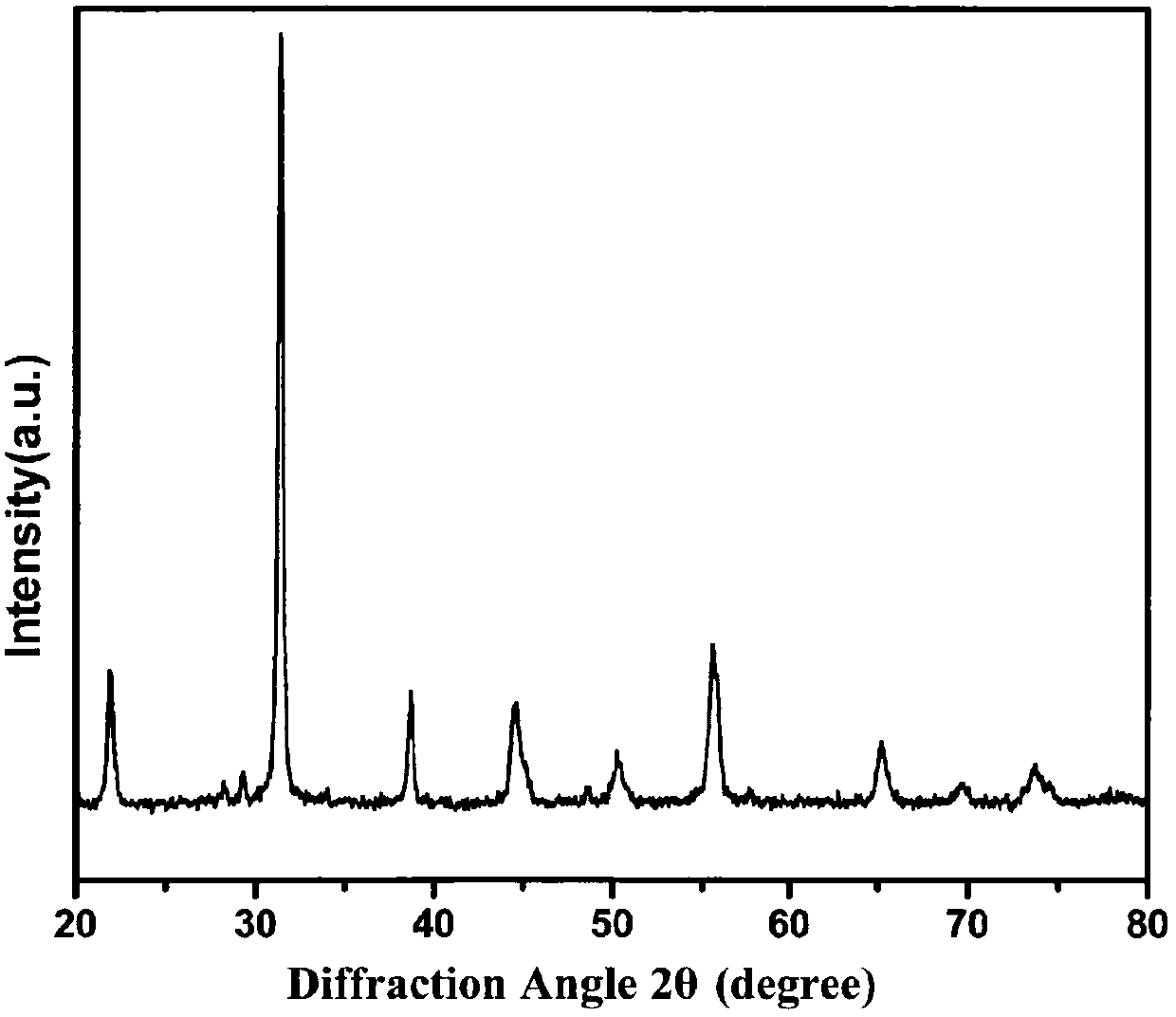
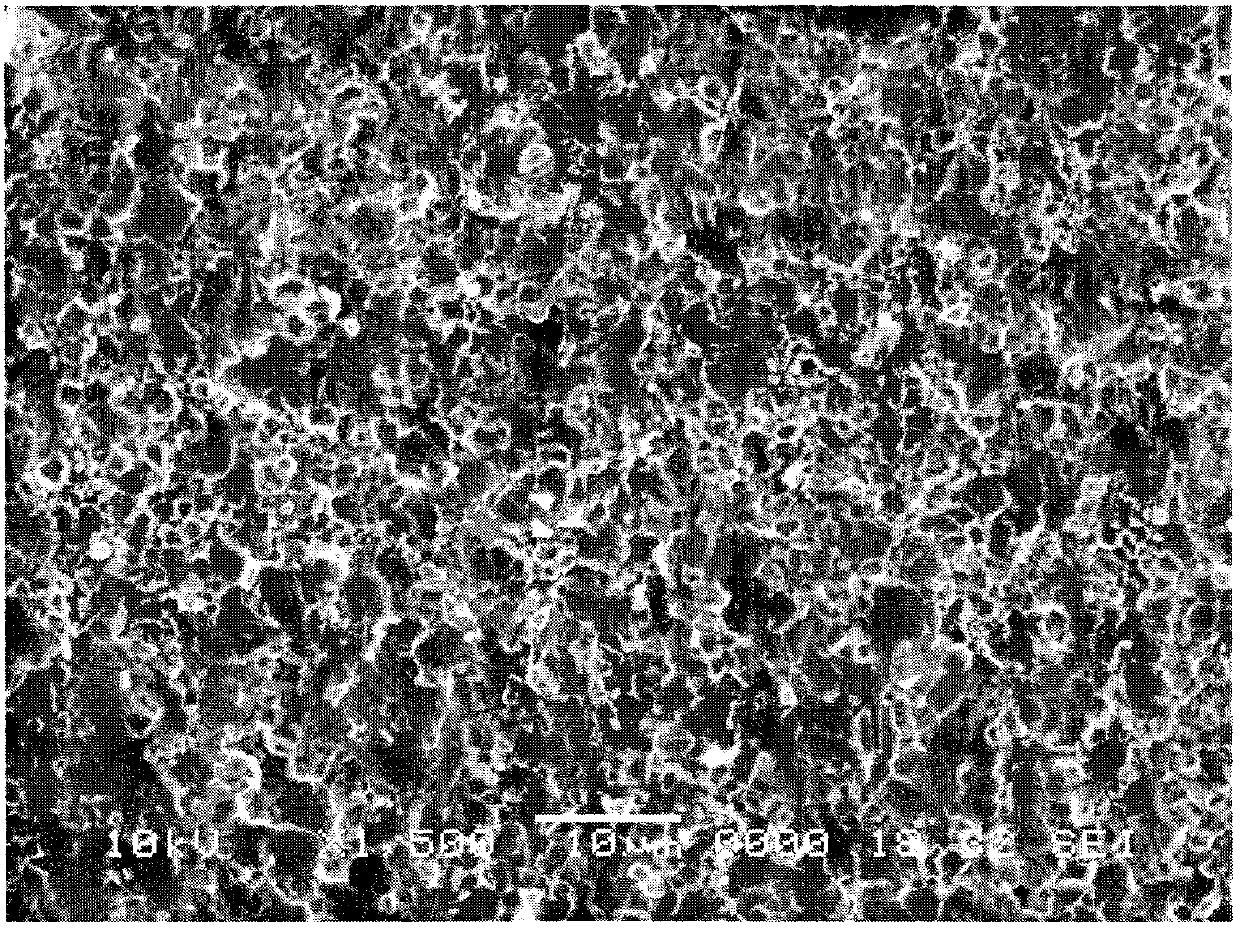
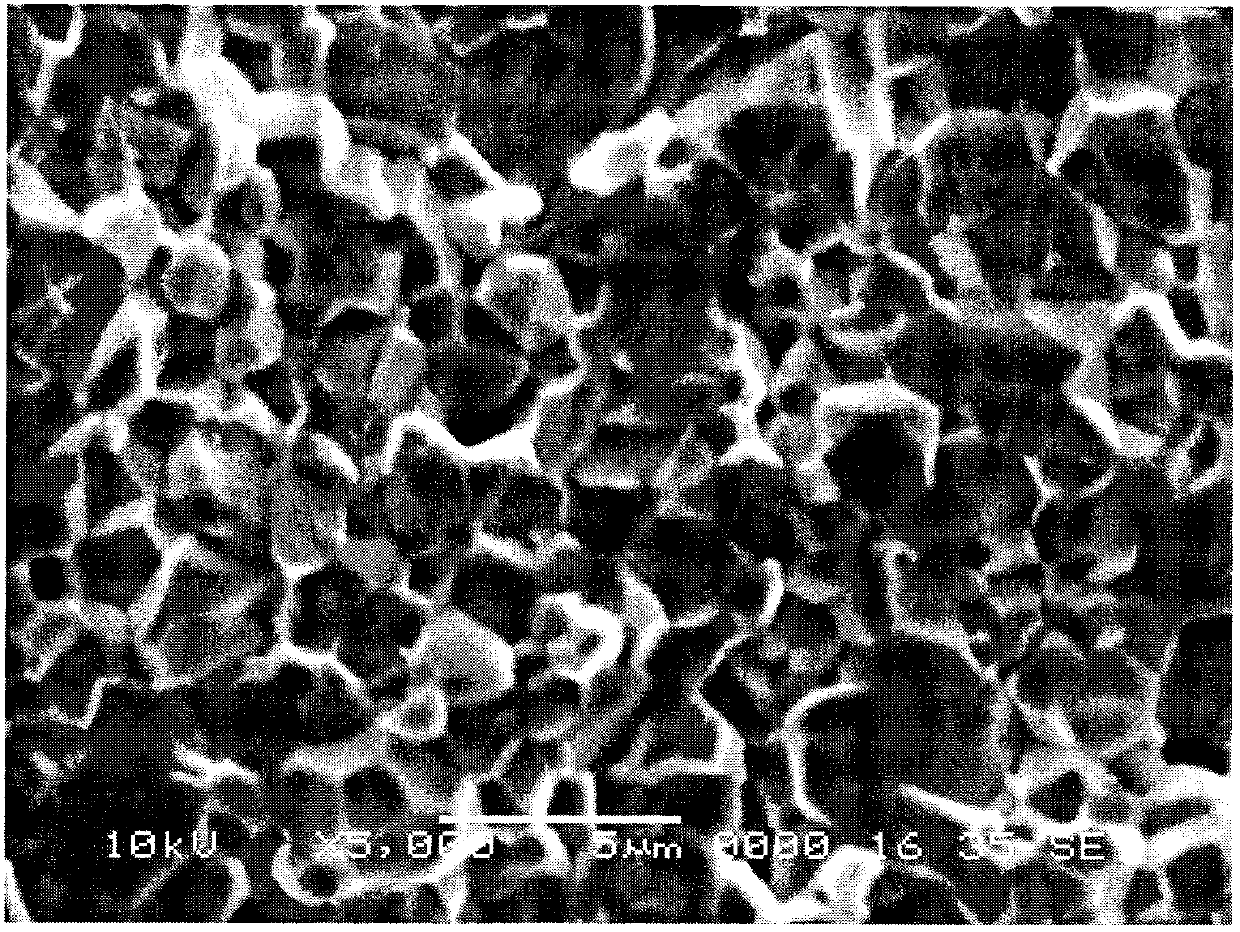
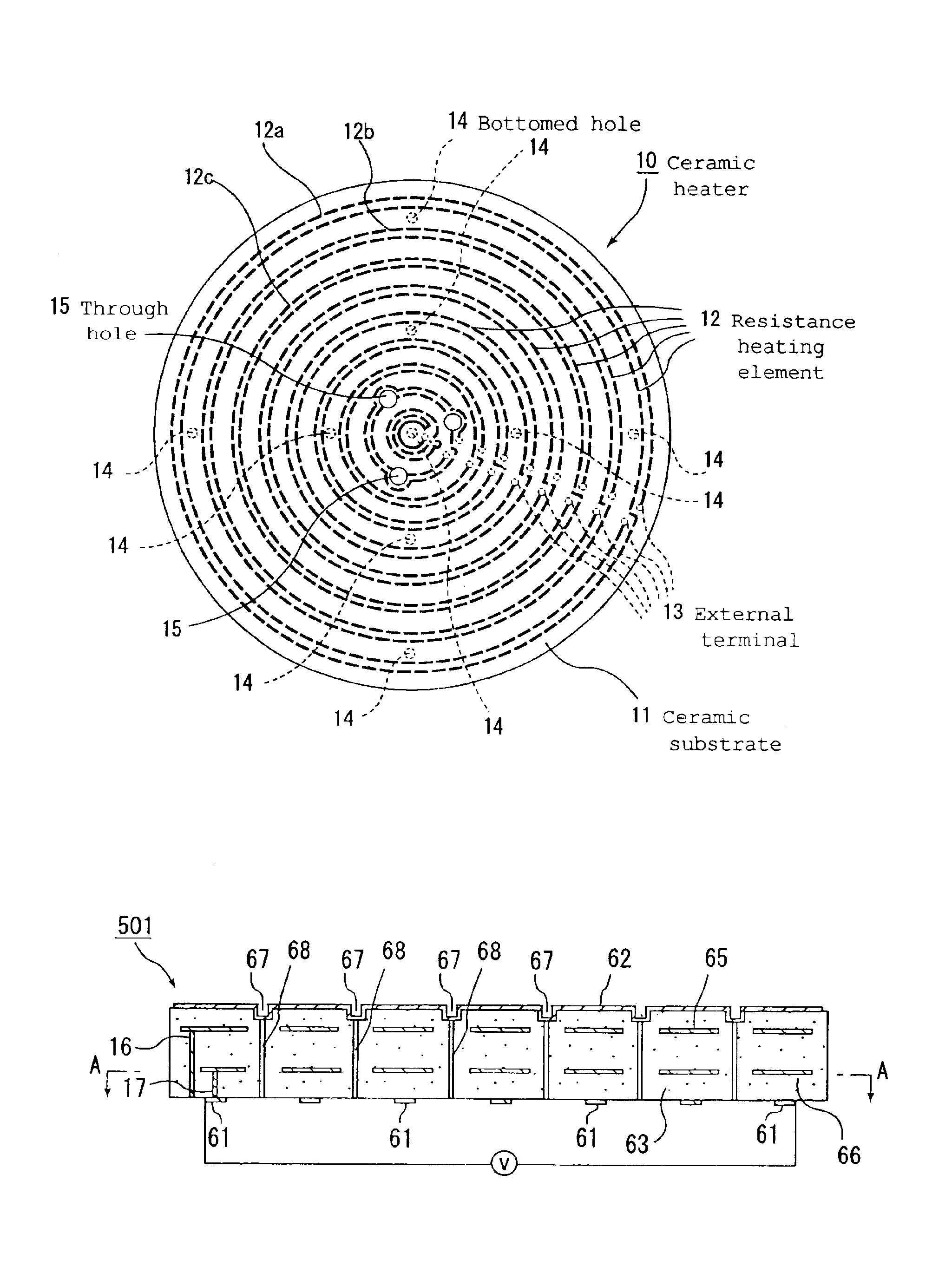
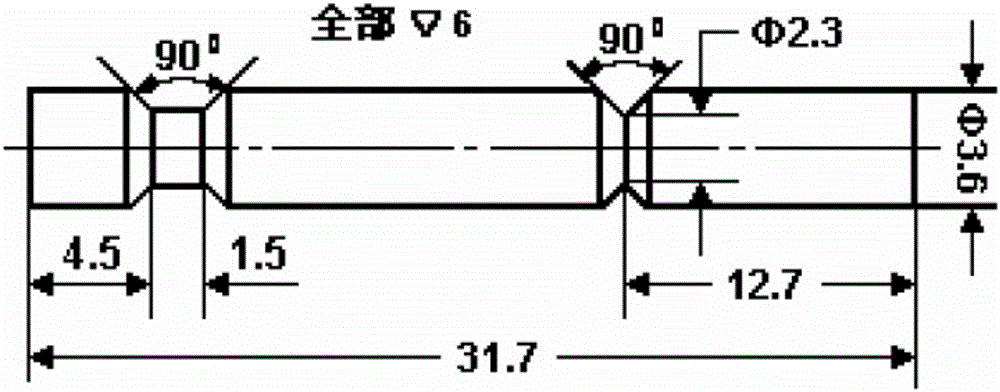
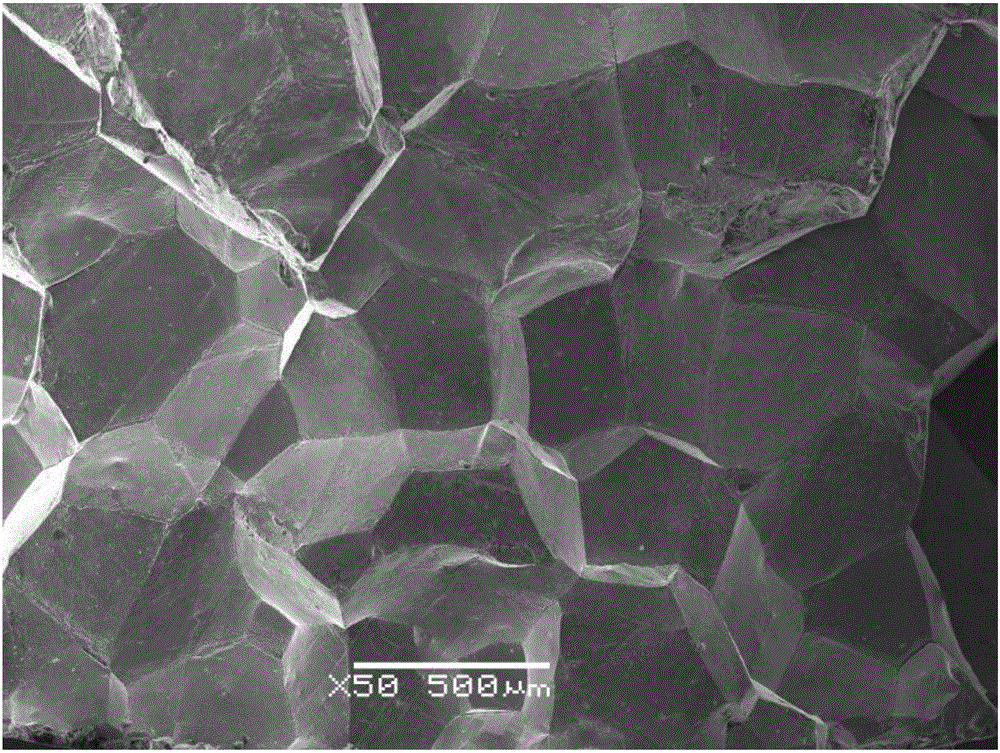
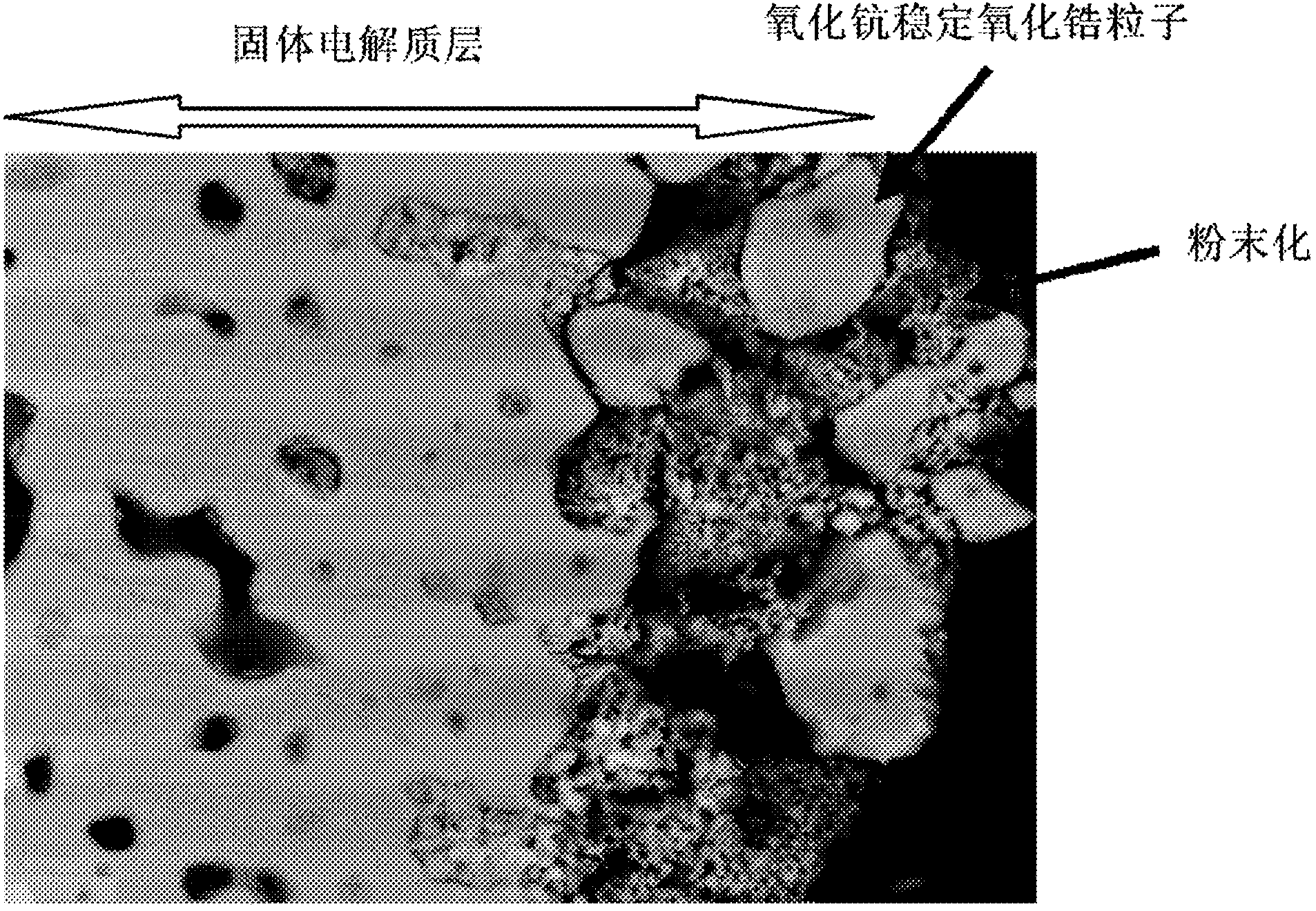
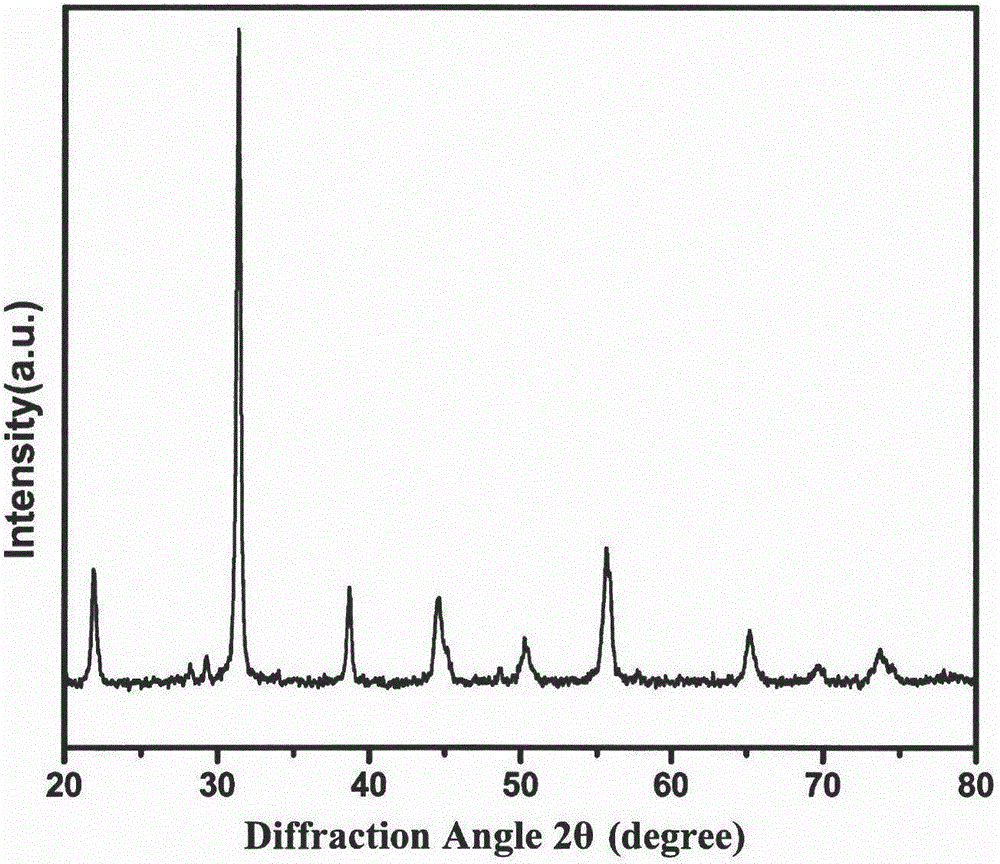
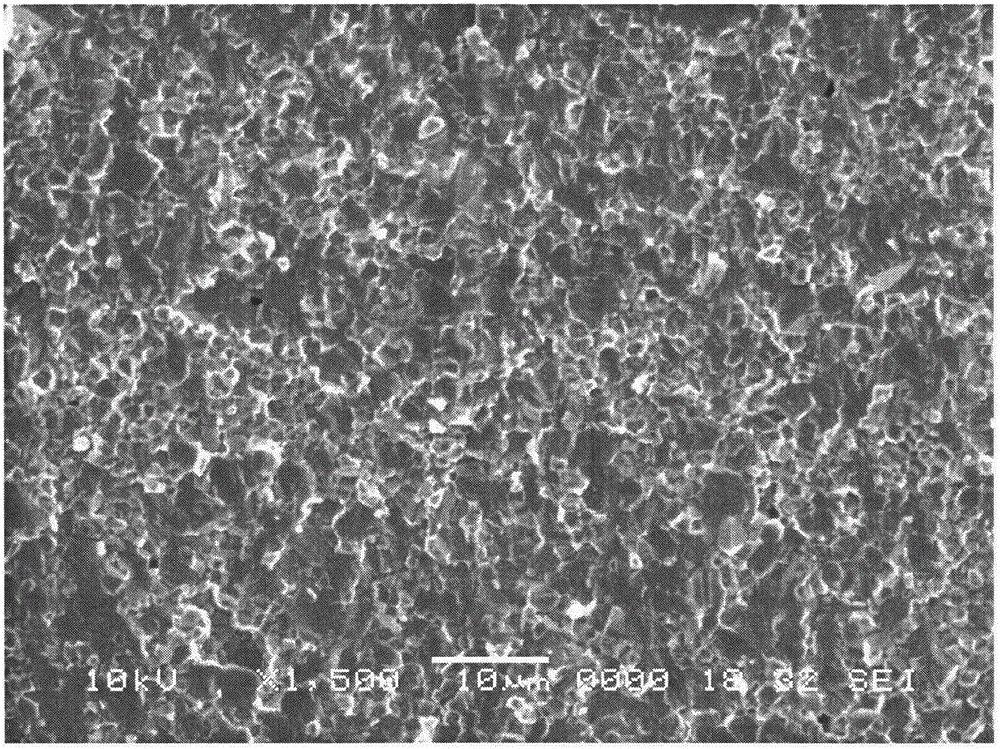
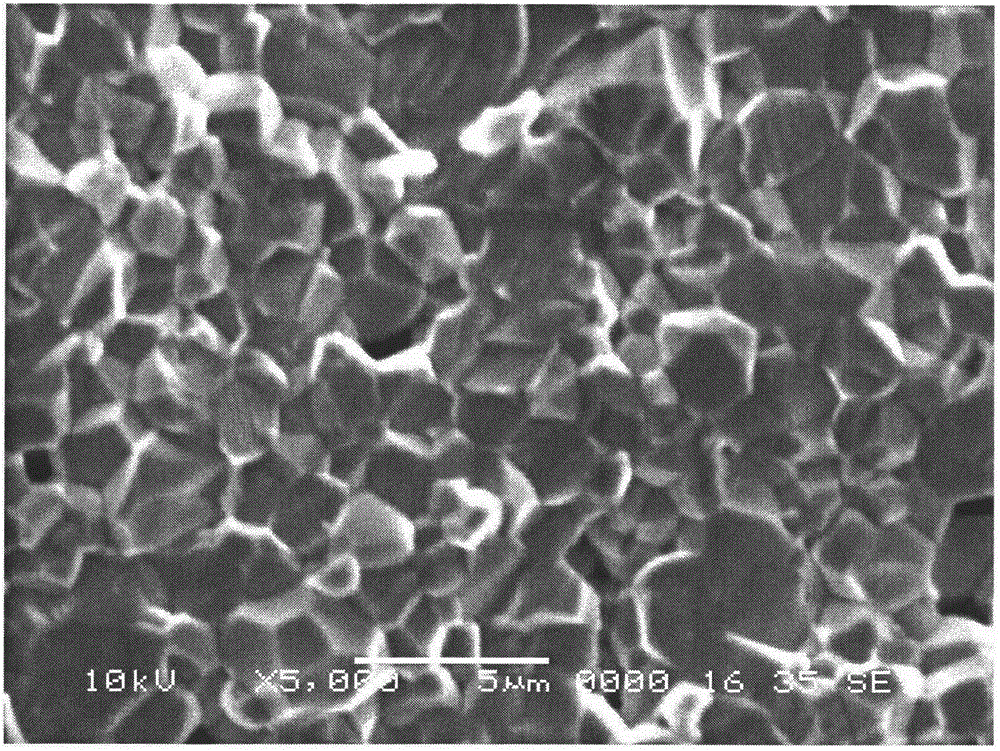
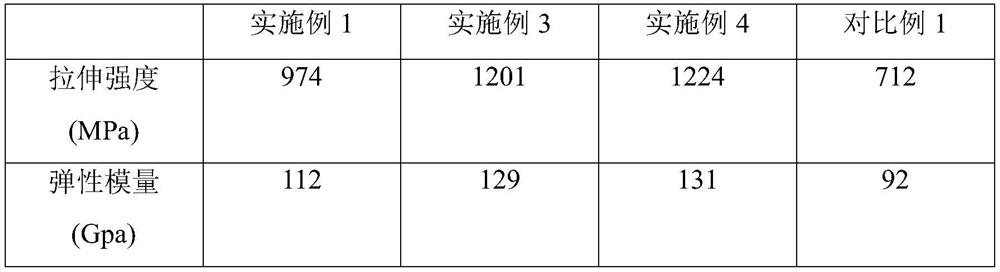
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Intergranular fracture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
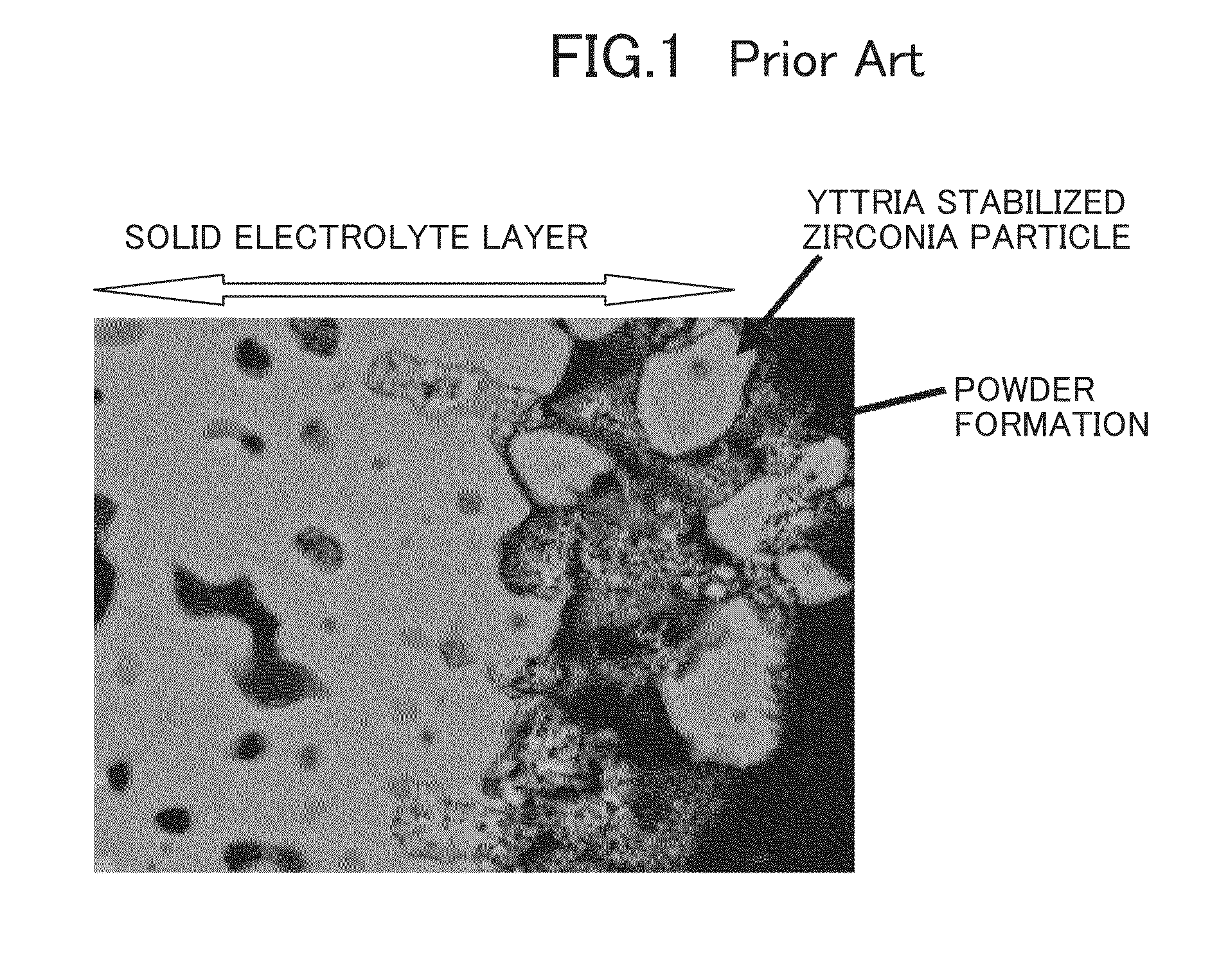
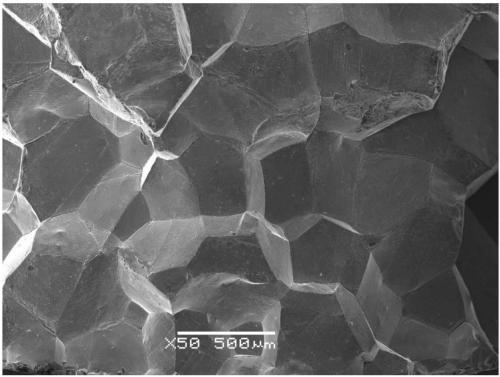
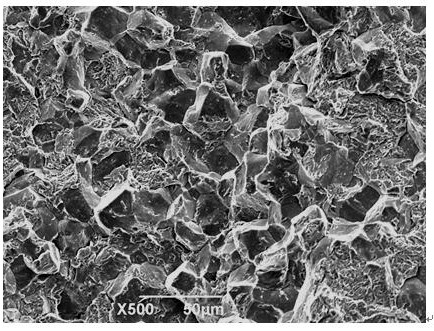
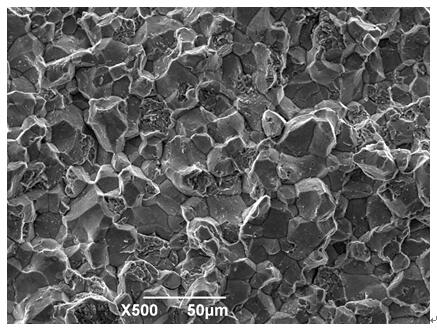
In certain materials and under certain conditions, the boundaries between the grains are the weakest regions in the material. An intergranular fracture is a type of fracture in which the crack propagates along the grain boundaries of the material, usually when these grain boundaries are weakened. Intergranular fracture is to be distinguished from the more commonly seen transgranular fracture, where the crack grows through the material grains rather than at the grain boundaries. Though less frequently observed, intergranular cracking is likely to occur if there is a hostile environmental influence and is favored by larger grain sizes and higher stresses. Intergranular cracking is possible at a wide range of temperatures. While transgranular cracking is favored by strain localization (which in turn is encouraged by smaller grain sizes), intergranular fracture is promoted by strain homogenization resulting from coarse grains.
