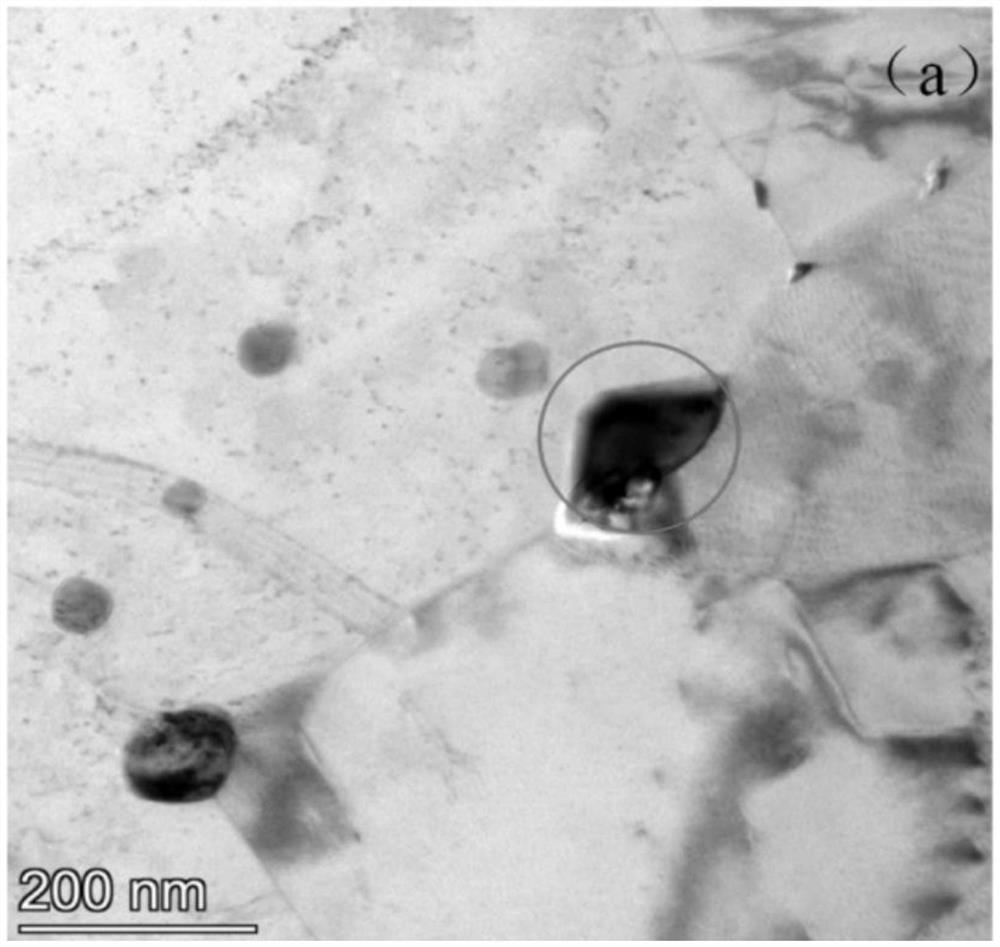
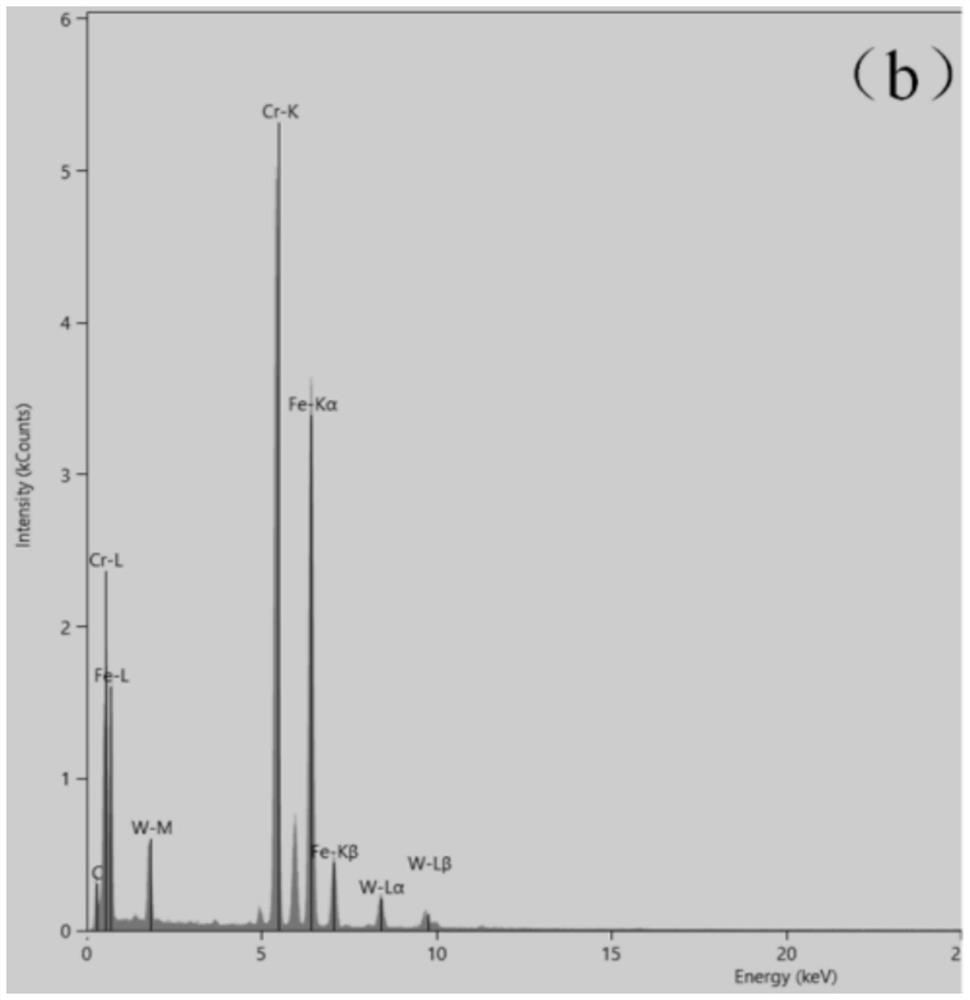
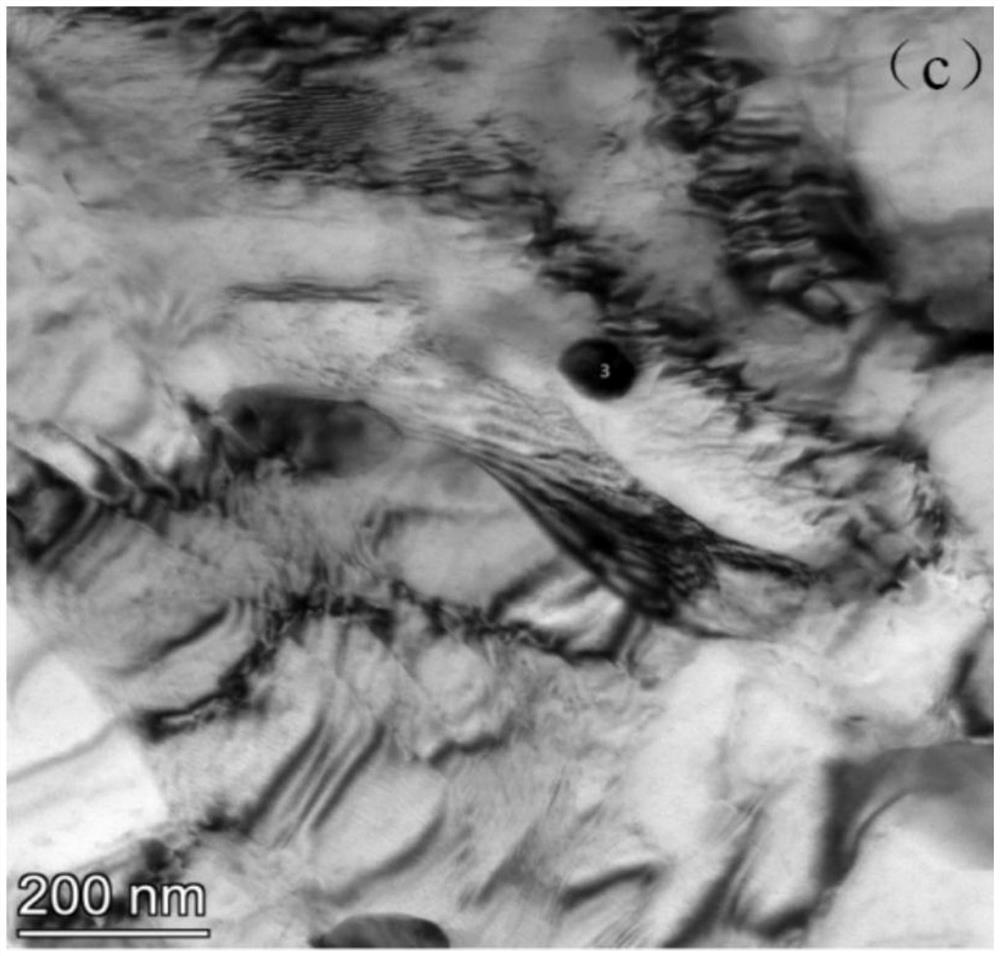
Ferrite martensite steel ladle shell material and preparation method thereof
A martensitic steel and cladding material technology, applied in the field of fourth-generation lead-bismuth cooled fast reactor structural materials, can solve the problems of insufficient ductility, high fuel consumption, etc., and achieve improved high temperature performance and neutron radiation resistance performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
[0066] A ferritic martensitic steel cladding material, the alloy comprising:
[0067] C: 0.08~0.16wt%, Mn: 0.30~0.8wt%, Si: 0.50~1.20wt%, Cr: 8.5~10.5wt%, W: 1.0~2.5wt%, V: 0.10~0.40wt%, Ta: 0.10-0.40wt%, Zr: 0.005-0.08wt%, La: 0.005-0.05wt%, N: 0.008-0.04wt%, and the rest are Fe and impurities.
[0068] The C, N content and Ta, V, Zr content in the alloy satisfy the following quantitative relationship:
[0069] 1.5 times (C+N) content≤(Ta+V+Zr) content≤3 times (C+N) content.
[0070] The impurities in the alloy and their content control meet the following conditions: S<0.003wt%, P<0.008wt%, B<0.01wt%, O<0.002wt%, H<0.001wt%.
[0071] As a further optimized technical solution, except for impurities, the main component of the alloy is Fe-9Cr-1.5W-0.5Mn-0.12C-0.15Ta-0.2V-0.02N-0.01Zr-0.03La-0.6Si.
[0072] A method for preparing a ferritic martensitic steel cladding material as described above, comprising the following process steps:
[0073] (1) Melting
[0074] (1.1) Carr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wall thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com