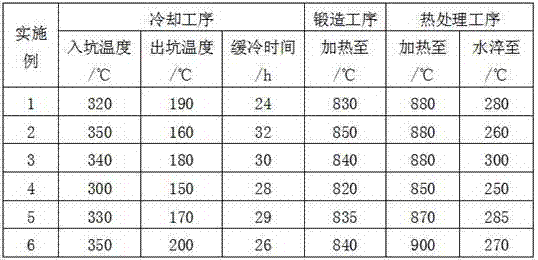
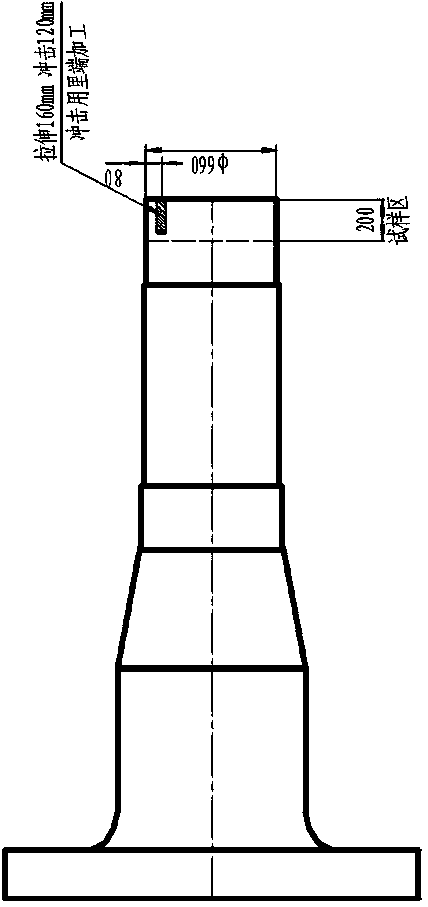
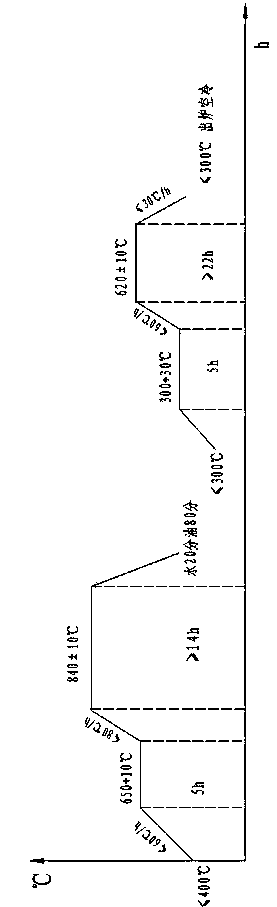
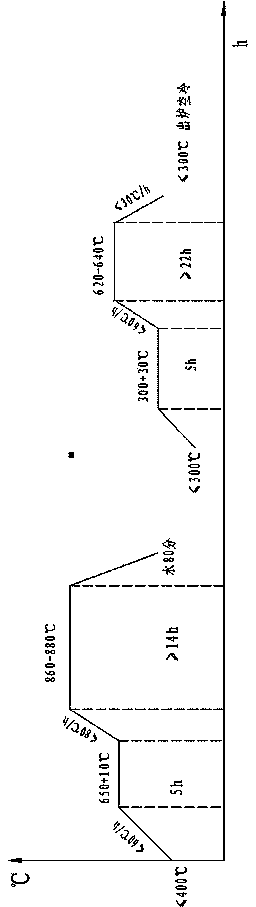
Patents
Literature
53results about How to "Raise the quenching temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Disk shearing blade and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101177765AImprove wear resistanceHigh strengthShearing machinesFurnace typesHigh intensityWear resistance
A disc scissors blade and its manufacturing method, the composition weight percentage of the material of the disc scissors blade is: C: 0.40-0.70%, Si: 0.50-1.2%, Mn: 0.20-0.50%, Ni: 1.00-1.50% %, Cr: 4.00-6.00%, Mo: 0.50-2.00%, V: 0.30-1.50%, Nb: 0.10-0.80%, P≤0.02%, S≤0.02%. The method introduces an electroslag remelting process into a common manufacturing method of disc shears, and increases the temperature of quenching and tempering heat treatment and final heat treatment. The disc scissors have good wear resistance and deformation resistance, and are suitable for slitting or trimming hot-rolled high-strength thick steel plates. In addition, the disc shear blade of the present invention also has a good use effect on disc shears in other similar working conditions, and can also be applied to disc shears for stripping or edge trimming of cold-rolled strip steel, and also has a promotional effect on non-ferrous metal disc shears. value and application prospects.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
Heat-treating process for hot-working die steel forgings
InactiveCN104498685AReduced risk of quench crackingRaise the quenching temperatureTemperingWarm water
The invention belongs to the technical field of heat treatment of heavy industry, and particularly relates to a heat-treating process for hot-working die steel forgings. The heat-treating process comprises the following steps: spheroidizing and annealing, quenching, cooling and tempering. The heat-treating process is suitable for 5CrNiMo die steel or H13 die steel; spheroidizing and annealing heat treatment is added before quenching, so that the preheating treatment structure of a workpiece is transformed into globular pearlite and cementite; the risk of a quenching crack of the workpiece is reduced; the quenching temperature is improved; austenization is relatively full; and the temperature of a quenching medium is improved. Warm water at 40-60 DEG C is adopted as the quenching medium, so that the performance of the workpiece is improved under the premise that no crack of the workpiece is ensured. Through combination of three improvement points, the performance of the workpiece, especially the impact strength is obviously improved; and the performance requirements are met.
