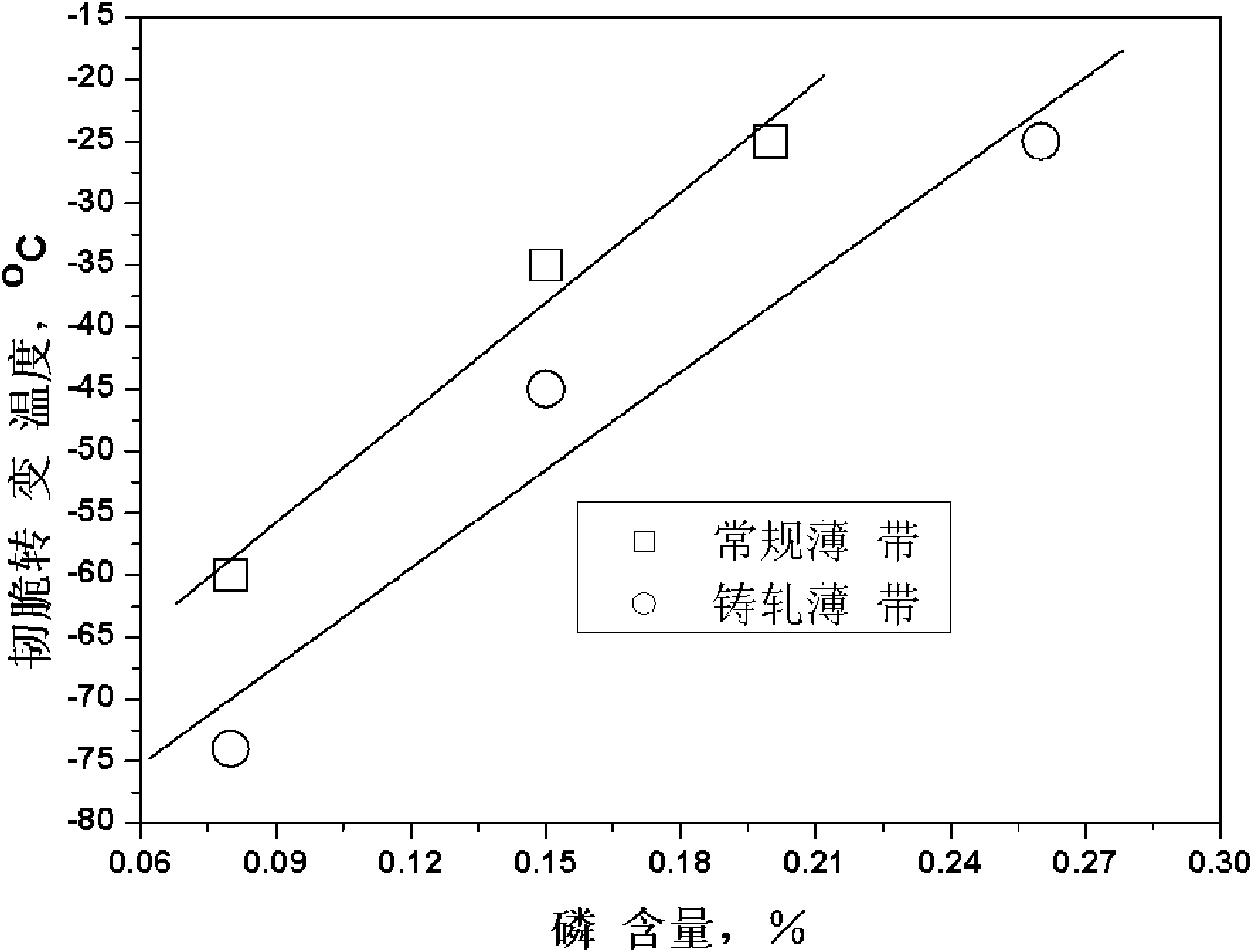
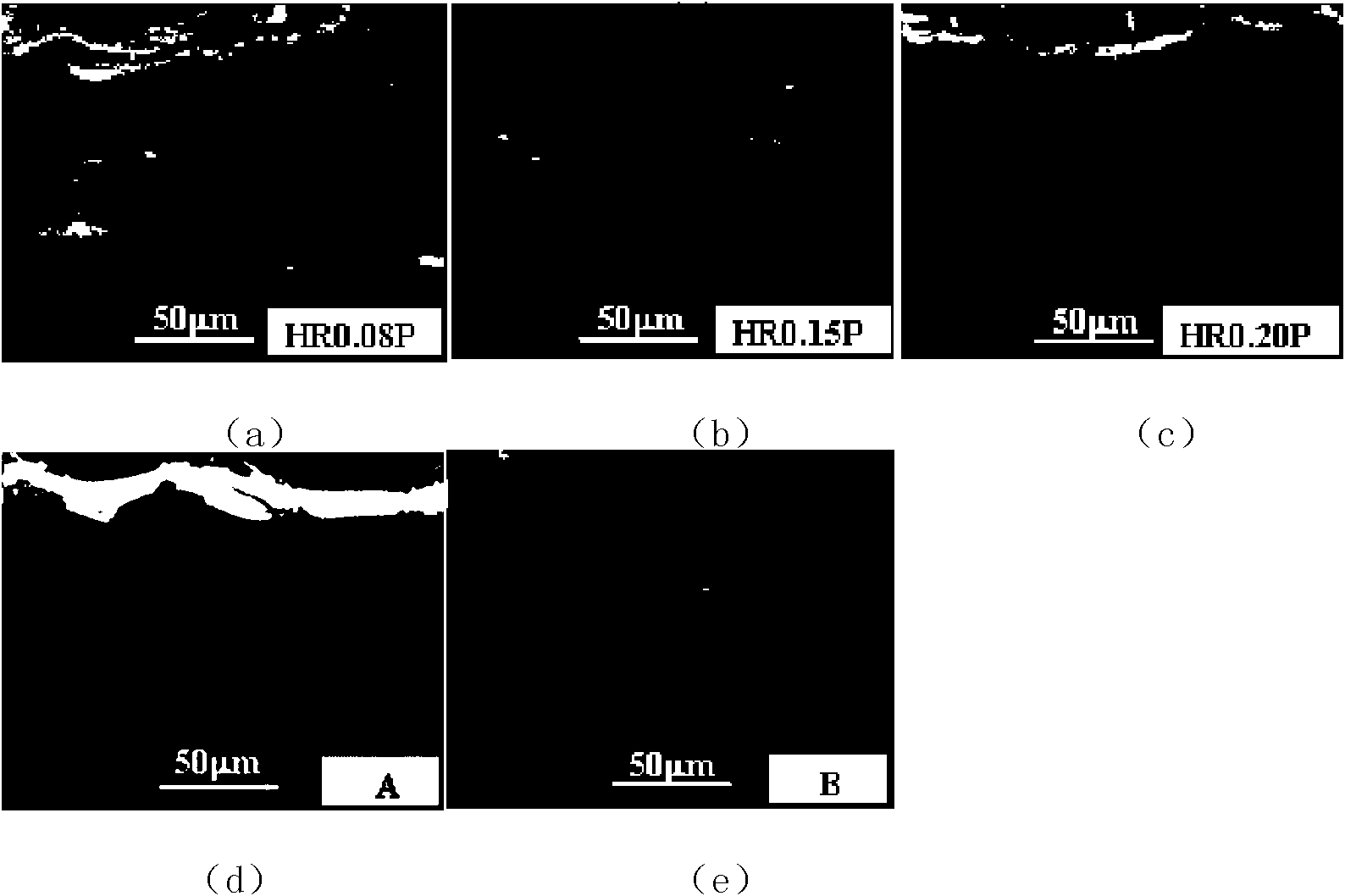
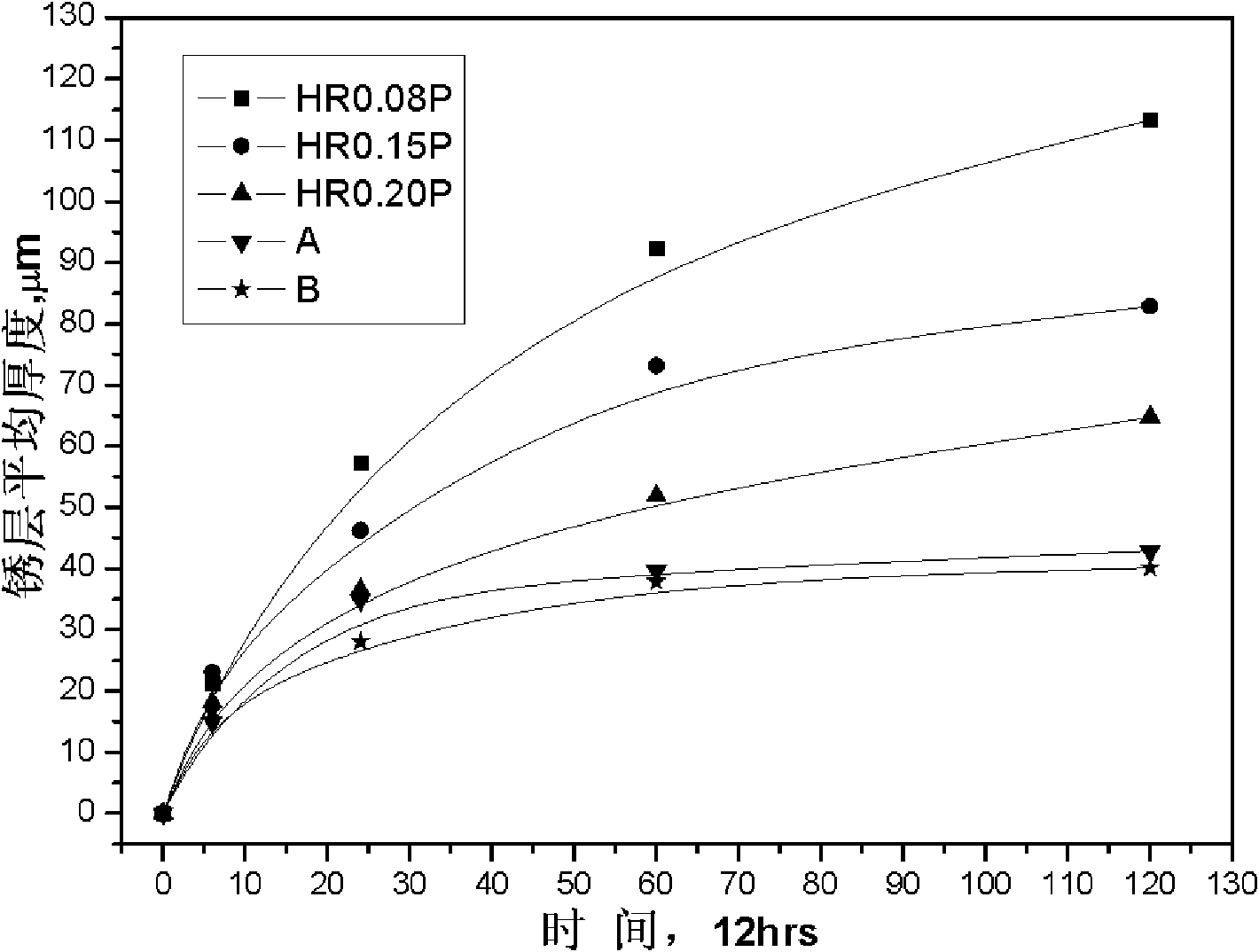
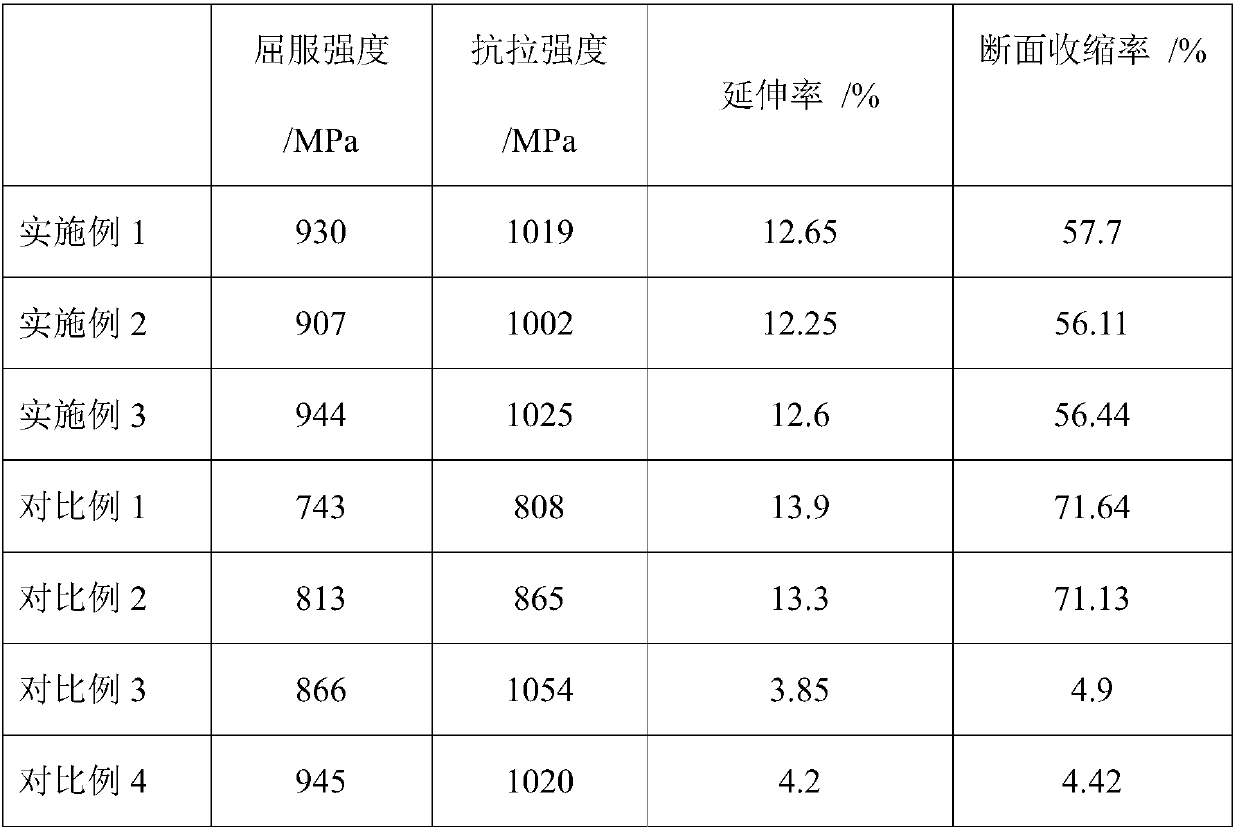
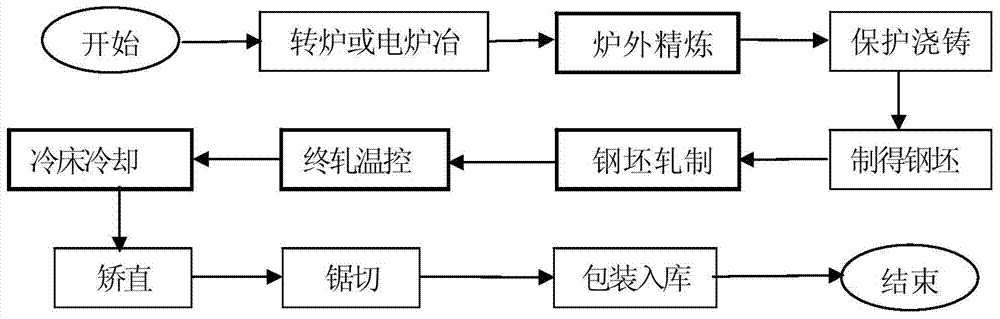
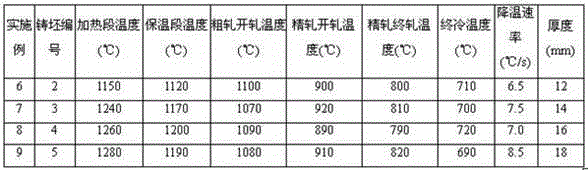
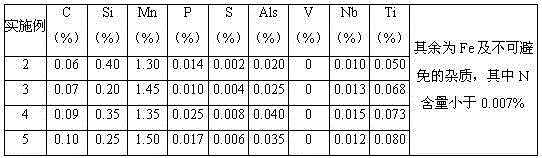
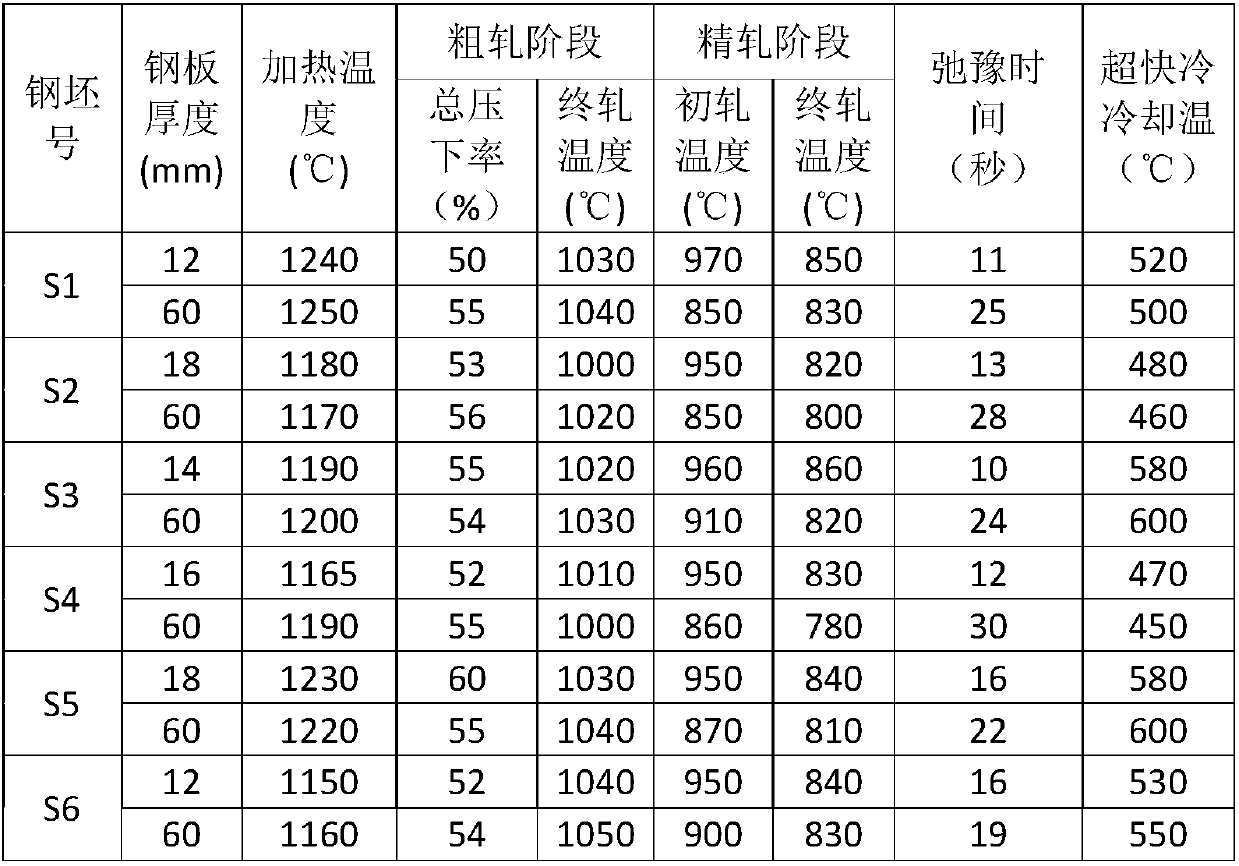
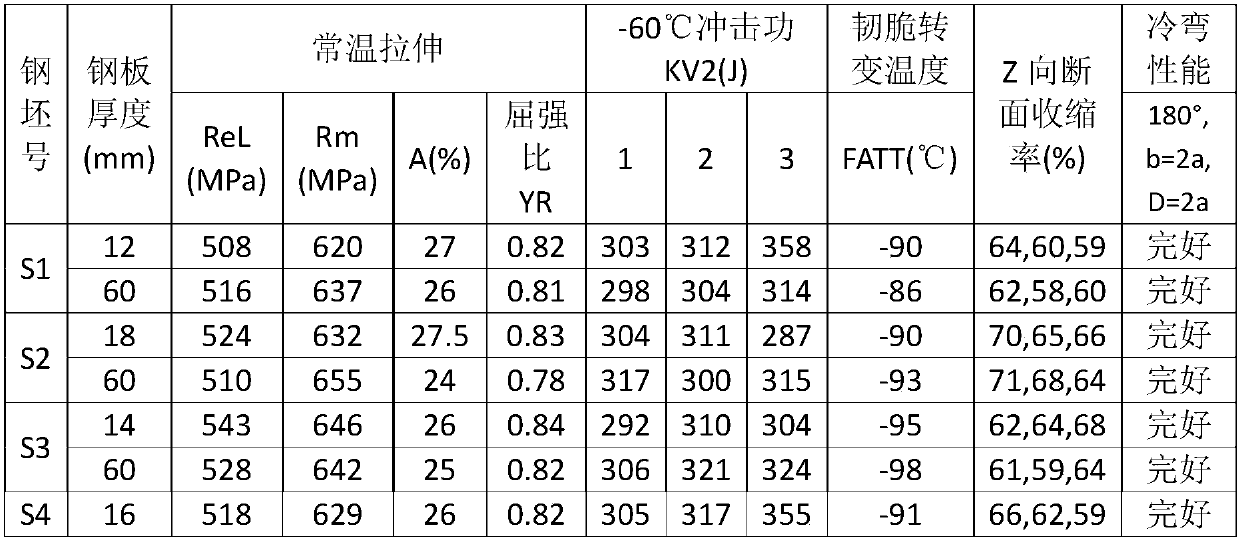
Patents
Literature
122results about How to "Reduce the ductile-brittle transition temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Production of cold rolling high-strength ultra-deep-drawing steel plate by bell-type furnace and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN101135025AHigh resistance to secondary processing brittlenessLess investmentTemperature control deviceHeat treatment process controlReduction rateHigh intensity
The process of producing cold rolled high strength extra-deep drawing steel sheet in a bell type furnace includes the following steps: 1. smelting and casting steel billet with chemical composition comprising C not more than 0.006 wt%, Si not more than 0.30 wt%, Mn 0.15-1.40 wt%, P not more than 0.08 wt%, S not more than 0.02 wt%, N 0.001-0.005 wt%, Al 0.03-0.06 wt%, B 0.0003-0.002 wt%, Ti 0.005-0.015 wt%, Nb 0-0.03 wt%, and Fe and inevitable impurity for the rest; 2. heating to 1100-1250 and rolling; 