Detection and characterization method of intergranular fracture and trans-granular fracture of WC grains in WC-Co alloy
A technology of transgranular fracture and intergranular fracture, which is applied in the direction of using a stable bending force to test the strength of materials, measuring devices, and testing the strength of materials with a single impact force.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: 5 cemented carbide samples with grade A and an average grain size of 1.6um were used to test the flexural strength, and the test results of each test strip were recorded according to serial numbers 1-5, as shown in Table 1.
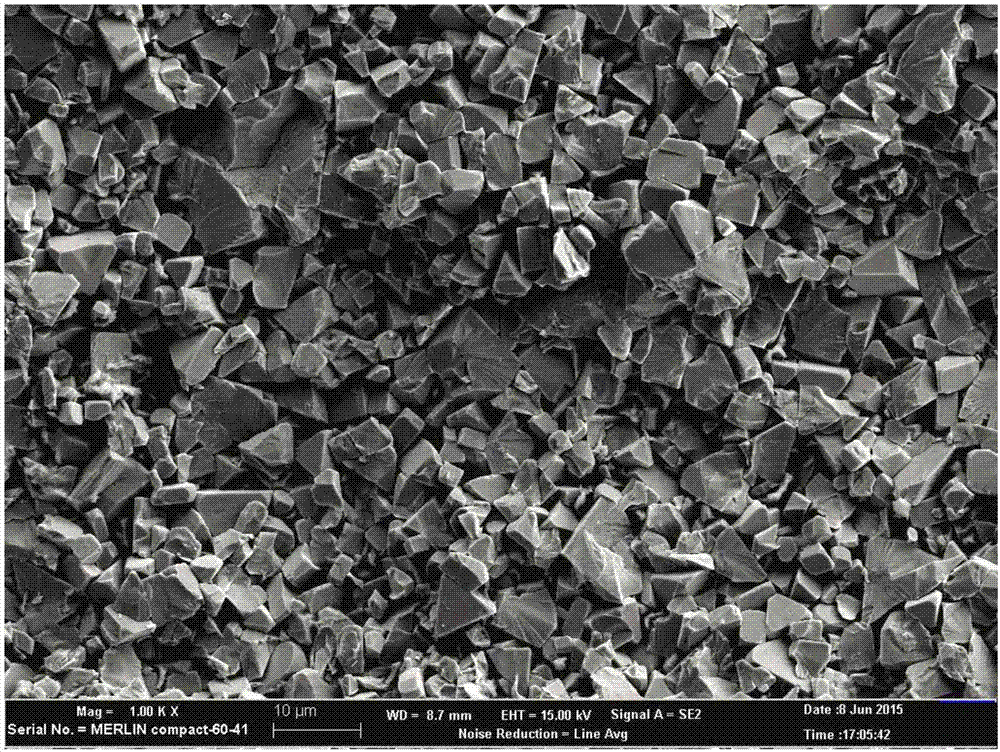
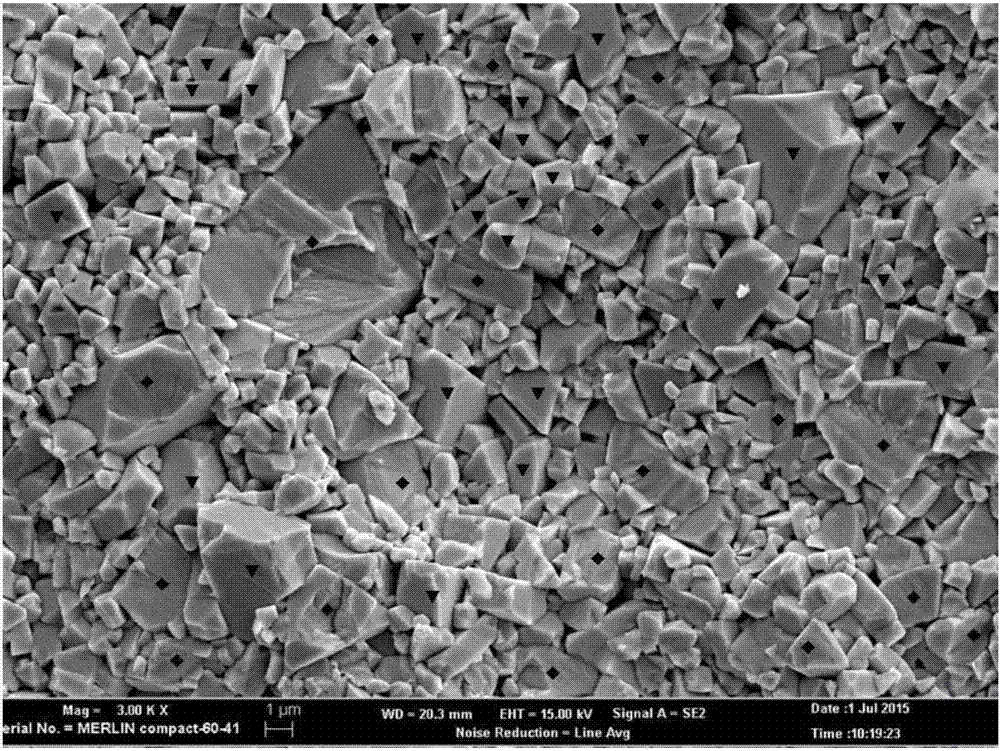
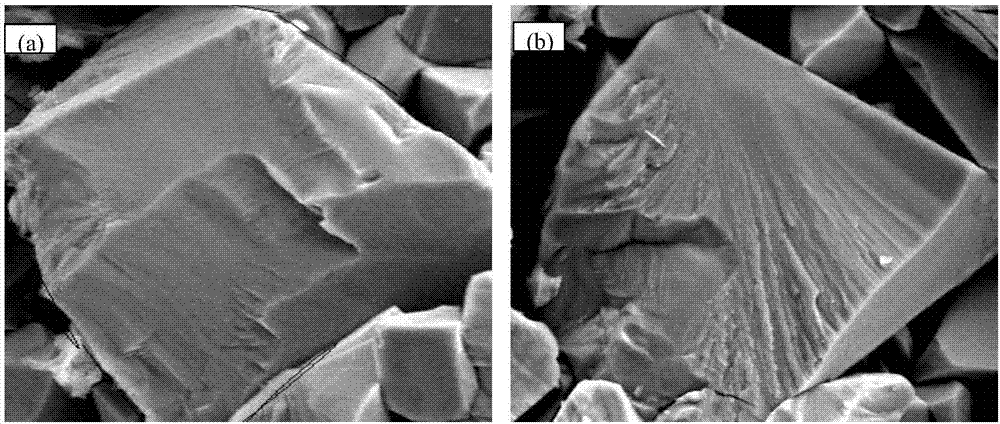
[0033] Then carry out the cohesive phase Co removal treatment on the fractured surface of the sample, that is, put the fractured sample into an HCl solution with a concentration of 5% to 37%, and corrode for 1 to 10 minutes until the cohesive phase is removed. The specific corrosion time is judged by the fact that the bonding phase Co on the fracture surface is completely removed, such as figure 1 Typical morphology of the cemented carbide fracture surface after removal of the binder phase Co. The morphology of the fracture surface of this sample after removing Co is as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0034] Then the above samples were cleaned and dried, that is, the fractured samples were first rinsed with distilled water, then cleaned wi...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2: 5 cemented carbide samples with brand B and an average grain size of 3.2um were used to test the flexural strength, and the test results of each test strip were recorded according to the serial numbers 1-5, see Table 2.
