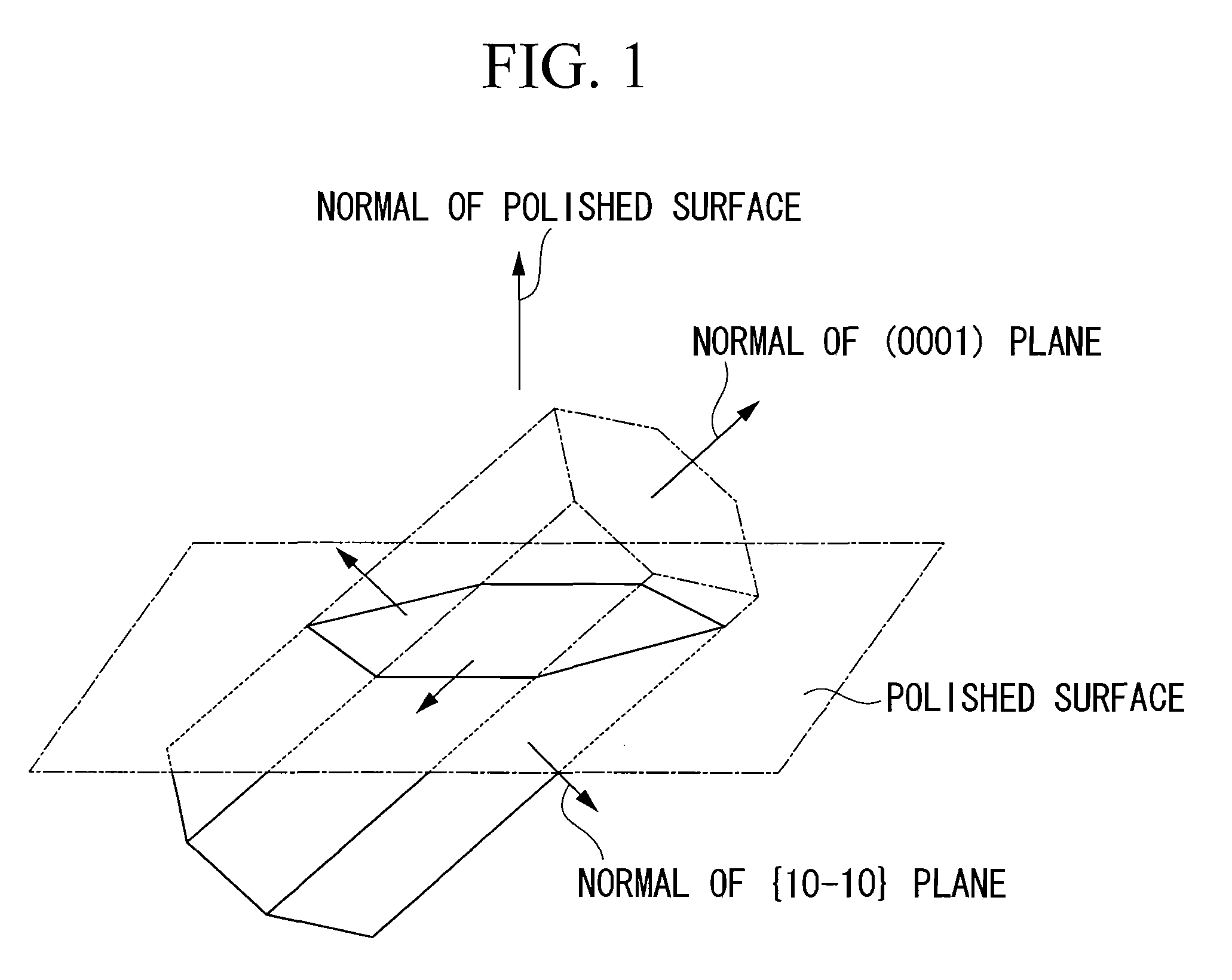
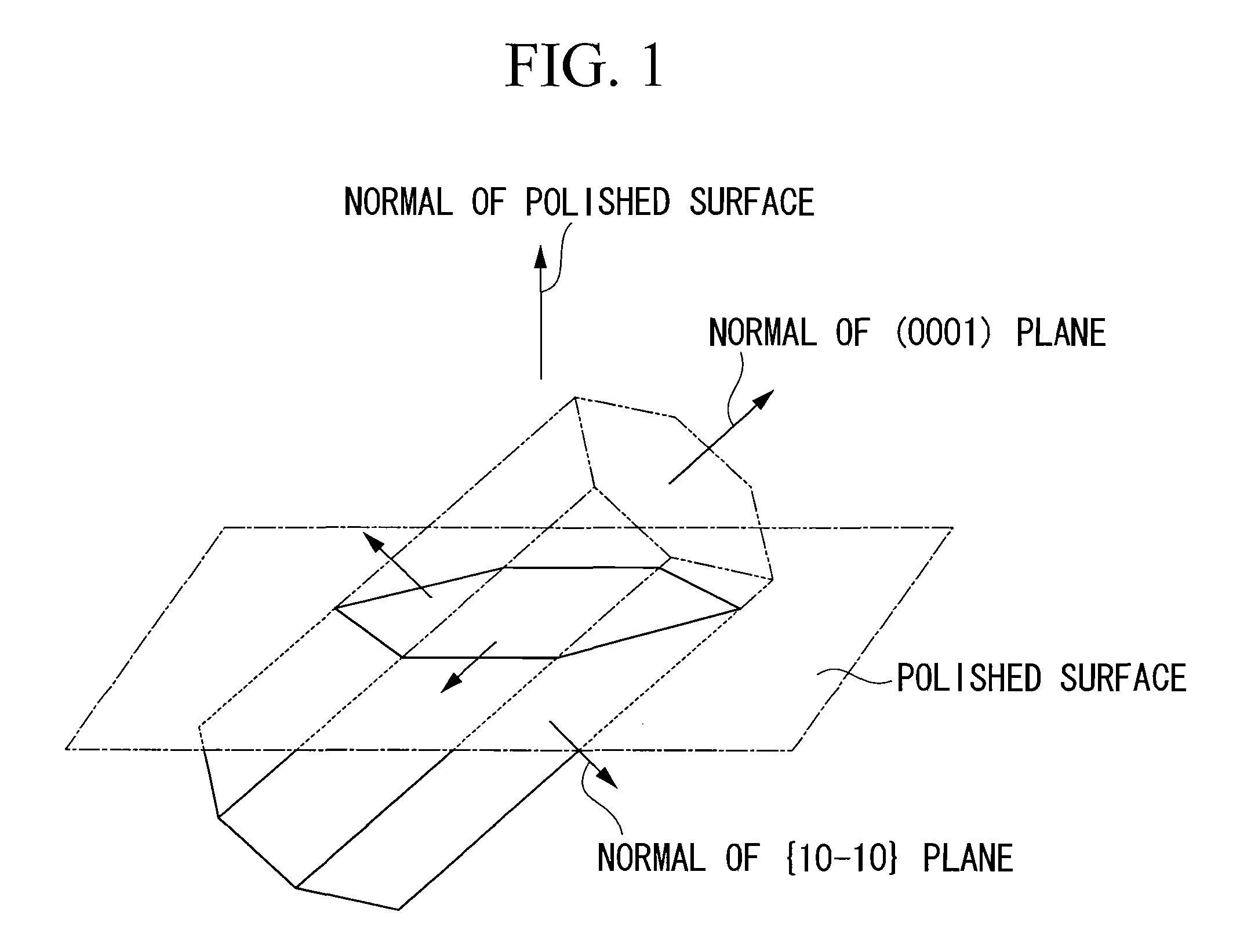
A surface coated cermet cutting tool comprising a tool body and a hard coating layer formed on the surface of the tool body, wherein the hard coating layer has a lower layer of a titanium compound layer and an upper layer of property-modified α type Al2O3 layer that has a crystal grain boundary orientation determined using a field emission type scanning electron microscope and an electron back-scattered diffraction pattern imaging device such that crystal grain boundary units of not less than 45% of all the grain boundaries show intersection angles of 15° or less between normals of (0001) planes and between normals of {10-10} planes, where a crystal grain boundary unit is a crystal grain boundary of adjacent pair of crystal grains.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Preparing method for zirconium boride dispersion strengthening tungsten powder
The invention discloses a preparing method for zirconium boride dispersion strengthening tungsten powder, and relates to metal tungsten powder preparing. In the preparing method, deionized water, ammonium metatungstate and nano zirconium boride particles are prepared into a solution according to the needed proportion, after being subjected to uniform stirring and ultrasonic scattering, the solution is injected into liquid nitrogen, a frozen precursor is obtained, the frozen and dried precursor is roasted in the argon atmosphere with the temperature ranging from 400 DEG C to 600 DEG C, reduction of (500 DEG C-650 DEG C)*2h+ (700 DEG C-900 DEG C)*1 h is conducted in the hydrogen atmosphere, the temperature rise rate is (2-10) DEG C / min, the hydrogen flow is (0.1-1.0) L / min, and the dispersion strengthening tungsten powder is obtained. A tungsten base body obtained through the tungsten powder is sintered, particles are evenly dispersed in the interiors of crystal grains and grain boundaries, the size of the particles is the nano level, an obtained block is subjected to the mechanical test, and it is proved that the mechanical performance of the block is obviously improved. The dispersion strengthening tungsten prepared through the method has very high grain-boundary strength; and meanwhile, compared with traditional metal carbide and rare earth oxide dispersion particles, zirconium boride dispersion strengthening can reach a higher strengthening and toughening effect under the smaller adding amount.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Halogen filament and process for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101083202AImprove grain boundary strengthHigh tensile strengthLamp incadescent bodiesRheniumPotassium
The invention provides a halogen filament and the making method thereof, as compared with traditional anti-drooping filament, W-Re alloy wire has high recrystallization temperature and greater crystal grain length-width ratio and contains K, Al and Si doping agents, and the crystal grain length-width ratio is greater than 15; and the content of Re in the alloy is 0.4-0.8mass%. And the concrete making process comprises: preparing alloy powder with Re content of 0.4-0.8mass%, and preparing W-Re alloy sintered bar by isostatic pressing, presintering and vertical sintering; making the sintered bar into W-Re alloy wire by rotary swaging and drawing and coiling the W-Re alloy wire into filament. And the filament has stable crystal grain structure and can better apply to halogen W lamps.