3. cold rolling in the reduction rate over 73 %; 4. annealing inside a hydrogen or nitrogen-hydrogen bell type furnace at 690-730 deg.c and 5. leveling after annealing. The steel sheet has strength up to 390 MPa, high elongation and r value, high ability of resisting rework brittleness, and ductile-brittle transition temperature lower than -40 deg.c.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Metal granular reinforced aluminum flux cored wire
ActiveCN102935562ASelf-brazingImprove wettabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCrack resistancePotassium
The invention discloses a metal granular reinforced aluminum flux cored wire. The metal granular reinforced aluminum flux cored wire comprises an outer silicon-aluminum alloy skin and a flux core filled in the skin, wherein the flux core is prepared by the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 5 to 20% of K3BF6, 0 to 35% of K2SiF6, 0 to 20% of K2GeF6, 0.8 to 20% of Cu-Ni alloy, 0 to 40% of Al-Si alloy, 0 to 30% of Cu-Si alloy, 0 to 5% of Al-Cu alloy and the balance of potassium fluoroaluminate. The metal granular reinforced flux core flux cored wire has the advantages that elements Ni, Si, Cu and B are added to the flux core in the form of intermediate alloy, so that the high processing performance is ensured, the wire is high in wettability and mobility, the low-temperature impact toughness and cracking resistance of a weld joint are improved, the ductile-brittle transition temperature is reduced, and the strength of the weld joint is improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Process for improving rare-earth high-strength steel impact toughness
The invention discloses a process for improving rare-earth high-strength steel impact toughness. The process comprises the following steps of KR desulfurization slagging off, converter smelting, LF refining, RH refining and rare-earth treating, continuous casting, heating, rolling, accelerated cooling and heat treating. According to the process, aiming at the influence on the microstructure of low-alloy high-strength steel in the case that rare-earth exists, a research shows that rare-earth cerium Ce can improve the forms of inclusions and purify grain boundaries, so that the strength of the grain boundaries is improved, the possibility that cracks extend due to the through defects is reduced, and the impact toughness is improved; and addition, the impact toughness can be improved throughrefining austenite grain boundaries, and meanwhile, adding the rare-earth cerium Ce can enable the ductile-brittle transition temperature of the steel to reduce by about 10 DEG C.
