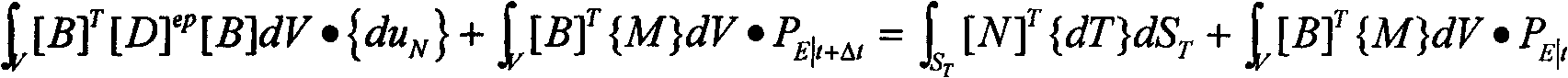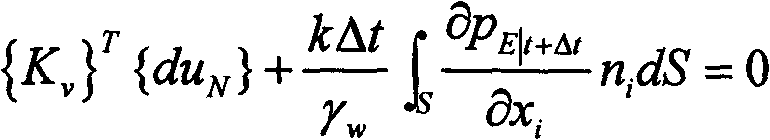Patents
Literature
47 results about "Yield surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
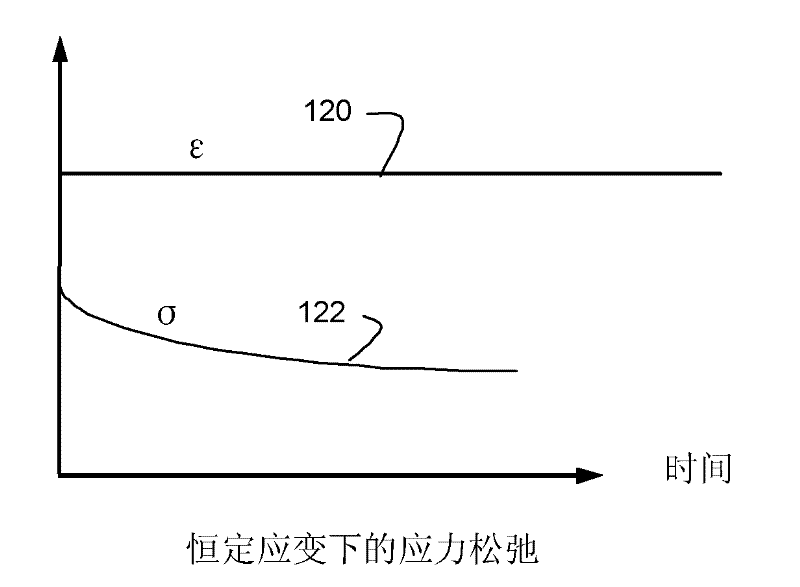
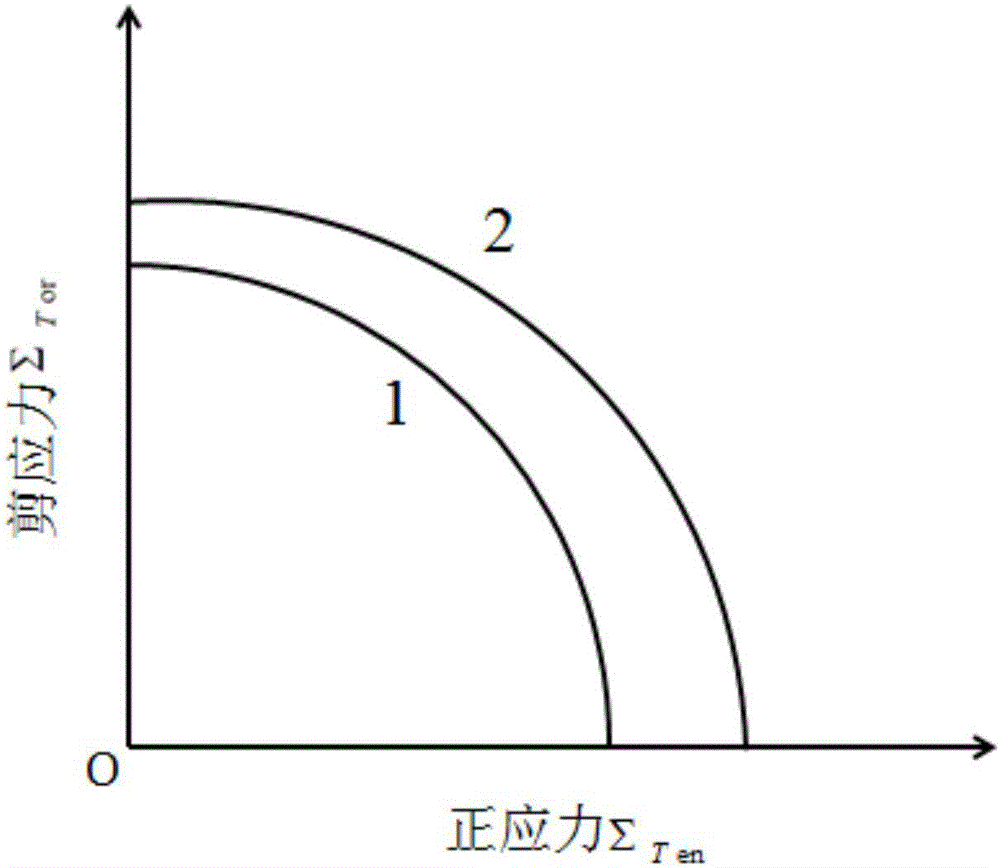
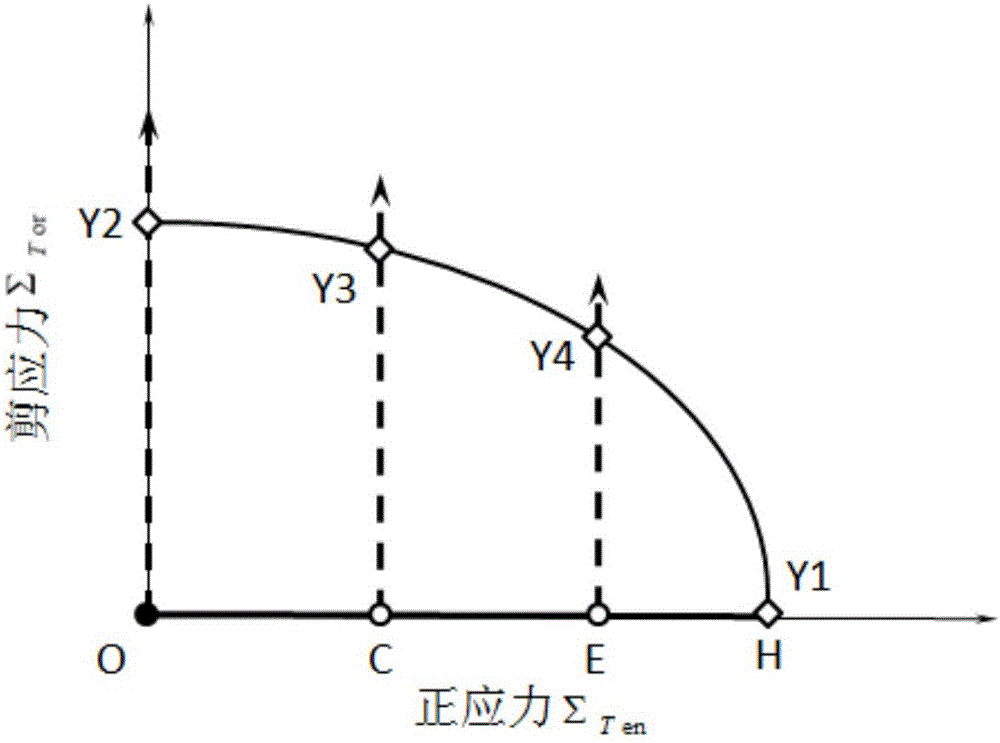
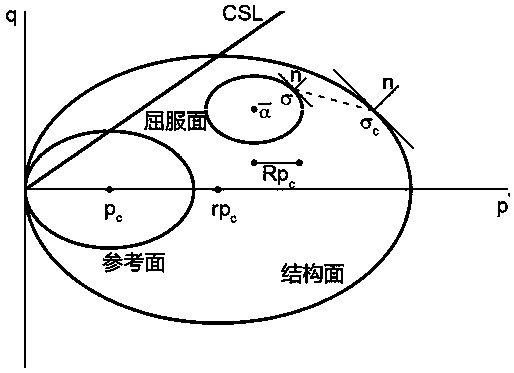
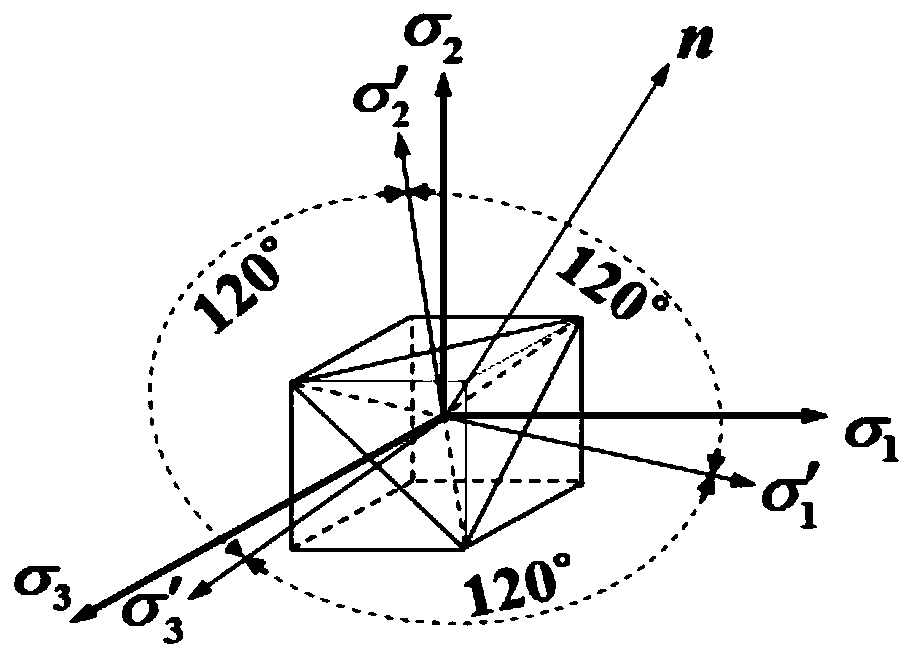
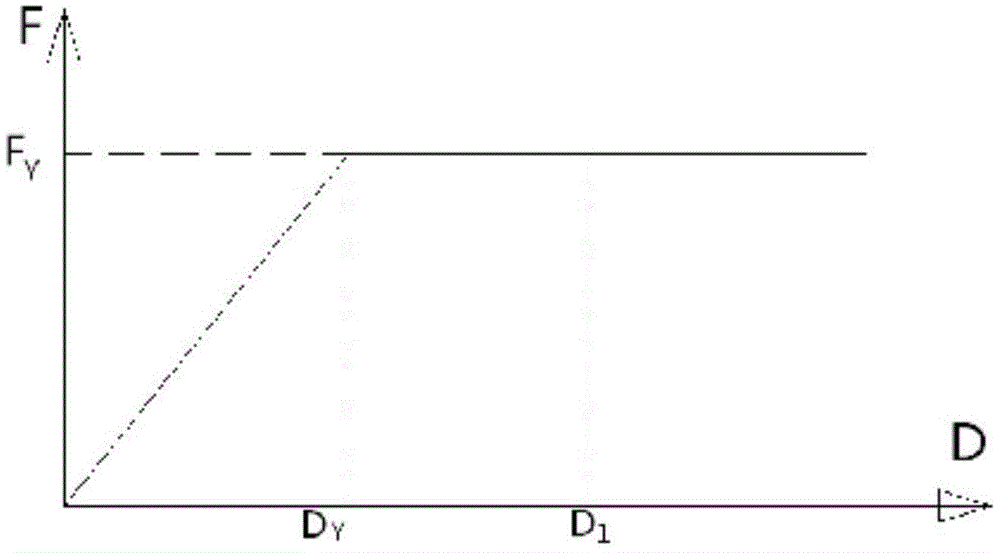
A yield surface is a five-dimensional surface in the six-dimensional space of stresses. The yield surface is usually convex and the state of stress of inside the yield surface is elastic. When the stress state lies on the surface the material is said to have reached its yield point and the material is said to have become plastic. Further deformation of the material causes the stress state to remain on the yield surface, even though the shape and size of the surface may change as the plastic deformation evolves.