Owner:XIAMEN HONGLU TUNGSTEN MOLYBDENUM IND CO LTD
High-strength continuous annealing cold rolling stamping automobile structural steel plate and production method thereof
InactiveCN111218609AHigh strengthStable mechanical propertiesFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionContinuous annealing
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy, and particularly relates to a high-strength continuous annealing cold rolling stamping automobile structural steel plate and a production method thereof. Aiming at the problems of high mechanical property directionality of the automobile structural steel plate prepared by a prior method, secondary machining brittleness after forming and the like, the steel plate is provided, and the steel plate is prepared from the chemical compositions in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 0.0040% of C, 0.20-0.30% of Si, 0.80-1.00% of Mn, 0.020-0.040% of Nb, 0.030-0.050% of Ti, 0.002-0.006% of N, 0.080-0.110% of P, 0-0.015% of S, 0.0005-0.0015% of B, 0.015-0.050% of Als and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The invention further provides the production method of the steel plate, the coiling temperature, cooling speed and other relevant parameters are accurately controlled, so that the mechanical properties of the steel plate are stable, the anisotropy is small, basically no lug phenomenon occurs, the problem of the secondary machining brittleness after forming is solved, and the promotion and application prospect is good.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
2-system aluminum alloy and smelting and casting method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of metal smelting, and relates to a 2-system aluminum alloy with high Fe and Ni content and a smelting and casting method thereof. The 2-system aluminum alloy comprises, in weight percent, 0.15-0.2% of Si, 1.4-1.6% of Fe, 1.4-1.6% of Ni, 2.6-2.8% of Cu, 1.7-1.9% of Mg, less than or equal to 0.1% of Zn, 0.06-0.09% of Ti, less than or equal to 0.1% of Mn, less thanor equal to 0.1% of Cr and the balance Al. The smelting and casting method includes the steps: performing smelting, refining, degassing, slag removal and casting on raw materials; performing castingby the aid of a semi-continuous casting process; adding 1.0-2.0% of yttrium aluminum intermediate alloys in the refining process; controlling casting temperature to be 690-700 DEG C, controlling casting speed to be 20-30mm / min, and connecting single water flow to be 15-16m<3> / h to obtain 2-system aluminum alloy cast ingots. The 2-system aluminum alloy cast ingots with high content of Fe and Ni produced by the smelting and casting method are less in shortcoming and good in heat resistance and has good economic benefits, finished product rate is increased, and energy consumption and production cost are reduced.
Owner:CHINA ZHONGWANG
Method for manufacturing alloy containing transition metal carbide, tungsten alloy containing transition metal carbide, and alloy manufactured by said method
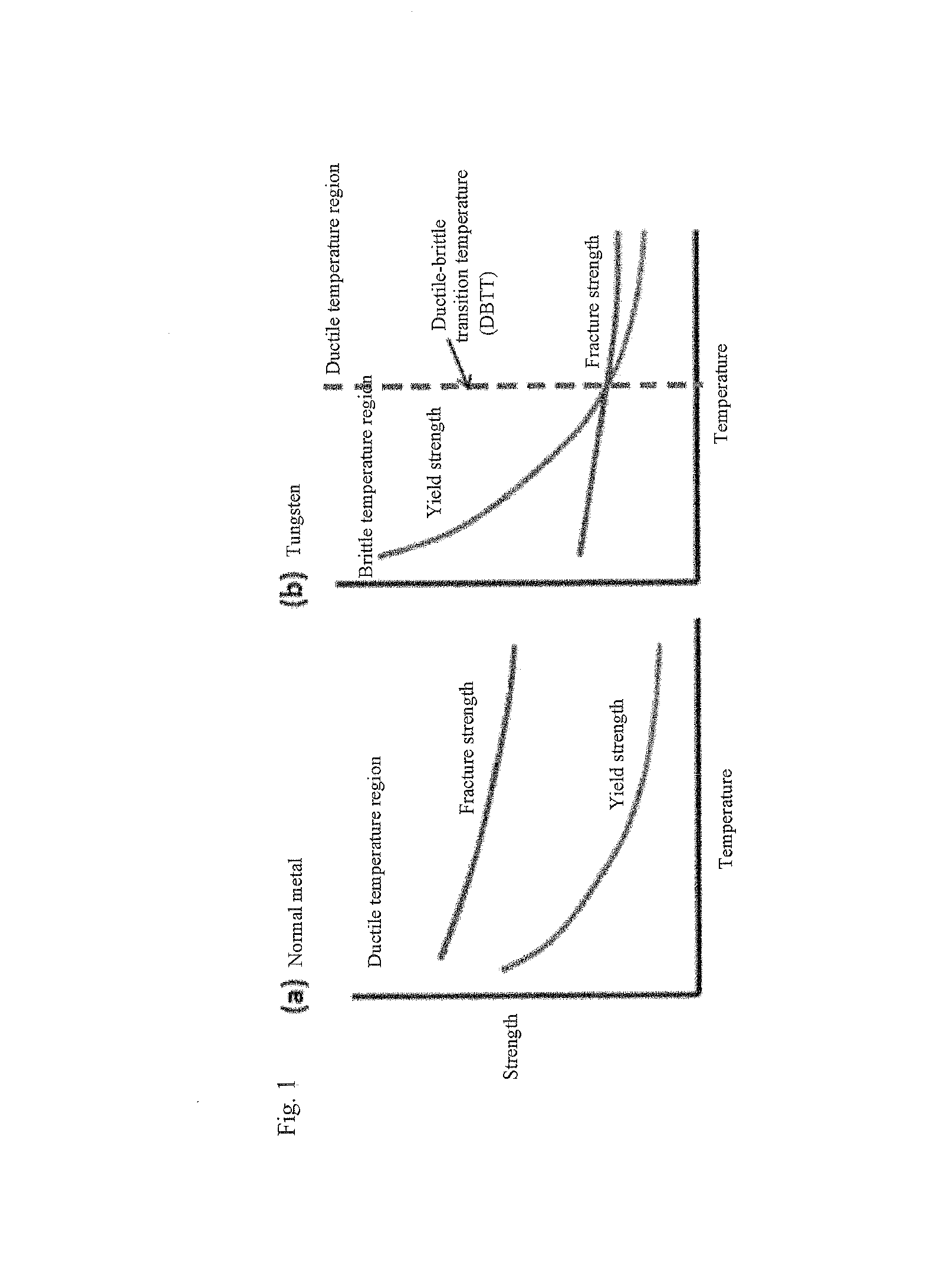
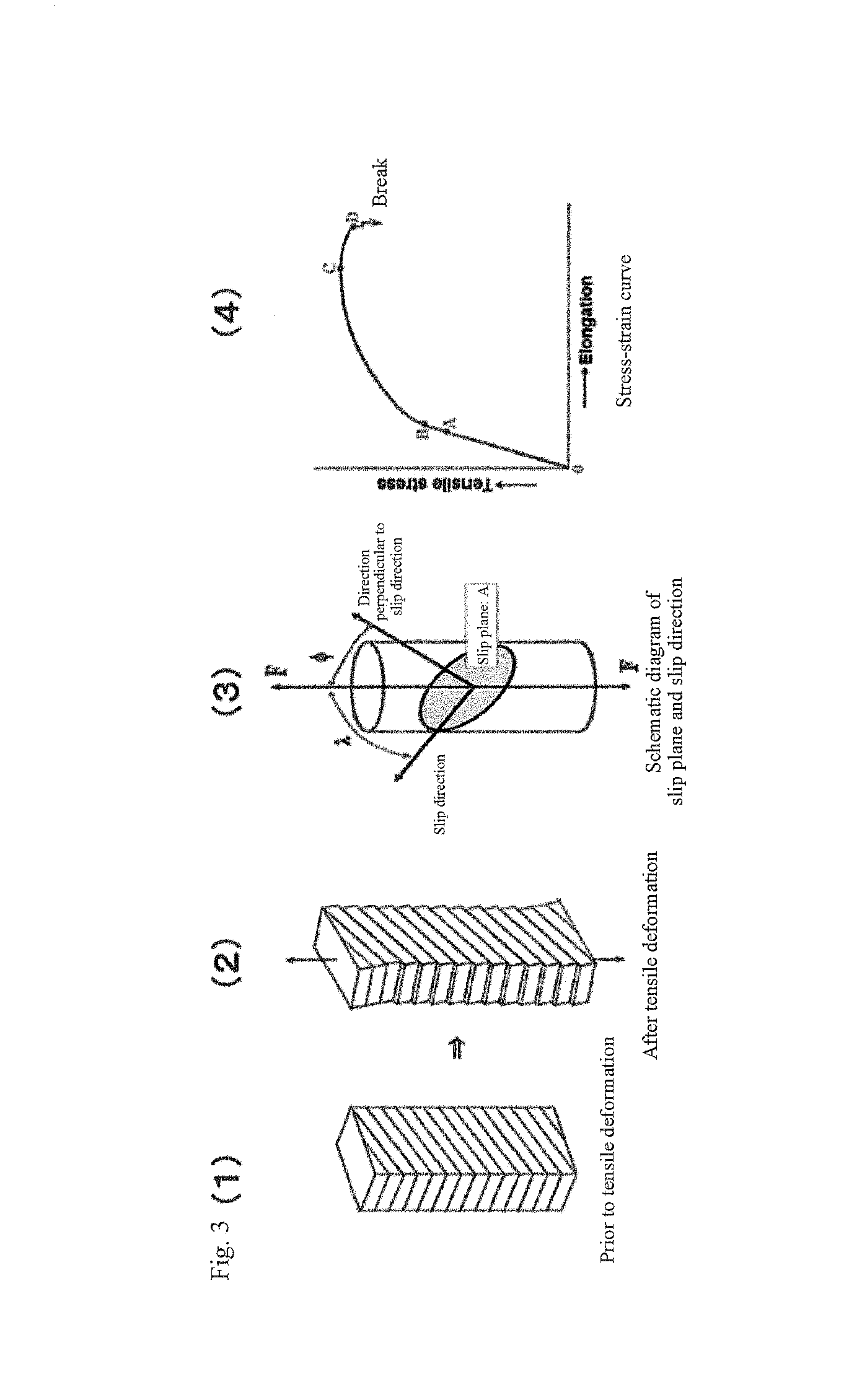
The present invention relates to the development of an alloy material with significantly improved low-temperature brittleness, recrystallization brittleness, and irradiation brittleness by the introduction of a recrystallization microstructure into an alloy, particularly a tungsten material, to significantly strengthen a weak grain boundary of the recrystallization microstructure. The present invention comprises the steps of: mechanically alloying at least one species selected from a group-IVA, VA, or VIA transition metal carbide and a metallic raw material; sintering base powders obtained through the mechanically alloying step, by using a hot isostatic press; and performing plastic deformation of at least 60% on the alloy obtained through the sintering step, at a strain rate between 10−5 s−1 and 10−2 S−1 and at a temperature between 500° C. and 2,000° C. It is therefore possible to obtain an alloy material with significantly improved low-temperature brittleness, recrystallization brittleness, and irradiation brittleness.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Surface coated cutting tool made of cermet having property-modified alpha type ai203 layer of hard coating layer