Metal / ceramic microlaminate material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101413101AImprove toughnessReduce toughnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingElectron beam physical vapor depositionMetal sheet
The invention provides a metal / ceramic micro-lamination material and a preparation method thereof. The method adopts an electron beam physical vapor deposition technology and alternately evaporates a metal target material and a ceramic material through an electron gun to prepare the metal / ceramic micro-lamination material. The thickness of a ceramic layer is 1 mu m; and the thickness of a metal layer is between 10 and 35 mu m, and the volume fraction ratio of the metal layer and the ceramic layer, namely the thickness ratio or the thickness ratio of layers is between 10 and 35. The metal target material is Ni-20Co-12Cr-4Al (weightt percent); and the ceramic target material is ZrO2(YSZ) containing 8 weight percent of Y2O3. The metal / ceramic micro-lamination material has large thickness ratio of layers; therefore, the material can keep the characteristic of good toughness of the metal material to a great extent. Simultaneously, the existence of a lamination structure limits the growth of columnar crystals in the metal layer and reduce the possibility that crack expands along the metal grain boundary. Compared with a monolayer EB-PVD metal sheet, the metal layer of the micro-lamination material has less probability of brittle intergranular fracture and higher strength.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Production method of fine-grain high-strength PMN-PZT (lead zirconate titanate) piezoelectric ceramic material
The invention discloses a production method of a fine-grain high-strength PMN-PZT (lead zirconate titanate) piezoelectric ceramic material. The production method comprises the following steps of: weighing raw materials including PbO, MgO, Nb2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Bi2O3 and MnO2 in a stoichiometric ratio of (x)Pb(Mg1 / 3Nb2 / 3)O3-(1-x)Pb(TiyZr(1-y))O3-(a)Bi2O3-(b)MnO2-(c)Nb2O5-(d)ZnO-(e)SnO2, wherein x is 0.35-0.40, y is 0.40-0.70, and a, b, c, d, e are 0-1%; carrying out the process steps of ball milling, calcining, secondary ball milling, pelleting, tabletting, adhesion eliminating, sintering and the like to obtain a product. Therefore, by adopting the production method, the synthesis temperature of PMN-PZ-PT in the prior art can be greatly reduced, the compactness of a ceramic sample is high, the grain is tiny (-2 microns), the grain size is uniform, and a fracture mode realizes conversion from an intergranular fracture mode to a trans-granular fracture mode, namely the grain-boundary strength is greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU VOCATIONAL UNIV
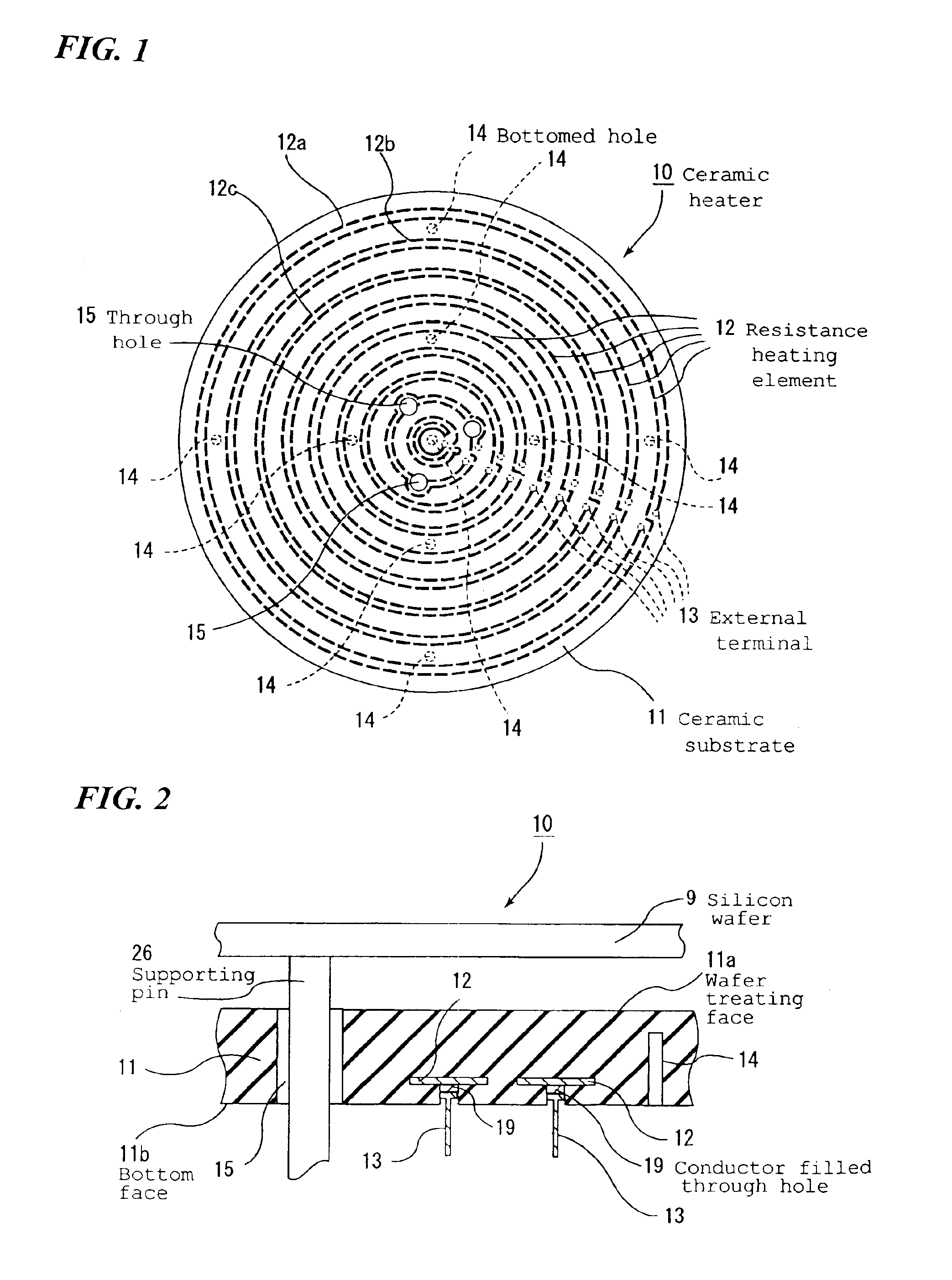
Ceramic substrate for manufacture/inspection of semiconductor
InactiveUS6888236B2Increase arcVolume resistivity dropSleeve/socket jointsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh fractureElectrical conductor
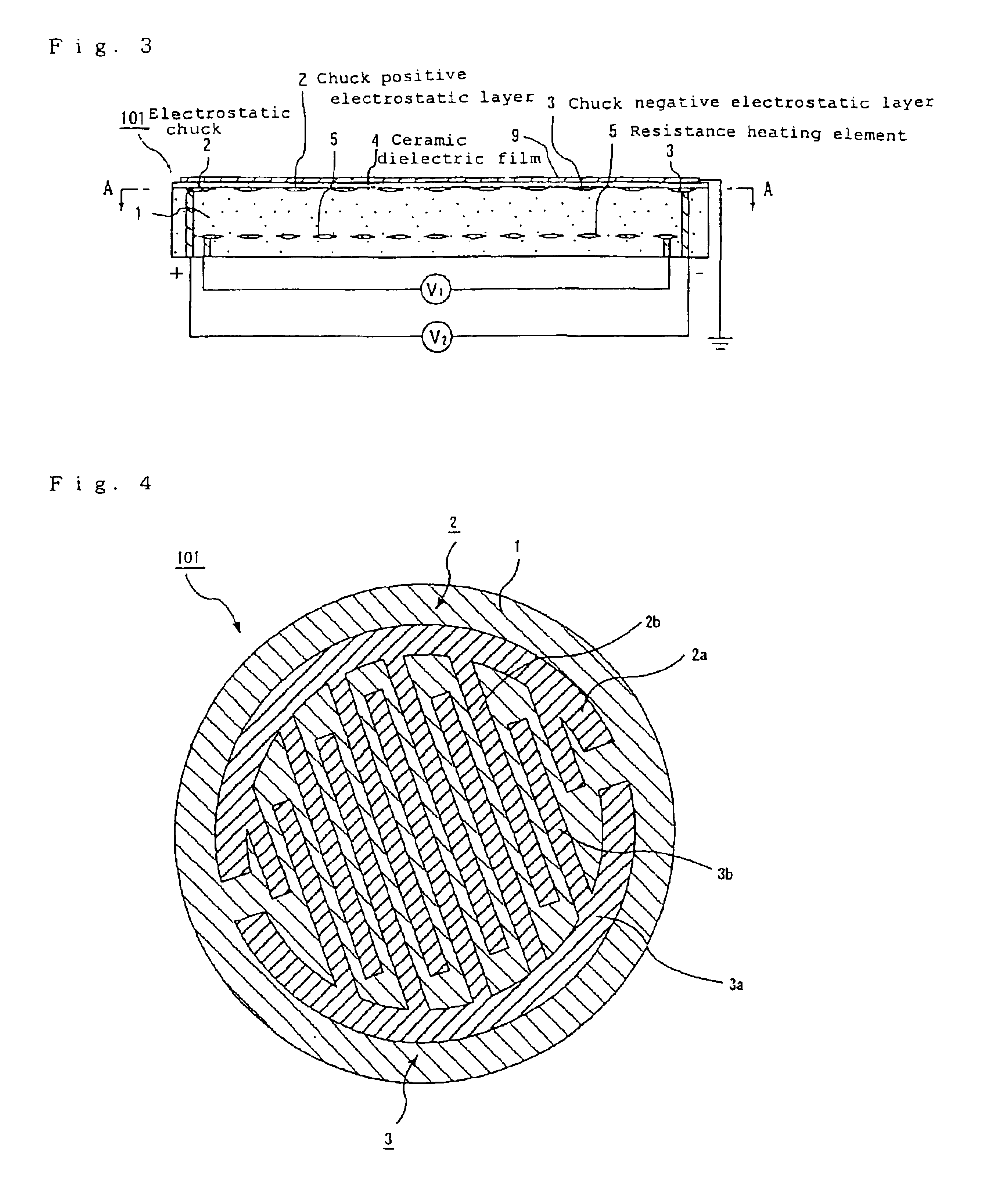
A ceramic substrate for a semiconductor producing / examining device which has high fracture toughness value, excellent thermal shock resistivity, high thermal conductivity and an excellent temperature rising and falling properties, can be used as a hot plate, an electrostatic chuck, a wafer prober and the like. A ceramic substrate, for a semiconductor producing / examining device, having a conductor formed inside or on the surface thereof has been sintered such that a fractured section thereof exhibits intergranular fracture.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