Owner:TONGYU HEAVY IND
Hardening and tempering technology of alloy-steel tube
ActiveCN102676780AStress reliefUniform internal organizationFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHydraulic cylinderFree cooling
The invention discloses a hardening and tempering technology of an alloy-steel tube, and through the technology, the hardened and tempered alloy-steel tube is high in intensity and hardness, has good abrasion resistance and high plasticity, bears great pressure, and has small deformation and less decarburization. The technology comprises the following steps of: (1) annealing treatment: warming to 870-880 DEG C at the speed of 20-25 DEG C / minute, keeping the temperature for 35-40 minutes, and then cooling to 500 DEG C below; (2) quenching treatment: warming to 930-935 DEG C at the speed of 5-10 DEG C / minute, keeping the temperature for 50-60 minutes, then cooling rapidly at the speed of 190-200 DEG C / second to 320-325 DEG C, and cooling naturally to 30-40 DEG C; and (3) tempering treatment: warming to 500-510 DEG C at the speed of 5-10 DEG C / minute, then keeping the temperature for 230-240 minutes, and then cooling naturally to room temperature, thus the hardened and tempered alloy-steel tube is high in intensity and hardness, has good abrasion resistance and high plasticity, bears great pressure, and has small deformation and less decarburization. The hardening and tempering technology of the alloy-steel tube provided by the invention is mainly applied to the hardening and tempering of the alloy-steel tube for a hydraulic cylinder barrel.
Sprocket tooth part induction heat treatment process
InactiveCN101838729AImproving the level of induction heat treatment processImprove craftsmanshipFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencyElectricitySprocket
The invention relates to a sprocket tooth part induction heat treatment process, which comprises the following steps: after installing an induction coil, installing a sprocket work piece at a work piece position in the induction coil, adjusting the heights of the induction coil and the sprocket work piece to ensure the centers of the induction coil and the sprocket tooth part to correspond with each other and to ensure the clearance to be uniform; supplying water and electricity to the induction coil and rotating the sprocket to ensure the tooth part to be heated; when the sprocket tooth part is heated to a quenching temperature, after the workpiece stays for 1.5-5 seconds in the air, leading the sprocket tooth part to enter into quenching oil vertically without rotation; taking the sprocket out of the quenching oil after quenching is finished, and washing after draining dry; and after draining dry again, putting the sprocket into a tempering furnace to be heated to a tempering temperature, and taking the sprocket out of the furnace when a holding time is reached. By adopting the sprocket tooth part induction heat treatment process, cracks or fracture of the sprocket tooth part can be avoided after the induction heat treatment, and after the induction heat treatment, the hardness of the sprocket tooth part is uniform, which differs within HRC 5 degrees, high-quality surface harness of the sprocket tooth part can be obtained, and the service life of the sprocket is prolonged.
Owner:王锦堂
Heat treatment method for inlaid backup roll sleeve
InactiveCN105543451AImprove wear resistanceHigh contact fatigue strengthFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencyHardnessIngot
The invention discloses a heat treatment method for an inlaid backup roll sleeve. The heat treatment method comprises the following steps: A, smelting a steel ingot, and then forging a roll sleeve blank, followed by rough machining and flaw detection; B, performing hardening and tempering on the roll sleeve blank, heating the roughed roll sleeve, and performing tempering on the roll sleeve; C, performing semi-finish turning machining and flaw detection on the roll sleeve; D, hoisting the semi-finish turning machined roll sleeve to a power-frequency quench machining tool, carrying out overall induction heating by using a dual-power frequency power source, adopting a water quenching method; subsequently, carrying out tempering; E, detecting metallographic structures of inner and outer surfaces of the roll sleeve, and detecting residual stress and hardness of the outer surface; F, performing finish machining on the roll sleeve; and G, assembling a roll shaft, and performing finish machining on the assembled roll. The heat treatment method for the inlaid backup roll sleeve of the present invention meets the requirements in structure, hardness and residual stress aspects, and meanwhile, such properties as abrasive resistance and contact fatigue strength of the roll sleeve also are improved.
Owner:SINOSTEEL XINGTAI MACHINERY & MILL ROLL
Heat treatment process for optimizing 42CrMo low-temperature impact absorbing energy
The invention provides a heat treatment process for optimizing 42CrMo low-temperature impact absorbing energy. According to the heat treatment process, during forging discharging, chemical compositions are controlled, the B element is added, and the hardenability is improved; and after forging, different high normalizing temperatures, different high hardening temperatures and the faster cooling manner are adopted, and the better low temperature impact toughness is obtained. In the discharging process, the chemical compositions are added, the B element is added, then forging is performed, forged materials are subjected to high-temperature normalizing and high-temperature tempering, then rough machining is carried out, materials obtained after rough machining is subjected to modulation treatment, and modulation treatment specifically includes high-temperature quenching and high-temperature tempering, and stress relief annealing is carried out after semifinishing.
Owner:WUXI HONGDA HEAVY IND
Heat treating process for eliminating mixed crystal of low-alloy quick-cutting steel
The invention discloses a low alloy high speed steel mischcrystal elimination heat treatment process. The process comprises an annealing procedure and a quenching procedure. The annealing procedure comprises the following steps: heating up a low alloy high speed steel ingot to 890 to 910 DEG C at the speed of 300 DEG C per hour; controlling an annealing cooling rate at 25 to 30 DEG C per hour when the temperature of the ingot is above 600 DEG C; and cooling the ingot in the furnace when the temperature of the ingot is less than or equal to 600 DEG C. The quenching procedure comprises the following steps: preheating the annealed steel ingot to 800 to 850 DEG C, and controlling the heating time to be 5 to 15 minutes; continuing to heat up the ingot and increase the temperature to 1,170 to 1,190 DEG C, and controlling the holding time to be 2 to 6 minutes; and cooling the ingot through interrupted quenching. The process improves the annealing temperature rising rate and the annealing heating temperature, thereby enabling an annealed structure to be closer to an equilibrium structure, effectively avoiding the uneven growth of quenching austenite grains in a subsequent temperature span easily producing mischcrystal, improving the quenching temperature of the low alloy high speed steel, and reaching the aim of improving the red hardness of the high speed steel while simultaneously obtaining high tenacity.