ActiveUS20070116985A1High hardnessImprove the heating effectPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesScanning electron microscopeElectron microscope
A surface coated cermet cutting tool comprising a tool body and a hard coating layer formed on the surface of the tool body, wherein the hard coating layer has a lower layer of a titanium compound layer and an upper layer of property-modified α type A12O3 layer that has a crystal grain boundary orientation determined using a field emission type scanning electron microscope and an electron back-scattered diffraction pattern imaging device such that crystal grain boundary units of not less than 45% of all the grain boundaries show intersection angles of 15° or less between normals of (0001) planes and between normals of {10-10} planes, where a crystal grain boundary unit is a crystal grain boundary of adjacent pair of crystal grains.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Machining method of a window and door aluminium alloy
The invention discloses a machining method of a window and door aluminium alloy. The window and door aluminium alloy comprises 6.50-10.50% of Zn, 2.50-3.50% of Cu, 2.10-2.50% of Mg, 0.40-0.60% of Mn,0.34-0.38% of Si, 0.19-0.25% of Cr, 0.11-0.15% of Ti, 0.02-0.05% of Mo, 0.22-0.26% of B, 0.05-0.09% of rare earth element RE and the balance of Al. The window and door aluminium alloy is prepared by using the steps of melting, slagging-off, heat preservation and standing, online refining, alloying, refining, on-line degassing, casting, homogenizing annealing, extrusion forming, heat treatment, shading, sealing treatment and the like. According to the machining method of the window and door aluminium alloy, by optimizing alloy components, a mixing ratio and a machining process, a problem that the strength and the casting performance of the aluminium alloy contradict each other can be effectively solved; and problems of large hot cracking tendency, poor corrosion resistance and poor high temperature strength of the aluminium alloy are solved.
Owner:阜阳力佳门业有限公司
A high-strength, high-conductivity, heat-resistant copper alloy material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistance copper alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistance copper alloy material comprises the following components: 0.2-1.0 wt% of Cr, 0.05-0.2 wt% of Mg, 0.03-0.2 wt% of Si, 0-0.1 wt% of Ni, 0-0.15 wt% of Ce, and the balance of Cu. The preparation method of the copper alloy comprises several steps of smelting-casting-homogenization-hot rolling-solid solution-combination, deformation and heat treatment. On component design of the copper alloy, cheap, easy-added and difficult-burnt elements are adopted to replace easy-burnt elements; through element component design of the alloy, the precipitation sequence of a precipitated phase and the nucleation and growth mechanism are changed, so that the alloy is excellent in high-temperature resistance and softening resistance; and through combination, deformation and heat treatment, the mechanical performance and the electric performance of the alloy are greatly improved, so that the tensile strength of the alloy reaches 530-620 MPa, and the electric conductivity reaches 75-87% IACS. The prepared high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistance copper alloy material is suitable for non-vacuum large-scale industrial manufacturing.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Intermediate alloy material and preparation method thereof
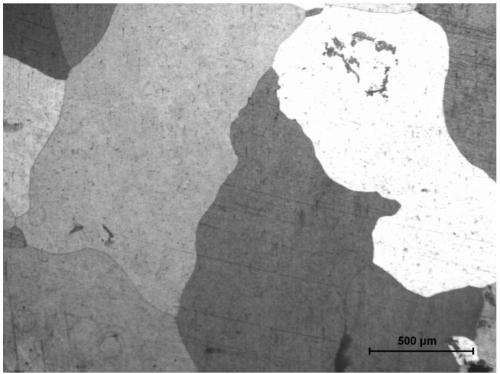
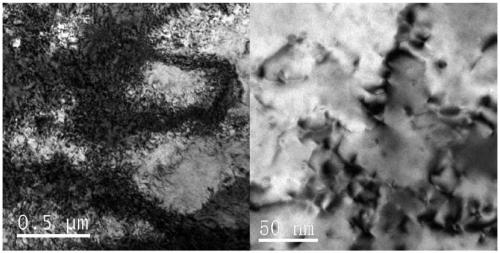
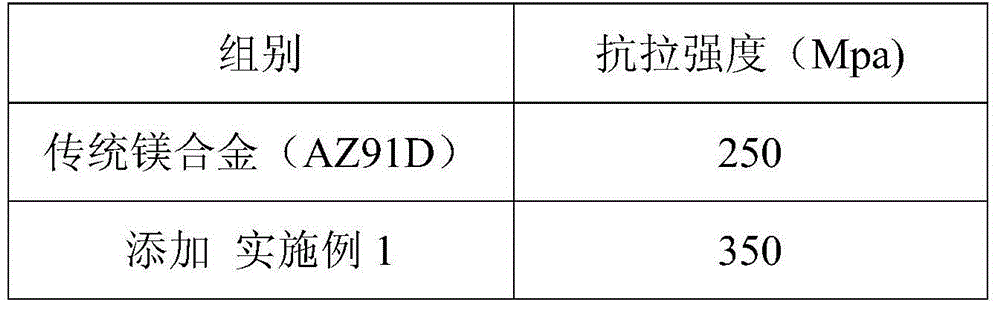
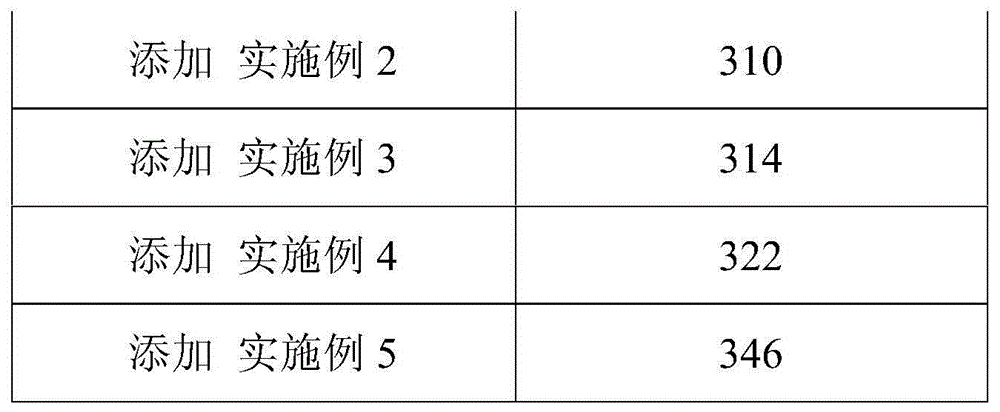
The invention relates to an intermediate alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The intermediate alloy material is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 66-71wt% of magnesium, 28-32wt% of red phosphorus, 0.3-1.5wt% of silicon carbide and 0.1-0.5wt% of rare earth. The preparation method comprises the steps of stirring, drying, vacuum smelting and the like. The intermediate alloy material provided by the invention is suitable for being added into a magnesium alloy material for the aerospace field, and the strength of the final magnesium alloy material can be effectively improved; and the strength can be improved from 200-300MPa to 310-350MPa.