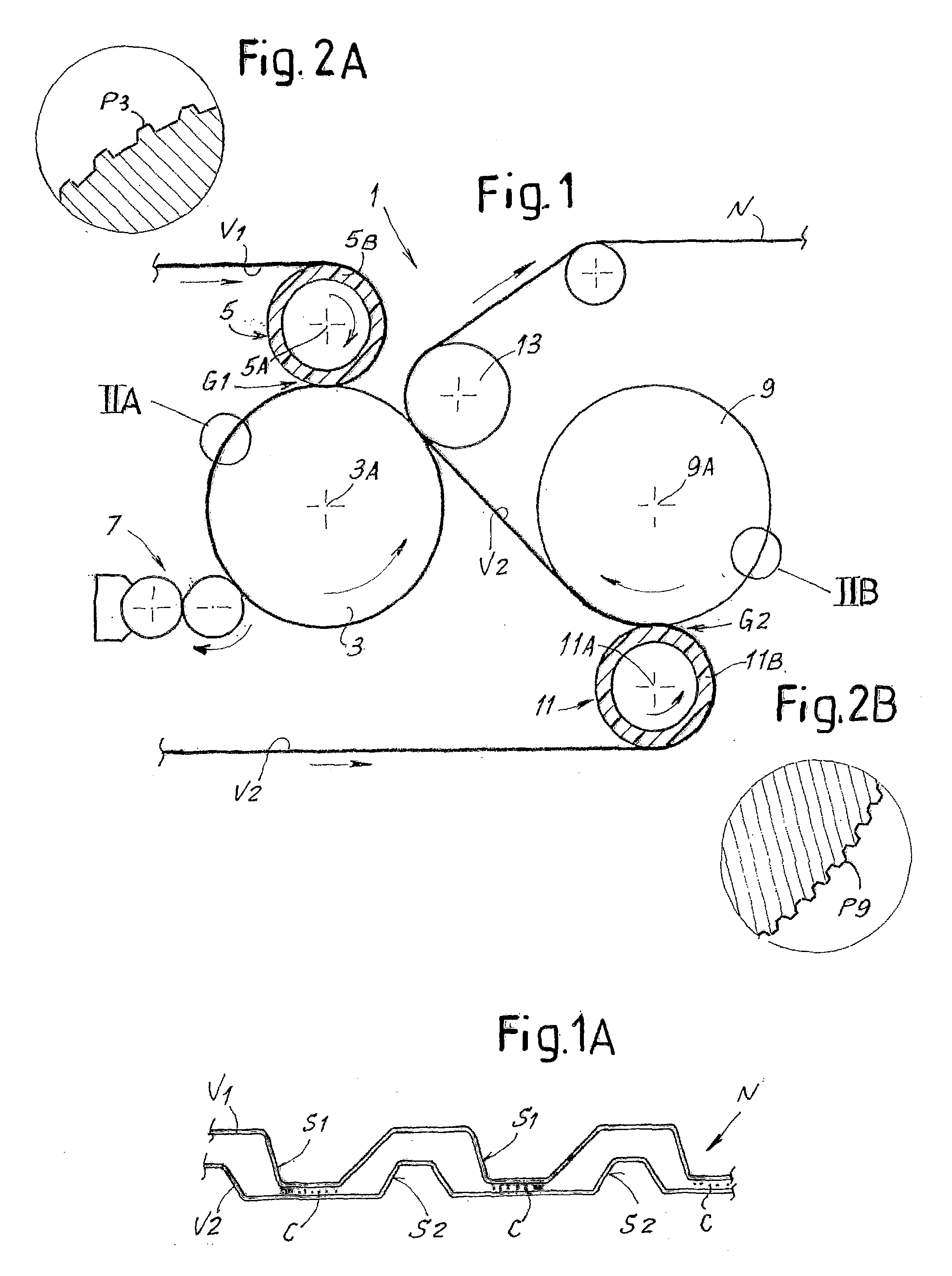
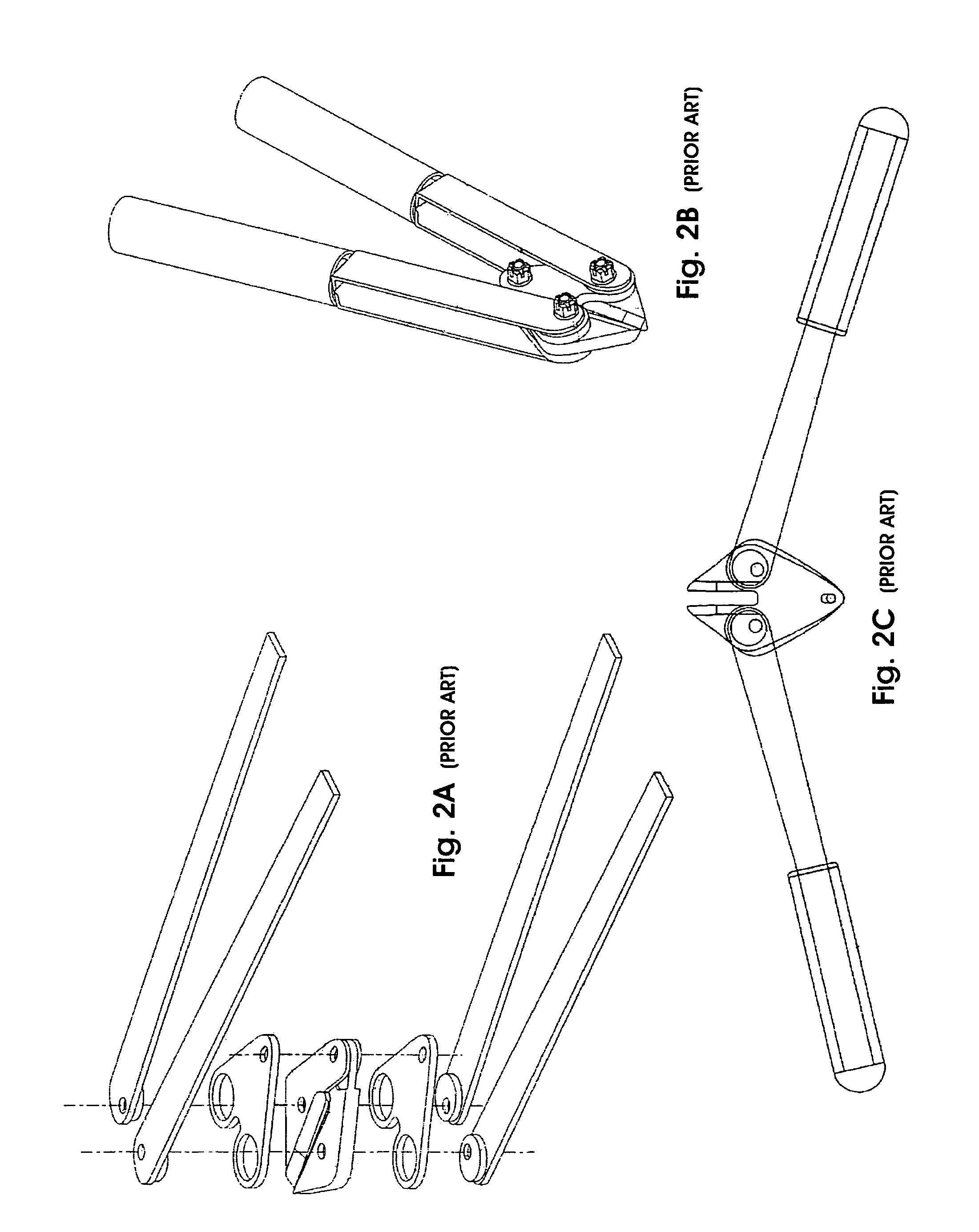
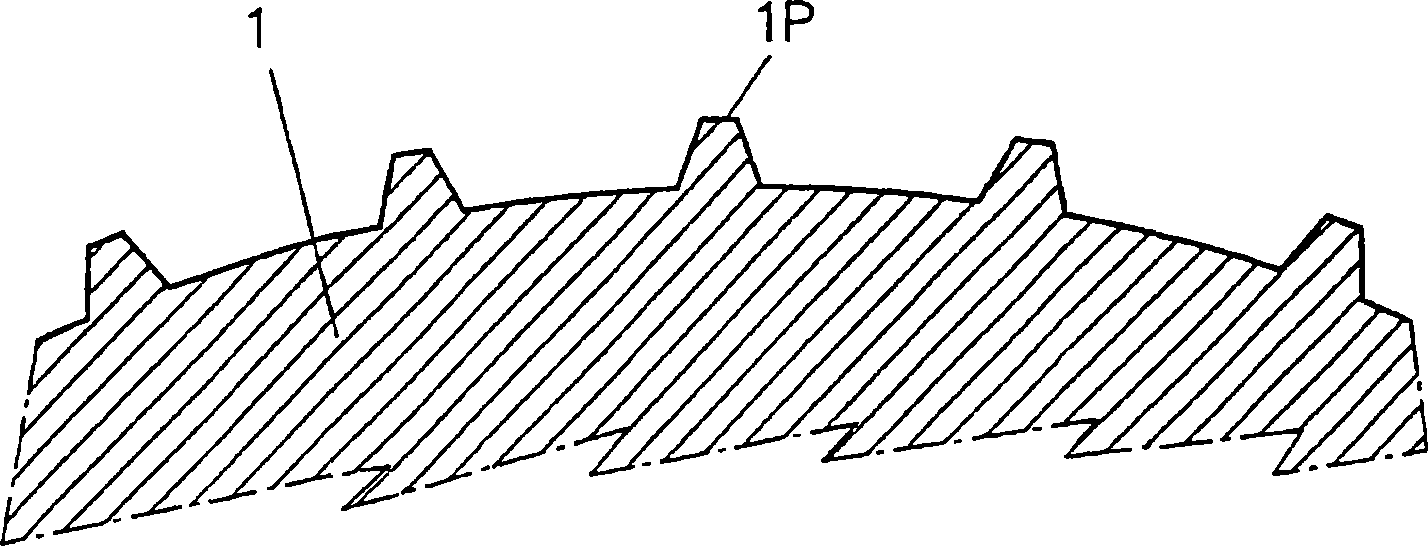
Embossing and laminating method and device for producing multi-ply web products and relative product
InactiveUS20070092700A1Overcomes drawbackIncrease the number ofMechanical working/deformationLaminationEngineeringYield surface
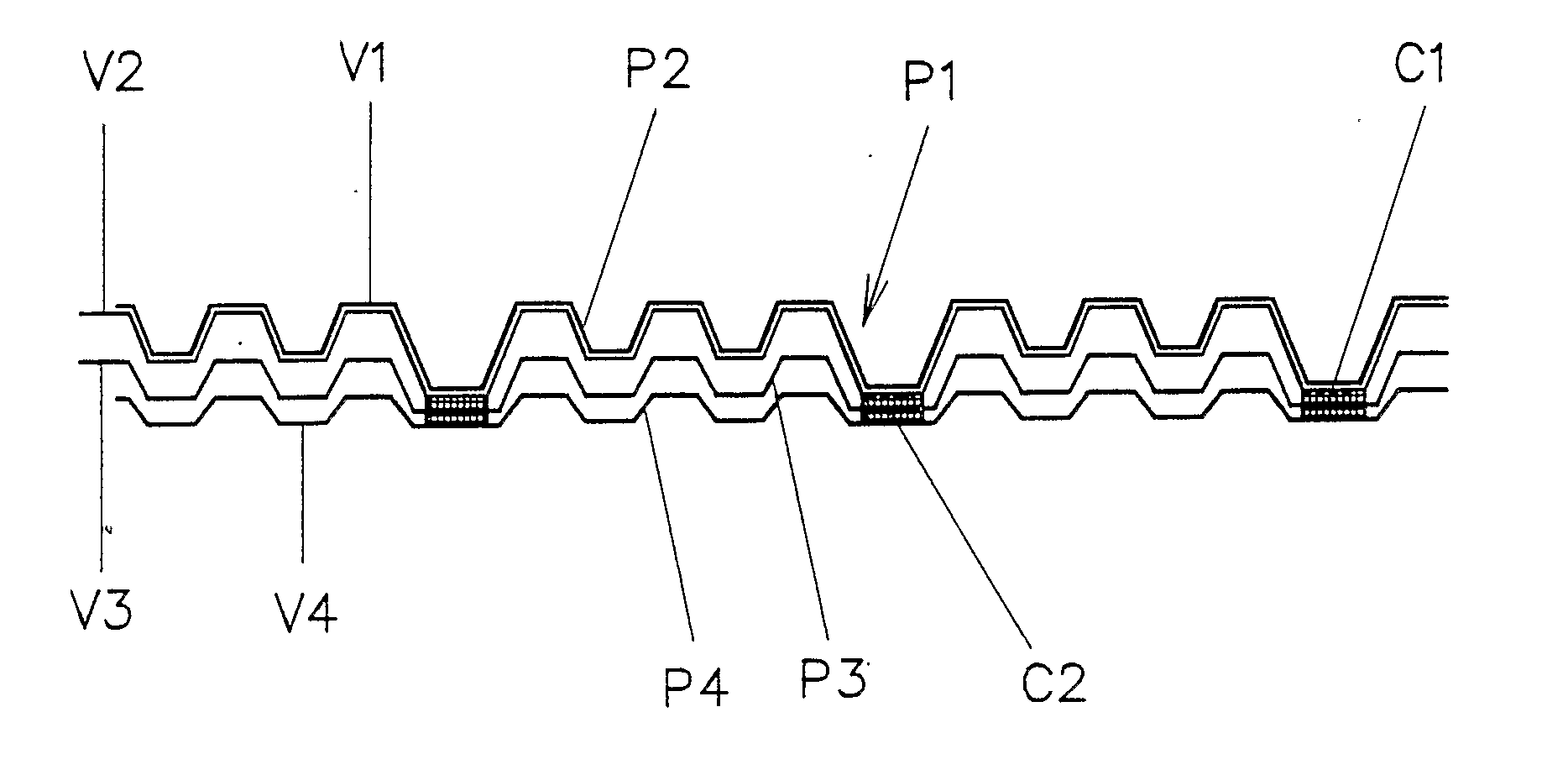
