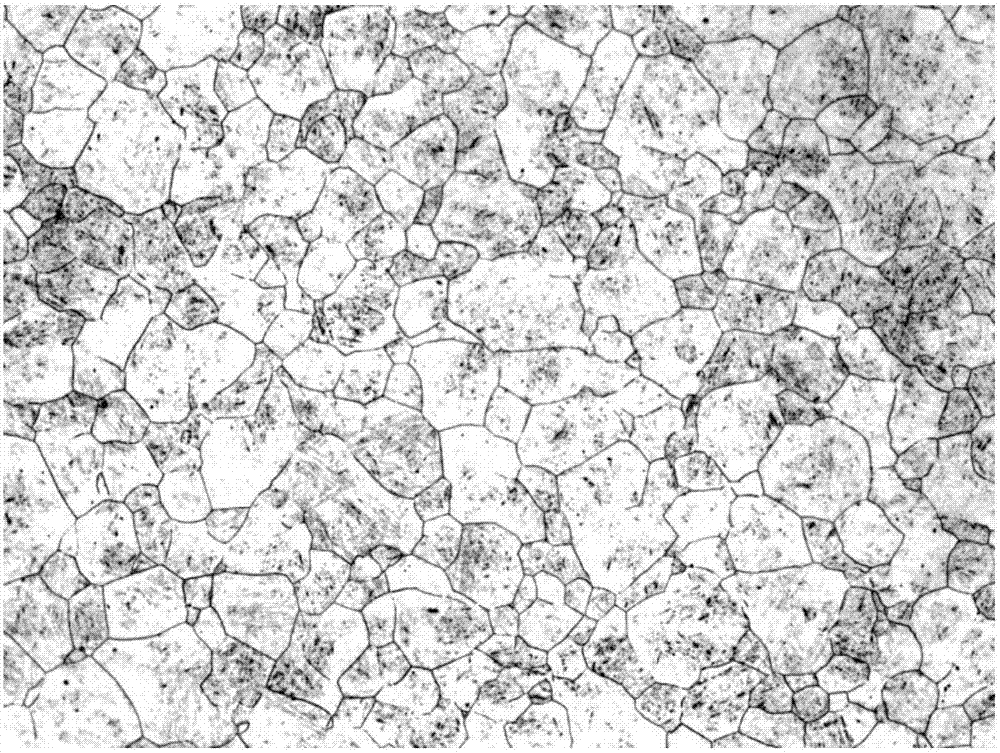
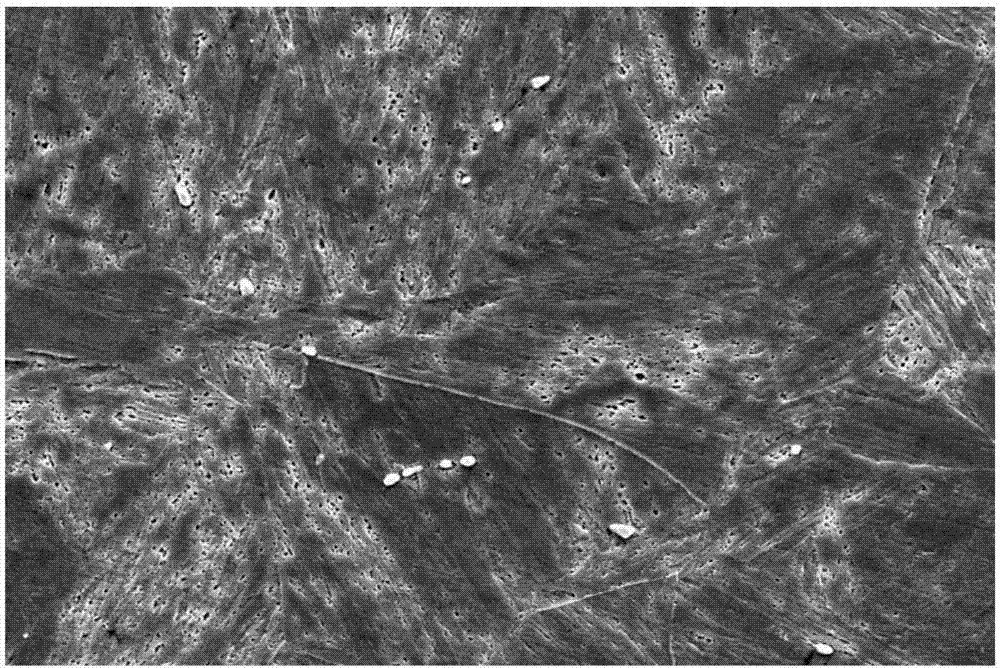
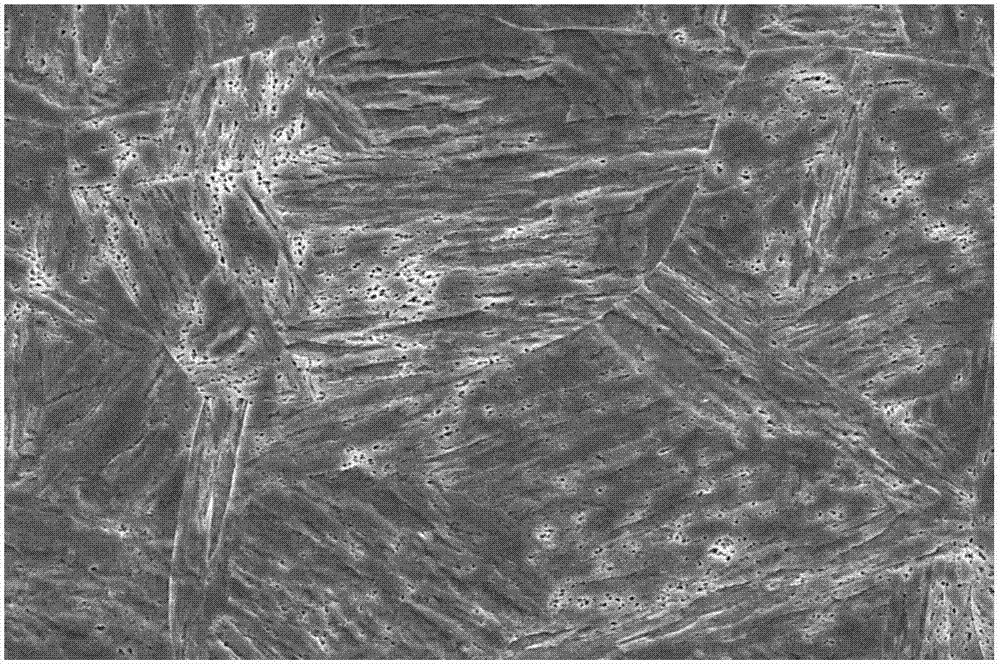
Heat treatment technique for improving low-temperature toughness of martensite-type heat-resistant steel containing large M23C6 precipitated phases
A low-temperature toughness and precipitated phase technology, which is applied in the field of heat treatment of steel materials, can solve the problems of difficult to eliminate large-sized M23C6 precipitated phases, low solid solution rate of precipitated phases, and difficulty in meeting standard requirements, so as to avoid re-precipitation and reduce lattice defects and quenching structure stress, the effect of shortening the soaking time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A heat treatment technology for improving the low-temperature toughness of martensitic heat-resistant steel containing large-size M23C6 precipitates, the specific steps are as follows:
[0031] Step 1, primary quenching: the selected chemical composition is: (C: 0.10%, Si: 0.22%, Mn: 0.78%, Cr: 12.0%, Ni: 2.50%, Mo: 1.65%, V: 0.32%, N: 0.033 %), and containing 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN martensitic heat-resistant steel forgings with large-sized M23C6 precipitates, in a box-type heating furnace, heated to 1100°C for 30 minutes to eliminate large-sized M23C6 precipitates in the structure and make the structure uniform melted, then oil-cooled and quenched;
[0032] Step 2, secondary quenching: heat the 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN steel after the primary quenching to 990°C for 45 minutes to refine the austenite grains, and then oil cooling and quenching;
[0033]Step 3, high-temperature tempering: heat the 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN steel after secondary quenching to 690°C for 120 minutes to fully recover the...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A heat treatment technology for improving the low-temperature toughness of martensitic heat-resistant steel containing large-size M23C6 precipitates, the specific steps are as follows:
[0042] Step 1, primary quenching: the selected chemical composition is: (C: 0.10%, Si: 0.22%, Mn: 0.78%, Cr: 12.0%, Ni: 2.50%, Mo: 1.65%, V: 0.32%, N: 0.033 %), and containing 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN martensitic heat-resistant steel forgings with large-sized M23C6 precipitates, in a box-type heating furnace, heated to 1080 ° C for 30 minutes to eliminate large-sized M23C6 precipitates in the structure and make the structure uniform melted, then oil-cooled and quenched;
[0043] Step 2, secondary quenching: heat the 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN steel after the primary quenching to 990°C for 40 minutes to refine the austenite grains, and then oil cooling and quenching;
[0044] Step 3, high-temperature tempering: heat the 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN steel after secondary quenching to 690°C for 120 minutes to fully recover ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A heat treatment technology for improving the low-temperature toughness of martensitic heat-resistant steel containing large-size M23C6 precipitates, the specific steps are as follows:
[0047] Step 1, primary quenching: the selected chemical composition is: (C: 0.10%, Si: 0.22%, Mn: 0.78%, Cr: 12.0%, Ni: 2.50%, Mo: 1.65%, V: 0.32%, N: 0.033 %), and containing 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN martensitic heat-resistant steel forgings with large-sized M23C6 precipitates, in a box-type heating furnace, heated to 1100°C for 40 minutes to eliminate large-sized M23C6 precipitates in the structure and make the structure uniform melted, then oil-cooled and quenched;
[0048] Step 2, secondary quenching: heat the 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN steel after the primary quenching to 980°C for 45 minutes to refine the austenite grains, and then oil cooling and quenching;
[0049] Step 3, high-temperature tempering: heat the 10Cr12Ni3Mo2VN steel after secondary quenching to 680°C for 120 minutes to fully recover th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com