[0043] Then, the binder phase Co removal treatment on the fracture surface of the sample is carried out, that is, the fracture sample is put into FeCl 3 In an etching solution in which the mass ratio of the solid to the HCl solution with a concentration of 5% to 37% is 1:2, etch for 1 to 10 minutes until the bonding phase is removed. The specific corrosion time is judged by the fact that the bonding phase Co on the fracture surface is completely removed, such as figure 1 Typical morphology of the cemented carbide fracture surface after removal of the binder phase Co. The fracture morphology of the fracture surface of this sample after removal of Co is as follows: Figure 6 shown.
[0044] Then the above samples were cleaned and dried, tha...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: 5 cemented carbide samples with the grade C and an average grain size of 3.2um were used to test the impact toughness, and the test results of each test strip were recorded according to the serial numbers 1-5, as shown in Table 3.
[0053] Then, the cohesive phase Co removal treatment on the fractured surface of the sample is performed, that is, the fractured sample is put into a 5% to 37% HCl solution, and corroded for 1 to 10 minutes until the cohesive phase is removed. The specific corrosion time is judged by the fact that the bonding phase Co on the fracture surface is completely removed, such as figure 1 Typical morphology of the cemented carbide fracture surface after removal of the binder phase Co. The fracture morphology of the fracture surface of this sample after removal of Co is as follows: Figure 8 shown.
[0054] Then the above samples were cleaned and dried, that is, the fractured samples were first rinsed with distilled water, then cleaned w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com