Owner:江苏华久特钢工具有限公司
High chrome alloy strengthened steel cast shot/sand and manufacturing process thereof
The invention relates to high-chrome alloy strengthening cast steel shot / grit and a manufacturing process thereof. The invention relates to alloy cast steel shot or cast steel grit used to clear and strengthen the surface of steel, and a manufacturing process thereof, which belongs to metal abrasive. The cast steel shot / grit is characterized in that the weight percentage is as follows: C: 0.75 percent to 1.00 percent, Cr: 0.60 percent to 1.50 percent, V: 0.05 percent to 0.20 percent, Ti: 0.05 percent to 0.20 percent, Si: 0.40 percent to 1.50 percent, Mn: 0.50 percent to 1.20 percent, P: less than or equal to 0.05 percent, S: less than or equal to 0.05 percent, and the rest is Fe. The high-chrome alloy steel shot belongs to the scope of eutectoid steel, and the adding of alloy elements improves the eutectic temperature of steel and prevents carbon from spreading. Therefore, the quenching temperature can be improved, which is good for pearlite to transform into austenite and the carbon to spread. Fine texture is changed to tempered martensite and tempered troostite. The carbide network of the alloy is lower than or equal to Grade 2 and basically kept to be Grade 1, which is higher than the international GB6484 / 6485-86; the standard carbide network is lower than or equal to Grade 3.
Owner:杨继玉
Preparation method of large hot-forging hot-work die steel
The invention discloses a preparation method of large hot-forging hot-work die steel, and belongs to the technical field of hot-work die steel. Comprising the following steps that firstly, an electric furnace is adopted, an electric furnace and electroslag remelting or a vacuum induction furnace is adopted for smelting to prepare a steel ingot, and the steel ingot comprises, by weight, 0.30%-0.39% of C, 0.35%-0.55% of Si, smaller than or equal to 0.002% of S, smaller than or equal to 0.02% of P, 0.50%-0.7% of Mn, 1.40%-1.70% of Mo, 2.60%-3.40% of Cr, 0.10%-0.30% of V, 0.80%-1.20% of Ni, smaller than or equal to 0.2% of Al + Nb, smaller than or equal to 0.1% of B and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities; 2, pre-cogging the steel ingot; thirdly, the pre-opened blank is subjected to high-temperature diffusion; 4, blank forging; and 5, normalizing and spheroidizing annealing. The method has the beneficial effects that by improving the components and the content of steel and using a new forging method, the obtained large-scale hot-forging hot-work die steel is good in obdurability, high in tempering stability and good in high-temperature strength, and the use requirements of the large-section hot-forging hot-work die steel can be met.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Heat process capable of lowering ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades
ActiveCN102220459AShort residence time at high temperatureFully solid solutionFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlChemical compositionTurbine blade
The invention provides a heat treatment process capable of lowering ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of turbine blades. When the heat treatment process is used, the problem that the process effect is susceptible to influences of chemical components of the raw material of the blades when the conventional sub-temperature annealing process is used to treat the turbine blades and the problem of high ductile-brittle transition temperature and intergranular fracture ratio of the turbine blades due to overlong high-temperature retention during heat treatment ofthe blades in the sub-temperature annealing process are solved. In the invention, the blades are uniformly placed in a common quenching material basket according to a technical scheme and then the quenching material basket is placed in a heat treatment quenching furnace. The heat treatment process is characterized in that: the blades are quenched twice in a quenching furnace; the temperature of primary quenching is 980 to 1070 DEG C; the temperature is kept constant for 1 to 3 hours; the cooling speed is 20 to 50 DEG C per minute; the temperature of secondary quenching is 900 to 1,000 DEG C; the temperature is kept constant for 15 to 120 minutes; the cooling speed is 30 to 50 DEG C minutes; and the temperature of the primary quenching is 20 to 100 DEG C higher than the temperature of the secondary quenching.
Owner:WUXI TURBINE BLADE
Process for quenching steel plate spring
InactiveCN102242247AReduce consumptionReduced propensity to decarbonizeFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHeating furnaceQuenching
The invention provides a process for quenching a steel plate spring, which comprises the following steps of: putting the steel plate spring into a heating furnace, heating to the temperature of between 930 and 950 DEG C, and preheating for 12 to 18 minutes; continuously heating to the temperature of between 1,020 and 1,065 DEG C, and keeping the temperature for 12 to 18 minutes; and putting the steel plate spring into quenching liquid for quenching. By the quenching process, the fatigue life of the steel plate spring can be prolonged, the production energy consumption of a product can be reduced, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:湖北神风汽车弹簧有限公司
Steel for heavy-duty loader tire protecting chain and production method thereof
ActiveCN106967924AIncrease yield pointHigh tensile strengthTemperature control deviceDecompositionHeavy duty
The invention discloses steel for a heavy-duty loader tire protecting chain and a production method thereof. The steel is composed of, by mass, 0.35-0.42% of C, 0.70-1.10% of Si, 0.85-1.20% of Mn, 0.035% P or less, 0.035% of S or less, 0.40-0.60% of Cr, 0.008-0.015% of Tal and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The protecting chain utilizes Si element to significantly improve the steel yield point, tensile strength, the quenching temperature, the hardenability, the corrosion resistance and antioxidant capacity through combining with Cr element; Mn element is utilized to improve the hardenability and refine a pearlite; Cr element is utilized to slow down the decomposition speed of an austenite, improve the hardenability, promote formation of a passive film on the surface of steel and improve the corrosion resistance of the steel; and Al element is utilized to reduce the sensitivity of the steel to a gap, refine the natural steel grain and increase the temperature of grain coarsening. According to the steel for the heavy-duty loader tire protecting chain and the production method thereof, the Rockwell hardness reaches to 55 or more, wear resistance is good, a converter and continuous casting production can be used, adding of precious metal elements is not needed, and cost is low.