Owner:BAOTOU IRON & STEEL GRP
Steel suitable for drill rod joint in low-temperature environment and heat treatment process of steel
InactiveCN102140610AOvercome shortcomingsIncrease low temperature toughness reserveDrilling rodsDrilling casingsFiberTrace element
The invention relates to steel suitable for a drill rod joint in a low-temperature environment and a heat treatment process of the steel. The steel used for a drill rod joint comprises the following components by weight percent: C 0.25-0.35%, Mn 0.50-1.00%, P<=0.015%, S<=0.008%, Mo 0.15-1.00%, Ni 0.75-1.50%, Cr 0.80-1.50%, two or more of Si<=0.30%, Al<=0.03%, V<=0.10%, Ti<=0.03% and Re<=0.005%, and the balance of Fe and inevitable trace elements. The heat treatment process of the steel suitable for a drill rod joint is as follows: heating the steel in a furnace to 900-960 DEG C; carrying out heat insulation for 1.0-1.5 hours; putting the steel into a quenching medium and cooling down completely; tempering at the temperature of 660-690 DEG C; carrying out heat insulation for about 2.0-2.5 hours; and then taking the steel out of the furnace. After the steel is treated according to the process, when the yield strength of the steel is 905MPa, longitudinal and full-size charpy impact power average value at -60 DEG C is 110J, the fracture fiber rate is 100% on the average, and the ductile-brittle transition temperature is -85 DEG C.
Owner:SHANGHAI HILONG DRILL PIPE MATERIALS INST +1
Batch annealing interstitial-free (IF) steel and production method thereof
ActiveCN102747281AImprove grain boundary distributionImprove the resistance to secondary processing brittlenessNiobiumManganese
The invention discloses batch annealing interstitial-free (IF) steel. The steel comprises, by mass, 0.0005-0.0035 of carbon, no more than 0.03 of silicon, 0.05-0.30 of manganese, no more than 0.008 of phosphorus, no more than 0.012 of sulphur, no more than 0.004 of nitrogen, 0.02-0.07 of aluminum, 0.04-0.09 of titanium, 0.003-0.015 of niobium, 0.0003-0.0020 of barium and the balance ferrum and trace elements. The invention also discloses a production method of the IF steel. By the aid of the steel and the method, the component design is proper, a process optimization method in which the batch is retreated and the stress and the recrystallization are performed is used, the crystal boundary distribution condition of the IF steel is improved, the ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) of the IF steel is lowered to below -60 DEG C, the secondary-processing brittle resistant performance of the IF steel is improved, and automatic industry requirements are met well.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
355MPa thick steel plate with low-temperature toughness and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of steel material production, and particularly relates to a 355MPa thick steel plate with low-temperature toughness and a preparation method thereof. The 355MPa thick steel plate with the low-temperature toughness is composed of the following components according weight percent: 0.04 to 0.14% of C, 0.2 to 0.5% of Si, 1.0 to 1.6% of Mn, less than 0.018% of P, less than 0.005% of S, 0.015 to 0.045% of Nb, 0.02 to 0.05% of V, 0.008 to 0.020% of Ti, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The thick steel plate has good low-temperature (-60 DEG C) impact toughness, and additionally, high strength, high toughness and good welding performance of the thick steel plate are achieved in the condition of the low-carbon content by adopting the preparation method.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Hot-rolled H-shaped steel with good low-temperature ductility at minus 60 DEG C and production method thereof
InactiveCN107227430AReduce the ductile-brittle transition temperatureImprove low temperature toughnessNiobiumManganese
The invention provides hot-rolled H-shaped steel with good low-temperature ductility at minus 60 DEG C and a production method thereof. The hot-rolled H-shaped steel is prepared from, by weight, 0.07%-0.15% of carbon, 0.15%-0.35% of silicon, 1.00%-1.45% of manganese, smaller than or equal to 0.020% of phosphorus, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of sulphur, 0.020%-0.060% of vanadium, 0.010%-0.060% of niobium, 0.10%-0.25% of nickel, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of Als, the balance iron and unavoidable impurities. Compared with the prior art, the H-shaped steel produced through the method has the extremely low ductile-brittle transition temperature and the good low-temperature ductility, the welding procedure and the procedures of visual inspection and weld seam detection after welding are reduced, and the cost of steel per ton can be reduced by 500 yuan or above.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-phosphorous weather-proof steel cast-rolling thin strip with negative phosphorous segregation on surface and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-phosphorous weather-proof steel cast-rolling thin strip with negative phosphorous segregation on the surface and a preparation method thereof. The chemical components of the thin strip in terms of percentage by mass are as follows: 0.061-0.099% of C, 0.15-0.75% of SiO, 0.20-0.49% of Mn, 0.07-0.30% of P, 0.02% or less of S, 0.25-0.50% of Cu, 0.30-1.25% of Cr, 0.12-0.65% of NiO, and Fe as remainder. The preparation method of the thin strip comprises the following steps of: melting, refining, casting and rolling the refining liquid steel by a double-roller thin strip casting and rolling device, and controlling the cast-on temperature at 1540-1600 DEG C and the casting and rolling speed at 12-60m / min, and presetting the roll-gap as 1-4mm; obtaining the cast-rolling strip with negative phosphorous segregation on the surface, with a thickness of 1-5mm; and then cold-rolling and annealing. The negative phosphorous segregation on the surface guarantees the strength and the plasticity of the thin strip and also greatly improves the anti-corrosion performance of the thin strip; the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature of the high-phosphorous weather-proofsteel cast-rolling thin strip with negative phosphorous segregation on the surface is about 10 DEG C lower than that of the products produced by common processes, and the tenacity of steel is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
H-shaped steel as well as application and production method of H-shaped steel
InactiveCN104073717AReduce the ductile-brittle transition temperatureStrong lamellar tear resistanceNiobiumManganese
The invention relates to H-shaped steel as well as an application and a production method of the H-shaped steel. The production method comprises the process steps of: molten steel pretreatment; converter smelting; argon blowing station; LF refining; fully-protective beam blank casting; H-shaped steel wire A rolling. The steel comprises the following chemical components: 0.08-0.18% of carbon, 0.15-0.35% of silicon, 1.00-1.45% of manganese, less than or equal to 0.020% of phosphorus, less than or equal to 0.010% of sulfur, 0.020-0.080% of vanadium, 0.010-0.060% of niobium, 0.10-0.25% of nickel, more than or equal to 0.015% of Als and a trace amount of other alloy elements. The H-shaped steel with the specification of 300*200, which is produced by using the production method of the H-shaped steel with -40 DEG C low-temperature toughness and Z-direction performance, has the -40 DEG C low-temperature toughness of more than 150J and the average Z15-direction section reduction value of larger than 27.5% and has extremely low ductile-brittle transition temperature and relatively strong lamellar tearing resistant property, and the quality of the H-shaped steel is improved.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
High-strength high-toughness high-hardenability high-speed axle steel and heat treatment method thereof