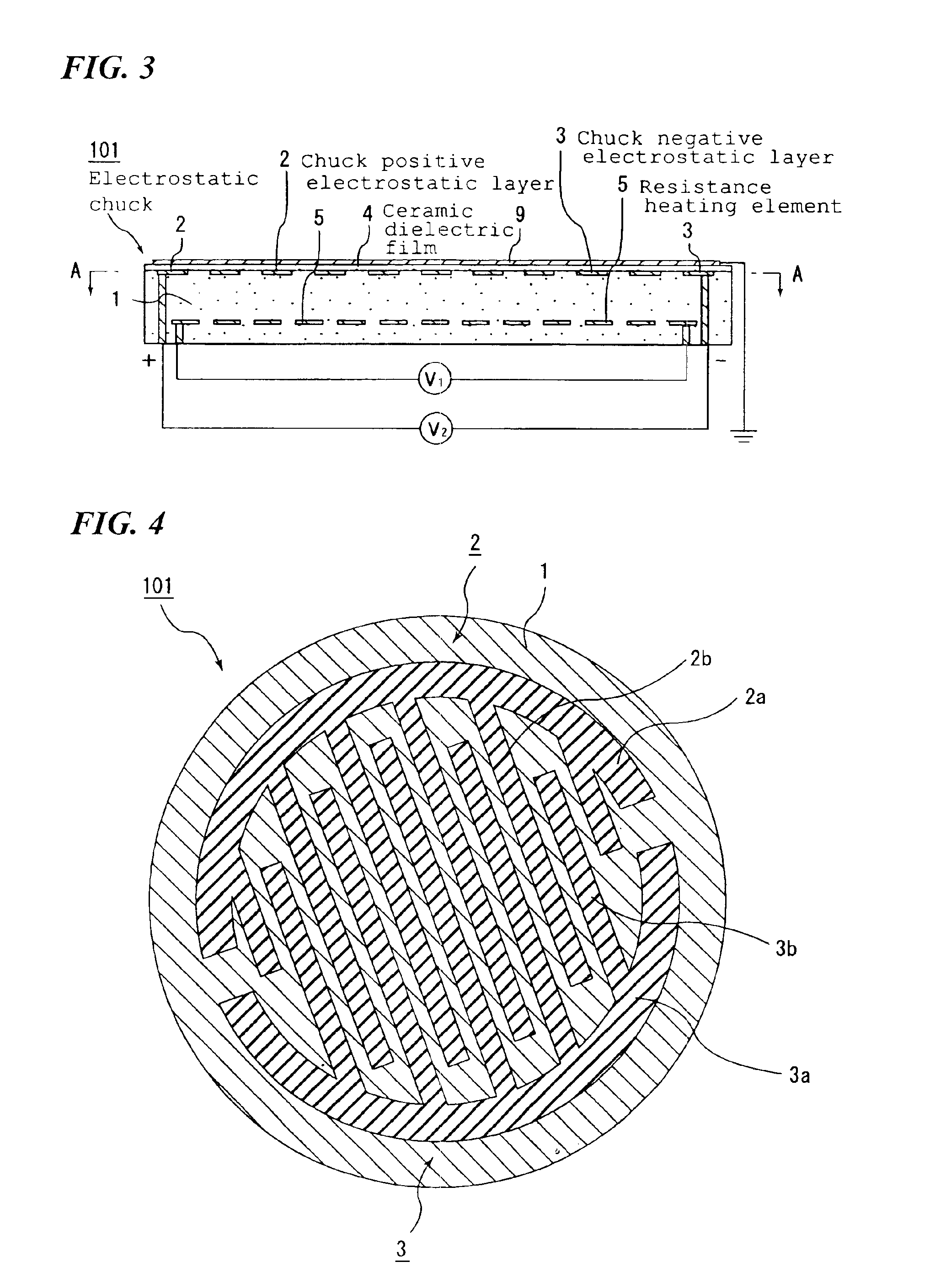
Ceramic substrate and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6878907B2Uniform temperatureReduce uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorHigh fracture
It is a an object of the present invention to provide a ceramic substrate for a semiconductor producing / examining device which has high fracture toughness value, exellent thermal shock resistivity, high thermal conductivity and an excellent temperature rising and falling properties, and is preferable as a hot plate, an electrostatic chuck, a wafer prober and the like. A ceramic substrate, for a semiconductor producing / examining device, having a conductor formed inside thereof or on the surface thereof of the present invention is the ceramic substrate, wherein said ceramic substrate has been sintered such that a fractured section thereof exhibits intergranular fracture.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Aluminum nitride sintered body and method of evaluation for the same
ActiveUS20050013761A1Effectively preventing droppingGood correlationSleeve/socket jointsNitrogen compoundsNitrideIntergranular fracture
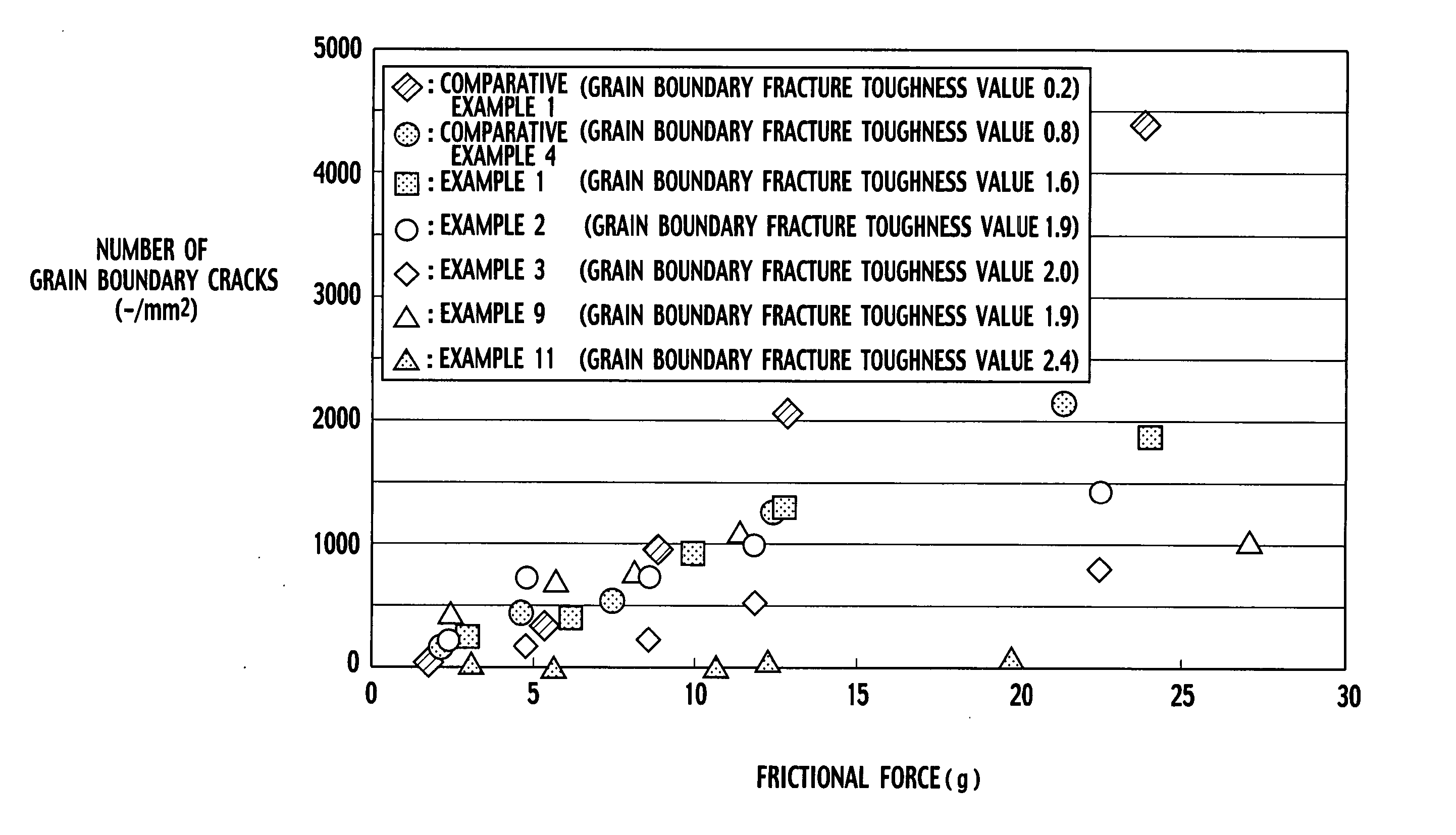
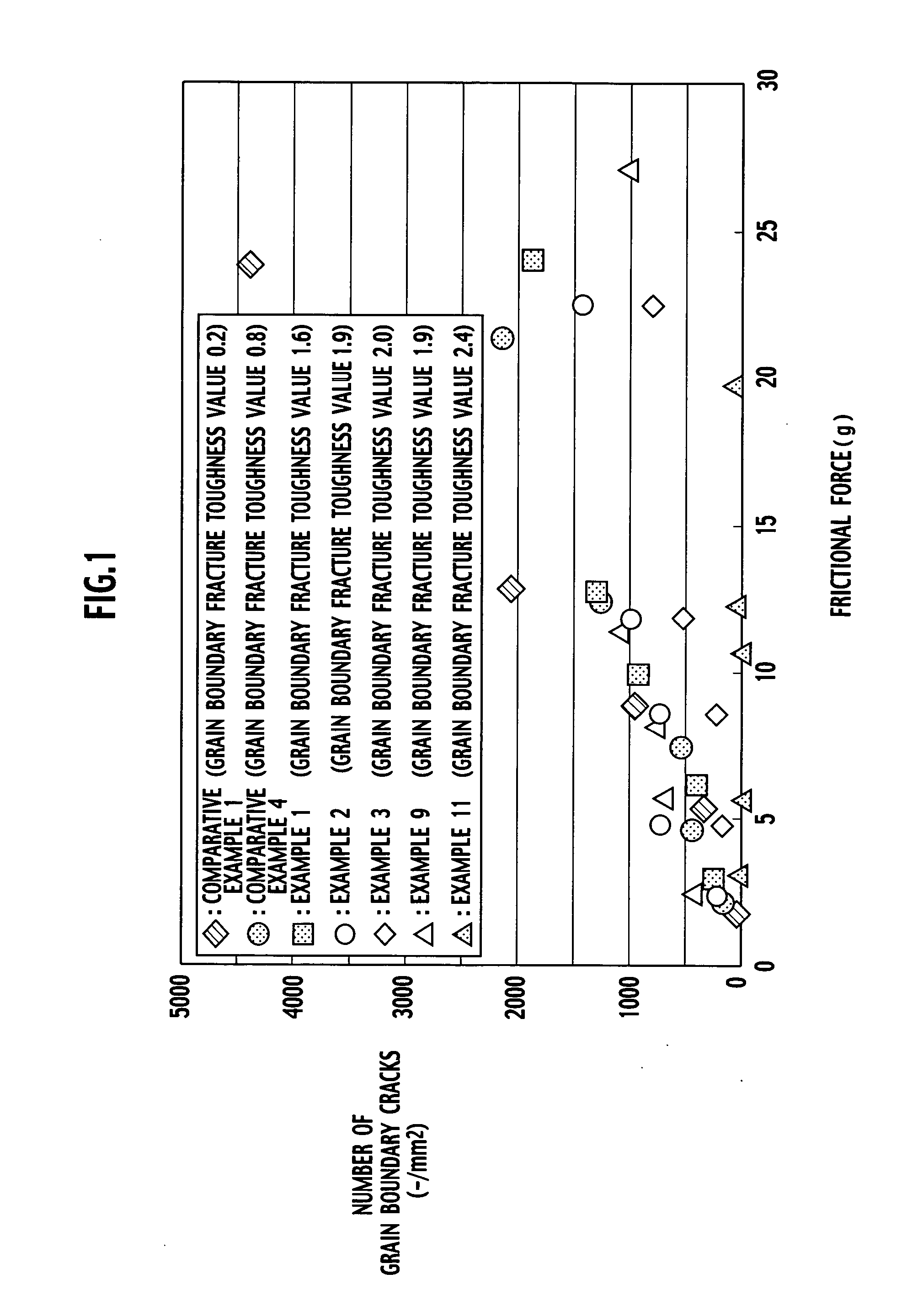
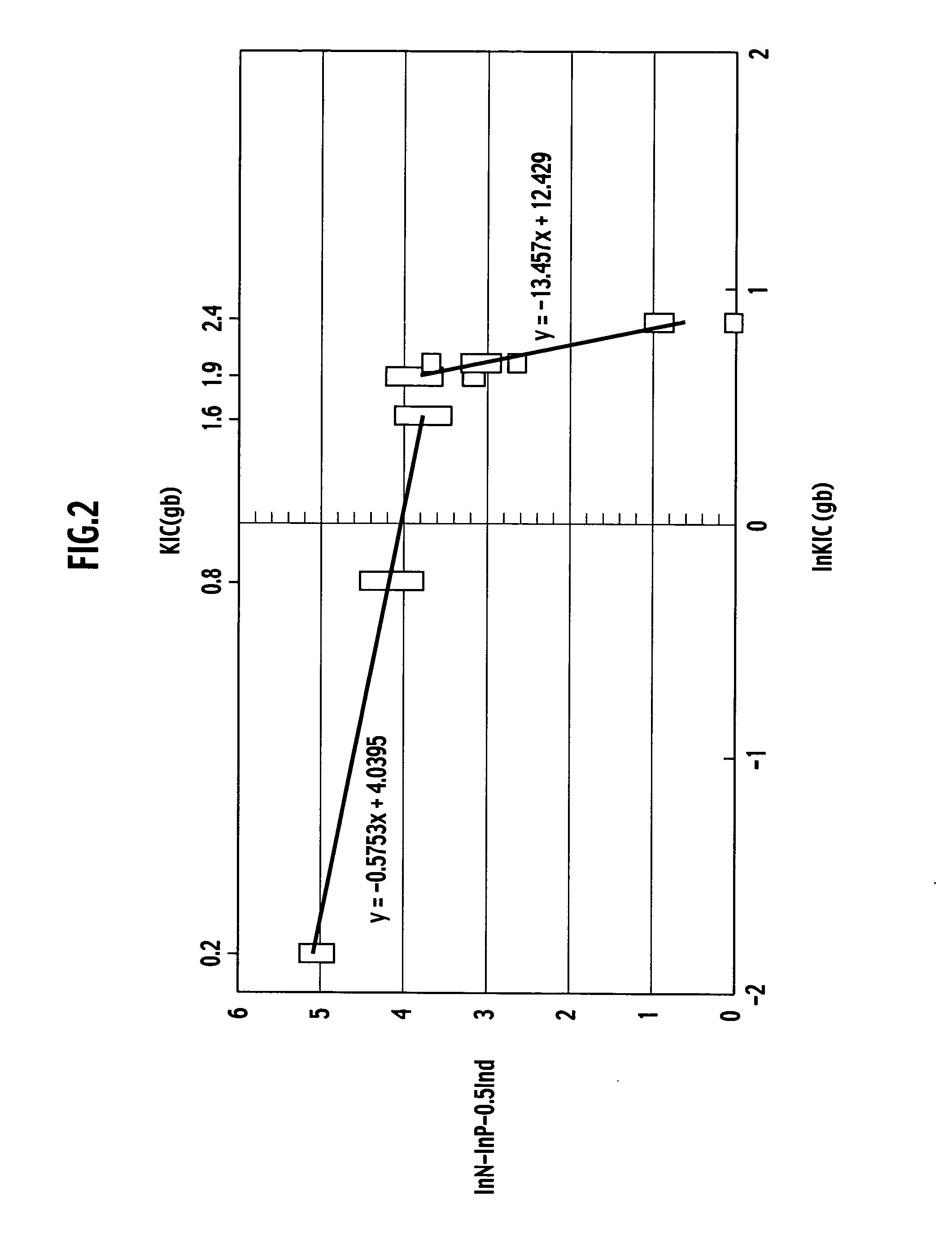
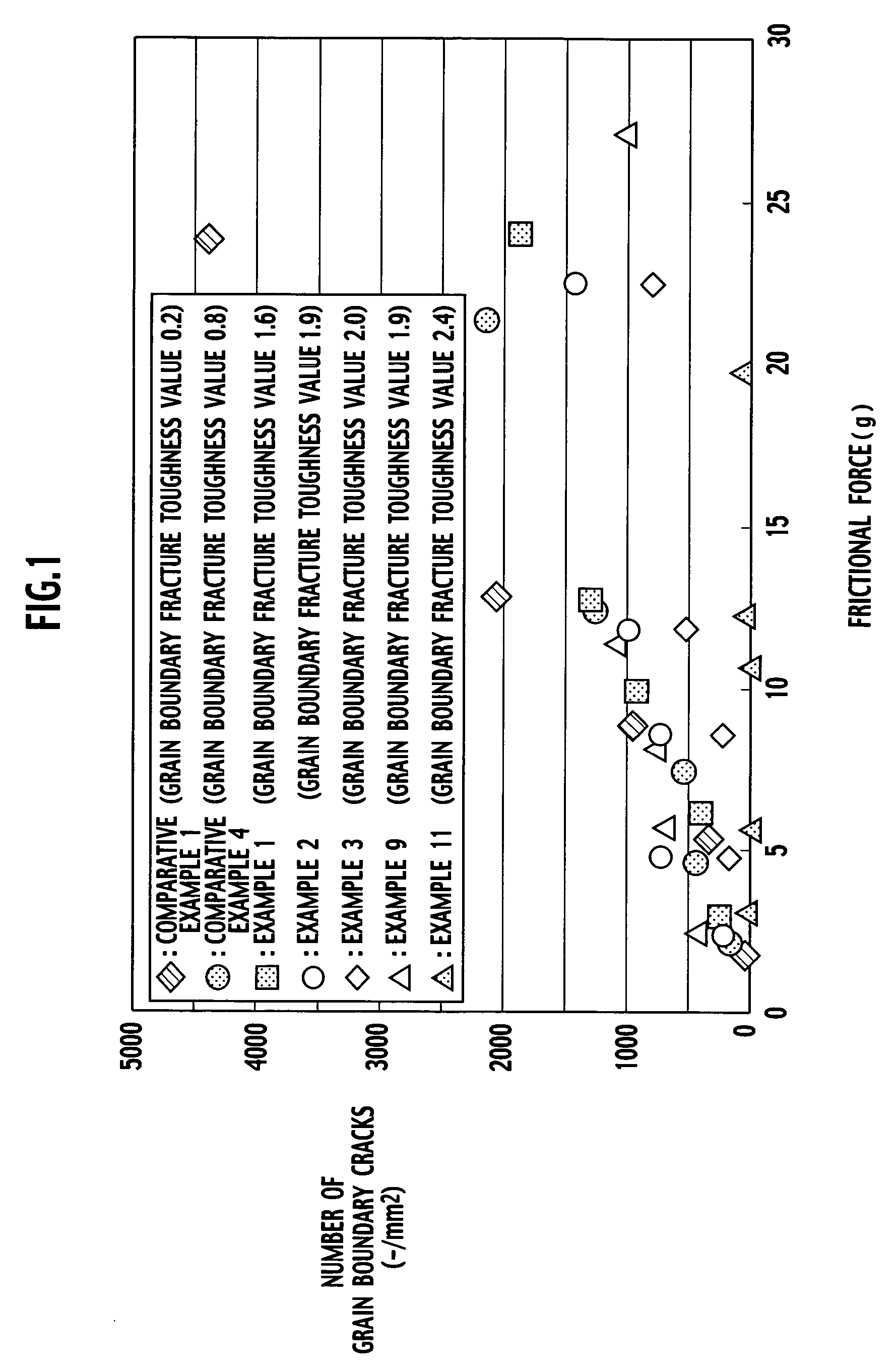
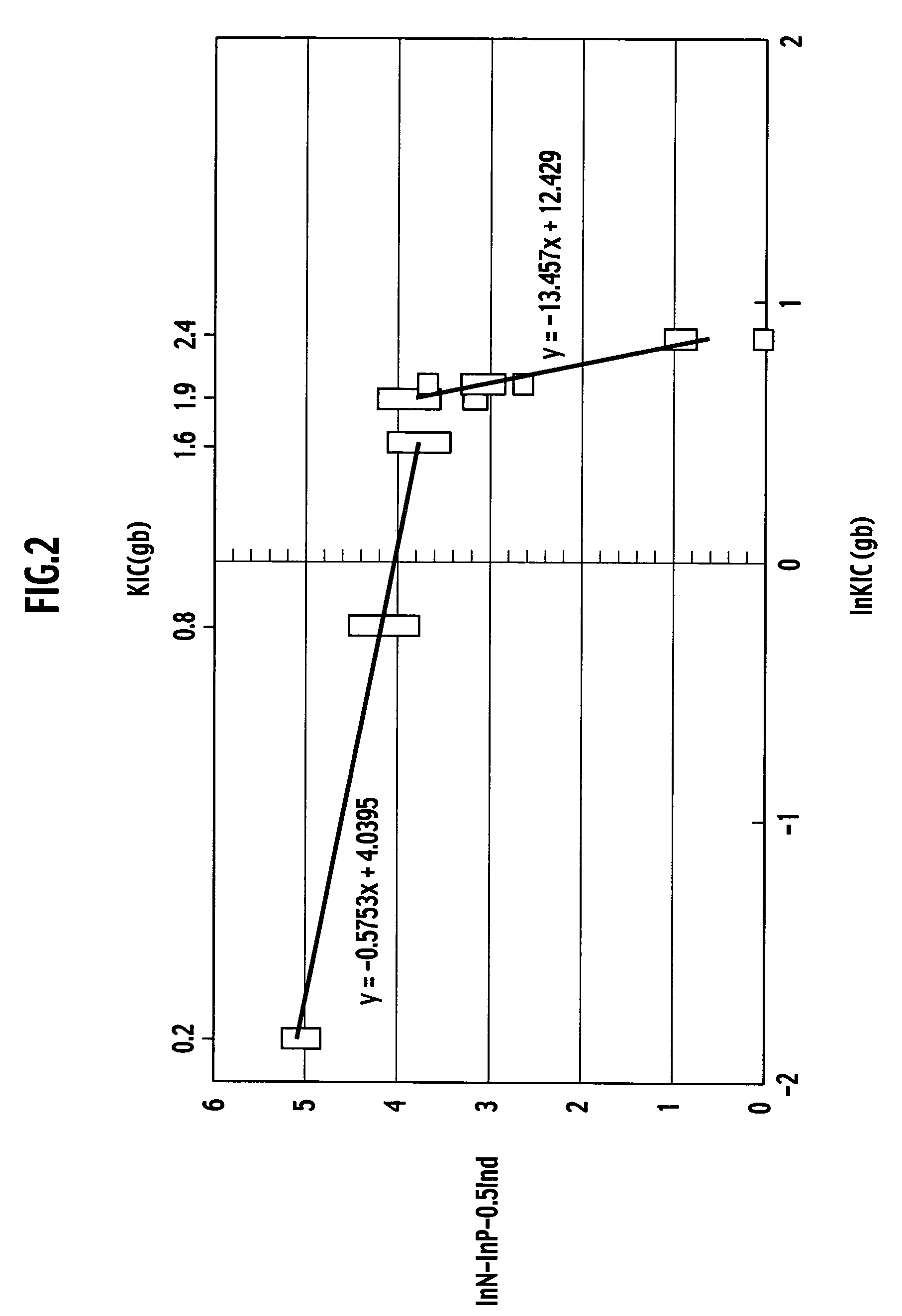
An aluminum nitride sintered body includes a polycrystalline structure in which grain boundary fracture toughness KICgb is 1.6 MPa·m1 / 2 or more. The grain boundary fracture toughness KICgb can be determined by the following equation: KICgb=KCIC·cos2(π·PIF / 200) where KIC is fracture toughness (MPa·m1 / 2), and PIF is a percentage of the intergranular fracture (%).
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Aluminum nitride sintered body and method of evaluation for the same
ActiveUS7288496B2Effectively preventing droppingGood correlationSleeve/socket jointsNitrogen compoundsIntergranular fractureNitride
An aluminum nitride sintered body is provided, including a polycrystalline structure in which grain boundary fracture toughness KICgb is 1.6 MPa·m1 / 2 or more. The grain boundary fracture toughness KICgb is determined by the equation KICgb=KIC·cos2(π·PIF / 200), wherein KIC is fracture toughness (MPa·m1 / 2), and PIF is a percentage of the intergranular fracture (%).
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Tensile fracture determining method for crack forming period of steel and iron material
ActiveCN108181170AImprove the accuracy of judgmentPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFailure analysisAnalysis method
The invention relates to a tensile fracture determining method for a crack forming period of a steel and iron material, which belongs to the technical field of failure analysis of a steel and iron material. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing a tensile sample comprising cracks, performing the breaking test, separating two crack surfaces, and determining the crack forming period according to characteristics of the existence of dimples of a micro-morphology of a fracture, cleavage, quasi-cleavage or intergranular fracture and the like. The method has the advantages that compared with the existing metallographic observation method, the tensile fracture analysis method does not damage the morphology of the crack and micro-tissues nearby the crack, so that the determination accuracy of the crack forming period can be improved, and the important evidence can be provided for analyzing the forming reason of the crack and making the preventive measures.