Owner:河北张宣高科科技有限公司
Heat treatment process for 42CrMo wind power spindle
InactiveCN104313288ASpeed up coolingImprove mechanical propertiesFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesThermodynamicsEngineering
The invention provides a heat treatment process for a 42CrMo wind power spindle. The heat treatment process comprises the following concrete steps: heating the wind power spindle with the temperature of less than 400 DEG C to 650-660 DEG C at the speed of less than 60 DEG C / h, keeping the temperature for 5 hours, heating to the temperature T at the speed of less than 80 DEG C / h, keeping the temperature for more than 14 hours, cooling by water for 80 minutes until the temperature of the wind power spindle is less than 300 DEG C, heating to 300-330 DEG C, keeping the temperature for 5 hours, heating to 620-640 DEG C at the speed of less than 60 DEG C / h, keeping the temperature for more than 22 hours, and cooling by air to less than 300 DEG C at the speed of less than 30 DEG C / h, wherein T is 860-880 DEG C. According to the heat treatment process, the quenching temperature is increased to be 860-880 DEG C, a workpiece is fully austenitized, the depth of a hardening layer is increased, the water-cooling time is prolonged to be 80 minutes to increase the cooling speed of the wind power spindle, a lower bainite or martensite structure is obtained, and the comprehensive mechanical property of the spindle is improved.
Owner:TONGYU HEAVY IND
Technology for optimizing 09 MnNiD low-temperature impact energy
InactiveCN109929981AMeet the requirements of low temperature impact energy absorptionReduce precipitationAbsorbed energyUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides a technology for optimizing a 09 MnNiD low-temperature impact energy. By means of the technology, it is ensured that the strength is best matched with ductility and toughness ofa 09 MnNiD material, and the requirement for low-temperature impact absorbing energy of a large forge piece is met. A conventional austenitizing temperature is used for conducting normalizing treatment on the 09 MnNiD forge piece, first-time high-temperature tempering is conducted, and therefore the tissue is adjusted, and grains are refined; afterwards, rough machining is conducted on the forgepiece, then the material obtained through rough machining is subjected to high-temperature quenching under the quenching temperature ranging from 920 DEG C to 950 DEG C, a deep hardening layer is obtained, and a fast cooling manner is adopted for cooling so as to reduce precipitation of brittle phases; afterwards, second-time high-temperature tempering is conducted, and the tissue is homogenized;and finally, the quenching temperature ranging from 850 DEG C to 885 DEG C is adopted for conducting subcritical quenching, tempering is conducted finally, and the corresponding 09 MnNiD material capable of being used for finish machining is obtained.
Owner:WUXI HONGDA HEAVY IND
7-series aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a 7-series aluminum alloy and a preparation method thereof. The 7-series aluminum alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 1.95-2.2% of magnesium, 0.04-0.1% of silicon, 0.04-0.06% of iron, 0.15-0.33% of copper, 0.023-0.028% of titanium, 5.68-6.05% of zinc, 0.16-0.26% of manganese, 0.02-0.05% of zirconium, and the balance of aluminum. The 7-series aluminum alloy has the advantages of the tensile strength of above 470, the yield strength of above 440, the Vickers hardness HV of above 160 and excellent rupture toughness and fatigue resistance.
Owner:SICHUAN FURONG TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Heat treatment method capable of improving elongation rate of PCrNi3MoVA material forge piece
The invention relates to a heat treatment method capable of improving an elongation rate of a PCRni3MOVA material forge piece. The method comprises the following steps that normalizing is conducted toheat to 610-650 DEG C firstly, then heating up to 880-900 DEG C is conducted, then heat preservation is conducted, and cooling to a room temperature is conducted; quenching is conducted to heat to 610-650 DEG C firstly, then heating up to 860-880 DEG C is conducted, the heat preservation is conducted, cooling and quenching are conducted, taking out of a furnace is conducted, and water cooling, air cooling, secondary water cooling and oil cooling are conducted for cooling and quenching; tempering at a high temperature is conducted to heat to 320-350 DEG C firstly, then preserving heat is conducted, and then heating up to 580-610 DEG C is conducted; after the furnace cooling to 400 DEG C is conducted, and taking out of the furnace is conducted for the air cooling. According to the method, the heat treatment mode of normalizing, cooling and quenching and high-temperature tempering is adopted, the material forge piece with a effective section phi 101 mm to phi 250 mm can be subjected to heat treatment, the elongation rate of the material forge piece subjected to the heat treatment can reach 16%-19%, technical requirements of an ultra-high pressure container forge piece can be met, andthe production process is high in operability.
Owner:武汉重工铸锻有限责任公司
Manufacturing method for scale breaking tension leveler working roll
ActiveCN103589850AImprove toughnessIncreasing the thicknessFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesStress distributionMedium frequency
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a scale breaking tension leveler working roll. By adopting Cr12MoVCo die steel as the material, the manufacturing method includes the steps of: rough turning, hardening and tempering, semi-finish turning, shaping treatment, coarse grinding of roll surface, preheating, medium frequency spray quenching, isothermal treatment, tempering, and finish machining, thus obtaining a finished product. Specifically, the preheating temperature is 400-450DEG C, the medium frequency spray quenching temperature is 1100-1200DEG C, the isothermal temperature is 200-250DEG C, and the tempering temperature is 500-550DEG C. In the invention, by changing the thermal treatment process, under the circumstance of obtaining quenched martensite on the surface, a transition layer is mainly based on bainite, high hardness and high wear resistance of the surface are retained, toughness of the transition layer and the core is increased, the occurrence of microcracking is reduced, and the fracture risk in use is avoided. The thickness of the transition layer is increased, the overall strength of the roll is increased, the stress distribution is more reasonable, and the grinding performance of the roll is improved.