Owner:SUZHOU RICHMOND ADVANCED MATERIAL TECH TRANSFER CO LTD
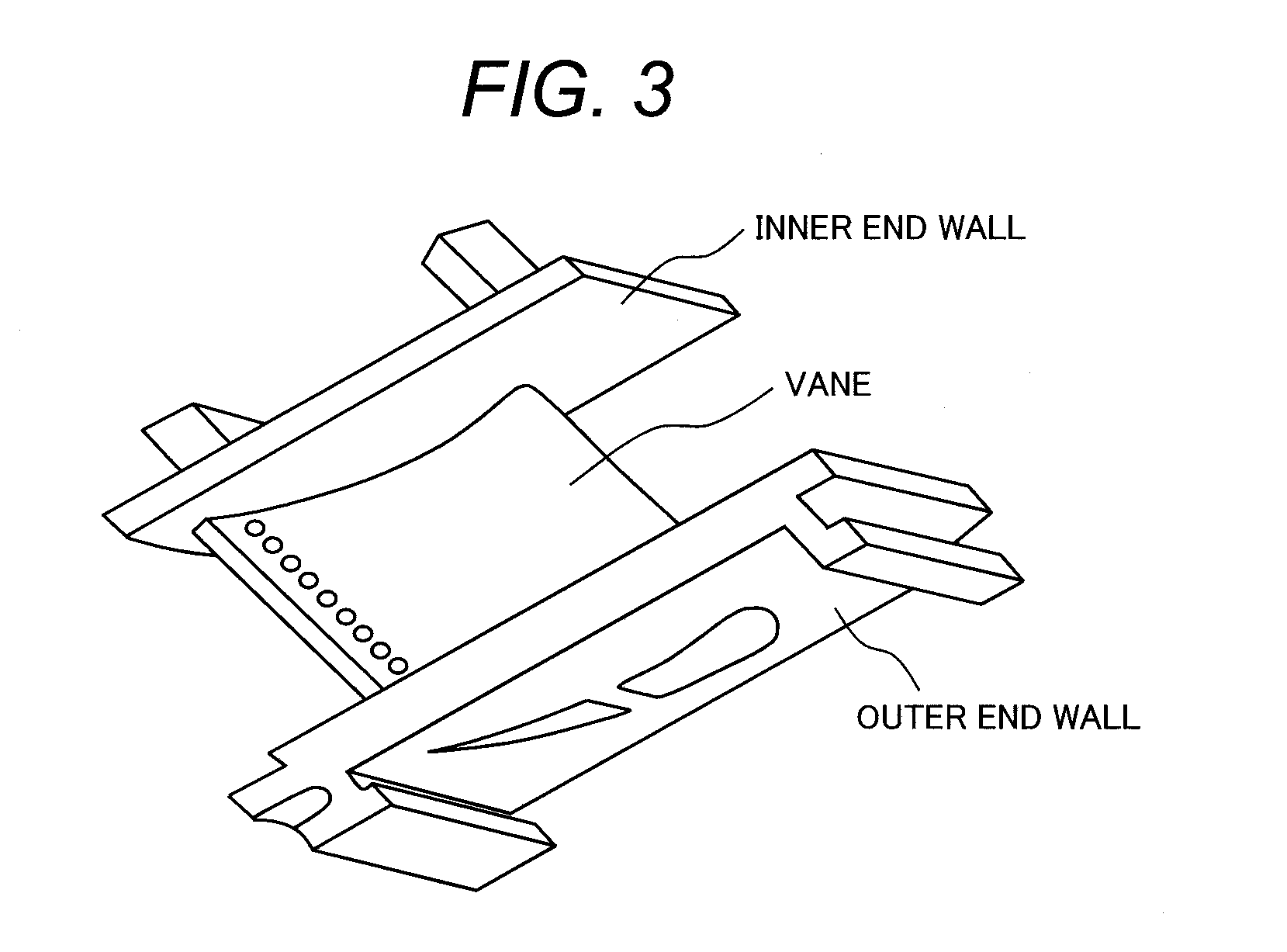
Heat process capable of lowering ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades
ActiveCN102220459AShort residence time at high temperatureFully solid solutionFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlChemical compositionTurbine blade
The invention provides a heat treatment process capable of lowering ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades. When the heat treatment process is used, the problem that the process effect is susceptible to influences of chemical components of the raw material of the blades when the conventional sub-temperature annealing process is used to treat the turbine blades and the problem of high ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of the turbine blades due to overlong high-temperature retention during heat treatment ofthe blades in the sub-temperature annealing process are solved. In the invention, the blades are uniformly placed in a common quenching material basket according to a technical scheme and then the quenching material basket is placed in a heat treatment quenching furnace. The heat treatment process is characterized in that: the blades are quenched twice in a quenching furnace; the temperature of primary quenching is 980 to 1070 DEG C; the temperature is kept constant for 1 to 3 hours; the cooling speed is 20 to 50 DEG C per minute; the temperature of secondary quenching is 900 to 1,000 DEG C; the temperature is kept constant for 15 to 120 minutes; the cooling speed is 30 to 50 DEG C minutes; and the temperature of the primary quenching is 20 to 100 DEG C higher than the temperature of the secondary quenching.