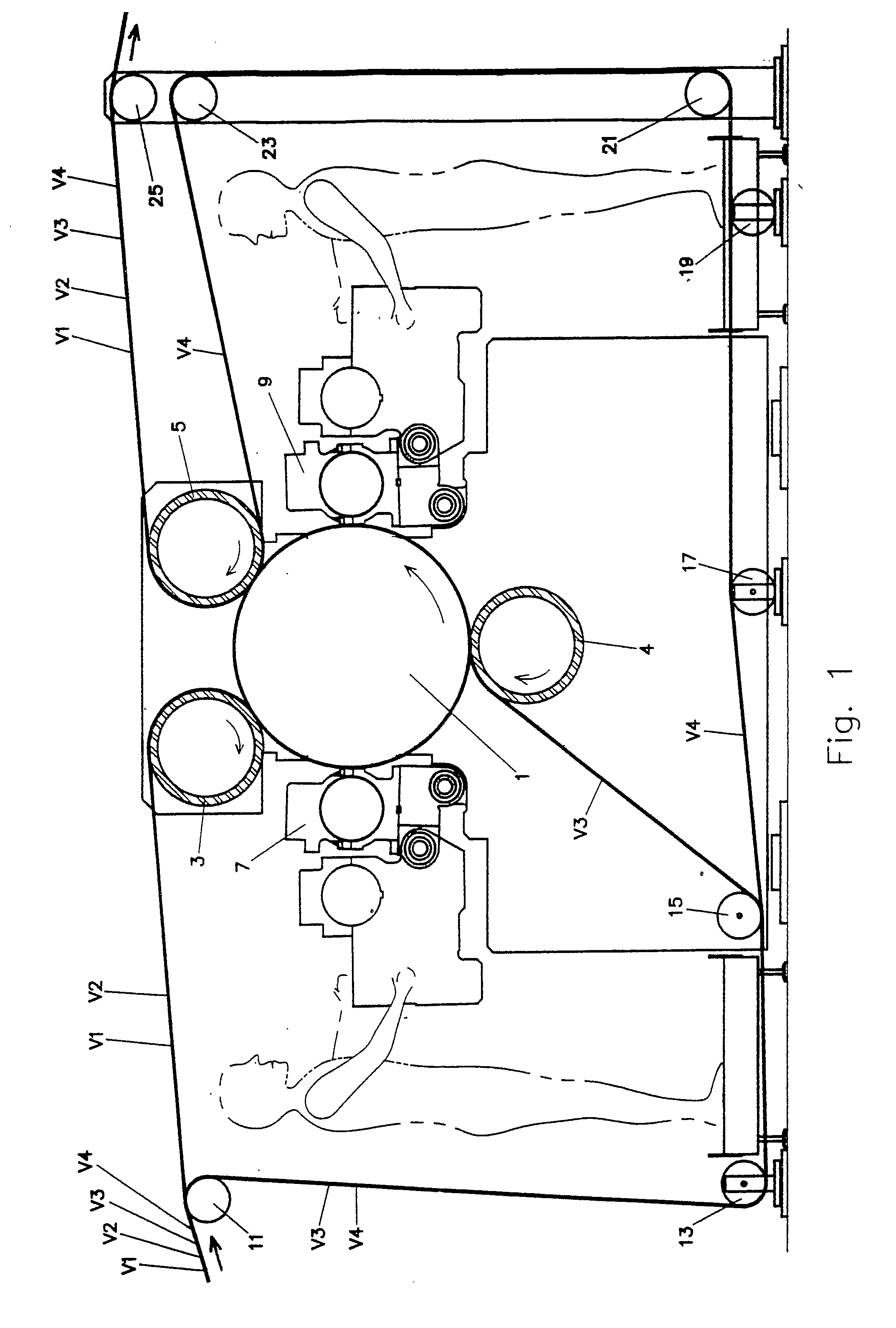
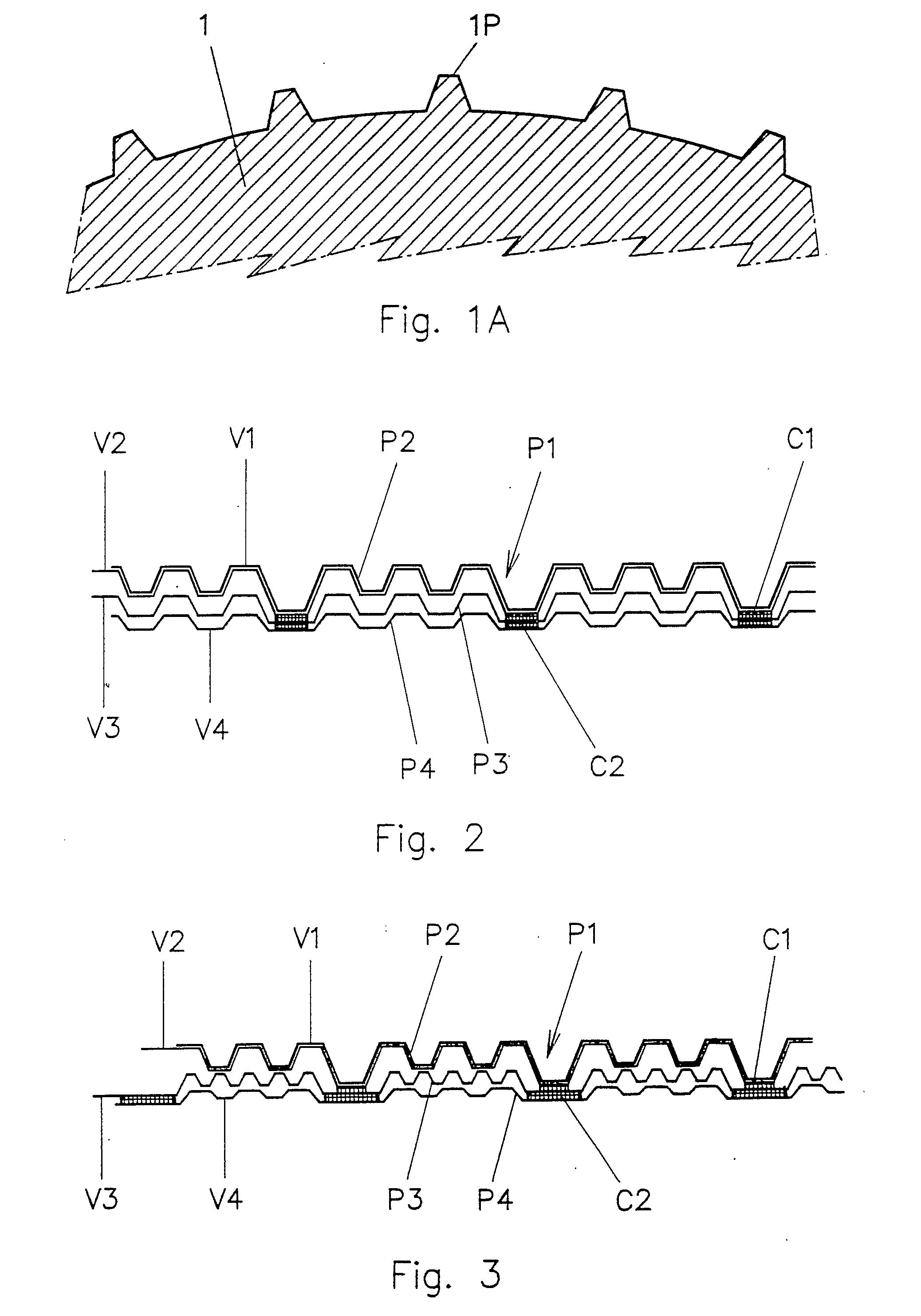
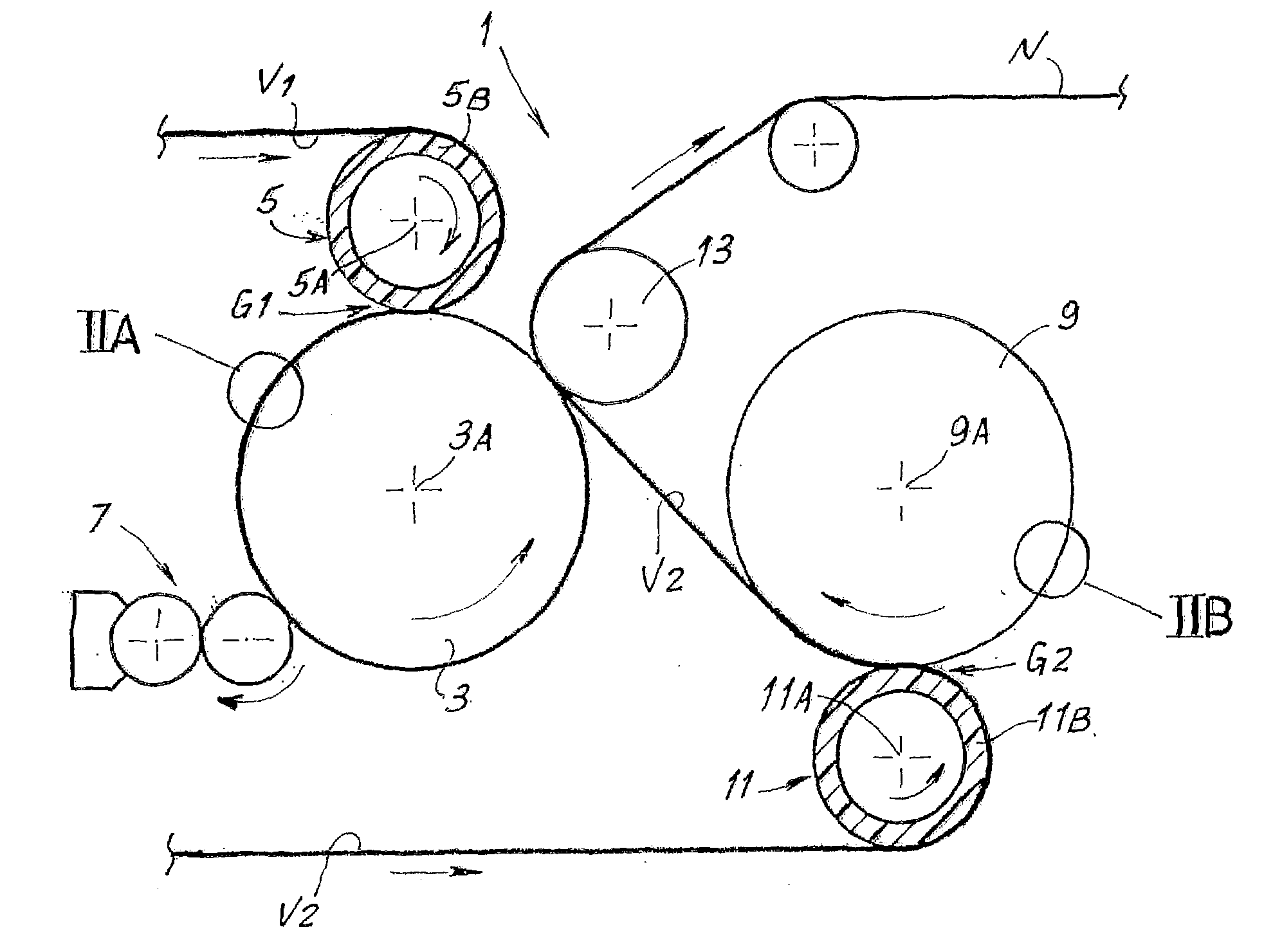
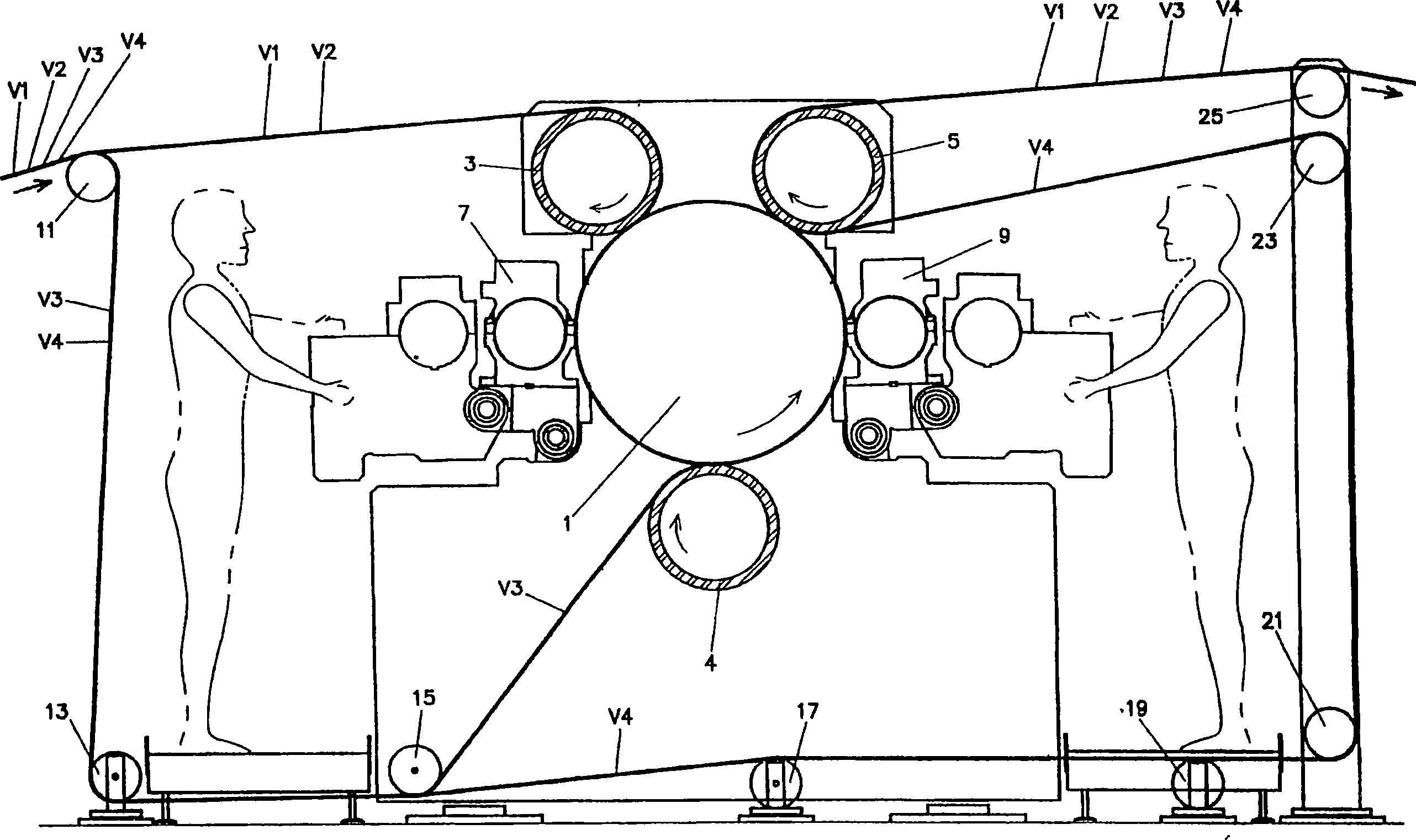
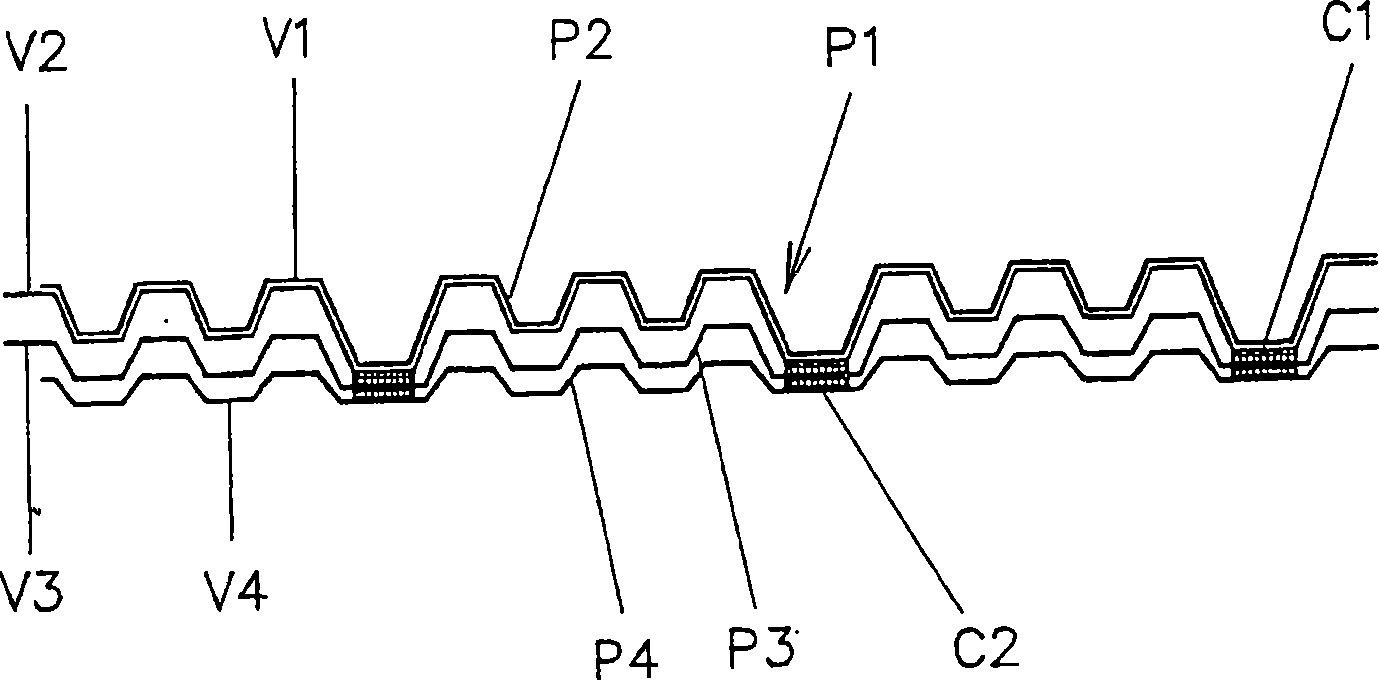
The embossing and laminating device comprises: a central embossing cylinder (1), provided with a plurality of protuberances (1P); at least three pressure rollers (3, 4, 5) disposed along the periphery of the embossing cylinder (1) and provided with a yielding surface, cooperating with the embossing cylinder; at least three paths to feed one or more plies (V1, V2, V4) between the central embossing cylinder and each pressure roller; at least a first gluing unit (7) disposed between two consecutive pressure rollers and cooperating with said central embossing cylinder.