The invention relates to high-strength high-toughness high-hardenability high-speed axle steel. The yield strength Rp0.2 of the axle steel is larger than or equal to 630 MPa, the strength of extensionRm is larger than or equal to 800 MPa, the ductility A is larger than or equal to 20%, the 5 mm notch indoor temperature longitudinal impact absorbing energy KU2 is larger than or equal to 80 J, andthe ductile-brittle transition temperature is lower than -40 DEG C; and a chemical component of the steel comprises B, and the weight percentage of the B is 0.0008%-0.0025%. Meanwhile, a preparing method of the steel is further provided. By means of the high-strength high-toughness high-hardenability high-speed axle steel and the preparing method have the beneficial effects that full play can be given to the effects of all elements in the axle steel sufficiently, and microscopic structures with wee crystalline grains and with martensite as a main are obtained. Through two times of quenching and high temperature tempering heat treatment are adopted, and therefore even fine grain austenite grains and Nb microalloy second-phase strengthened martensitic structures can be obtained, excellent matching of high strength, high toughness and high hardenability is achieved, and finally the high-speed axle steel has the good anti-shock, anti-fatigue service performance and the like, excellent strength and toughness matching and good hardenability.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST +1
Brass flux-cored brazing filler metal with reducing agents and flow aids and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104907722AImprove wettabilityImprove liquidityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaIngot castingWeld seam
The invention discloses brass flux-cored brazing filler metal with reducing agents and flow aids. The brass flux-cored brazing filler metal comprises a brazing filler metal pipe with a spiral lap seam, the brazing filler metal pipe is formed by rotatably rolling strip-shaped brass base brazing filler metal, and a welding wire and a flux core prepared from brass brazing flux, the reducing agents and the flow aids are wrapped by the brazing filler metal pipe. In the preparation process, the brass base brazing filler metal is molten according to a conventional method for ingot casting and is processed into strip-shaped brazing filler metal, then the brazing filler metal is rotatably rolled to the brazing filler metal pipe with the spiral lap seam, and in the rolling process, the welding wire and the flux core are added into the brazing filler metal pipe. A brass flux-cored brazing filler metal wire or bar or brazing filler metal ring are manufactured through rolling or drawing. The brass flux-cored brazing filler metal has the advantages that Sn, Ni, Si and other elements are added into the brazing filler metal in the form of the welding wire, when the content of alloy elements in the brass brazing filler metal is low, the excellent processing performance can still be kept, the brazing filler metal can achieve good wettability and fluidity, meanwhile, weld strength, low-temperature impact toughness and the anti-cracking ability are improved, and ductile-brittle transition temperature is lowered.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Manufacturing method of ultra low temperature and high intensity fine grain simple steel flange
ActiveCN101254577AHigh strengthImprove impact performanceMetal-working apparatusFurnace typesQuenchingImpurity
The invention relates to the manufacture method of micro-alloy fine-grain low-carbon steel flange with ultralow temperature and high strength performance, which can manufacture micro-alloy fine-grain low-carbon steel flange from low-carbon micro-alloy fine-grain high-strength steel by forging and heat treatment processes. The steel contains following chemical components (by weight percentage): C 0.12 to 0.18%, Si 0.15 to 0.35%, Mn 1.2 to 1.6%, and trace elements V 0.02 to 0.06%, Al 0.025 to 0.040%, N 0.001 to 0.002%, Fe in balance, and inevitable impurities. The method comprises the following steps: temperature-controlled forging, heat treatment of semi-product and cutting of final product, wherein the beginning temperature of forging is 1,050 DEG C plus or minus 20 DEG C, the final temperature of forging is 900 DEG C plus or minus 20 DEG C, and the semi-product is air-cooled after forging; the heat treatment of the semi-product is executed by adopting quenching and high-temperature tempering process; and a workpiece is subjected to metal cutting after the heat treatment. The method of the invention can obviate the use of expensive Ni alloy steel, and can meet the requirement for -50 DEG C low-temperature toughness and high strength.
Owner:JIANGYIN HENGRUN HEAVY IND
W-Mo-Re-HfC alloy material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108796333AGood room temperature and high temperature mechanical propertiesGood mechanical propertiesTungstenMicrostructure
The invention discloses a W-Mo-Re-HfC alloy material. The W-Mo-Re-HfC alloy material is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 10% to 30% of molybdenum, 1% to 25% of rhenium, 0.2% to 10%of hafnium carbonate and the balances tungsten and inevitable impurities. The invention further provides a preparation method of the W-Mo-Re-HfC alloy material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (I) carrying out ball milling and uniformly mixing molybdenum powder, rhenium powder, hafnium carbonate powder and tungsten powder; and carrying out crushing and sieving after hydrogen reduction to obtain mixed powder; and (II) sintering the mixed powder in a vacuum hot-press sintering furnace, and then cooling the mixed powder with the furnace to obtain the W-Mo-Re-HfC alloy material. The preparation method of the W-Mo-Re-HfC alloy material disclosed by the invention is simple in a technological process; the prepared alloy material is low in oxygen content; the microstructure is uniform; a base body consists of W, Mo and Re solid solution phases; good plasticity is realized; submicron and nanometer HfC phases are uniformly distributed in the base body so that the alloymaterial is excellent in plasticity and also has good room-temperature and high-temperature strength.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Precipitation strengthened heat resistant steel and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN107587080AReduce the ductile-brittle transition temperaturePromote precipitationRoom temperatureIngot
The invention relates to precipitation strengthened heat resistant steel and a preparation process of the precipitation strengthened heat resistant steel. The components of an alloy meet the followingrange requirements by mass percent: 003-0.06% of C, 6-10% of Ni, 8-13% of Cr, 1.5-2.4% of Al, less than or equal to 3% of Co, less than or equal to 0.1% of Nb, less than or equal to 0.1% of Zr, and the balance of Fe; the prepared alloy is smelted into an alloy mother liquid and is finally prepared into an alloy ingot; the alloy ingot is rolled into a sheet at the temperature range of 850-1100 DEGC; and the rolled sheet is subjected to solid solution treatment and aging treatment to obtain the precipitation strengthened heat resistant steel. The heat resistant steel is excellent in room temperature toughness and has an excellent strength property at the same time. The room temperature tensile strength of the alloy is not lower than 1000 MPa, the yield strength exceeds 900 MPa, the room temperature elongation percentage is higher than 12%, and the reduction of area is higher than 50%.
Owner:CHINA HUANENG GRP CO LTD +1
Preparation method of high-toughness Q345 grade hot-rolled equal angle steel for iron tower
ActiveCN103938063AImprove mechanical propertiesStrong enoughRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsFree coolingTower
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-toughness Q345 grade hot-rolled equal angle steel for an iron tower. The method comprises the following steps: 1) smelting a billet: preparing the billet by adopting converter or electric furnace smelting, external refining and protective casting, wherein the carbon equivalent is not more than 0.42%; 2) rolling the billet: rolling the billet according to the sequence of elongation pass, slitting pass and finishing pass, wherein the total compression ratio is not less than 5 and the mean coefficient of elongation of the finishing pass is not less than 1.12; 3) controlling the finishing rolling temperature, wherein the finishing rolling temperature is 930-880 DEG C; 4) cooling with a cooling bed, wherein when the steel temperature is more than 400 DEG C, natural cooling and auxiliary air cooling or fog cooling are adopted; when the steel temperature is less than 400 DEG C, spray cooling is adopted; 5) entering a conventional subsequent procedure and finally preparing the high-toughness Q345 grade hot-rolled equal angle steel for the iron tower. The impact toughness of the angle steel at low temperature is improved while ensuring that the angle steel has sufficient strength by adopting the preparation method.