Owner:WUXI TURBINE BLADE
Method for improving high temperature plasticity of steel
ActiveCN107881289AImprove high temperature plasticityPromoting dispersive precipitationAustenite grainAlloy
The invention belongs to the field of steel-making continuous casting production of micro-alloy high-strength steel, and discloses a method for improving the high temperature plasticity of steel basedon a synergistic effect of magnesium treatment and two-times cooling. By the synergistic effect of a magnesium treatment process and a novel two-times cooling control process, components, the size and the distribution state of second-phase particles in a micro-alloy high-strength steel casting blank can be effectively controlled, the thickness of a proeutectoid ferrite film distributed along an original austenite grain boundary is controlled, the percentage reduction of area of the casting blank is increased significantly through detection with Gleeble3800 and is higher than 50%. Thus the effects that method can significantly improve the high temperature plasticity of the micro-alloy high-strength steel and the surface crack defects of the casting blank can be overcome effectively are verified.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Surface modified coating cutting blade and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105506580AImprove antioxidant capacityReduce residual stressLayered productsChemical vapor deposition coatingHeat resistanceUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a surface modified coating cutting blade and a preparation method thereof. The cutting blade comprises a blade matrix and a coating deposited on the blade matrix, the coating contains an MT-TiZrCN coating and an outermost Al(Zr)2O3 modified coating with a corundum structure; the Al(Zr)2O3 modified coating has (300) crystal face strong texture orientation, and the strength ratio I(300) / I(110) of the orientation crystal surface is 0.5-2.5. The preparation method includes: sequentially depositing a TiN layer, an MT-TiZrCN coating, a TiCxNyOz layer, an alpha-Al2O3 layer and an Al(Zr)2O3 modified coating on the blade matrix, thus obtaining the surface modified coating cutting blade. The surface modified coating cutting blade provided by the invention has excellent heat resistance, anti-tipping performance and anti-adhesion performance, and is suitable for general milling processing and other aspects of steel and stainless steel.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CEMENTED CARBIDE CUTTING TOOLS CO LTD
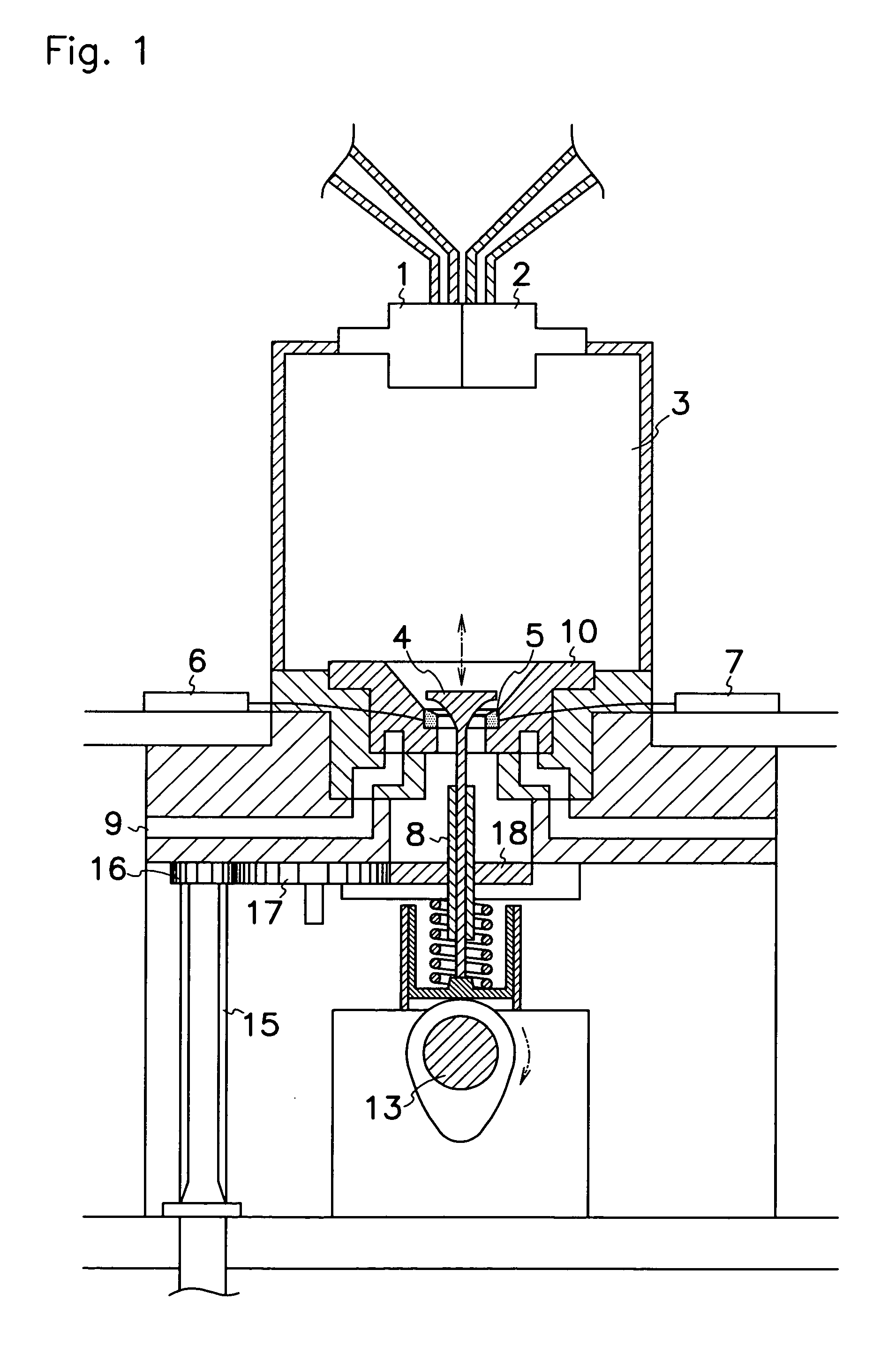
Electric-resistance-welded steel pipe for boiler having excellent stress corrosion cracking resistance, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN109477173AExcellent resistance to stress corrosion crackingCrack suppressionFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHardnessStress corrosion cracking
Provided is an electric-resistance-welded steel pipe for a boiler, having excellent stress corrosion cracking resistance, and in which ferrite grain boundary strength of a weld part is increased, andcracking in the weld part is suppressed. The component composition of the present invention includes, in terms of mass%, 0.05-0.35% C, 0.10-0.35% Si, 0.25-1.50% Mn, 0.035% or less of S, 0.035% or lessof P, 0.005-0.050% Al, 0.010% or less of N, and 0.010% or less of O, and furthermore includes, optionally and selectively, at least one of 1.00% or less of Cr, 1.00% or less of Mo, 2.00% or less of Ni, 2.00% or less of Cu, 0.0030% or less of B, 0.20% or less of Nb, 0.20% or less of V, 0.20% or less of Ti, 0.0050% or less of Ca, and 0.0050% or less of Mg, the remainder being Fe and unavoidable impurities, the difference between the hardness at an outermost layer of a base material part and the hardness at a position at a depth of 1 / 2 the thickness of the base material part being 20 Hv or less,and the difference between the hardness of a welding abutment part to an extent 1 mm from an outer surface and the hardness of the base material part to an extent 1 mm from the outer surface being 20Hv or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Doped perovskite solar cell and preparation method thereof