Owner:FABIO PERINI SPA
Embossing Roller, Embossing Unit, Embossing Method And Embossed Product
ActiveUS20140044923A1Uniform deformationUniform weakeningMechanical working/deformationConfectioneryEngineeringYield surface
The embossing unit includes at least one embossing roller with a rotation axis and a substantially cylindrical surface with a plurality of embossing protuberances with linear extension; a pressure roller with a yielding surface; an embossing nip defined between the pressure roller and the embossing roller; a feed path of a web material extending through said the embossing nip. Along the linear extension thereof the embossing protuberances have a variable inclination with respect to the rotation axis of the embossing roller and a variable cross section along the longitudinal extension of the embossing protuberances.
Owner:ENGRAVING SOLUTIONS
Two-stage attachment for cutting, crimping etc, and mechanical method thereof
Owner:BRAILOVSKIY ALEKSANDR M
Method for Producing Improved Rubberized Concrete using Waste Rubber Tires
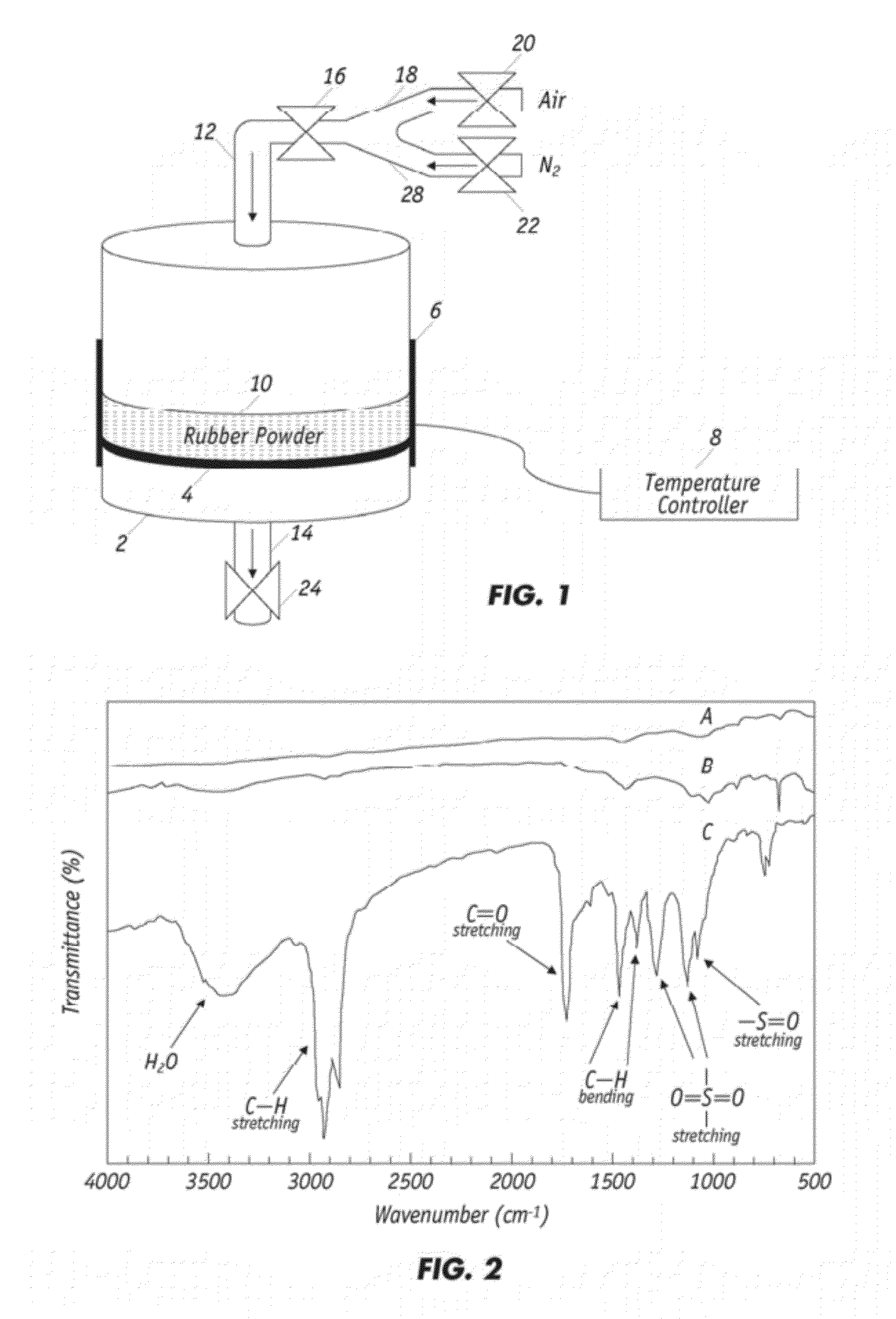
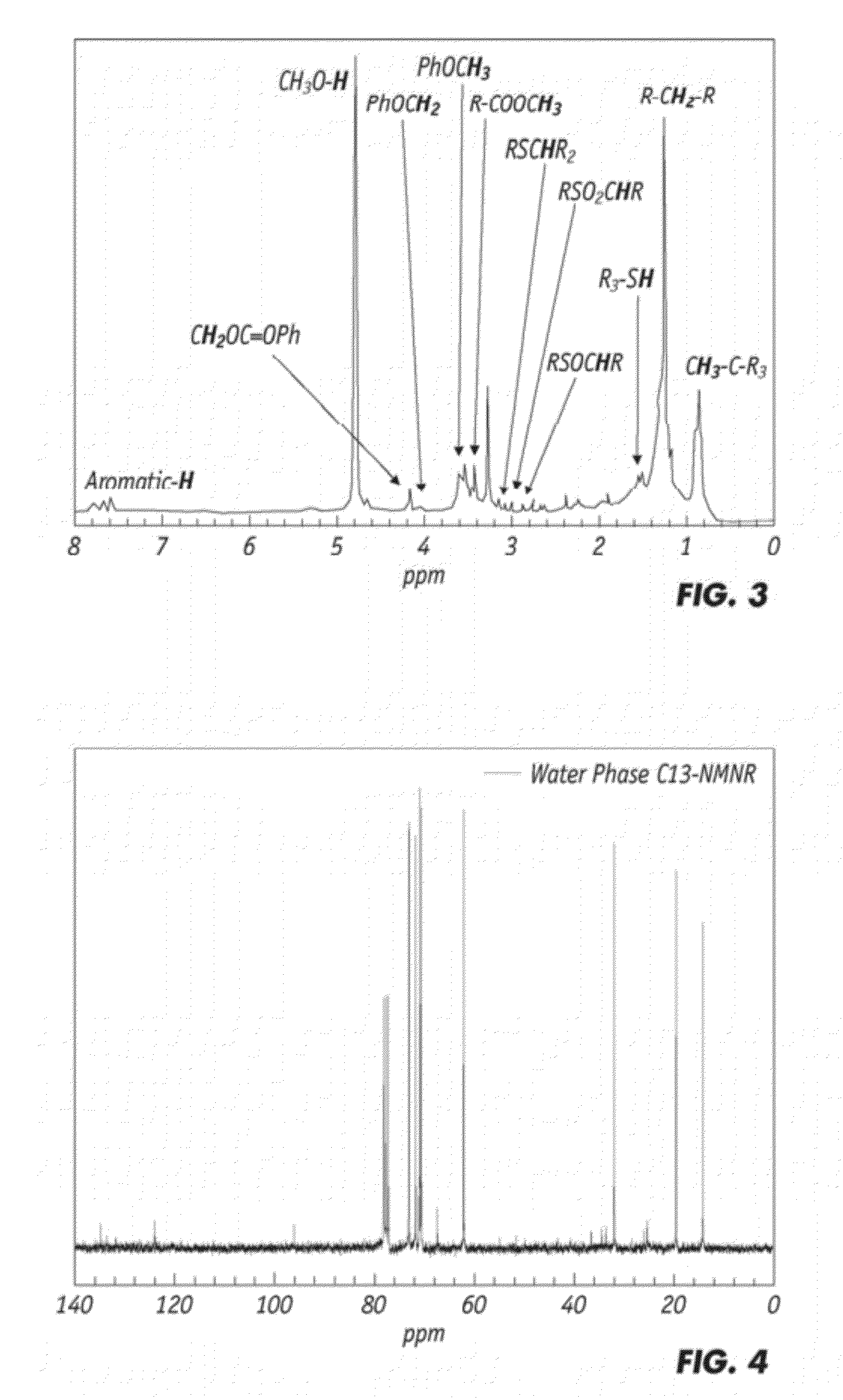
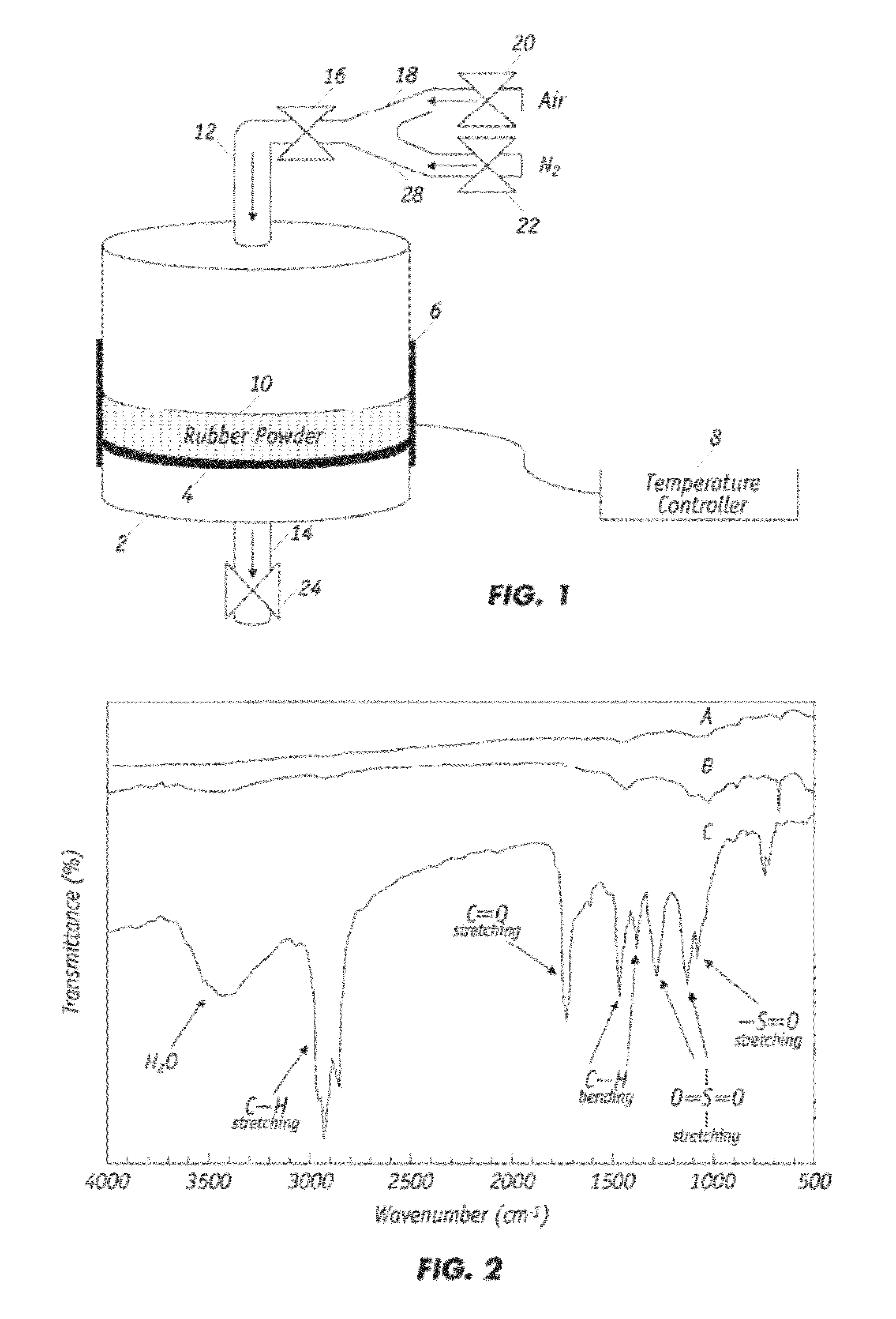
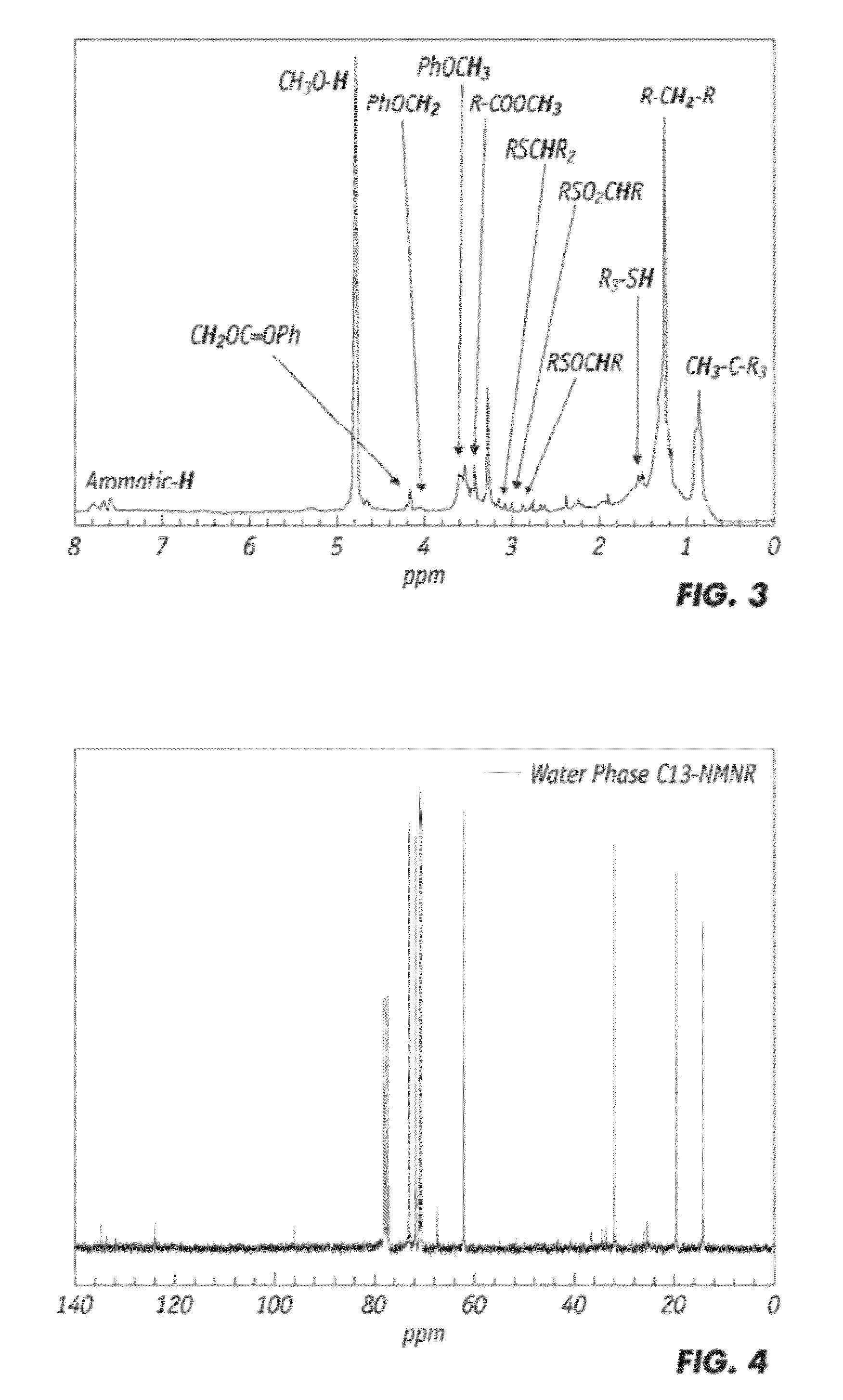
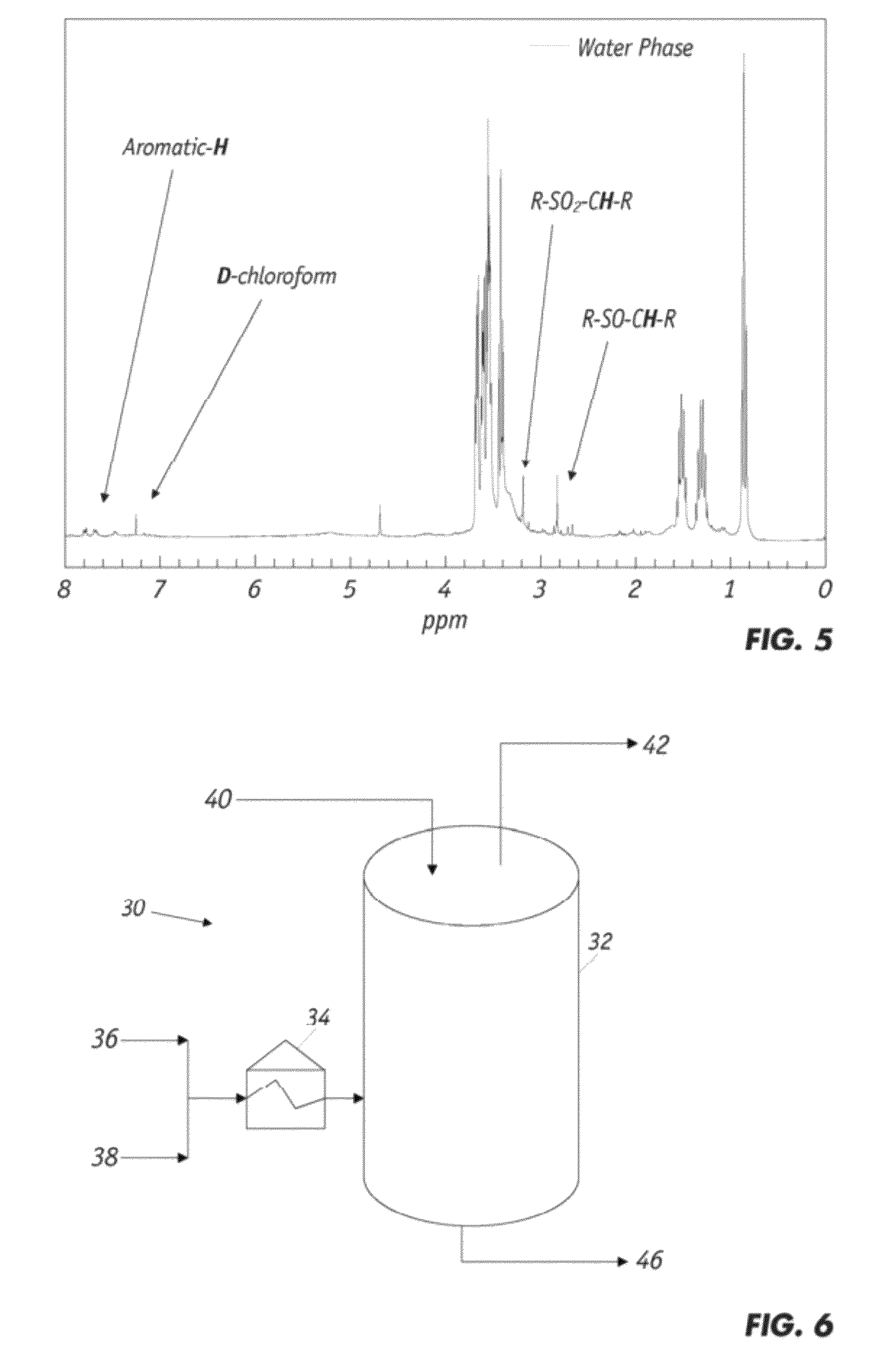
ActiveUS20120252910A1Improve bindingImprove mechanical propertiesPlastic recyclingPaper coatingPartial oxidationWaste rubber
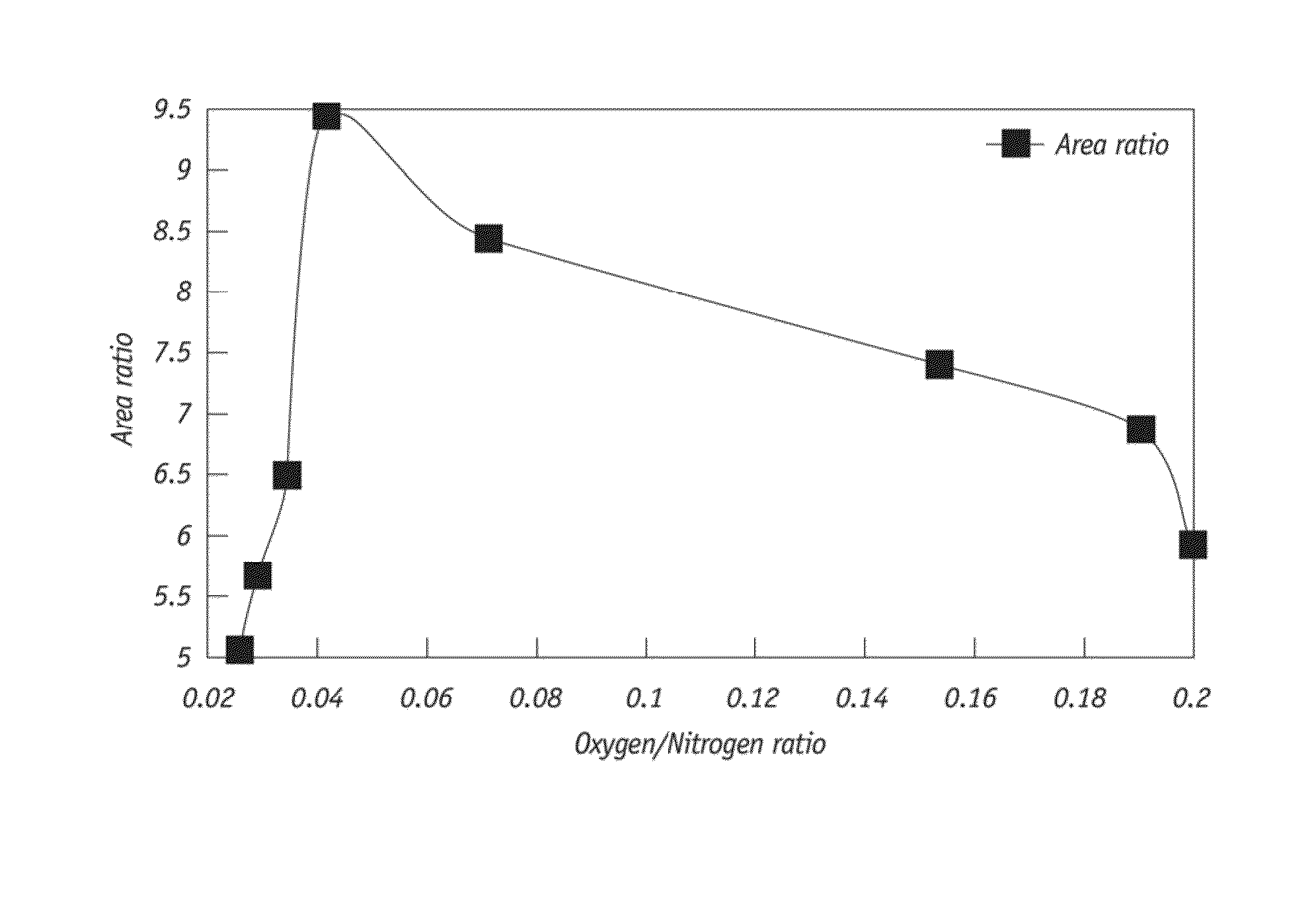
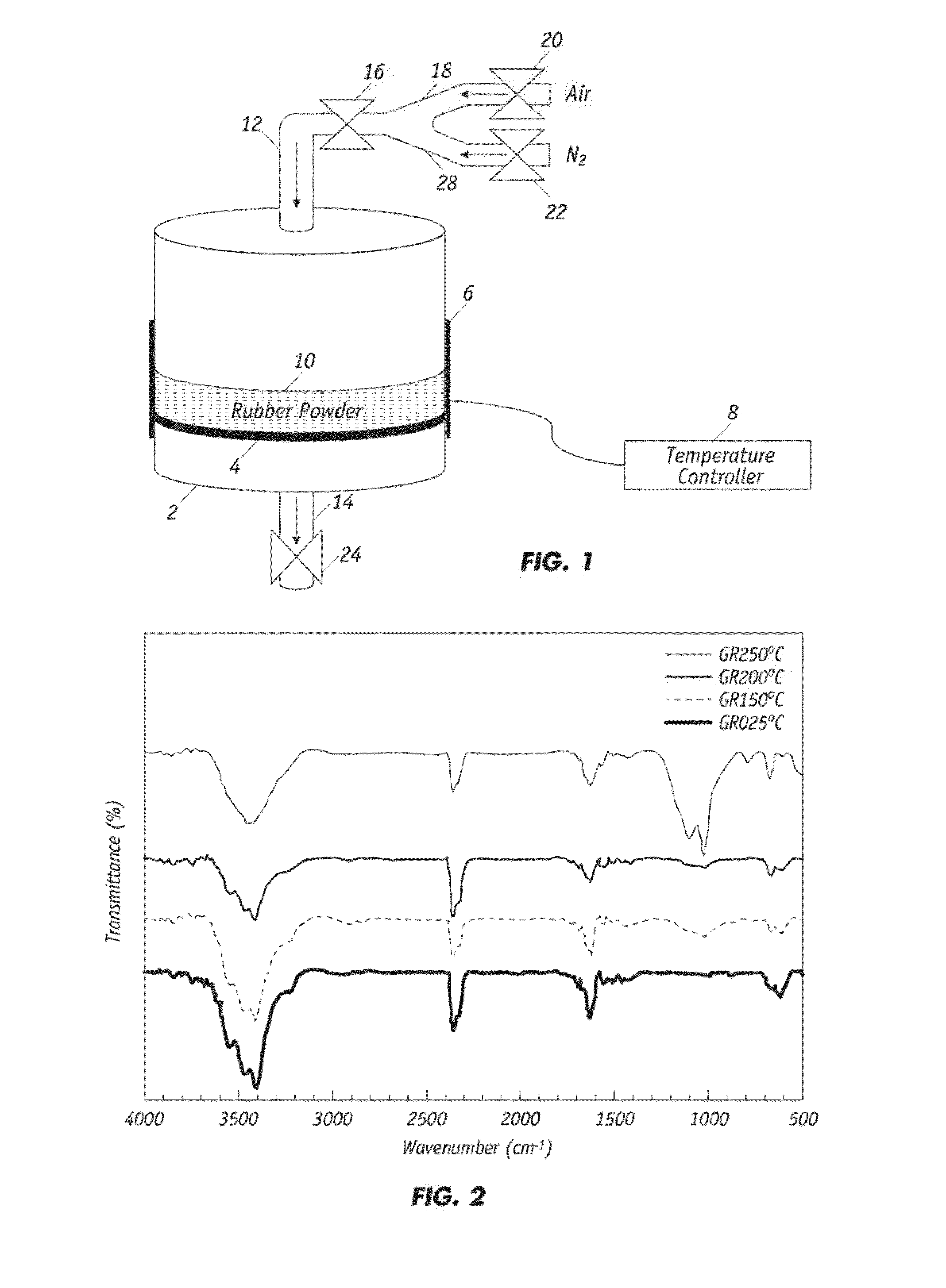
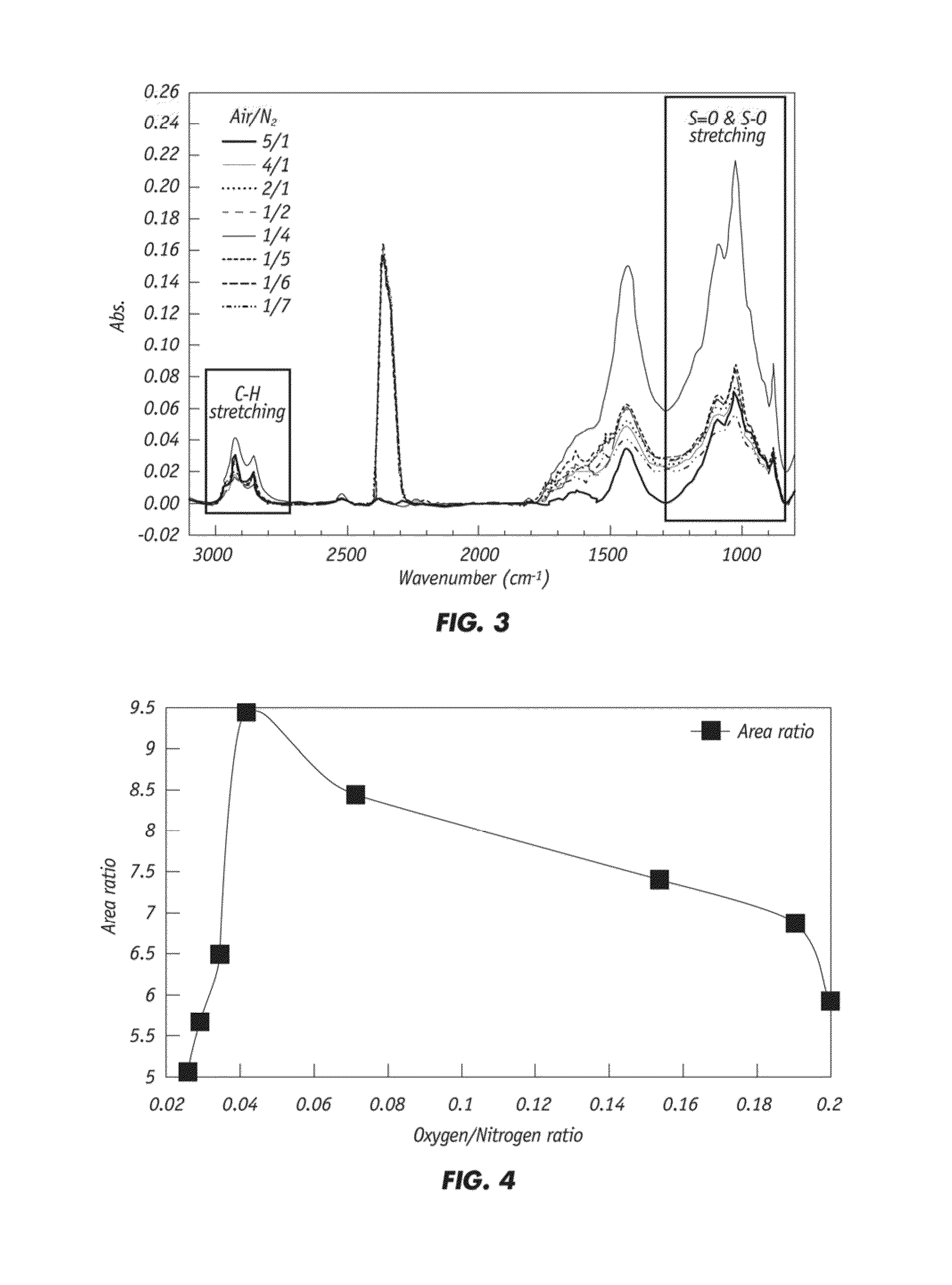
Partial oxidation of crumb rubber derived from environmental hazardous waste tires yields surface treated crumb rubber and a gas condensate which are used as blending stocks for making rubberized concrete with substantially improved mechanical strength as compared to the conventional rubberized concrete. The chemically more active rubber surface becomes hydrophilic, so it interacts with the hydrophilic surface of surrounding cement matrix much stronger. The gas condensate co-produced in the partial oxidation reactor consists of mainly active sulfur oxides (R—SOx—R) and serves as an excellent bonding agent to further enhance the bonding strength between the partially oxidized rubber particles and the cement mixes. The mechanically improved rubberized concrete is more versatile than conventional rubberized concrete.