Owner:BEIJING GUOWANG FUDA SCI & TECH DEV +1
690 MPa grade high-strength low-yield-ratio medium-manganese steel medium-thickness steel and manufacturing method
The invention discloses 690 MPa grade high-strength low-yield-ratio medium-manganese steel medium-thickness steel and a manufacturing method, and relates to the technical field of steel smelting. Thesteel comprises the following chemical components of, in percentage by mass, 0.05%-0.10% of C, 4.1%-4.7% of Mn, 0.15%-0.4% of Si, less than or equal to 0.010% of P, less than or equal to 0.003% of S,0.01%-0.05% of Ti, less than or equal to 0.6% of Ni + Cr + Mo, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The requirements of ultra-high strength steel safety performance and construction cost in acomplex environment in the field of engineering machinery can be met.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Flux-cored wire for additive manufacturing and preparation method of low-alloy high-strength steel
ActiveCN111360449AShorten the production cycleEasy to produceAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusRare-earth elementSheet steel
The invention discloses a flux-cored wire for additive manufacturing. The wire comprises a flux core and sheet steel. The flux core is composed of, by mass percent, 2.00%-3.83% of ferromanganese powder, 16.95%-20.85% of nickel powder, 8.35%-11.65% of chromium powder, 1.05%-3.00% of molybdenum powder, 0.90%-1.62% of ferrovanadium powder, 0.05%-0.10% of boron powder, 2.16%-10.82% of ferrotitanium powder, 0.5%-1.5% of ferrosilicon powder, 0.50%-1.00% of aluminum-magnesium powder, 0.80%-1.00% of rare earth elements and the balance being iron powder, wherein the sum of the mass percents of the components is 100%. The flux-cored wire is a wire used for arc additive manufacturing of low-alloy steel applied to a fan impeller. The invention further discloses a preparation method of low-alloy high-strength steel. The flux-cored wire has excellent comprehensive mechanical properties; and by the adoption of an additive manufacturing mode, the low-alloy high-strength steel can meet the requirementon the mechanical properties and is efficient and convenient to use.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Corrosion-resistant metal coating used for outer surface of gear box
ActiveCN106498290AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove antistatic performanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesMetal coatingCorrosion resistant
The invention discloses a corrosion-resistant metal coating used for the outer surface of a gear box. The corrosion-resistant metal coating comprises, by mass, 0.06%-0.08% of C, 0.15%-0.18% of Mn, 10.76%-10.79% of Cr, 2.12%-2.15% of Ni, 0.13%-0.15% of Mg, 0.21%-0.23% of Mo, 0.25%-0.27% of Co, 0.06%-0.08% of V, 0.42%-0.44% of Ti, 0.22%-0.25% of Na, 0.17%-0.19% of Ga, 0.22%-0.25% of Ce, 0.16%-0.18% of Nd, 0.32%-0.38% of La and the balance Fe.
Owner:南京创贝高速传动机械有限公司
Ultra-fine-grain ultra-high-obdurability high-speed axle steel and heat treatment method thereof
Provided is ultra-fine-grain ultra-high-obdurability high-speed axle steel. The axle steel comprises uniform fine-grained austenite grains and an Nb micro-alloyed nanometer second-phase-enhanced martensite structure. The average grain size of the austenite grains is below 10 micrometers. The axle steel comprises, by mass percentage, 0.00-0.06% of Nb and 0.16-0.30% of V. The invention further provides a heat treatment method for the steel. The method comprises the steps that the functions of each element in the axle steel are fully played, two-time quenching and high-temperature tempering heattreatment is adopted, and finally a high-speed axle has good serviceability such as impact resistance and fatigue resistance, excellent obdurability matching and good hardenability. The average grainsize of the austenite grains in the structure of the axle steel is below 10 micrometers, the yield strength Rp0.2 is larger than or equal to 900 MPa, the tensile strength Rm is larger than or equal to1,000 MPa, the elongation rate A is larger than or equal to 15%, the 5-mm gap longitudinal impact absorbing energy KU2 at the room temperature is larger than or equal to 100 J, and the ductile-brittle transformation temperature is lower than negative 80 DEG C.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST +1
Steel sheet having excellent low-temperature toughness and method for producing same
The invention discloses a steel plate with excellent low-temperature toughness. The steel plate comprises the following chemical elements in percentage by mass: 0.02-0.15% of C; 0.10% to 0.5% of Si; 0.30% to 1.60% of Mn; 0.10% to 1.00% of Cr; 0.30% to 1.00% of Ni; 0.005% to 0.10% of Ti; 0-0.60% of Mo; 0.10% to 0.80% of Cu; 0.01% to 0.06% of Al; 0.003-0.06% of Nb, 0-0.08% of V, and 0 < N < = 0.035%; and the balance of Fe and other inevitable impurities. In addition, the invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the steel plate with excellent low-temperature toughness, which comprises the following steps: (1) smelting and casting; (2) heating; (3) rolling; and (4) cooling.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-strength high-toughness Cu-containing steel and production method thereof
The invention provides high-strength high-toughness Cu-containing steel and a production method thereof. The steel comprises the following chemical components in percent by weight: 0.04-0.07 percent of C, 0.25-0.45 percent of Si, 0.60-1.00 percent of Mn, 0.01-0.03 percent of Als, 2.40-3.20 percent of Ni, 1.20-1.60 percent of Cu, 0.65-0.90 percent of Cr, 0.30-0.60 percent of Mo, 0.02-0.04 percent of Nb, 0.01-0.03 percent of Ti, less than or equal to 0.015 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of S and the balance of iron and inevitable impurities. The production method comprises the following steps of: performing total molten iron smelting by using a duplex process, performing external refining through converter top-blown or top and bottom composite blowing, performing whole-course protection casting during continuous casting, and slowly cooling after a continuous casting billet is off line; controlling the heating temperature of the billet to be 1,150-1,250 DEG C and the heating time to be 3.5-5 hours, controlling the open rolling temperature to be 1,050-1,100 DEG C during rough rolling, controlling the open rolling temperature to be 890-920 DEG C during finish rolling, and controlling the finished rolling temperature to be 800-860 DEG C during finish rolling; performing heat treatment, wherein the quenching temperature is 860-920 DEG C, the temperature keeping time is 0.5-3.5 hours; and performing water cooling; keeping the tempering temperature to be 620-690 DEG C, wherein the temperature keeping time is 1-7 hours; and performing air cooling. The steel plate has the yield strength of more than or equal to 690MPa, the Charpy impact work of a V-shaped notch at the temperature of 80 DEG C below zero is more than 120J, and the ductile-brittle transition temperature is lower than 80 DEG C below zero.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Automotive axle housing steel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104630629AHigh strengthHigh and cold shapingManufacturing convertersAlloyMechanical property
The invention relates to automotive axle housing steel. The automotive axle housing steel comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.06-0.10% of C, 0.20-0.40% of Si, 1.30-1.50% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.025% of P, less than or equal to 0.008% of S, 0.020-0.040% of Als, 0.010-0.015% of Nb, 0.050-0.080% of Ti and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the automotive axle housing steel. The preparation method comprises the following steps of converter smelting, LF refining, casting, roughing and finishing. By adding less alloying elements Ti and Nb and controlling the content of N and controlled rolling and cooling process, 600MPa-grade steel is obtained and has excellent mechanical properties and formability.
