Methods and systems using a numerical model to describe polymeric material properties
A polymer material and material performance technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, CAD numerical modeling, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem that numerical simulation will not be effective or accurate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
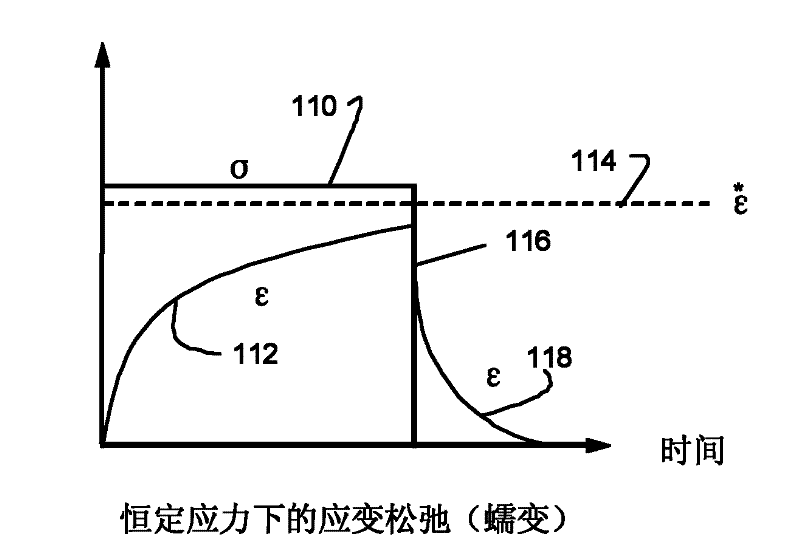
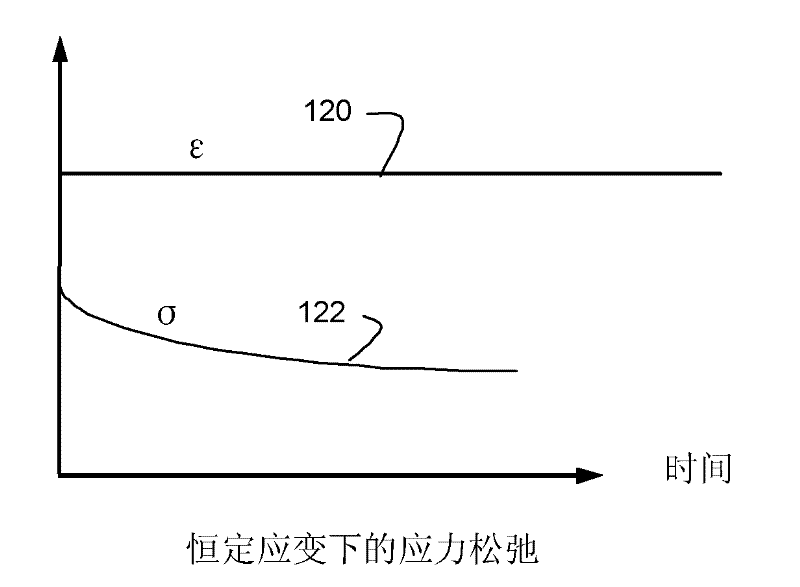
[0015] When a material is subjected to external loads, it undergoes stress and strain relaxation. Figure 1A and Figure 1B These relaxation behaviors are shown schematically. exist Figure 1A In , when a constant stress 110 is applied, the strain increases along a path 112 and gradually approaches the steady-state strain ε*114. When the applied stress is removed at 116 , the strain then returns to its original value along decay path 118 . exist Figure 1B In , when a constant strain 120 is applied, the stress follows a decay path 122 to a steady state value. This relaxation behavior is typically modeled by including viscous elements in the normal elastic model. Viscoelastic models, such as Maxwell model and Voigt model, have been proposed to simulate the behavior of polymer materials under mechanical loading. However, the Maxwell model can accurately describe the stress decay with time, as Figure 1B , but fails to accurately predict the creep response of the material un...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com