Owner:宜兴市鑫源辊业有限公司
Heat treatment technique for improving low-temperature toughness of martensite-type heat-resistant steel containing large M23C6 precipitated phases
InactiveCN107227395AElimination of precipitated phaseGuaranteed StrengthAustenite grainUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a heat treatment technique for improving the low-temperature toughness of martensite-type heat-resistant steel containing large M23C6 precipitated phases. According to the heat treatment technique, the martensite-type heat-resistant steel 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN containing the large M23C6 precipitated phases is heated to the temperature of 1070-1100 DEG C and is above the coarsening temperature of austenite grains, heat preservation is conducted for 30-45 minutes, the large M23C6 precipitated phases are eliminated quickly through high temperature heating so as to make the structure homogenized, then oil quenching or air cooling quenching is conducted; the martensite-type heat-resistant steel is heated again to the temperature of 960-990 DEG C after cooling, heat preservation is conducted for 30-45 minutes, the austenite grains are heated and refined at a low temperature, then oil quenching or air cooling quenching is conducted; and the martensite-type heat-resistant steel subjected to secondary quenching is heated again to the temperature of 670-690 DEG C and tempered for 90-120 minutes, quenched martensite is fully recovered through high-temperature quenching, and air cooling is conducted. Through the heat treatment technique secondary quenching and high-temperature tempering, the large M23C6 precipitated phases are eliminated quickly, the austenite grains are refined, and the quenched martensite is fully recovered quickly, so that the low-temperature toughness of the martensite-type heat-resistant steel containing the large M23C6 precipitated phases is improved significantly on the premise of ensuring good strength.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Method for incremental heat treatment of escalator chain plate
ActiveCN101775472AHigh strengthEliminate internal stressFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesQuenchingInternal stress
The invention relates to a method for incremental heat treatment of an escalator chain plate, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: forming four different temperature zones with a mesh belt type furnace for heat treatment in the atmosphere of methanol gas for incremental increase of the quenching temperature of an escalator chain plate, and annealing at the temperature of 155 DEG C plus or minus 5 DEG C for 2.9-3.1 hours after quenching, wherein four different temperatures are 810 DEG C plus or minus 5 DEG C, 820 DEG C plus or minus 5 DEG C, 830 DEG C plus or minus 5 DEG C and 840 DEG C plus or minus 5 DEG C in sequence. Since the mesh belt type furnace for heat treatment is used for forming the four different temperature zones so as to incrementally increasing the quenching temperature of the escalator chain plate, the invention enhances the strength of the escalator chain plate on the premise that no high internal stress is generated. Moreover, the invention adopts annealing after quenching, thereby eliminating the internal stress generated during quenching and improving the toughness of the escalator chain plate.
Owner:HENGDA FUJI ELEVATOR
Multi-element micro-alloy strengthening steel shot/sand and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN103014563AReduce contentReduce segregationFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCarbideNational standard
The invention provides multi-element micro-alloy strengthening steel shot / sand and a production process thereof. The invention relates to alloy steel shot / steel sand for carrying out cleaning and strengthening treatment on the surface of a steel product, and a manufacturing process, and belongs to metal abrasives. The alloy steel shot / steel sand comprises the following components by mass percent (%): 0.60-1.00% of C, 0.40-1.50% of Si, 0.50-1.20% of Mn, 0.15-0.90% of Cr, 0.10-0.20% of W, 0.10-0.20% of Ti, 0.07-0.20% of Mo, less than or equal to 0.05% of P, less than or equal to 0.05% of S and the balance of Fe. Alloy elements are added into multi-element micro-alloy steel so that the eutectoid temperature of the steel is improved and the dispersion of carbon is stopped. Therefore, the quenching temperature is high, and the conversion from pearlite to austenite and the dispersion of carbon are easy to realize. A metallographic structure is changed into a tempered martensite and a tempered troostite. An alloy net-like carbide is less than or equal to grade 2, is basically stabilized to grade 1 and is higher than national standard GB6484 / 648586 that a ruled net-like carbide is less than or equal to grade 3.
Owner:杨继会
Online extrusion production technology for 7A04 high-strength bar
The invention belongs to the technical field of aluminum alloy extrusion technology, and relates to an online extrusion production technology for a 7A04 high-strength bar. The temperature of an extrusion barrel head in an extruder is controlled to range from 450 DEG C to 500 DEG C and is increased compared with the original temperature, the temperature of an extrusion die is set to range from 500 DEG C to 520 DEG C, and the heating temperature of a 7A04 aluminum alloy cast ingot is set to range from 380 DEG C to 420 DEG C, the product extrusion speed is controlled to range from 1.5 m / min to 2.5 m / min, and the temperature of the 7A04 high-strength bar before quenching is larger than or equal to 380 DEG C. After the 7A04 high-strength bar is placed for 2 days and nights, precipitation heat treatment of (125+ / -5) DEG C x (16-20)h is conducted. According to the 7A04 high-strength bar prepared through the extrusion production technology, by utilization of a non-standard extruder and strict control over various technology parameters in the extrusion production technology, the purpose of online production of the 7A04 high-strength bar is achieved, various properties of the 7A04 high-strength bar can meet the using requirement, the production capability of the enterprise is greatly improved, and the production cost is saved for the enterprise.