Owner:BEIJING BEIYE FUNCTIONAL MATERIALS CORP
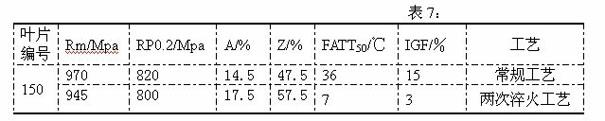
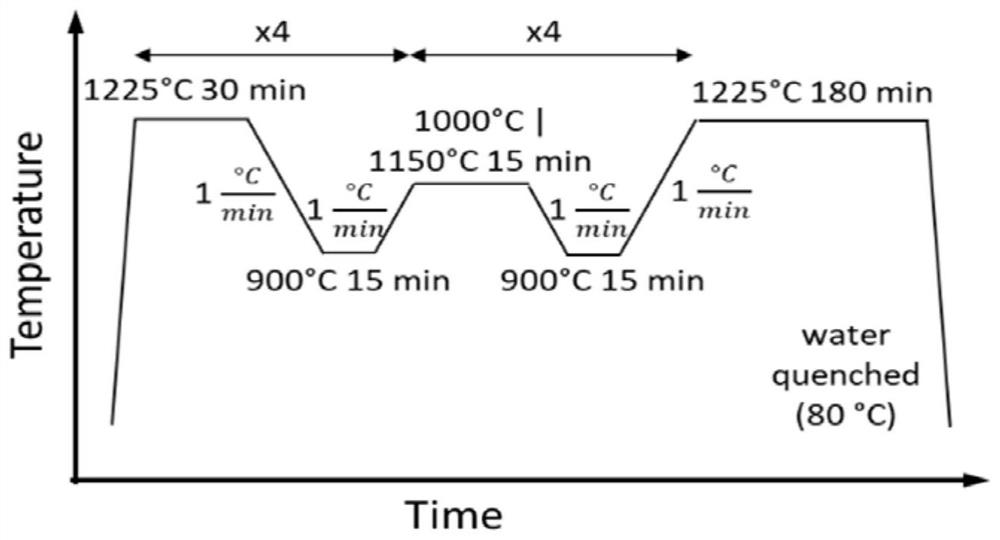
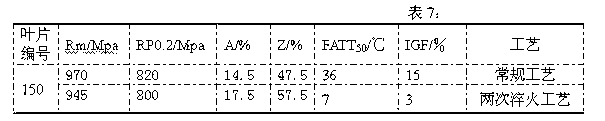
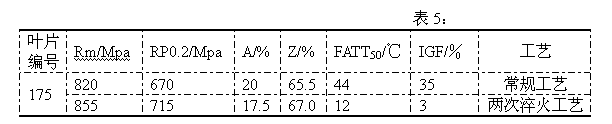
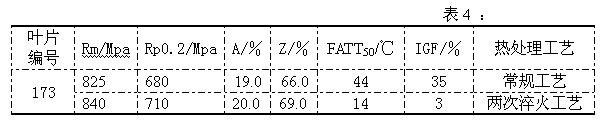
Heat process capable of lowering ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades
ActiveCN102220459AShort residence time at high temperatureFully solid solutionFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlChemical compositionTurbine blade
The invention provides a heat treatment process capable of lowering ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades. When the heat treatment process is used, the problem that the process effect is susceptible to influences of chemical components of the raw material of the blades when the conventional sub-temperature annealing process is used to treat the turbine blades and the problem of high ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of the turbine blades due to overlong high-temperature retention during heat treatment ofthe blades in the sub-temperature annealing process are solved. In the invention, the blades are uniformly placed in a common quenching material basket according to a technical scheme and then the quenching material basket is placed in a heat treatment quenching furnace. The heat treatment process is characterized in that: the blades are quenched twice in a quenching furnace; the temperature of primary quenching is 980 to 1070 DEG C; the temperature is kept constant for 1 to 3 hours; the cooling speed is 20 to 50 DEG C per minute; the temperature of secondary quenching is 900 to 1,000 DEG C; the temperature is kept constant for 15 to 120 minutes; the cooling speed is 30 to 50 DEG C minutes; and the temperature of the primary quenching is 20 to 100 DEG C higher than the temperature of the secondary quenching.
Owner:WUXI TURBINE BLADE
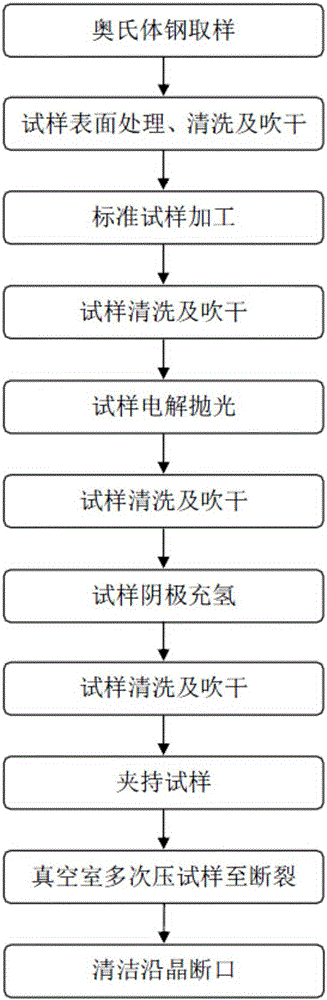
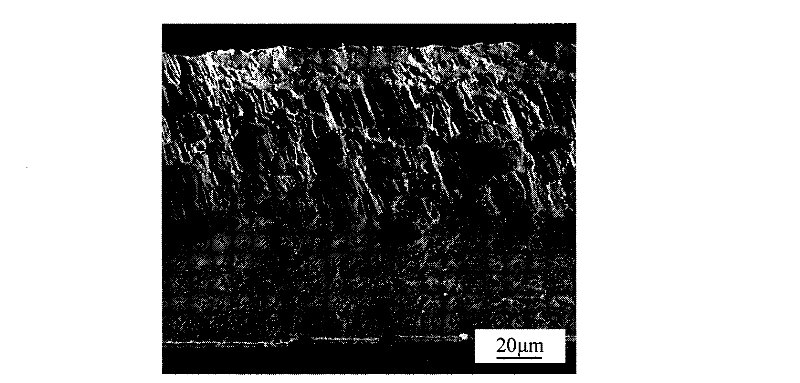
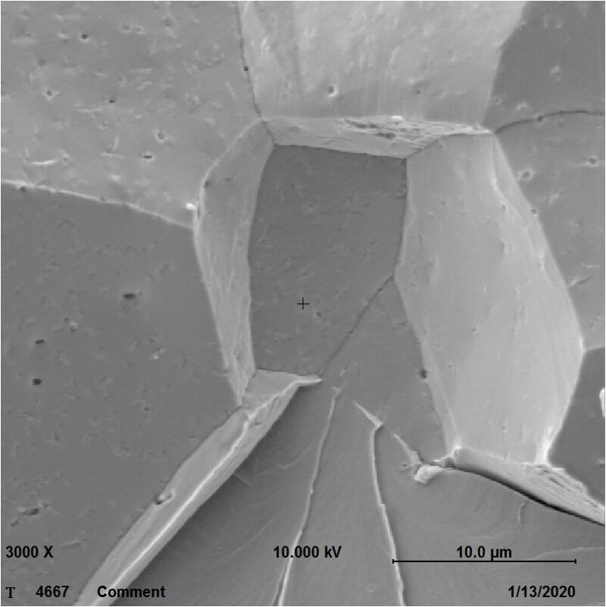
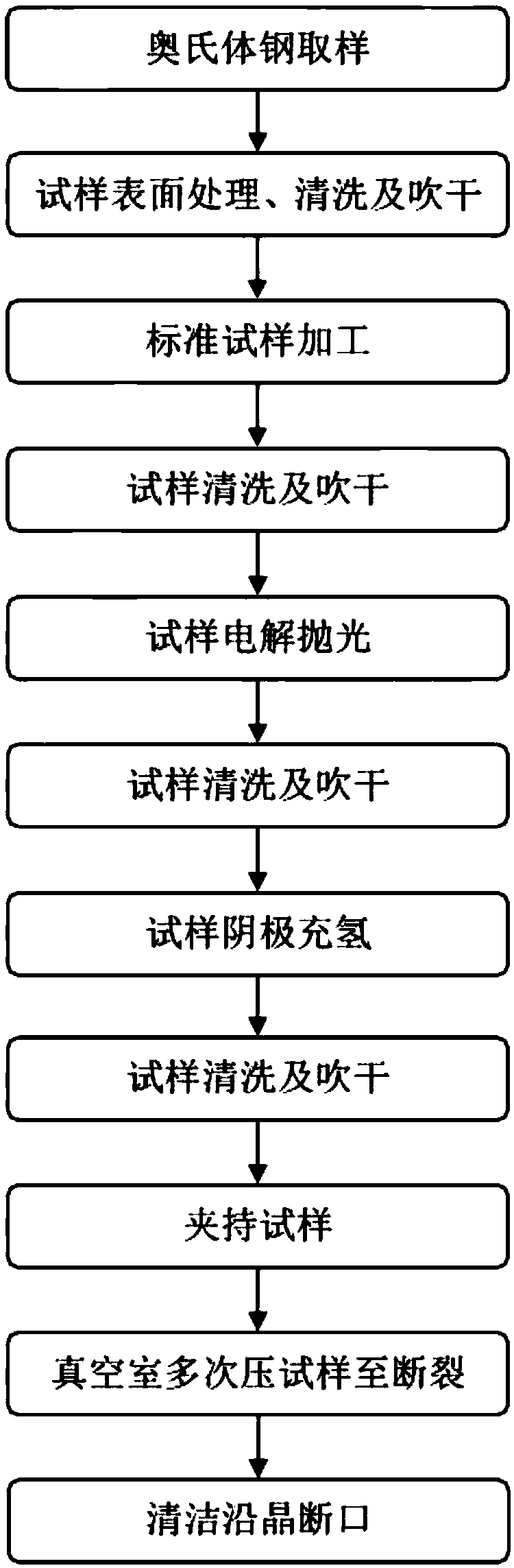
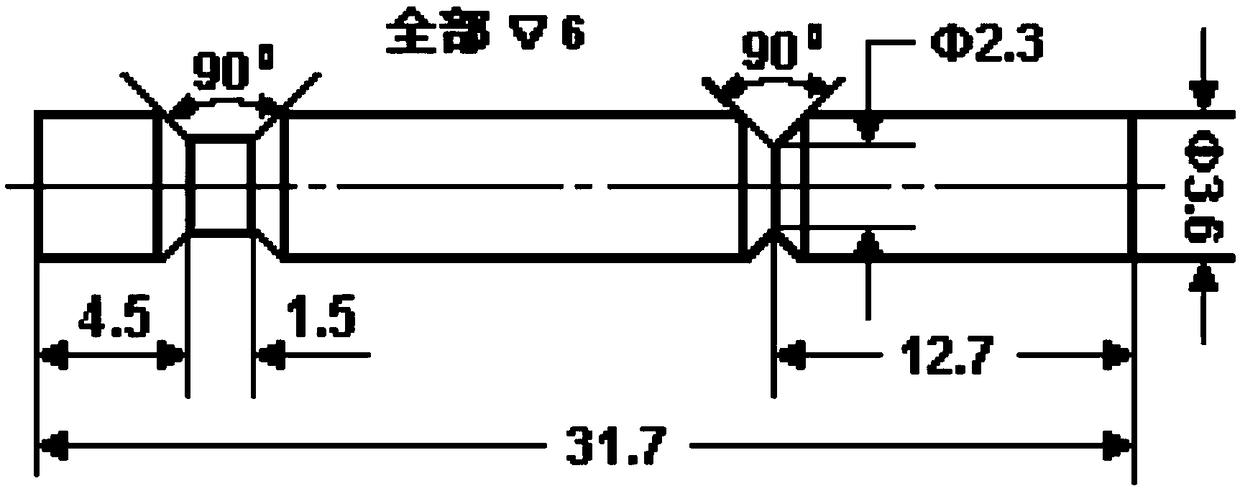
Method for obtaining intergranular fracture from austenite steel and application of method
The invention provides a method for obtaining an intergranular fracture from austenite steel and application of the method. According to the method, after the surface of an austenite steel sample is electrolytic-polished, the austenite steel sample is subjected to cathodic hydrogen charging; then the two ends of the austenite steel sample are clamped for a while, and the austenite steel sample is put into a surface analyzing device; under the vacuum environment, the preset fracture of the austenite steel sample is primarily pressed for many times, then the preset fracture of the austenite steel sample is pressed to be broken at a time, and the intergranular fracture is obtained. The method is simple in technique and short in time consumption; operation steps are simple and controllable and easy to achieve; and the austenite steel fracture obtained through the method is a typical intergranular fracture, pollution can be effectively avoided, objective and accurate evidences can be provided for component analysis of a grain boundary, and the intergranular fracture is applicable to component analysis of the grain boundary of austenite steel.
Owner:BEIJING CISRI GAONA TECH +1
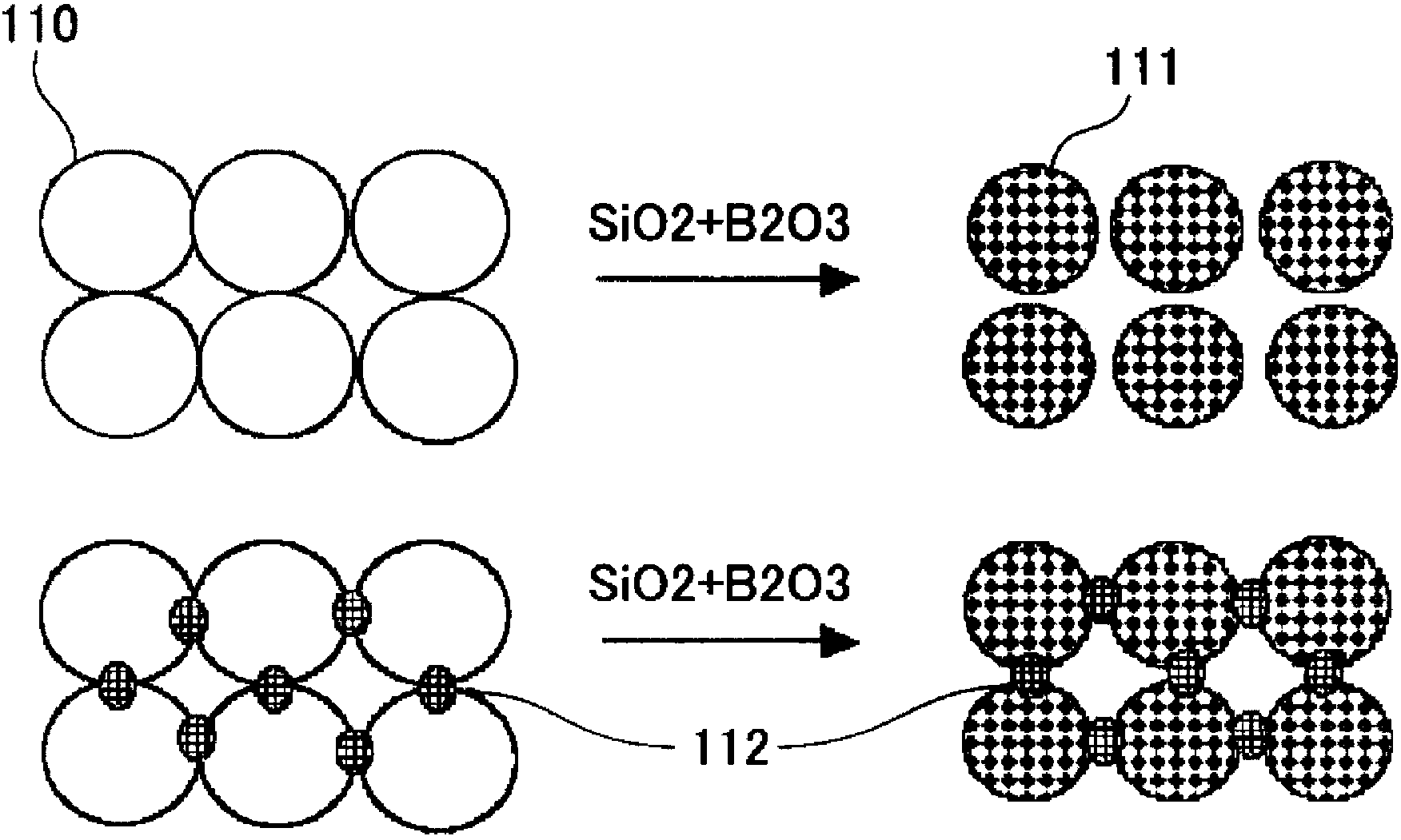
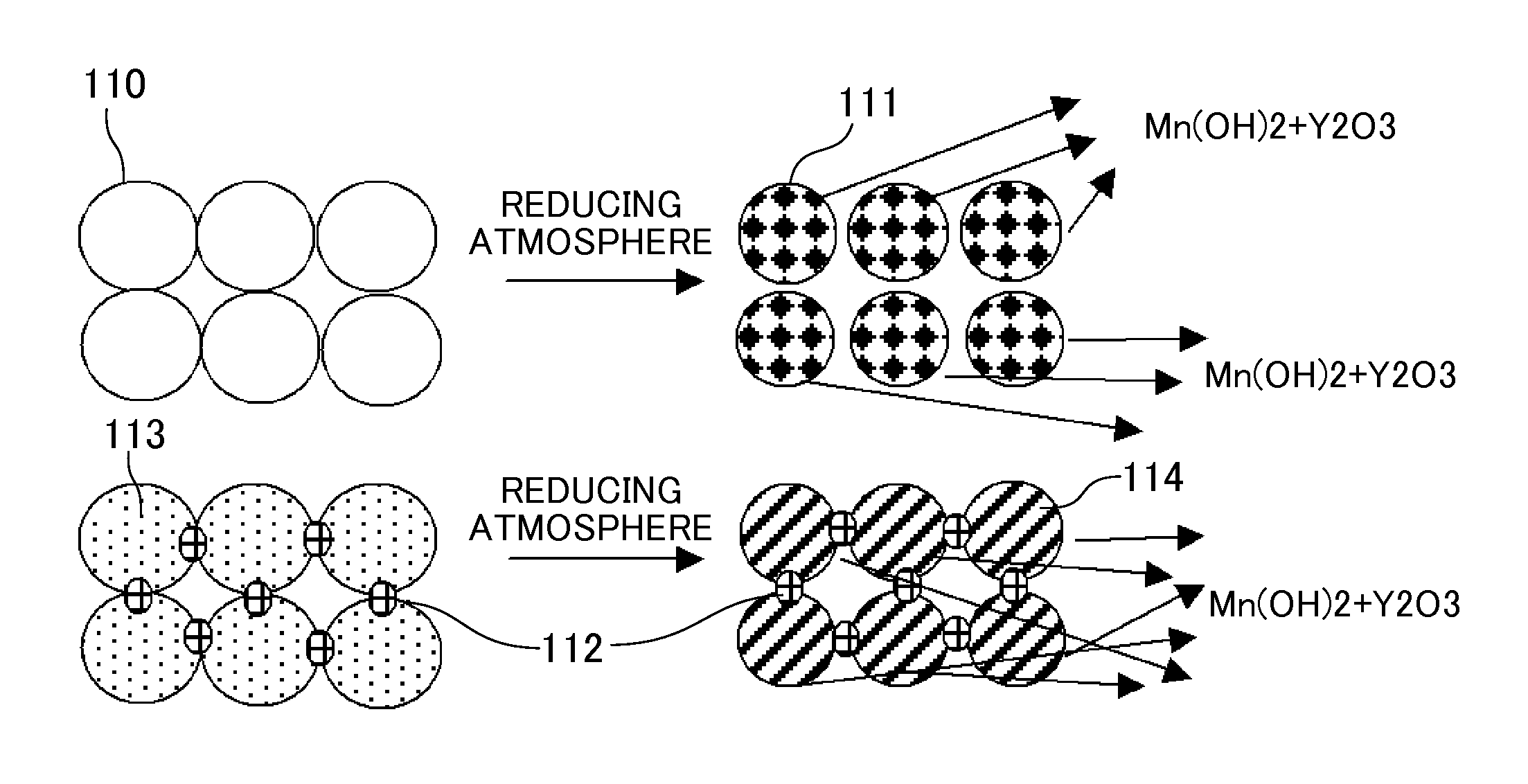
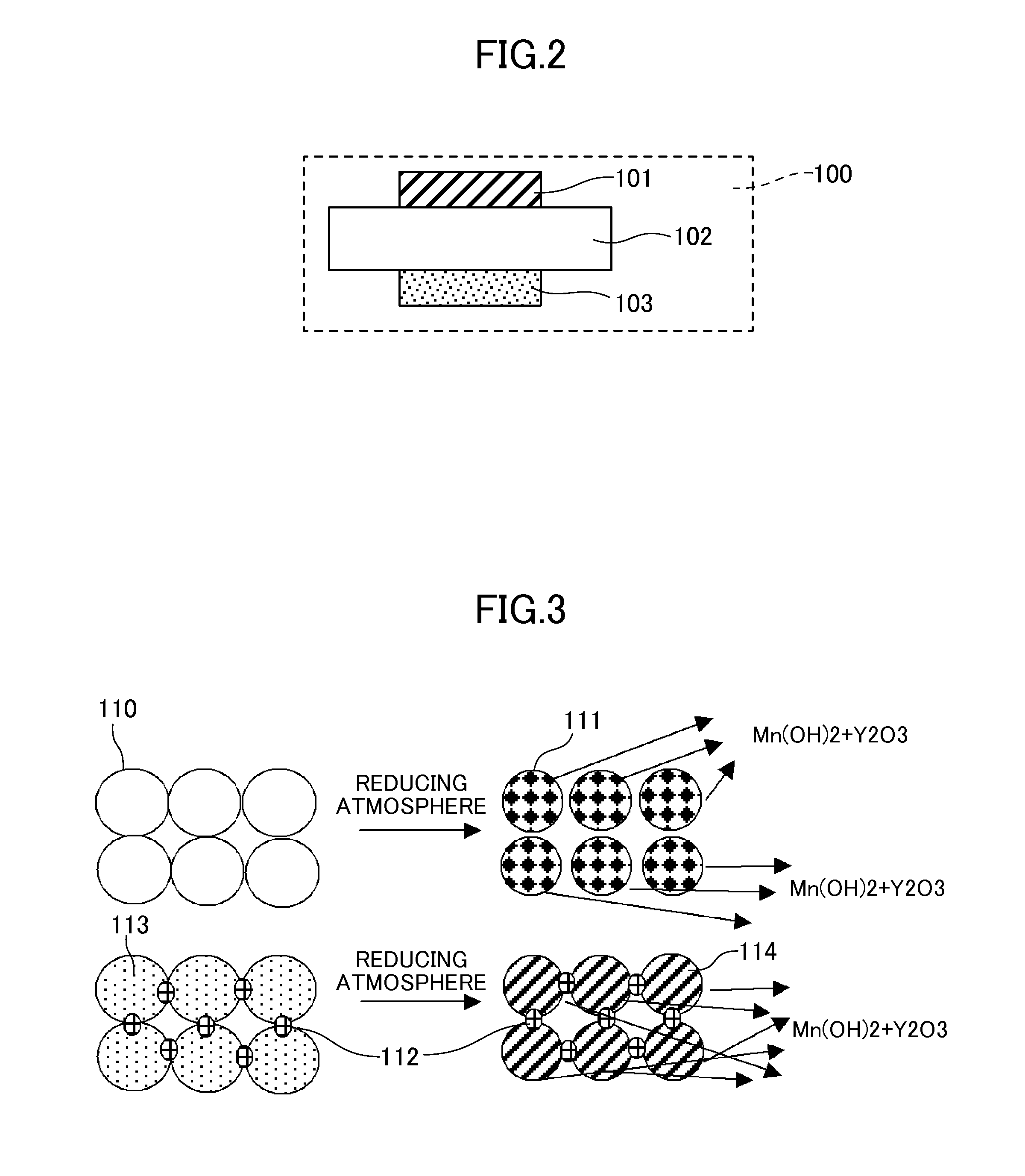
Solid electrolyte material and solid oxide fuel cell provided with same
InactiveCN103477483AInhibit chalking and peelingFinal product manufactureOxide conductorsFuel cellsIntergranular fracture
Provided is a solid electrolyte material which, while maintaining high oxygen ion conductivity, minimizes the discomposition of scandia caused by impurities such as silicon in the fuel gas, and improves intergranular strength in order to eliminate intergranular fracture caused by crystalline modification. The solid electrolyte material is a zirconia solid electrolyte material having scandia and a lanthanoid oxide and / or yttria dissolved therein, and has alumina further added thereto.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Method for preparing neodymium iron boron magnetic powder for sintered magnet