Owner:HEBEI PUYANG IRON & STEEL
Weather-proof steel plate and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a weather-proof steel plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The weather-proof steel plate comprises, by mass percentage, 0.04-0.10% of C, 0.18-0.35% of Si, 1.00-1.60% of Mn, 0.008-0.015% of P, 0.25-0.45% of Cu, 0.40-0.60% of Cr, 0.30-0.50% of Ni, 0.02-0.05% of Alt, 0.01-0.05% of Nb, and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurities. Through the reasonable composition proportion, the steel plate can obtain excellent welding performance under the condition of the low P content, meanwhile has ultrahigh strength, high toughness and high weather resistance, and well meets the requirement of application to a monorail turnout. According to the manufacturing method of the weather-proof steel plate, through the two-stage rolling process, austenite grain structures are refined repeatedly, the strength of the steel plate is improved, quenching and tempering are not needed during production, production cost is reduced, and the production period is shortened.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-hardenability and high-strength ultra-thick marine steel plate and production method thereof
The invention relates to a high-hardenability and high-strength ultra-thick marine steel plate. The high-hardenability and high-strength ultra-thick marine steel plate is 60-150 mm thick and is composed of the chemical components of, by weight percentage, 0.04-0.08% of C, 4-9% of Mn, 0.10-0.25% of Si, 0.01-0.03% of Als, 0.2-0.5% of Mo, 0.025-0.050% of Nb, less than or equal to 0.04% of S, less than or equal to 0.007% of P, and Fe and impurity elements as balance. The high-hardenability and high-strength ultra-thick marine steel plate can solve the phenomenon of non-uniformity of thickness direction texture and performance, expand the thickness specification to 150 mm with low-temperature toughness still meeting the operating requirements at -80 DEG C and obtain low yield ratio under equal yield strength conditions, specifically, the parts of 1 / 4 and 1 / 2 thickness of the steel plate reach a yield strength not lower than 690 MPa, a yield ratio not higher than 0.86, an elongation percentage not lower than 20%, and a -80 DEG C low-temperature impact energy greater than 100 J.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Ferrite martensite steel ladle shell material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112695256AImprove high temperature performanceImprove neutron radiation resistance performanceNuclear energy generationFurnace typesLead bismuthMachining deformation
The invention belongs to the technical field of fourth-generation lead bismuth cooling fast reactor structural materials, and particularly relates to a ferrite martensite steel ladle shell material and a preparation method thereof. The ferrite martensite steel ladle shell material comprises the components of 0.08wt%-0.16wt% of C, 0.30wt%- 0.8wt% of Mn, 0.50wt%-1.20wt% of Si, 8.5wt%-10.5wt% of Cr, 1.0wt%-2.5wt% of W, 0.10wt%-0.40wt% of V, 0.10wt%-0.40wt% of Ta, 0.005wt%-0.08wt% of Zr, 0.005wt%-0.05wt% of La, 0.008wt%-0.04wt% of N, and the balance Fe and impurities. The preparation method of the ferrite martensite steel ladle shell material comprises the following process steps of (1) smelting; (2) casting; (3) forging; (4) extruding; (5) pipe blank machining and heat treatment; (6) multi-pass cold rolling and intermediate heat treatment of the alloy; and (7) final heat treatment of the pipe. According to the ferrite martensite steel ladle shell material and the preparation method thereof, through the innovative component design, the optimized pipe machining deformation process and the heat treatment technology, the microstructure of the material is improved, grains are refined, and therefore the comprehensive performance of the alloy is improved.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Low-temperature-resistant H-shaped steel and production process thereof
ActiveCN104018074AReduce the ductile-brittle transition temperatureGood impact resistance at low temperatureChemical compositionManganese
The invention discloses low-temperature-resistant H-shaped steel comprising the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.08-0.13% of C, 0.15-0.35% of Si, 1.25-1.45% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.01% of P, less than or equal to 0.01% of S, 0.02-0.05% of V and the balance of Fe and impurity elements. The rolling technological parameters are as follows: the heating temperature ranges from 1220 DEG C to 1240 DEG C, the initial blooming temperature ranges from 1050 DEG C to 1150 DEG C, the initial finish rolling temperature ranges from 930 DEG C to 950 DEG C, and the final finish rolling temperature ranges from 780 DEG C to 900 DEG C; the cooling technological parameters are as follows: a rolled piece is cooled to the interval of 550-650 DEG C at the speed of 100-150 DEG C / s to generate phase change, then, the rolled piece is heated to 700-750 DEG C, and finally, the H-shaped steel is naturally cooled to room temperature. The H-shaped steel can have extremely low ductile-brittle transition temperature and favorable low temperature impact resistance in high and cold areas and low-temperature environments with the temperature of 40 DEG C below zero and even lower.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Steel for drill pipe body suitable for arctic-alpine areas