Owner:CHINA ZHONGWANG
Wear-resistant steel rod and production method thereof
InactiveCN105018704AExtended service lifeExcellent grinding abilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesPearliteDecarburization
Owner:郑州赫芃新材料科技有限公司
Medium carbon-rare earth alloy strengthening cast steel shot/grit and preparation technology thereof
ActiveCN106337154AGranularityIncrease productionFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesNiobiumGrain structure
The invention provides medium carbon-rare earth alloy strengthening cast steel shot / grit and a preparation technology thereof, and belongs to the technical field of metal abrasives. The medium carbon-rare earth alloy strengthening cast steel shot / grit is characterized by being prepared from, by mass, 0.30%-0.85% of C, 0.30%-1.50% of Si, 0.30%-1.50% of Mn, 0.10%-0.15% of Re, 0.10%-0.90% of Cr, 0.01%-0.04% of Nb, smaller than or equal to 0.05% of P, smaller than or equal to 0.05% of S and the balance Fe. According to the medium carbon-rare earth alloy steel, by adding rare earth, molten steel is purified, and a grain structure of steel is refined; the strength, the hardness and the wear resistance are improved through chromium; niobium forms a carbide, and therefore the hardness and the wear resistance are improved; by means of alloy elements, the eutectoid temperature of the steel is increased, and diffusion of carbon is prevented. Accordingly, increase of the quenching temperature is beneficial for conversion from pearlite to austenite and diffusion of carbon. A metallographic structure is converted into tempered martensite and tempered troostite.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
Heat treatment process for ribbon of 1/10mm*12mm steel measuring tape
InactiveCN106834656AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove toughnessFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlRoom temperatureHardness
Aheat treatment process for a ribbon of a 0.1mm*12mm steel measuring tape comprises the following steps: A, discharging; B, quenching: the ribbon is heated in a continuous heating furnace which is 4000-5000 mm long, the furnace operates at the firebox temperature of 1000-1050 DEG C and the constant running speed of 140-180 mm / s, and methanol is dropped at an inlet of the heating furnace at the rate of 40-60 drops / min during advancing of the ribbon; the ribbon is cooled in a template; C, tempering: the ribbon is tempered in a continuous tempering furnace with length of 6000-8000 mm after being quenched by the template; D, blowing: the ribbon is blown cold with argon after being discharged from the furnace. With adoption of a hot quenching process, the ribbon subjected to quenching has both hardness and toughness, so that the mechanical properties of the material are further improved. The silvery white and bright surface of the ribbon at the room temperature is guaranteed by adopting argon blowing cooling.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Preheat treatment process for super-strong high-toughness carburizing steel bar and forge piece
PendingCN114317897AImprove hardenabilityImprove temper resistanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesTemperingHeat conservation
The invention belongs to the field of material processing, and relates to a preheat treatment process for a super-strong high-toughness carburizing steel bar and a forge piece, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out primary high-temperature tempering on the bar and the forge piece which are subjected to thermoplasticity forming at the heating temperature of 670-710 DEG C and the heat preservation time of 8-20 hours, and carrying out furnace cooling or air cooling to room temperature; then incomplete annealing is conducted, the heating temperature ranges from 950 DEG C to 1000 DEG C, the heat preservation time ranges from 1 h to 3 h, and furnace cooling or air cooling is conducted to the room temperature; and finally, secondary high-temperature tempering is conducted, the heating temperature ranges from 670 DEG C to 710 DEG C, the heat preservation time ranges from 8 h to 20 h, and furnace cooling or air cooling is conducted to the room temperature. Through the pre-heat treatment, the structure inheritance caused by high-temperature heating before the super-strong high-toughness carburizing steel bar and the forge piece are subjected to plastic forming is eliminated, fine crystal grains are obtained after final heat treatment, the hardness of the bar or the forge piece is reduced, the residual stress is eliminated, and the cutting machining performance is improved.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Heat treatment technology for die-casting die steel
InactiveCN104178602AImprove mechanical propertiesMore dissolvedProcess efficiency improvementCarbideDie casting
The invention relates to a heat treatment technology for die-casting die steel. The steps of heat treatment are as follows: 1. quenching: loading raw material into a furnace at 550 DEG C, preserving heat for 40 min; heating to 1,150 DEG C, preserving heat for 110-130 min, and then discharging the raw material and cooling the raw material with oil to room temperature; 2. tempering: tempering the raw material three times, with the heating temperature of 560-700 DEG C and the heat preservation time of 90 min in each tempering. according to the heat treatment technology, as the quenching temperature rises, the quenching hardness is improved, more carbide is dissolved, the austenite alloying extent is increased, and thus martensite is strengthened; tempering that is performed once in the traditional technology is performed three times, so that residual low-hardness austenite in the material is fully changed into high-hardness secondary martensite to improve the mechanical property of a die. The service life of the die treated according to the heat treatment technology can reach 4,500 times, the cost of the die is lowered and the production efficiency is increased.
Owner:TIANJIN JINGXIN METAL PROD
Manufacturing process of high chrome alloy strengthened steel cast shot/sand
The invention relates to a process for manufacturing a high-chrome alloy strengthening cast steel shot / grit and belongs to the metal abrasive materials. The process comprises the following steps: smelting and obtaining a molten steel with a weight percentage of: 0.75 percent to 1.00 percent of C, 0.60 percent to 1.50 percent of Cr, 0.05 percent to 0.20 percent of V, 0.05 percent to 0.20 percent of Ti, 0.40 percent to 1.50 percent of Si, 0.50 percent to 1.20 percent of Mn, P<= 0.05 percent, S<= 0.05 percent, and the balance of Fe, adding FeSiMg8RE7 which accounts for 0.2-0.5% of the molten steel total weight for a modification, at a quenching temperature of 835 DEG C, using water as a quenching agent, and medium temperature tempering. The high-chrome alloy steel shot belongs to the scope of eutectoid steel, and the addition of alloy elements improves an eutectic temperature of the steel and prevents carbon from spreading. Therefore, the quenching temperature can be improved, which is good for pearlite to transform into austenite and the carbon to spread. Fine texture is changed to tempered martensite and tempered troostite. The carbide network of the alloy is lower than or equal to Grade 2 and basically kept to be Grade 1, which is higher than the international GB6484 / 6485-86; the standard carbide network is lower than or equal to Grade 3.