ActiveCN108133796AImprove magnetismImprove coercive forceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsHydrogenCoupling
The invention provides a method for preparing neodymium iron boron magnetic powder for a sintered magnet, and belongs to the field of magnetic materials. The method includes the followingprocesses that neodymium iron boron powder particles are prepared by adopting a gas atomization method, crystalline grains inside the powder particles grow to 1-3 microns by vacuum heat treatment, the intergranular fracture of the powder particles occurs after hydrogen decomposing, and single crystal particles with a particle size of 1 to 3 microns are finally obtained after dehydrogenation. The method has theadvantages that the neodymium-rich phase of the neodymium iron boron particles prepared by the gas atomization method is evenly distributed at the boundary ofNd2Fe14B main phase crystalline grains, and the neodymium-rich phase uniformly covers the surface of the Nd2Fe14B main phase crystalline grains in the form of a thin layer by means of hydrogen absorption intergranular fracture, so that the neodymium-rich phase in the finally prepared sinteredneodymium iron boronmagnetuniformly covers the periphery of the Nd2Fe14B main phase crystalline grains in the form of a thin layer, demagnetizationexchange coupling is greatly enhanced, neodymium iron boroncrystalline grains prepared by the method are fine and uniform, and the magnetic properties of the obtained neodymium iron boron magnet, particularly the coercive force, are high after orientation molding, sintering and tempering treatment areconducted on the neodymium iron boron magnetic powder prepared by the method.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Solid electrolyte material and solid oxide fuel cell provided with same
InactiveUS20130316266A1High oxygen ion conductivitySuppresses extractionFinal product manufactureConductive materialFuel cellsUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a solid electrolyte material provided which, while maintaining a high oxygen ion conductivity, minimizes the extraction of scandia caused by impurities such as silicon in the fuel gas, and has improved intergranular strength in order to eliminate intergranular fracture caused by crystalline modification. The solid electrolyte material is a zirconia solid electrolyte material having yttria dissolved therein, has cubic crystals as the main ingredient, and is further characterized by having a lanthanoid oxide dissolved therein.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Detection and characterization method of intergranular fracture and trans-granular fracture of WC grains in WC-Co alloy
ActiveCN107389711ASolve the fracture processing problemSolve processing problemsMaterial strength using steady bending forcesMaterial strength using single impulsive forceQuality controlAlloy
The invention discloses a detection and characterization method of intergranular fracture and trans-granular fracture of WC grains in WC-Co alloy. The method successively comprises the following steps: conducting a bending strength test or an impact toughness test on a hard alloy test strip and recording a result; carrying out surface binder phase Co removal treatment on a fracture sample of a sample strip; cleaning and drying; observing trough a scanning electron microscope, and taking view pictures of different parts; counting grain number of hard phase WC grains of intergranular fracture and trans-granular fracture in the fracture sample (the total number is not lower than 200), calculating the proportion of trans-granular fracture grains, namely trans-granular fracture rate being characterized in the specification, and catalyzing and obtaining the relation between trans-granular fracture rate and bending strength or impact toughness. According to the invention, qualitative and quantitative analysis of intergranular fracture and trans-granular fracture of WC grains with hard phase alloy fractures can be carried out. The method of the invention plays a guiding role in quality control and scientific study of hard alloys.
Owner:ZHUZHOU HARD ALLOY GRP CO LTD
Low-temperature sealing glass and preparation method thereof