InactiveCN102071363AReduce the ductile-brittle transition temperatureHigh impact energyDrilling rodsDrilling casingsTrace elementTransition temperature
The invention relates to a kind of steel for the drill pipe body suitable for arctic-alpine areas. The steel comprises the following components by weight percent: 0.20-0.30% of C, 0.17-0.35% of Si, 0.60-1.0% of Mn, 0.015% or less of P, 0.008% or less of S, 0.7-1.0% of Cr and 0.75-1.0% of Ni. The steel also comprises two or more of 0.03% or less of Al, 0.10% or less of V, 0.6% or less of Mo, 0.03% or less of Ti, 0.03% or less of Re and 0.02% or less of Ca, and the balance Fe and inevitable trace elements. When the yield strength is 995MPa, the temperature is -60 DEG C, the longitudinal direction of the steel is detected and the size is 3 / 4, the Charpy impact energy is 85J, the fracture fibre rate is 100% and the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature is -75 DEG C.
Owner:SHANGHAI HILONG DRILL PIPE MATERIALS INST +1
Low-nickel type medium-chromium ferrite stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
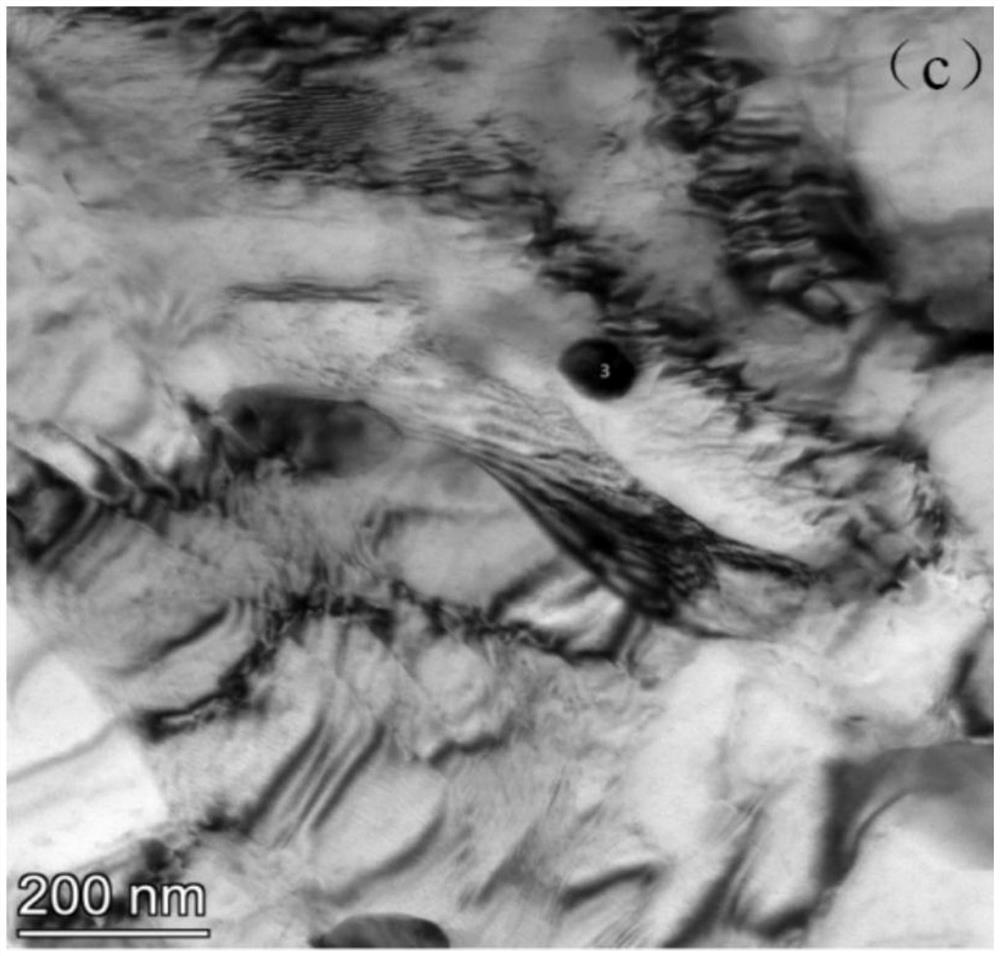
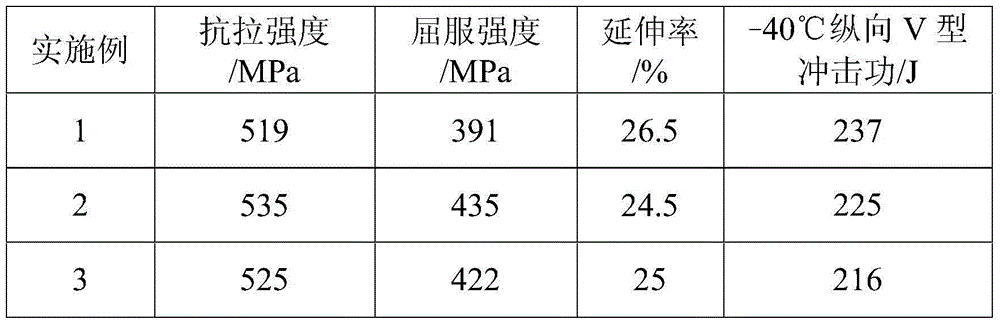
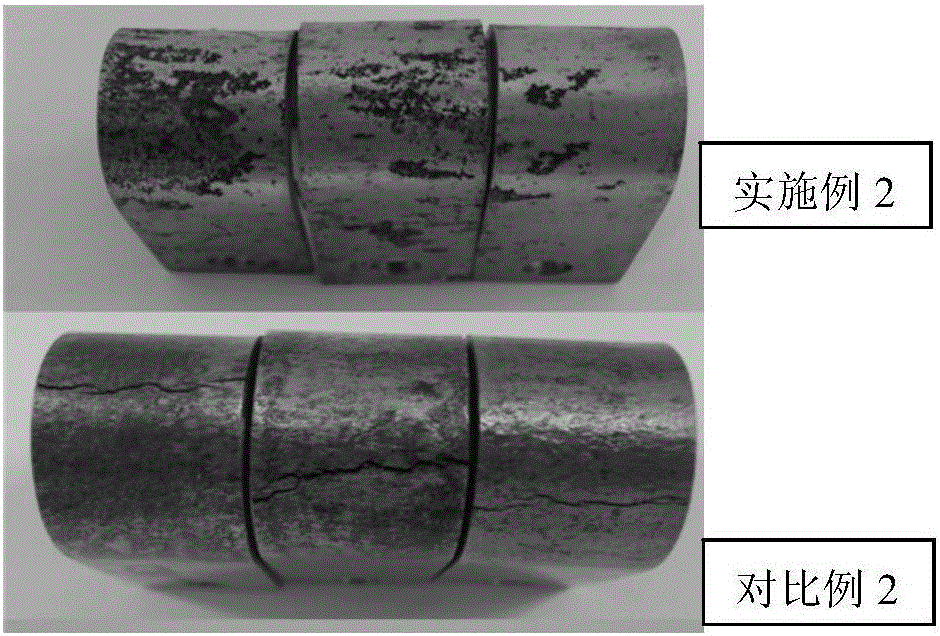
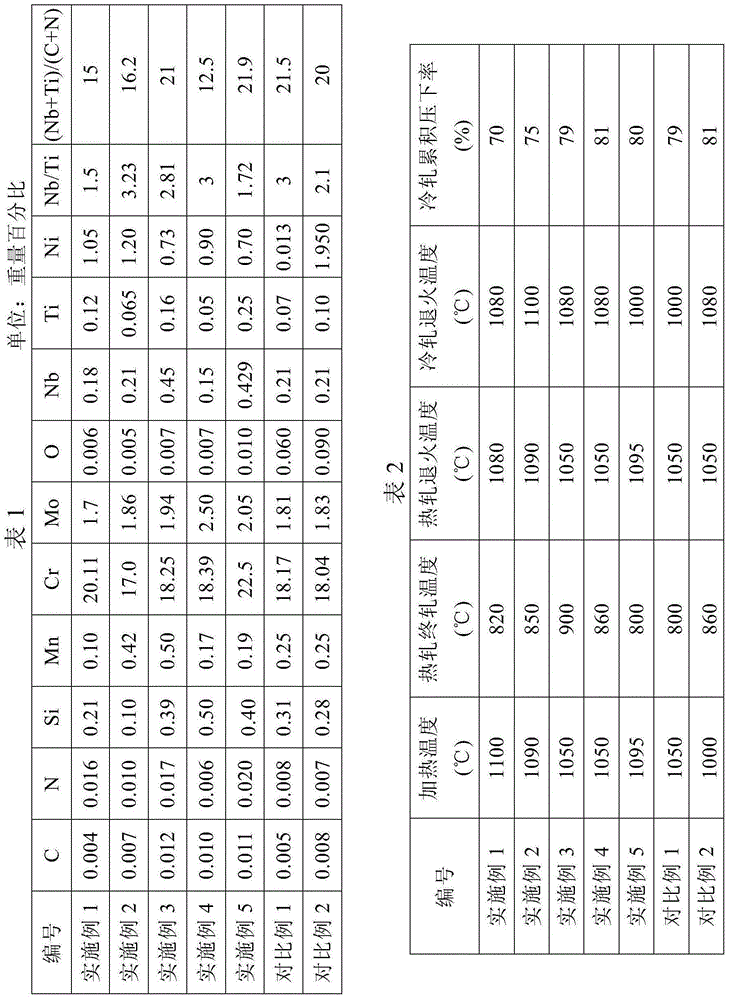
The invention discloses low-nickel type medium-chromium ferrite stainless steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The low-nickel type medium-chromium ferrite stainless steel comprises, by weight, 0.7%-1.2% of Ni, 0.002%-0.012% of C, 0.002%-0.020% of N, 0.10%-0.50% of Si, 0.1%-0.50% of Mn, 17.00%-22.50% of Cr, 1.70%-2.50% of Mo, 0.15%-0.45% of Nb, 0.05%-0.25% of Ti, 0.005%-0.010% of O, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The following relational expressions are met, wherein (C+N) is smaller than or equal than 0.030%, Nb / Ti is equal to 1.5-4, and (Nb+Ti) / (C+N) is equal to 12-22. The low-nickel type medium-chromium ferrite stainless steel obtained through the method has excellent low-temperature toughness and high strength; the ductile-brittle transition temperature is smaller than or equal to -40 DEG C, the yield strength is larger than or equal to 330MPa, and strength of extension is larger than or equal to 445MPa; and the metallographic structure is a pure ferrite equiaxed grain structure.
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL
Tungsten-zirconium carbide-rhenium alloy with high-temperature stability and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a tungsten-zirconium carbide-rhenium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The alloy mainly comprises metal tungsten, wherein the alloy also includes 0.2wt percent to 1.0wt percent of zirconium carbide, and 0.5wt percent to 3.0wt percent of rhenium. The preparation method comprises the following steps of putting metal tungsten powder, zirconium carbide powder and rhenium powder in a protective atmosphere or a vacuum or alcohol in proportion to be mixed uniformly for obtaining mixed powder, first putting the mixed powder under pressure of 200MPa to 600MPa to press for obtaining a green compact, afterwards, putting the green compact in the protective atmosphere or the vacuum, and sintering and molding the green compact at a temperature of 1500 DEG C to 2200 DEG C to prepare a target product. The tungsten-zirconium carbide-rhenium alloy prepared by the invention has excellent performances of higher high-temperature strength and plasticity and a high recrystallization temperature.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrapure smelting method of low-alloy high-strength steel
ActiveCN102534122AHigh thermodynamic stabilityGuaranteed ultra-pure smelting processRaw materialDenitrification
The invention relates to the field of vacuum induction smelting, particularly an ultrapure smelting technical method of low-alloy high-strength steel. A CaO refractory material is utilized to form a crucible, and a vacuum induction smelting method is utilized to acquire the ultrapure low-alloy high-strength steel. In the melting period, carbon in the alloy raw material is utilized to carry out primary stage deoxidization and denitrification; in the refining period, the refining temperature is enhanced to reinforce the thermodynamicical and dynamic conditions for deoxidization and desulfurization, and effective deoxidization and desulfurization are carried out on the crucible wall part and the molten steel surface; and in the deoxidization and desulfurization period, strong deoxidizer and desulfurizer are added to carry out end deoxidization and desulfurization on the alloy so as to further lower the oxygen and sulfur contents in the alloy, so that the oxygen content is controlled below 10ppm, the sulfur content is controlled below 30ppm, and the nitrogen content is controlled below 30ppm. The invention can effectively improve the low-temperature impact toughness of the low-alloy high-strength steel, and further lower the tough-brittle transition temperature, thereby widening the application range of the low-alloy high-strength steel, enhancing the hot working properties of thealloy and acquiring the high-quality low-alloy high-strength steel.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com