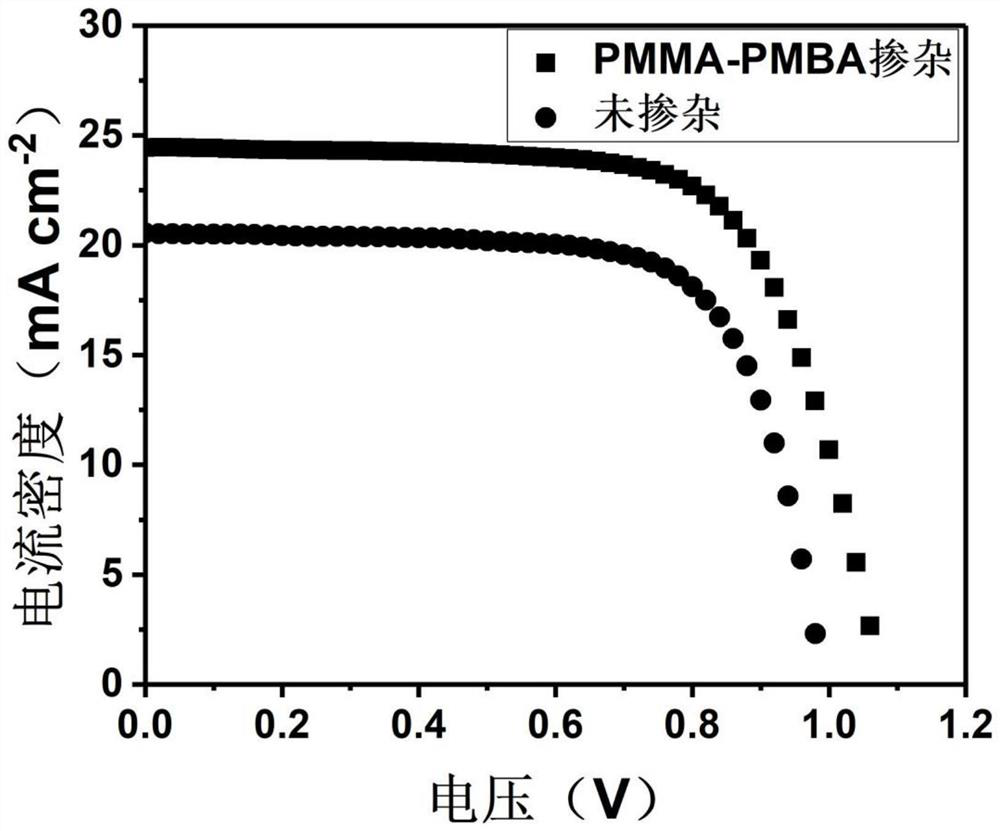
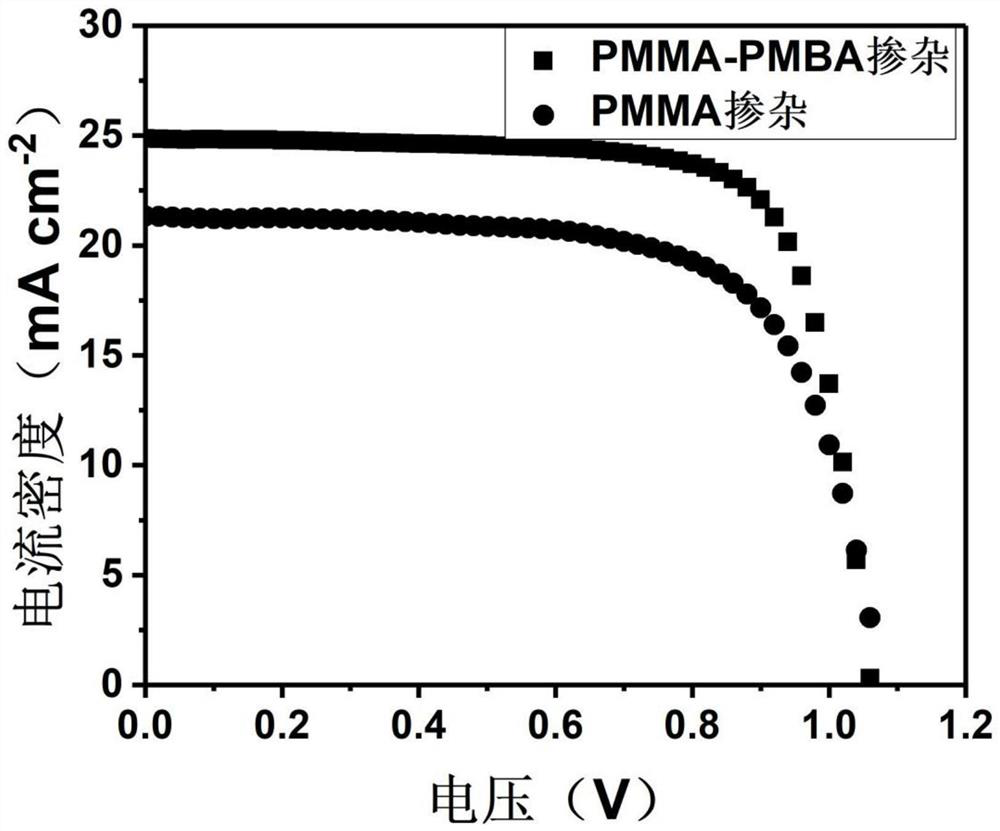
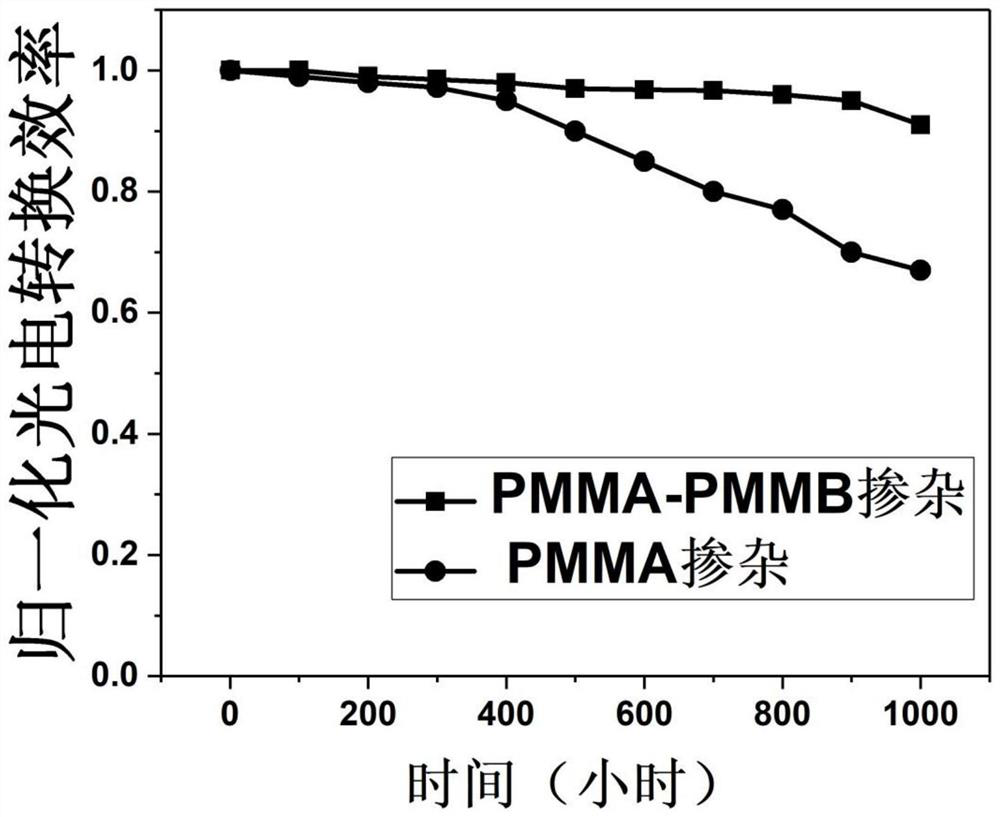
ActiveCN114141952AExcellent self-healing performanceHas hydrophobic propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringChemistry
The invention provides a doped perovskite solar cell. The doped perovskite solar cell comprises a substrate layer, a first charge transport layer, a passivated perovskite layer, a second charge transport layer and an electrode layer which are in contact in sequence, the passivated perovskite layer comprises a perovskite material and a self-repairing polymer; the self-repairing polymer is a polymethyl methacrylate-n-butyl acrylate copolymer. According to the perovskite solar cell, the self-repairing polymer containing the polar functional group carbonyl is added into the perovskite layer, the polymer can be coordinated with Pb < 2 + > or Sn < 2 + >, non-coordinated atoms at the grain boundary are passivated, and the function of passivating the grain boundary is achieved; meanwhile, the polymer has good self-repairing capacity, and the grain boundary strength in the polycrystalline perovskite thin film can be enhanced; in addition, the polymer has a hydrophobic property and can block water vapor invasion, so that the stability of perovskite is improved. The invention also provides a preparation method of the doped perovskite solar cell.
Owner:HUANENG NEW ENERGY CO LTD +1
Ni-based casting superalloy and cast article therefrom
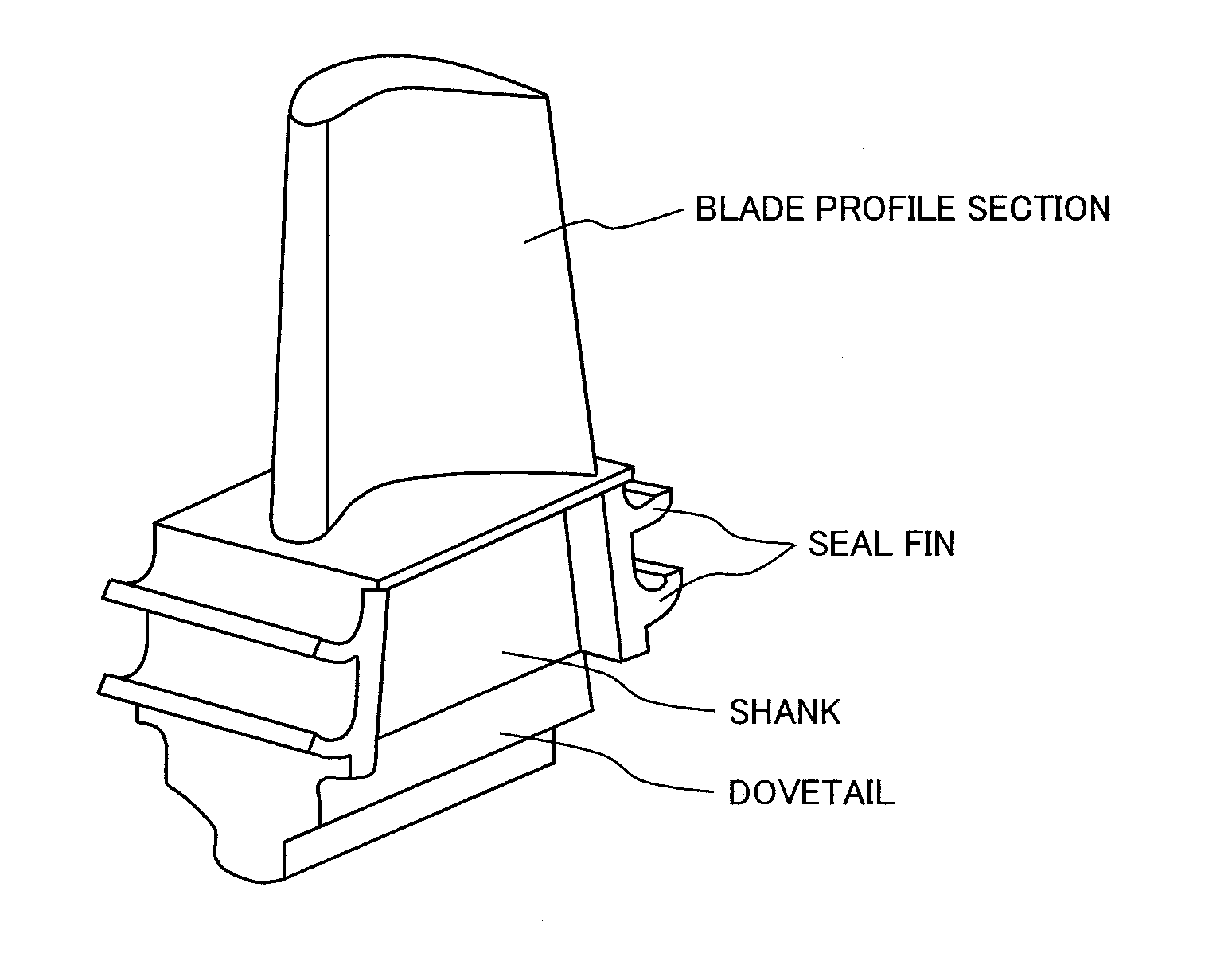
ActiveUS20150147226A1Low costImprove balanceBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesSuperalloyGrain boundary
It is an objective of the invention to provide a low cost Ni-based casting superalloy suitable for casting articles having a far better balance among a high-temperature mechanical strength, a grain boundary strength and a oxidation resistance than conventional Ni-based superalloy cast articles. There is provided an Ni-base casting superalloy including: in mass %, 0.03 to 0.15% of C; 0.005 to 0.04% of B; 0.01 to 1% of Hf; 0.05% or less of Zr; 3.5 to 4.9% of Al; 4.4 to 8% of Ta; 2.6 to 3.9% of Ti; 0.05 to 1% of Nb; 8 to 12% of Cr; 1 to 6.9% of Co; 4 to 10% of W; 0.1 to 0.95% of Mo; 0.02 to 1.1% of Si and / or 0.1 to 3% of Fe; and the balance including Ni and incidental impurities.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Iron-based sintered alloy with dispersed hard particles
An iron-based sintered alloy having improved thermal and mechanical strength is provided. The iron-based sintered alloy with dispersed hard particles comprises: a matrix comprising, by weight, 0.4 to 2% silicon (Si), 2 to 12% nickel (Ni), 3 to 12% molybdenum (Mo), 0.5 to 5% chromium (Cr), 0.6 to 4% vanadium (V), 0.1 to 3% niobium (Nb), 0.5 to 2% carbon (C), and the reminder of iron (Fe); and hard particles comprising 60 to 70% molybdenum (Mo), 0.3 to 1% boron (B), 0.1% or less carbon (C), and the reminder of iron (Fe). The hard particles are dispersed in the matrix in an amount in the range of 3 to 20% based on the entire alloy. They are sintered to produce the iron-based sintered alloy. Addition of boron into the ferromolybdenum hard particles enhances the wettability of the ferromolybdenum hard particles to prevent the hard particles from falling off the matrix. Thus, the adhesive property between the matrix and the hard particles is improved, thereby enhancing the thermal and mechanical strength of the iron-based sintered alloy.