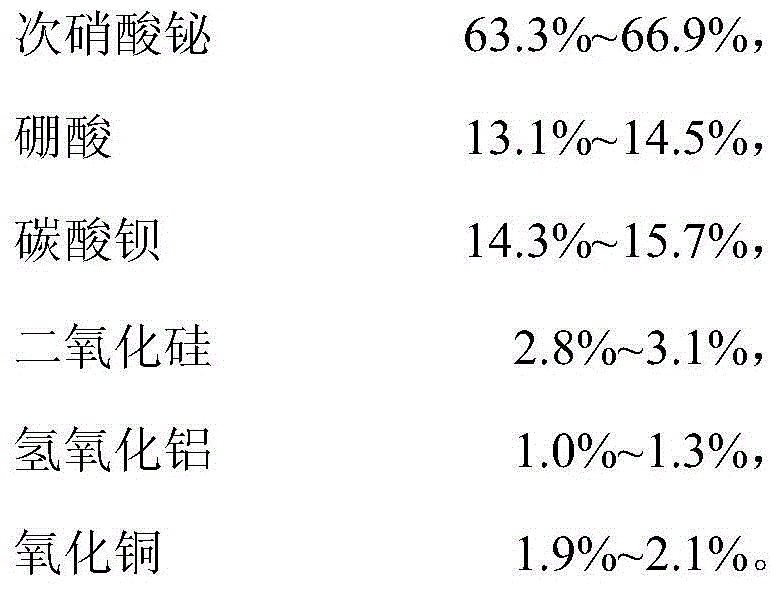
ActiveCN103739200AGuaranteed toughnessWill not cause brittle fractureAluminium hydroxideCopper oxide
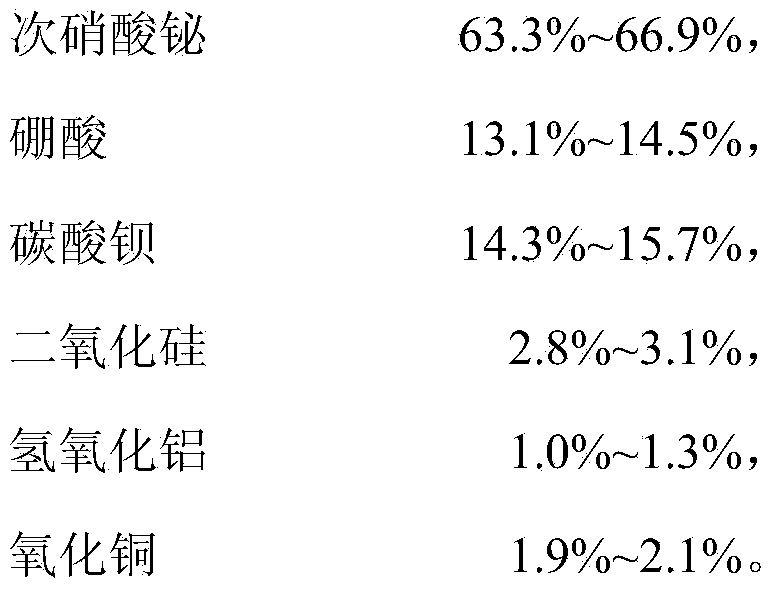
The invention relates to low-temperature sealing glass and a preparation method thereof. The low-temperature sealing glass comprises the compositions in percent by weight: 63.3%-66.9% of bismuth subnitrate, 13.1%-14.5% of boric acid, 14.3%-15.7% of barium carbonate, 2.8%-3.1% of silica, 1.0%-1.3% of aluminium hydroxide and 1.9%-2.1% of copper oxide; and the balance is unavoidable impurities. Undamaged sintering effect can be reached at low temperature when the low-temperature sealing glass is prepared according to requirements; the low-temperature sealing glass has good sealing performance; and when sintering is performed at the temperature, because the temperature is low and crystal grains of the material grow slowly, the material crystal grains does not show obvious growth and the material keeps original toughness when sintering is finished and the material crystal grains are subjected to microstructure analysis, so that intergranular fracture of a hot electrode at high temperature cannot be caused.
Owner:SUZHOU CHANGFENG AVIATION ELECTRONICS
Toughened silicon carbide and method for making the same
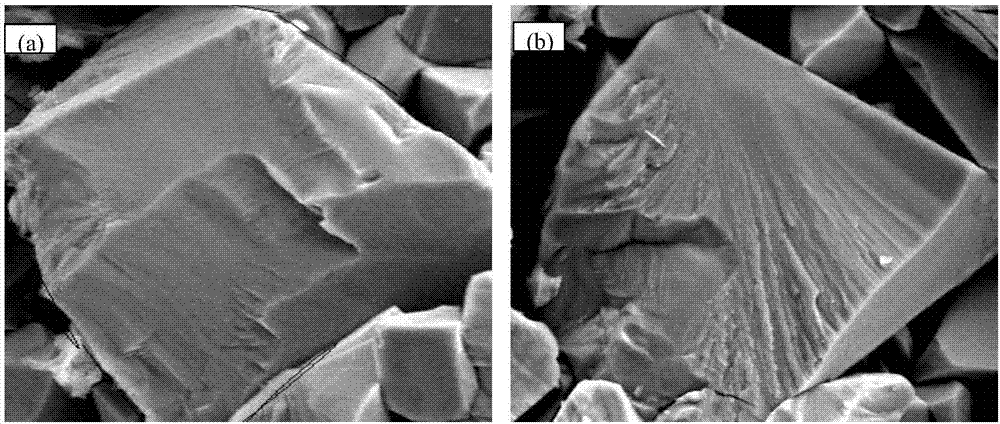
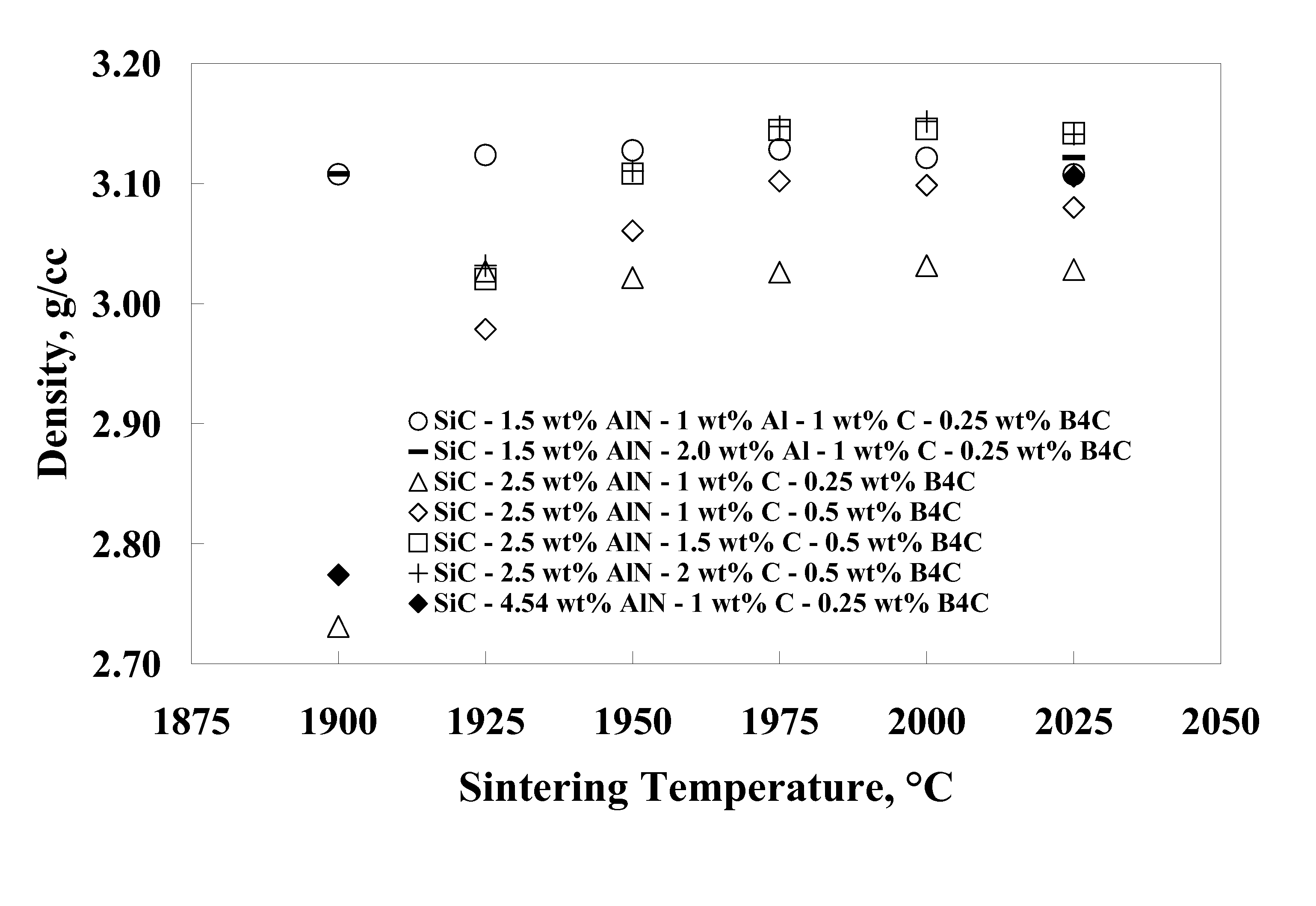
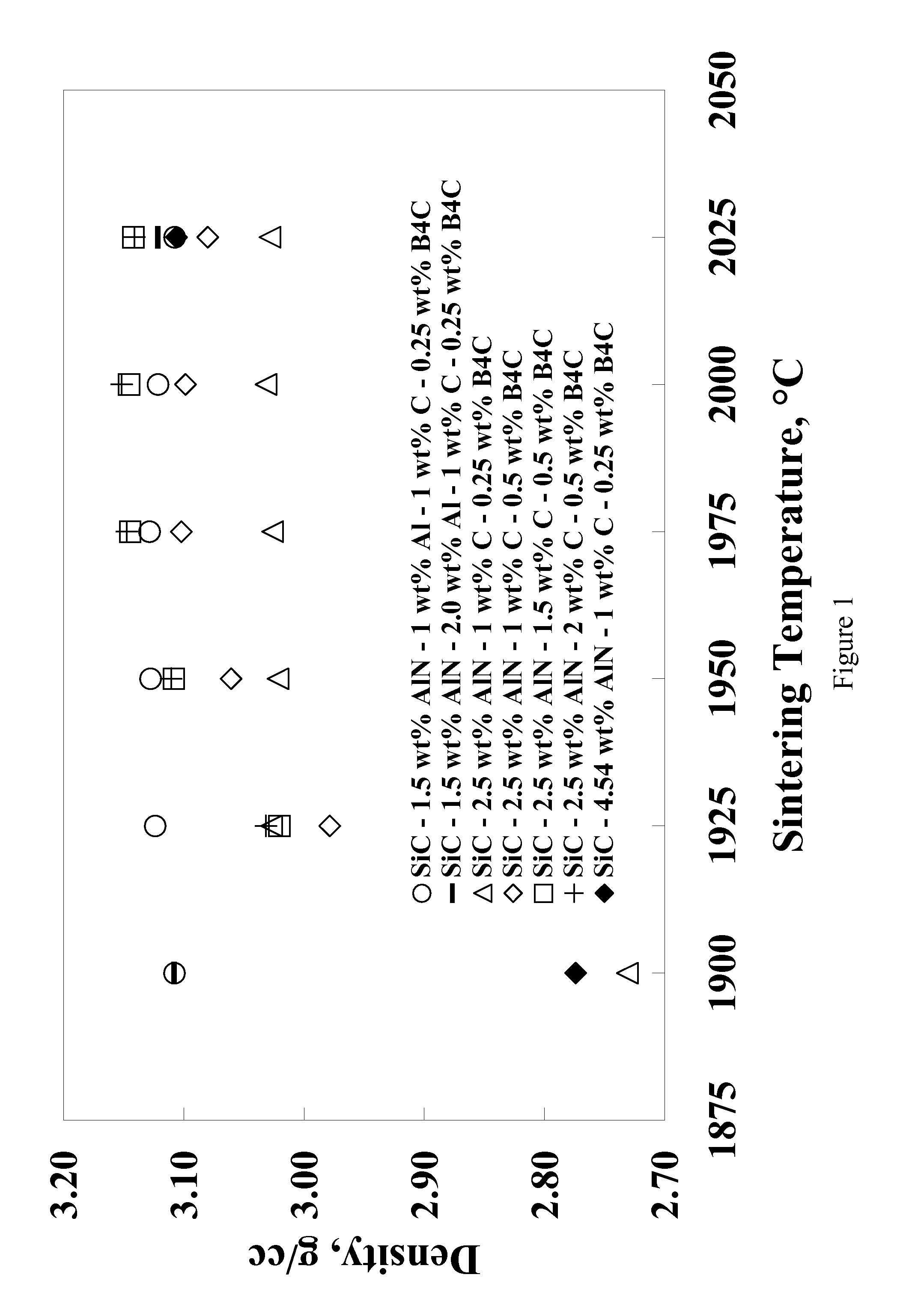
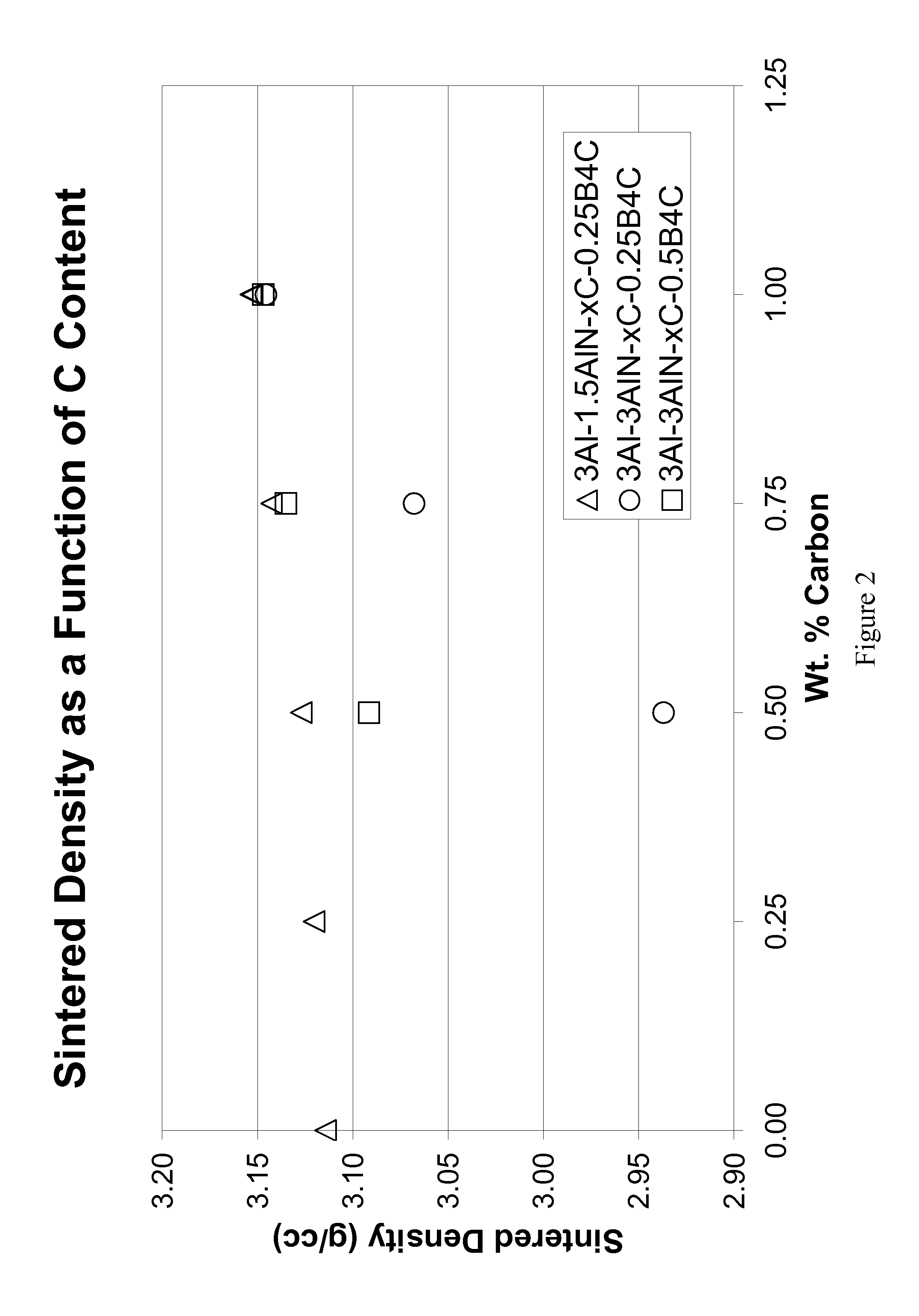
Pressureless sintering of silicon carbide with fracture toughness in excess of about 4 MPa-m1 / 2 as measured by the single-edge precracked beam (SEPB) technique while maintaining a density greater than 3.1 g / cc for compositions with SiC greater than about 94 wt. % is made possible through the use of metallic Al to promote sintering and grain growth. Boron and carbon may be used as traditional sintering aids, with nitrogen to suppress grain growth, and additions of yttrium and / or lanthanide elements to promote intergranular fracture.
Owner:COORSTEK INC
Solid electrolyte material and solid oxide fuel cell provided with same
InactiveCN103477482AInhibit chalking and peelingNon-metal conductorsFinal product manufactureFuel cellsUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a solid electrolyte material provided which, while maintaining a high oxygen ion conductivity, minimizes the extraction of scandia caused by impurities such as silicon in the fuel gas, and has improved intergranular strength in order to eliminate intergranular fracture caused by crystalline modification. The solid electrolyte material is a zirconia solid electrolyte material having yttria dissolved therein, has cubic crystals as the main ingredient, and is further characterized by having a lanthanoid oxide dissolved therein.
Owner:TOTO LTD
A kind of preparation method of highly dispersed ultrafine neodymium oxide
ActiveCN111304469BImprove finenessEasy to shapeLanthanide oxides/hydroxidesRare earth metal compounds preparation/treatmentDispersityMicron scale
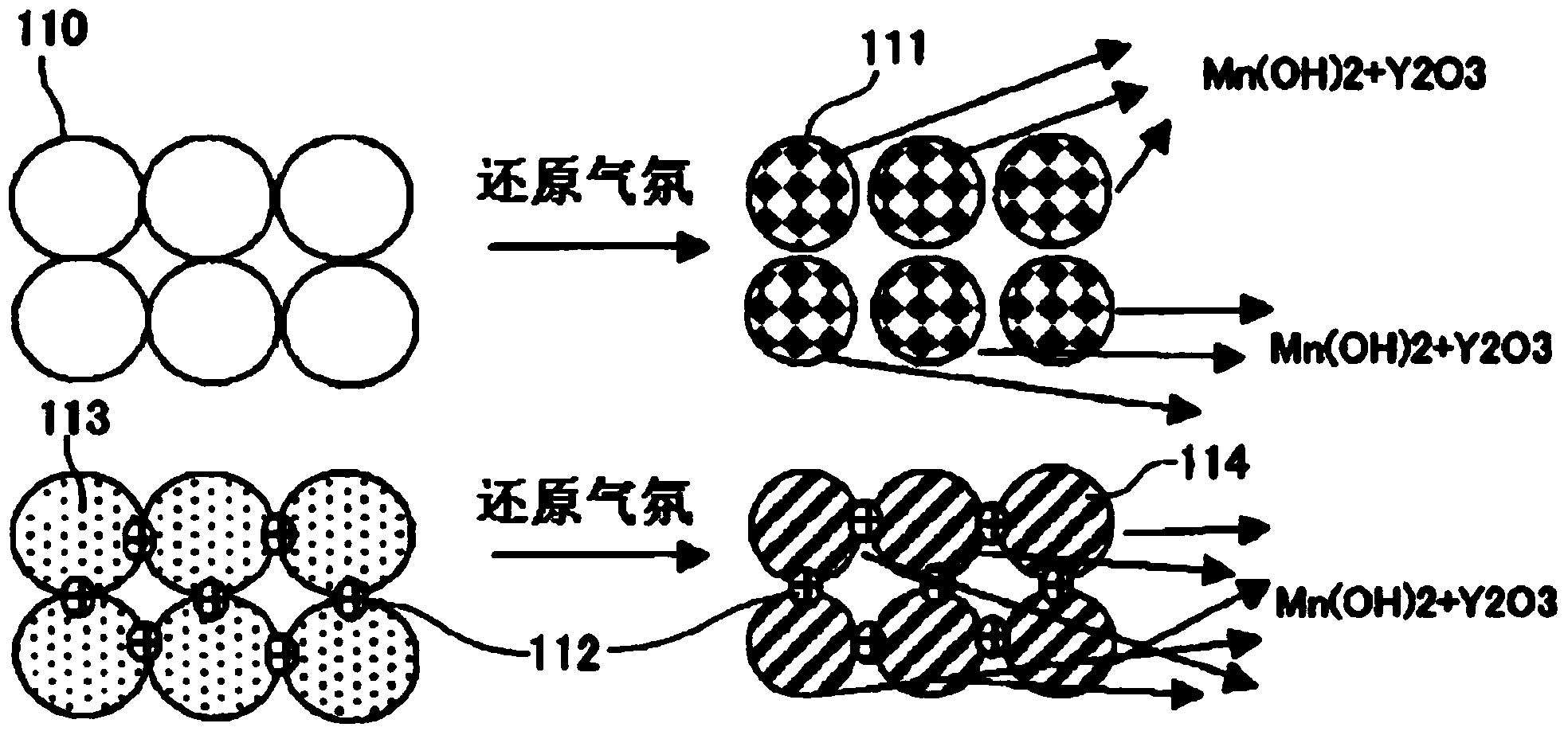
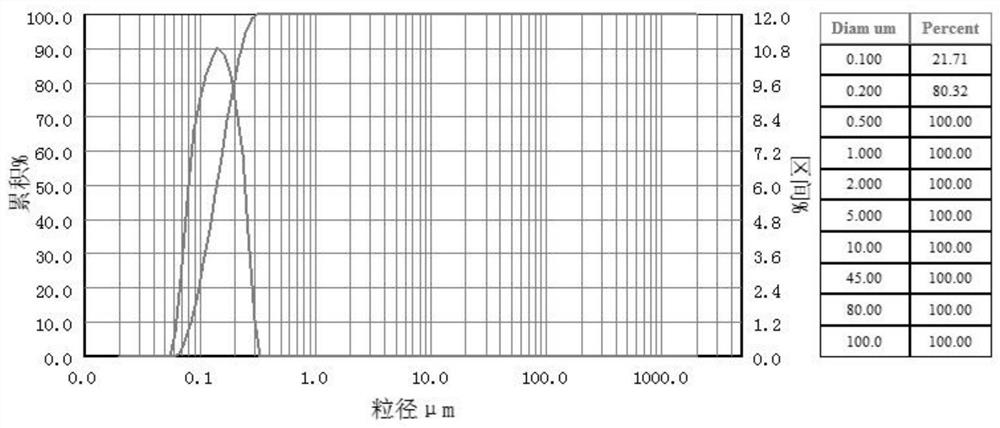
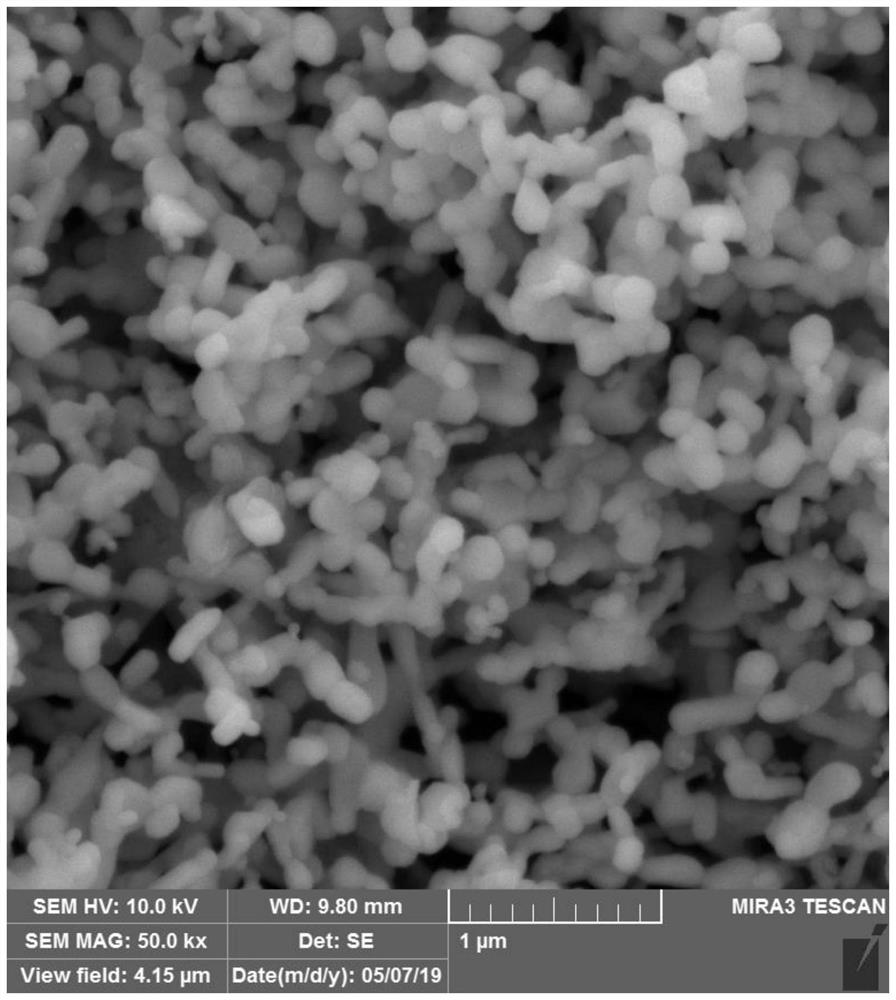
The present invention relates to a preparation method of highly dispersible ultrafine neodymium oxide. The preparation method of the highly dispersible ultrafine neodymium oxide includes processes such as mixing ingredients, extraction, chemical precipitation, burning, hydrogen crushing and oxidation; the present invention combines Chemical precipitation and hydrogen crushing process, chemical precipitation to obtain neodymium fluoride, after calcining to obtain micron-sized neodymium oxide, and then hydrogen absorption to remove residual single-phase neodymium, calcining and oxidation again to improve purity, single crystal neodymium absorbs hydrogen and expands in the hydrogen absorption stage Grain boundary breakage occurs at the micro level, resulting in intergranular fracture, improving the fineness of neodymium oxide and optimizing the particle shape; the production process is simple, the product particle size and dispersion are good, and the particles are uniform spherical and almost monodisperse under the scanning electron microscope. It is used as an additive Can be evenly dispersed in the material.