Owner:杨继玉
Thermal treatment method for ultralow-temperature high-strength steel for compressor
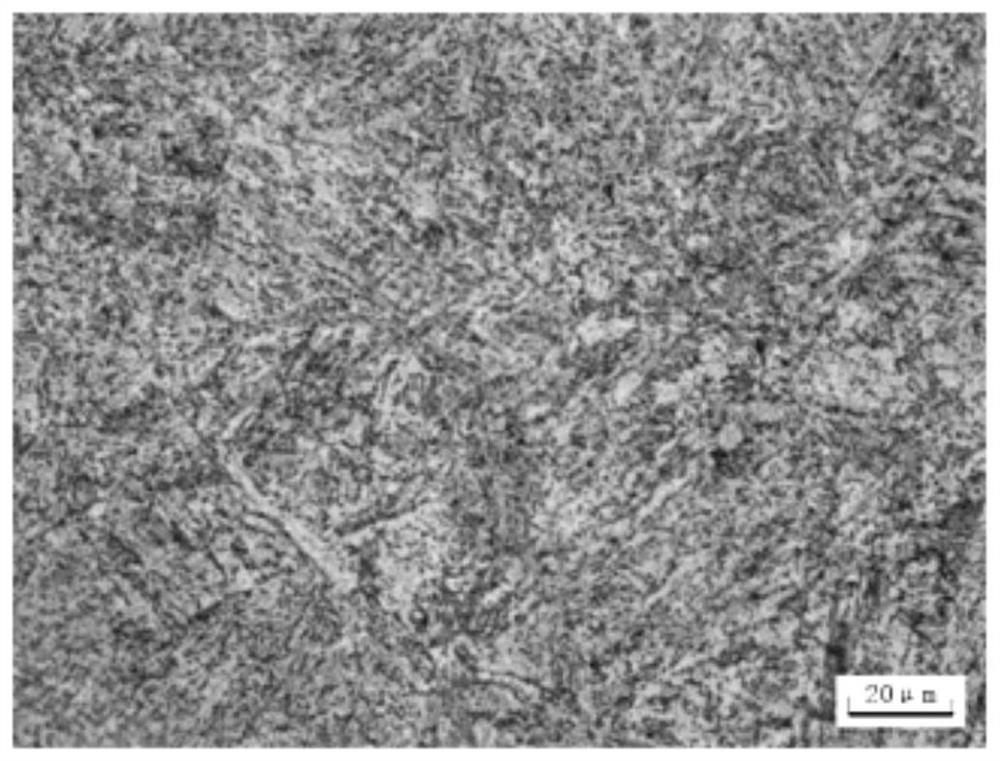
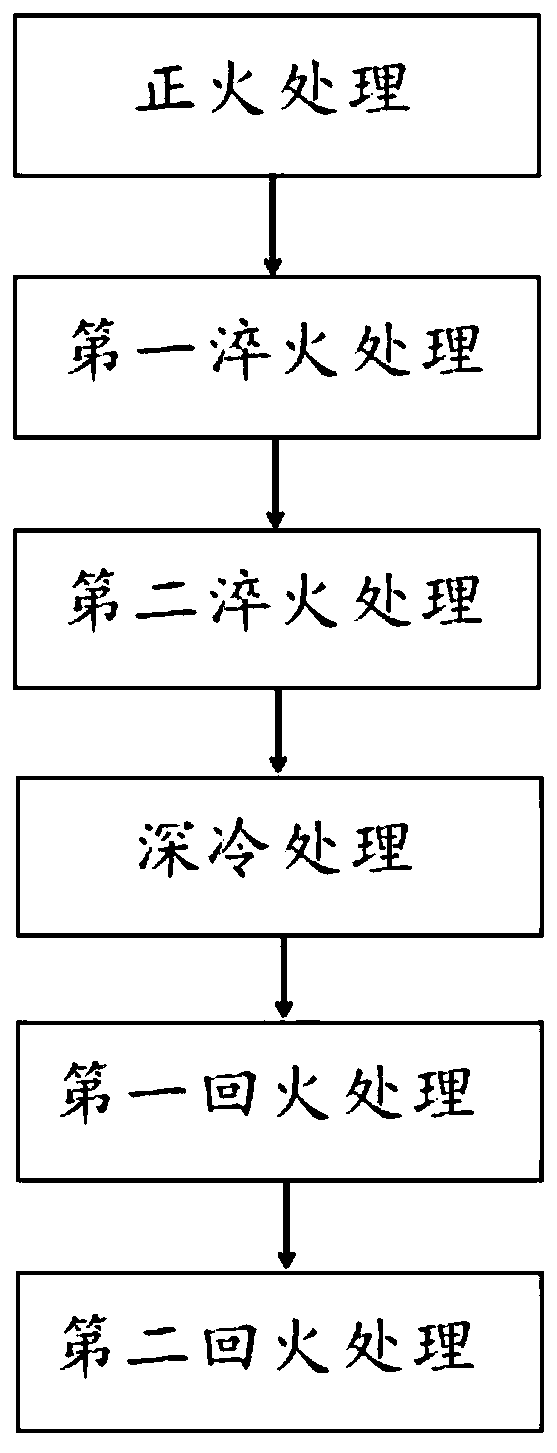
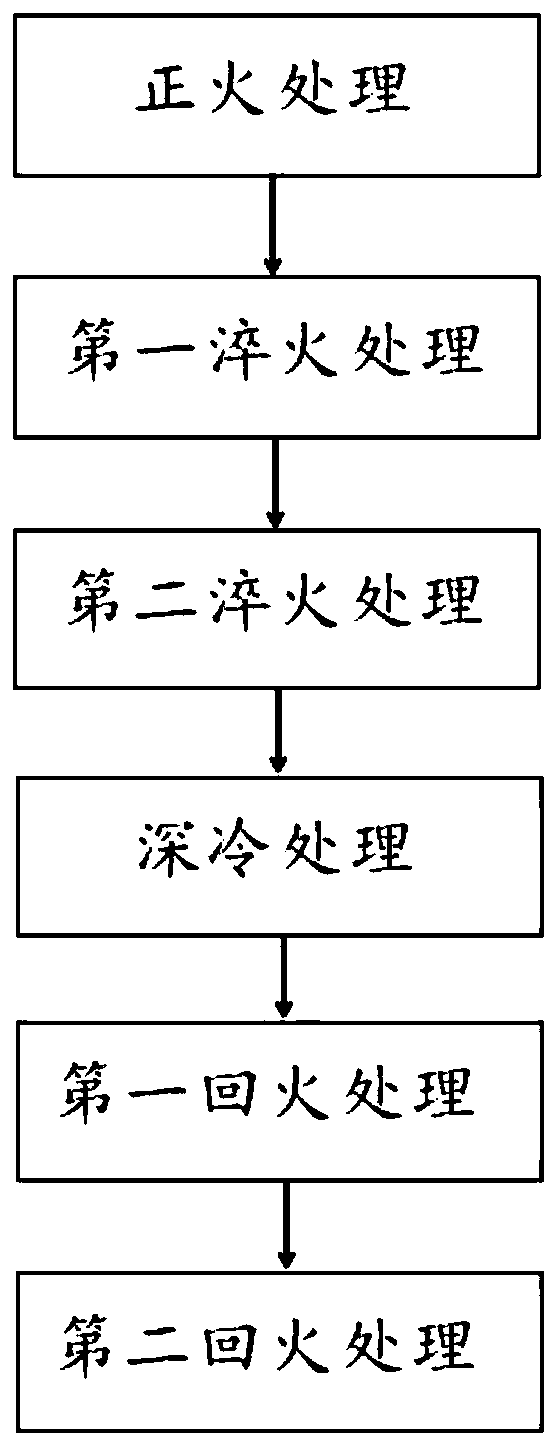
The invention discloses a thermal treatment method for an ultralow-temperature high-strength steel for a compressor. An existing thermal treatment process for 25Cr2Ni3Mo steel improves a normalizing temperature, a quenching temperature, quenching times, a cooling medium, tempering times and a cooling medium on the basis of normalizing, quenching and tempering, and adds quenching times, tempering times and cryogenic treatment. The 25Cr2Ni3Mo steel material treated by the thermal treatment method can improve tensile strength and yield strength by 5%, improves plasticity by 10%, can improve low-temperature impact toughness by 30% or more, and can meet requirements, on strength, plasticity, especially impact toughness of ultralow-temperature high-strength steel, in a centrifugal compressor forstandard API617 petroleum, chemistry and gas industry.
Owner:SHENYANG TURBO MASCH CORP
High-strength container steel plate and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114293109AImprove plastic toughnessImprove hardenabilityTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionEconomic benefits
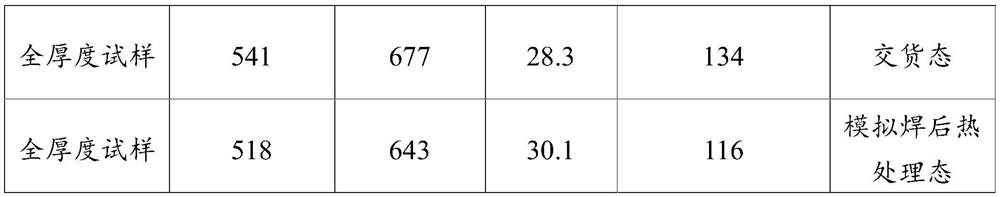
The invention provides a high-strength container steel plate and a preparation method thereof. The steel plate comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.12%-0.16% of C, 0.20%-0.30% of Si, 1.05%-1.35% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, less than or equal to 0.005% of S, 0.020%-0.040% of Al, 0.020%-0.030% of Nb, 0.010%-0.020% of Ti, 0.20%-0.30% of Cr and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The high-strength container steel plate still has extremely high strength, plasticity and low-temperature impact toughness after simulated postweld heat treatment, and has high economic benefits.