Owner:RIKEN CO LTD
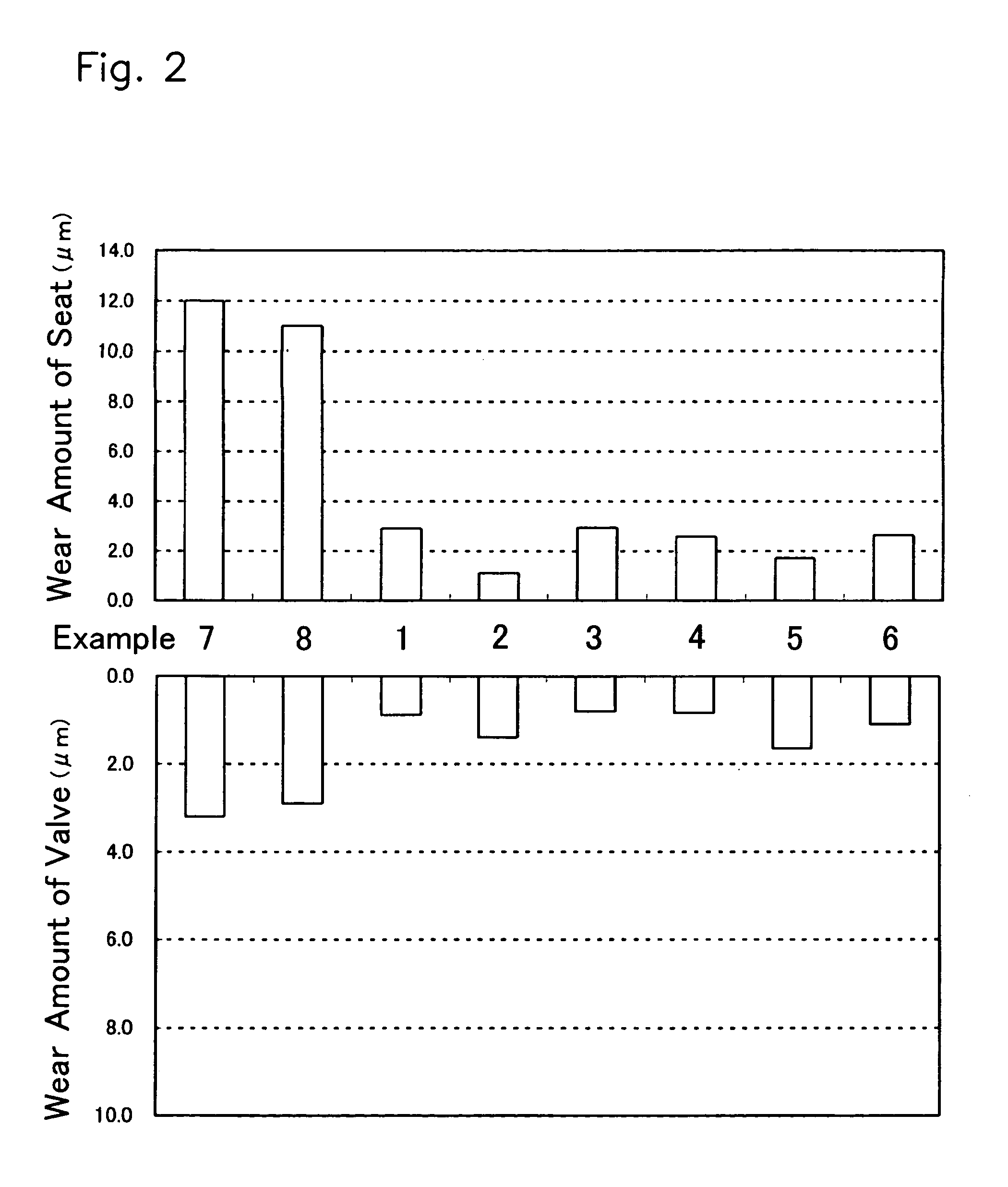
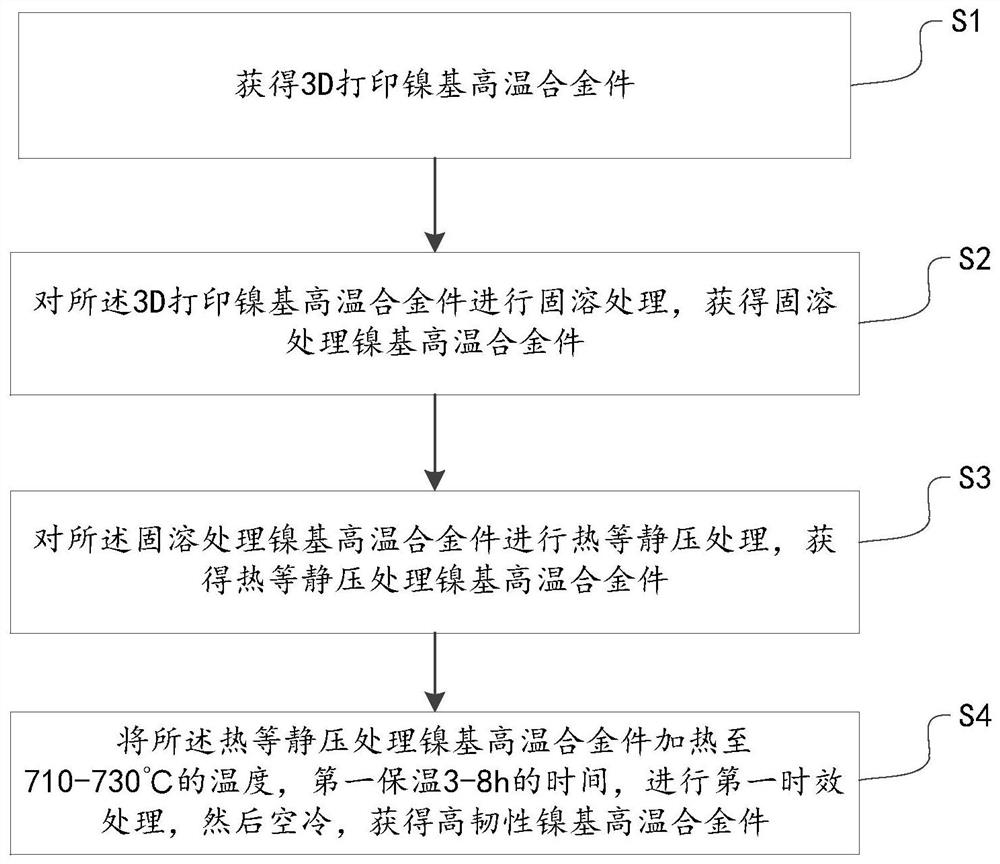
Method for improving toughness of 3D printing nickel-based high-temperature alloy part
ActiveCN112828310AReduce internal stressImprove high temperature strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySolution treatmentSuperalloy
The invention provides a method for improving the toughness of a 3D printing nickel-based superalloy part, and belongs to the technical field of 3D printing. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the 3D printing nickel-based superalloy part; making solution treatment to the 3D printing nickel-based high-temperature alloy part to obtain a nickel-based high-temperature alloy part subjected to solution treatment; performing hot isostatic pressure treatment to the nickel-based high-temperature alloy part subjected to solution treatment to obtain a nickel-based high-temperature alloy part subjected to hot isostatic pressure treatment; and heating the nickel-based high-temperature alloy part subjected to hot isostatic pressure treatment to 710 DEG C-730 DEG C and holding the alloy part for 3-8 h for the first time, and performing first aging treatment and air cooling to obtain the high-toughness nickel-based high-temperature alloy part. According to the nickel-based high-temperature alloy part treated through the method, at the temperature of 1000 DEG C, the yield strength ranges from 128 MPa to 142 MPa1000 DEG C, the tensile strength ranges from 150 MPa to 168 MPa, the ductility ranges from 17% to 19.5%, and the toughness is high.