Owner:赣州嘉源新材料有限公司
Low-temperature high-product-of-strength-and-elongation high manganese steel plate and processing technology thereof
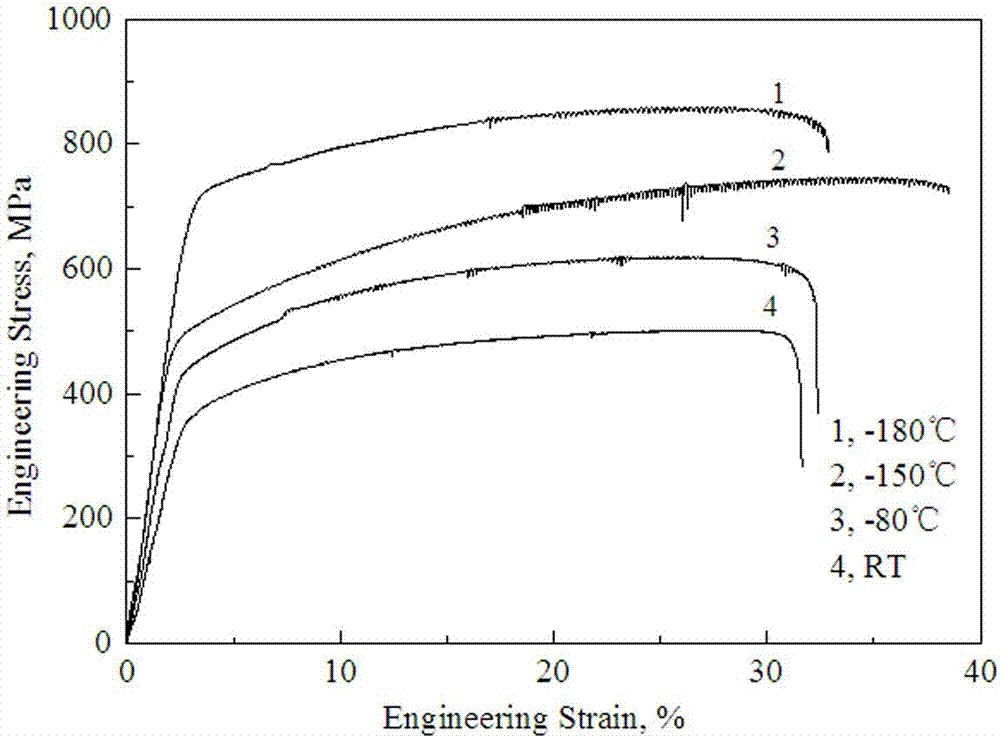
The invention discloses a processing method of a low-temperature plastic high manganese steel plate. The processing method comprises the processing steps of high manganese steel smelting, steel ingot post-processing, and plate forming by cogging and rolling. The concrete steps are as follows: A. high manganese steel smelting: a material formula includes the following ingredients in percentage by weight: 30-36 percent of Mn, 0.02-0.06 percent of C, 0-0.01 percent of S and 0-0.008 percent of P, the balance being Fe; B. steel ingot post-processing: a high manganese steel ingot formed by smelting is heat-treated for 2-4 hours at a temperature of 1,150-1,200 DEG C, and then transferred to a room-temperature water quenching pool to be homogenized to be subjected to solution treatment; C. plate forming by cogging and rolling: after solution treatment, the high manganese steel ingot is cogged, and then is hot-rolled and tempered to be homogenized. When being stretched and deformed at a low temperature (for example -180 DEG C), the low-temperature plastic high manganese steel plate has the characteristics of typical brittle fracture (i.e. intergranular fracture), but the low-temperature plastic high manganese steel plate has uniform elongation percentage above 18% and higher yield strength and tensile strength, so that the low-temperature plastic high manganese steel plate is suitable for low-temperature environments such as low-temperature pressure vessels.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
A kind of fe-mn-al-ni-cu superelastic alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a Fe-Mn-Al-Ni-Cu superelastic alloy and a preparation method thereof, comprising 25-40% of Mn, 10-20% of Al, 1-15% of Ni, 1- 10% of Cu, the rest is Fe; prepared by the following steps: (1) batching according to atomic percentage content, fully smelting and mixing in vacuum or inert gas protection to obtain castings; (2) castings obtained in step (1) Homogenizing treatment, and then deforming to obtain the desired sample alloy; (3) Selecting the directional annealing process and / or the cyclic heat treatment process as required to control the grain size. The invention can effectively improve the single crystal preparation efficiency of cyclic heat treatment and directional annealing, improve the grain growth rate of the alloy, and avoid the tendency of intergranular fracture caused by conventional abnormal grain growth promoting elements Ti and Al in FeMnAlNi alloy.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Heat process capable of lowering ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades
ActiveCN102220459BShort residence time at high temperatureFully solid solutionFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlChemical compositionTurbine blade
The invention provides a heat treatment process for reducing the ductile-brittle transition temperature and the intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades, which can effectively avoid the problem that the process effect is easily affected by the chemical composition of blade raw materials when the existing sub-temperature annealing process is used to treat turbine blades , and can solve the problem of high ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of the blade caused by the blade staying at high temperature for too long in the existing sub-temperature annealing process. Put the blades evenly into the general quenching basket according to the process plan, and then put the quenching basket into the heat treatment quenching furnace, which is characterized in that: the blades are quenched twice in the quenching furnace, and the first quenching temperature is 980℃~1070℃, heat preservation for 1 hour to 3 hours, cooling rate 20℃ / minute~50℃ / minute, the second quenching temperature is 900℃~1000℃, heat preservation for 15 minutes~120 minutes, cooling rate 30℃ / minute ~50°C / min, and ensure that the first quenching temperature is 20°C to 100°C higher than the second quenching temperature.
Owner:WUXI TURBINE BLADE
A kind of production method of fine-grained high-strength PMN-PZT piezoelectric ceramic material
The invention discloses a production method of a fine-grain high-strength PMN-PZT (lead zirconate titanate) piezoelectric ceramic material. The production method comprises the following steps of: weighing raw materials including PbO, MgO, Nb2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Bi2O3 and MnO2 in a stoichiometric ratio of (x)Pb(Mg1 / 3Nb2 / 3)O3-(1-x)Pb(TiyZr(1-y))O3-(a)Bi2O3-(b)MnO2-(c)Nb2O5-(d)ZnO-(e)SnO2, wherein x is 0.35-0.40, y is 0.40-0.70, and a, b, c, d, e are 0-1%; carrying out the process steps of ball milling, calcining, secondary ball milling, pelleting, tabletting, adhesion eliminating, sintering and the like to obtain a product. Therefore, by adopting the production method, the synthesis temperature of PMN-PZ-PT in the prior art can be greatly reduced, the compactness of a ceramic sample is high, the grain is tiny (-2 microns), the grain size is uniform, and a fracture mode realizes conversion from an intergranular fracture mode to a trans-granular fracture mode, namely the grain-boundary strength is greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU VOCATIONAL UNIV
High-flexibility copper rod and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113088754AEliminate hot brittlenessGood flexibilityMetallic material coating processesHeat resistanceTi-Cu alloy
The invention discloses a high-flexibility copper rod and a preparation method thereof. Copper and titanium are compounded to prepare a copper-based alloy, the flexibility and strength of the material are improved, zirconium is added in the compounding process, titanium is dissolved in the copper in a solid mode, meanwhile, diffusion of the titanium element on a grain boundary can be hindered through addition of zirconium, and thus the heat resistance of the titanium-copper alloy is remarkably improved; the titanium-copper alloy and boron are crushed and then sintered under high pressure, so that secondary recombination of the grain boundary is performed, the boron located at the grain boundary inhibits continuous precipitation of beta-Cu4Ti at the grain boundary during sintering, intergranular fracture is reduced, and the flexibility is improved; the addition of the Mg-Zn-Al alloy inhibits non-uniform nucleation of an equilibrium phase of the titanium-copper alloy at the grain boundary, twin boundary, dislocation and other defects, so that grains are more regular, meanwhile, distribution of a second phase is improved, the hot brittleness of the alloy is eliminated, the metal strength is improved, and the mechanical property of the alloy is improved.
Owner:JIANGXI ZHONGSHENG METAL
Metal / ceramic microlaminate material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101413101BImprove toughnessReduce toughnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingElectron beam physical vapor depositionMetal sheet
The invention provides a metal / ceramic micro-lamination material and a preparation method thereof. The method adopts an electron beam physical vapor deposition technology and alternately evaporates a metal target material and a ceramic material through an electron gun to prepare the metal / ceramic micro-lamination material. The thickness of a ceramic layer is 1 mu m; and the thickness of a metal layer is between 10 and 35 mu m, and the volume fraction ratio of the metal layer and the ceramic layer, namely the thickness ratio or the thickness ratio of layers is between 10 and 35. The metal target material is Ni-20Co-12Cr-4Al (weightt percent); and the ceramic target material is ZrO2(YSZ) containing 8 weight percent of Y2O3. The metal / ceramic micro-lamination material has large thickness ratio of layers; therefore, the material can keep the characteristic of good toughness of the metal material to a great extent. Simultaneously, the existence of a lamination structure limits the growth of columnar crystals in the metal layer and reduce the possibility that crack expands along the metal grain boundary. Compared with a monolayer EB-PVD metal sheet, the metal layer of the micro-lamination material has less probability of brittle intergranular fracture and higher strength.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A kind of preparation method of NdFeB magnetic powder for sintered magnet
ActiveCN108133796BImprove magnetismImprove coercive forceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsHydrogenCoupling
The invention provides a method for preparing neodymium iron boron magnetic powder for a sintered magnet, and belongs to the field of magnetic materials. The method includes the followingprocesses that neodymium iron boron powder particles are prepared by adopting a gas atomization method, crystalline grains inside the powder particles grow to 1-3 microns by vacuum heat treatment, the intergranular fracture of the powder particles occurs after hydrogen decomposing, and single crystal particles with a particle size of 1 to 3 microns are finally obtained after dehydrogenation. The method has theadvantages that the neodymium-rich phase of the neodymium iron boron particles prepared by the gas atomization method is evenly distributed at the boundary ofNd2Fe14B main phase crystalline grains, and the neodymium-rich phase uniformly covers the surface of the Nd2Fe14B main phase crystalline grains in the form of a thin layer by means of hydrogen absorption intergranular fracture, so that the neodymium-rich phase in the finally prepared sinteredneodymium iron boronmagnetuniformly covers the periphery of the Nd2Fe14B main phase crystalline grains in the form of a thin layer, demagnetizationexchange coupling is greatly enhanced, neodymium iron boroncrystalline grains prepared by the method are fine and uniform, and the magnetic properties of the obtained neodymium iron boron magnet, particularly the coercive force, are high after orientation molding, sintering and tempering treatment areconducted on the neodymium iron boron magnetic powder prepared by the method.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for obtaining intergranular fractures in oriented silicon steel
PendingCN112858359AImprove permeabilityDelay transitionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationThioureaStandard samples
The invention discloses a method for obtaining intergranular fractures in oriented silicon steel. The method comprises the following steps of: processing an oriented silicon steel sample into an Auger electron spectrometer standard sample; cleaning the surface of the standard sample; carrying out hydrogen charging, namely putting a preset fracture of the standard sample into a thiourea-containing solution of a hydrogen charging device, and taking the oriented silicon steel sample as a cathode; placing a platinum sheet and taking the platinum sheet as an anode; performing hydrogen charging on the cathode for 12-50 h at the hydrogen charging current of 1.25-1.35 A, the hydrogen charging current density of 0.1-0.8 A / m<2> and the hydrogen charging voltage of 36-39 V; and performing surface analysis. The method is simple in process, convenient to operate and short in consumed time, the used poisoning agent is thiourea, so that the problem that extremely toxic arsenic trioxide is adopted as the poisoning agent, and the human health is greatly threatened is solved, the obtained fractures of the oriented silicon steel are typical intergranular fractures, and the method is suitable for grain boundary segregation behavior and grain boundary microcell component analysis of the oriented silicon steel.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method of obtaining intergranular fracture in austenitic steel and its application
The invention provides a method for obtaining an intergranular fracture from austenite steel and application of the method. According to the method, after the surface of an austenite steel sample is electrolytic-polished, the austenite steel sample is subjected to cathodic hydrogen charging; then the two ends of the austenite steel sample are clamped for a while, and the austenite steel sample is put into a surface analyzing device; under the vacuum environment, the preset fracture of the austenite steel sample is primarily pressed for many times, then the preset fracture of the austenite steel sample is pressed to be broken at a time, and the intergranular fracture is obtained. The method is simple in technique and short in time consumption; operation steps are simple and controllable and easy to achieve; and the austenite steel fracture obtained through the method is a typical intergranular fracture, pollution can be effectively avoided, objective and accurate evidences can be provided for component analysis of a grain boundary, and the intergranular fracture is applicable to component analysis of the grain boundary of austenite steel.
Owner:BEIJING CISRI GAONA TECH +1
Spring steel austenite grain size detection method
ActiveCN112304993BApparent grain boundary brittlenessEasily brokenMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationWire rodAustenite grain
The method for detecting austenite grain size of spring steel includes the following process steps: (1) Sampling: take a spring steel wire rod sample with a length of 150~200mm; (2) Heat treatment: heat the sample in an environment of 860±10°C and keep the temperature After 55~65min, put it into fast-flowing water for quenching to obtain a complete martensite structure; (3) Sample preparation: cut a 1~2mm deep crack in the middle of the heat-treated sample, soak it with dilute sulfuric acid solution After 24~30 hours of passing cotton wrapped in the crack, the sample is knocked off along the crack to form a fracture; (4) Detection: observe the fracture with a scanning electron microscope, identify the grain boundary, and use the straight line intercept method to determine the grain. Spend. In the present invention, the directly quenched sample is prepared by the fracture method and then infiltrated with hydrogen to form the intergranular fracture section, the intergranular morphology is observed by scanning electron microscope, and the grain size information is obtained by software and the intercept method.
Owner:HUNAN VALIN XIANGTAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Tensile Fracture Judgment Method for Crack Formation Period of Iron and Steel Materials
ActiveCN108181170BImprove the accuracy of judgmentPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFractographyCrazing
The invention relates to a tensile fracture determining method for a crack forming period of a steel and iron material, which belongs to the technical field of failure analysis of a steel and iron material. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing a tensile sample comprising cracks, performing the breaking test, separating two crack surfaces, and determining the crack forming period according to characteristics of the existence of dimples of a micro-morphology of a fracture, cleavage, quasi-cleavage or intergranular fracture and the like. The method has the advantages that compared with the existing metallographic observation method, the tensile fracture analysis method does not damage the morphology of the crack and micro-tissues nearby the crack, so that the determination accuracy of the crack forming period can be improved, and the important evidence can be provided for analyzing the forming reason of the crack and making the preventive measures.
Owner:BEIJING BEIYE FUNCTIONAL MATERIALS CORP
A heat treatment method for electric arc additive manufacturing of high-strength titanium alloy and a reinforced high-strength titanium alloy
ActiveCN111826594BReduce residual stressSolving intergranular fracture problemsAdditive manufacturing apparatusTitaniumTitanium alloy
The invention provides a heat treatment method for manufacturing a high-strength titanium alloy by electric arc additive manufacturing and a reinforced high-strength titanium alloy, which belong to the field of titanium alloys. In the present invention, after the first heat treatment is performed on the high-strength titanium alloy manufactured by arc additive material, the first cooling is performed to the temperature of the second heat treatment, and the second heat treatment is performed; then the second cooling is performed to room temperature, and then the temperature is raised to the temperature of the third heat treatment to perform the third heat treatment. ; The temperature of the first heat treatment is 10-30°C above the β-transition point of the high-strength titanium alloy produced by arc-added materials, and the time is 15-30 minutes; the temperature of the second heat-treatment is below the β-transition point of the high-strength titanium alloy produced by arc-added materials 40-75°C, the time is 1h; the temperature of the third heat treatment is 500-550°C, and the time is 4-6h. The high-strength titanium alloy treated by the heat treatment method provided by the invention produces a "feather-like" grain boundary α phase at the grain boundary, which prevents intergranular fracture during stretching and can remove residual stress in the titanium alloy.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
A kind of low temperature sealing glass and preparation method thereof
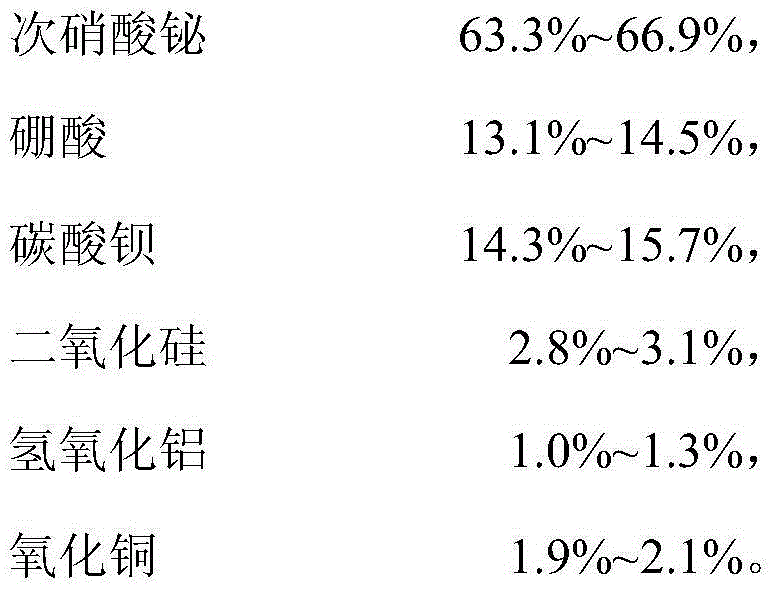
ActiveCN103739200BGuaranteed toughnessWill not cause brittle fractureAluminium hydroxideCopper oxide
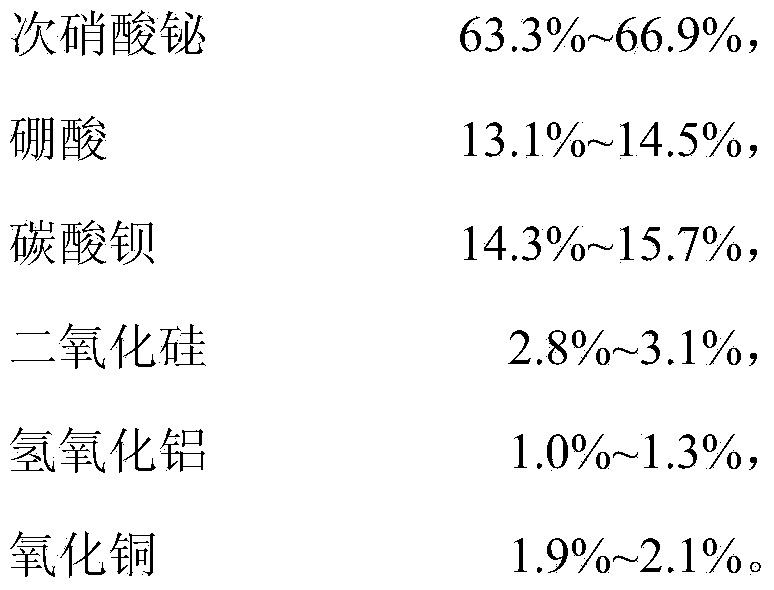
The invention relates to low-temperature sealing glass and a preparation method thereof. The low-temperature sealing glass comprises the compositions in percent by weight: 63.3%-66.9% of bismuth subnitrate, 13.1%-14.5% of boric acid, 14.3%-15.7% of barium carbonate, 2.8%-3.1% of silica, 1.0%-1.3% of aluminium hydroxide and 1.9%-2.1% of copper oxide; and the balance is unavoidable impurities. Undamaged sintering effect can be reached at low temperature when the low-temperature sealing glass is prepared according to requirements; the low-temperature sealing glass has good sealing performance; and when sintering is performed at the temperature, because the temperature is low and crystal grains of the material grow slowly, the material crystal grains does not show obvious growth and the material keeps original toughness when sintering is finished and the material crystal grains are subjected to microstructure analysis, so that intergranular fracture of a hot electrode at high temperature cannot be caused.
Owner:SUZHOU CHANGFENG AVIATION ELECTRONICS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com