Owner:HEBEI PUYANG IRON & STEEL
A silicon-based oxynitride phosphor and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106433623BReduce the difficulty of sinteringIncrease productivityLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyNitrogen oxides
The invention discloses silicon-based nitrogen oxide fluorescent powder as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A general chemical formula of the fluorescent powder is Q.(Si<3>N<4>)<K>, wherein in the formula, k is more than 0.8 and less than 1.2. The fluorescent powder is synthesized through the following two steps: firstly synthesizing a precursor Q and then synthesizing the silicon-based nitrogen oxide fluorescent powder, wherein a general chemical formula of the precursor Q is M<x>(Si,A<2>)O<2+x>:yEu<2+>, zA<1><3+>; in the formula, M is at least one of Sr, Ba, Mg, Ca, Zn, Cu and Mn; A1 is at least one of Y, La, Sc and Er; A2 is not added or A2 is Ge; x is not less than 1.9 and not more than 2.1; y is not less than 0.005 and not more than 0.2; z is not less than 0.01 and not more than 0.2. The fluorescent powder provided by the invention can be effectively excited by 300nm-470nm wavelength to emit blue-green light or green-yellow light with peak wavelength of 490nm-560nm, has high quantum efficiency, narrow full width at half maximum (FWHM) and high thermal quenching temperature and can be matched with blue chips-ultraviolet chips to be applied to the field of white LED or display.
Owner:HEBEI LIFU CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com