Owner:HUBEI SANJIANG AEROSPACE GRP HONGYANG ELECTROMECHANICAL
Preparation method of elastic damping SBS material
The invention discloses a preparation method of an elastic damping SBS material, comprising the following steps: Step 1, carrying out a reaction between calcium lactate, lauryl sodium sulfate, water, glucose and sodium carbonate, centrifuging, washing, and drying to obtain first powder; Step 2, adding yttrium nitrate, neodymium oxide, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol and sodium polyacrylate into the first powder, uniformly mixing, and sintering to obtain second powder; Step 3, adding glycol, water, linoleic acid, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, styrene and potassium sulphate into the second powder, reacting, filtering, and grinding so as to obtain third powder; Step 4, uniformly mixing SBS, the third powder, polystyrene, ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene, carbon black, terpene resin, lanthanum oxide, cerium oxide, zirconium oxide, polyetheretherketone resin, oxidized polyethlene wax, macadamia shell powder, metallocene polyethylene and bamboo fiber, and mixing to obtain the elastic damping SBS material. The SBS material has advantages of high strength and good elasticity.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Aluminum alloy for high-strength corrosion-resistant doors and windows and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109161746AImprove toughnessAccelerated corrosionSurface reaction electrolytic coatingRare-earth elementUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy for high-strength corrosion-resistant doors and windows, which comprises 6.50-10.50% of Zn, 2.50-3.50% of Cu, 2.10-2.50% of Mg, 0.40-0.60% of Mn, 0.34-0.38% of Si, 0.19-0.25% of Cr, 0.11-0.15% of Ti, 0.02-0.05% of Mo, 0.22-0.26% of B, 0.05-0.09% of rare-earth element Re, and the balance of Al. The aluminum alloy is prepared by the steps of melting, slag-off, heat preservation, standing, on-line refining, proportioning, refining, on-line degassing, casting, uniform annealing, extrusion molding, heat treatment, coloring and pore sealing. By optimizing the composition, proportion and processing technology of the alloy, the contradiction between the strength and the casting performance of the aluminum alloy can be effectively solved, and the problems of large thermal cracking tendency, poor corrosion resistance and poor high temperature strength of the aluminum alloy are solved.
Owner:阜阳力佳门业有限公司
Creep-resistant, rhenium-free nickel base superalloy
ActiveUS20140119941A1Improve grain boundary strengthImprovement in fracture lifePropellersPump componentsRheniumTitanium
Disclosed is a nickel base alloy which is substantially free of rhenium and has a solidus temperature of more than 1320° C. Precipitates of a γ′-phase are present in a γ-matrix with a fraction of 40 to 50 vol % at 1050° C. to 1100° C., and a γ / γ′ mismatch at 1050° C. to 1100° C. is from −0.15% to −0.25%. The alloy comprises 11 to 13 at % aluminum, 4 to 14 at % cobalt, 6 to 12 at % chromium, 0.1 to 2 at % molybdenum, 0.1 to 3.5 at % tantalum, 0.1 to 3.5 at % titanium, 0.1 to 3 at % tungsten. The tungsten content of the γ-matrix is greater than that in the precipitated γ′-phases.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
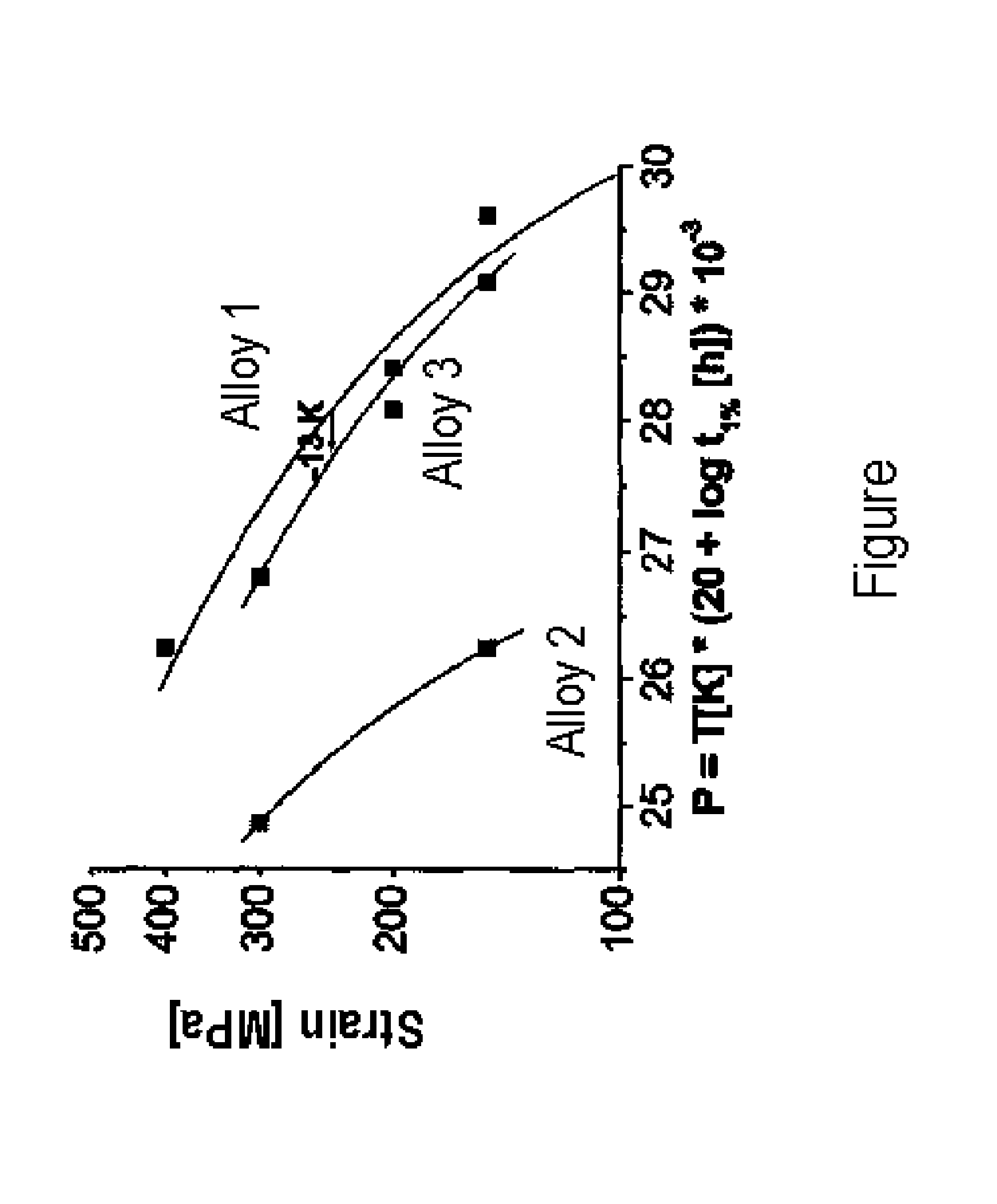
Heat treatment of alloys having elements for improving grain boundary strength
Heat treatment of alloys having elements for improving grain boundary strength is disclosed. Components directly after castings often reveal low or no transverse grain boundary strength, so that cracks do appear and decrease the yield rate. The provided measures do not lead to low transverse grain boundary strength but maintains efficient grain boundary strength, so that the yield rate of components without cracks is increased.
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
High-strength hot-dip galvanized stamping car structure steel plate and production method thereof
InactiveCN111218608AGood resistance to secondary processing brittlenessStable mechanical propertiesHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesMechanical propertyImpurity
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy, and particularly relates to a high-strength hot-dip galvanized stamping car structure steel plate and a production method thereof. In view of the problems such as high mechanical property directionality and secondary processing brittleness after forming of an car structure steel plate prepared by an existing method, the steel plate is provided by the invention and is prepared from the chemical components in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 0.0040% of C, 0.10-0.15% of Si, 0.60-0.70% of Mn, 0.030-0.040 of Nb, 0.040-0.050% ofTi, 0.002-0.006% of N, 0.060-0.075% of P, 0-0.012% of S, 0.0005-0.0015% of B, 0.020-0.060% of Als, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The invention further provides the production methodof the steel plate. Relevant parameters such as the coiling temperature and the cooling speed are precisely controlled, the mechanical properties of the obtained steel plate are stable jointly, anisotropy is small, a coating is good in adhesion, the convex lug phenomenon is basically avoided after forming, the problem of secondary processing brittleness after forming is solved, and using and popularization prospects are good.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com