Owner:SHIN CHUANG TECH CO LTD
Stress-strain relationship simulation method, spring back prediction method, and spring back analyzing device
ActiveCN105122033ASpringback ForecastMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesDesign optimisation/simulationBack stressAlgorithm
This method acquires an experimental value for a stress-strain relationship by plastically deforming an elastic-plastic material by displacing or applying a load on same. A calculator: identifies, by using the acquired experimental value, a material parameter contained in an elastic-plastic constitutive model as a prescribed first formula expressing a kinematic hardening incremental vector (dαij) for a yield surface in the elastic-plastic constitutive model that is defined as the function for stress and back stress; identifies a material parameter contained in a prescribed second formula on the basis of the prescribed first formula into which the identified material parameter is substituted and the acquired experimental value; and simulates the stress-strain relationship of the elastic-plastic material by using the prescribed first formula and the prescribed second formula, into which the identified material parameters are substituted, and the elastic-plastic constitutive model.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
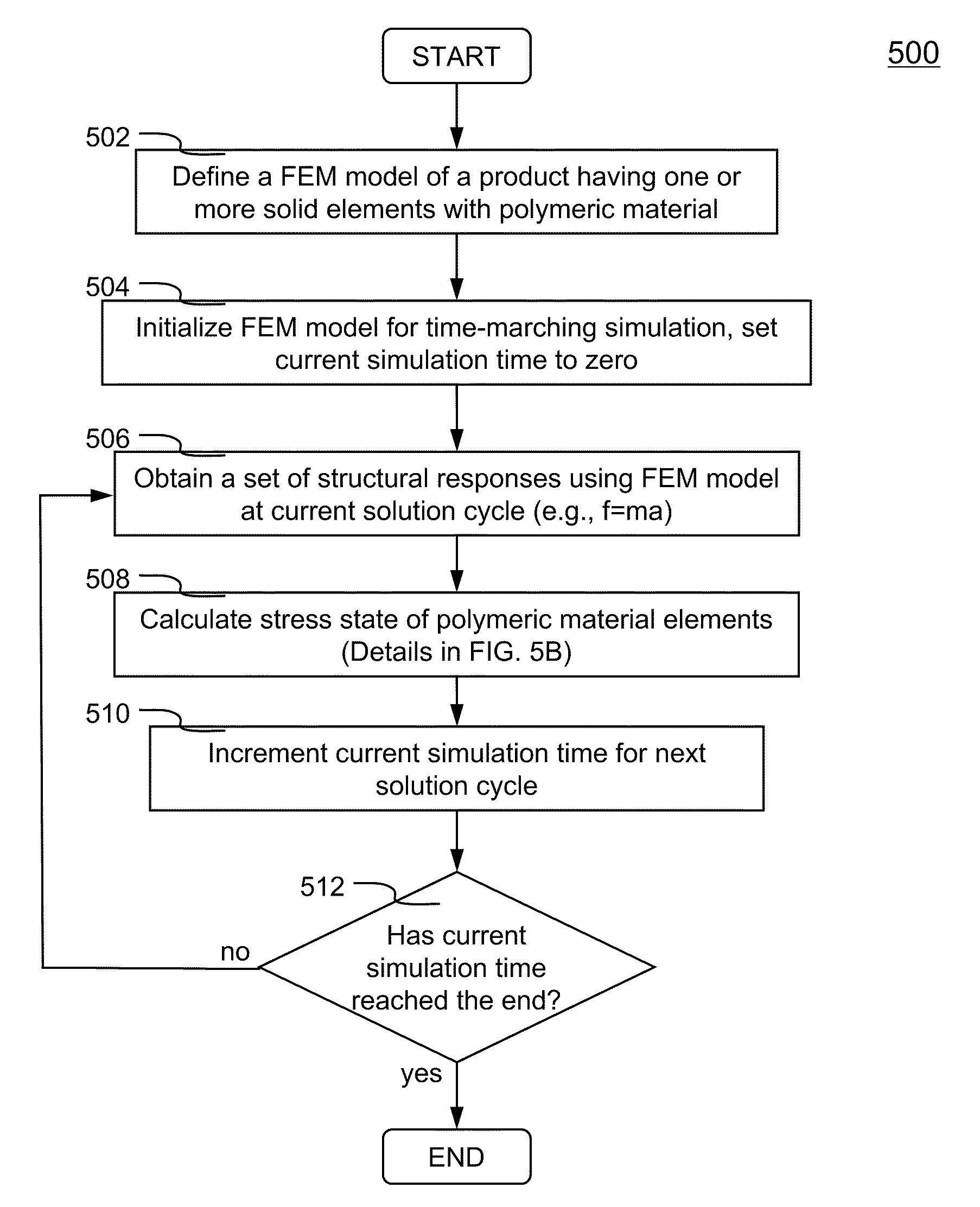
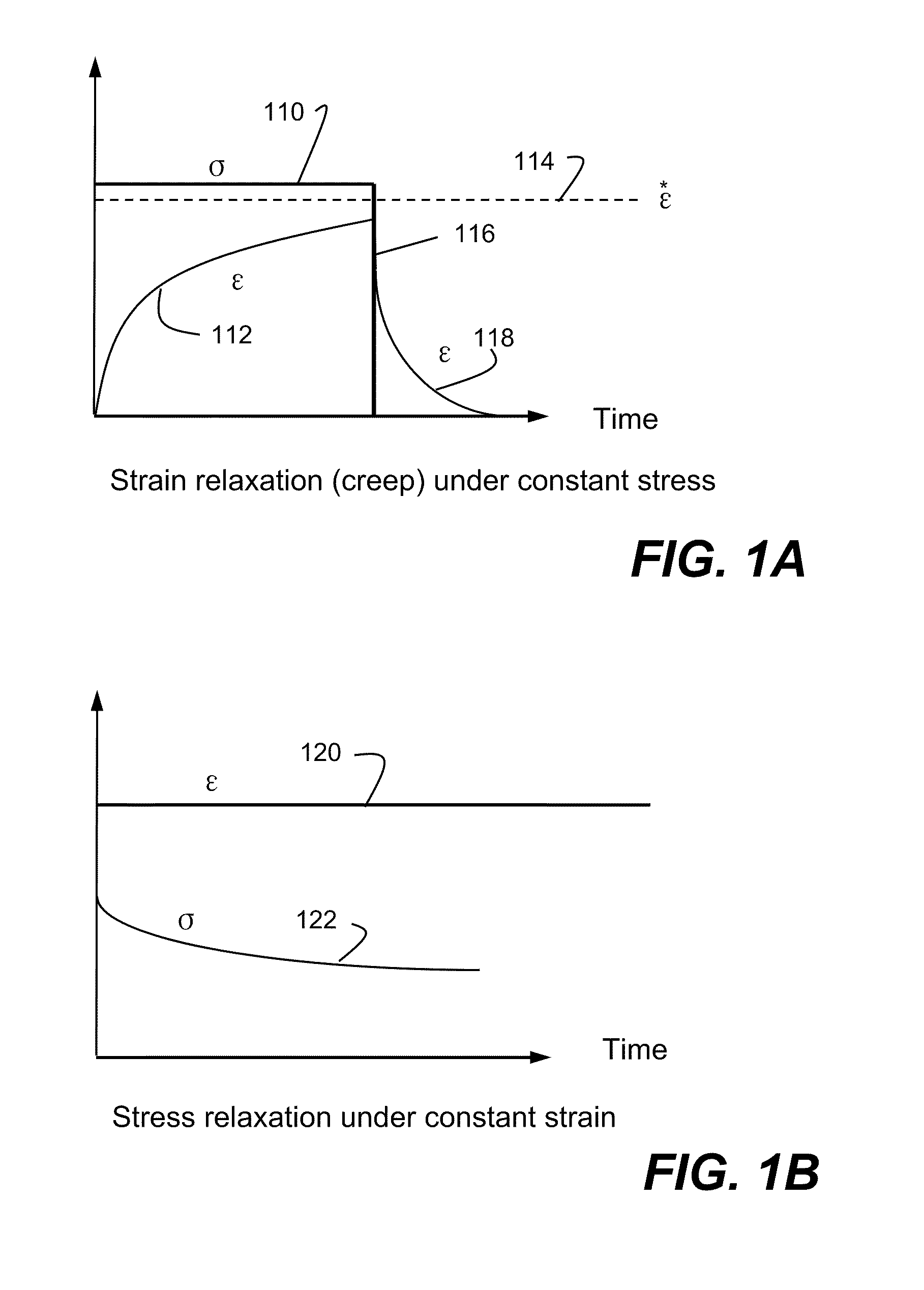
Methods and systems using a numerical model to describe polymeric material properties
InactiveCN102254060ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelNumerical models
Methods and systems using a numerical model to describe polymeric material properties are disclosed. FEM model of a product is defined. FEM model includes one or more solid elements of polymeric material. In a time-marching simulation of the product under loads, stress state of the solid elements is calculated from deformation gradient tensors. Stress state incorporates the Mullins effect and strain hardening effect, also includes elastic stress, viscoelastic stress and back stress. A yield surface is defined to determine whether the elements are under plastic deformation. Plastic strain is obtained to update the deformation gradient tensor, which is then used to recalculate the stress state. Calculations continue until updated stress state is within a tolerance of the yield surface, at which time the results of polymeric material elements are obtained. The numerical model takes into account all characteristics of a polymeric material.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Method for measuring yield surface of metal material
ActiveCN106610357AReflect the evolution law of the yield surfaceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesShape changeMetallic materials
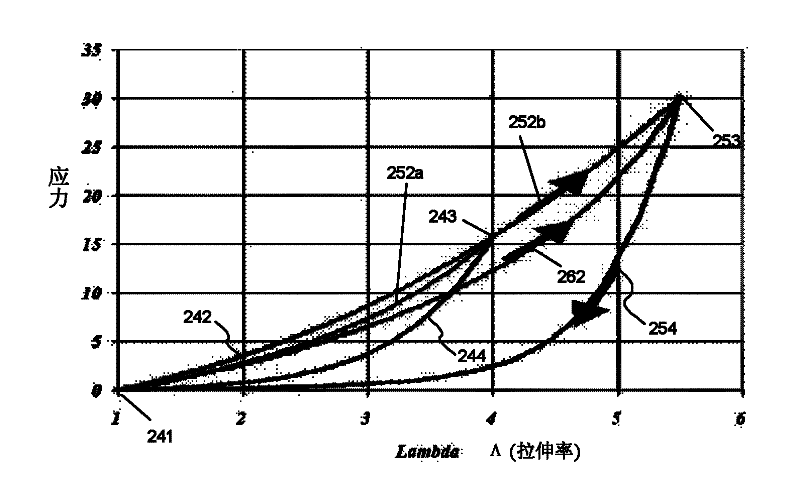
The invention discloses a method for measuring a yield surface of a metal material. The method utilizes a prestretching-torsion deformation loading path to determinate a later yield surface evolution rule and comprises (1) preparing a stretching-torsion combined test sample according to material mechanical test standards, (2) determining a stretching and torsion stress-strain curve and determining stretching and torsion yield strength values, (3) determining an initial yield surface, (4) determining a prestretching-torsion pre-deformation loading path to realize prestretching-torsion pre-deformation loading, (5) determining a later stretching stress-strain curve and determining stretching yield strength after pre-deformation, and (6) determining a later yield surface. The yield surface determined by the loading path has obvious shape change, shows plastic deformation anisotropic behaviors of the metal material in a complex loading way and is especially suitable for metal materials having strong anisotropic mechanical properties.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Normalization method for fatigue characteristics of asphalt mixture under different stress states
InactiveCN108956286ATo achieve the purpose of normalizationImprove unityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStructural fatigueYield surface
The invention discloses a normalization method for fatigue characteristics of an asphalt mixture under different stress states. The strength yield surface of the asphalt mixture based on a yield criterion is established by combining strength and fatigue test at different loading speeds under different stress states with a Desai strength yield surface model, a fatigue characteristic analysis technology based on the yield criterion is provided, and a normalization model for the fatigue characteristics of the asphalt mixture in different stress states is obtained. The fatigue characteristic analysis technology and the normalization model can be used to eliminate a difference between the fatigue test results of the asphalt mixture under different test conditions and make up for the deficiencyof no accurate evaluation of the fatigue performances of the asphalt mixture in traditional S-N fatigue equation; and the method realizes the unified expression of the fatigue performances of the asphalt mixture under different test conditions, and provides a theoretical, technologic and technical basis for realizing the scientific transformation from material fatigue to structural fatigue.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
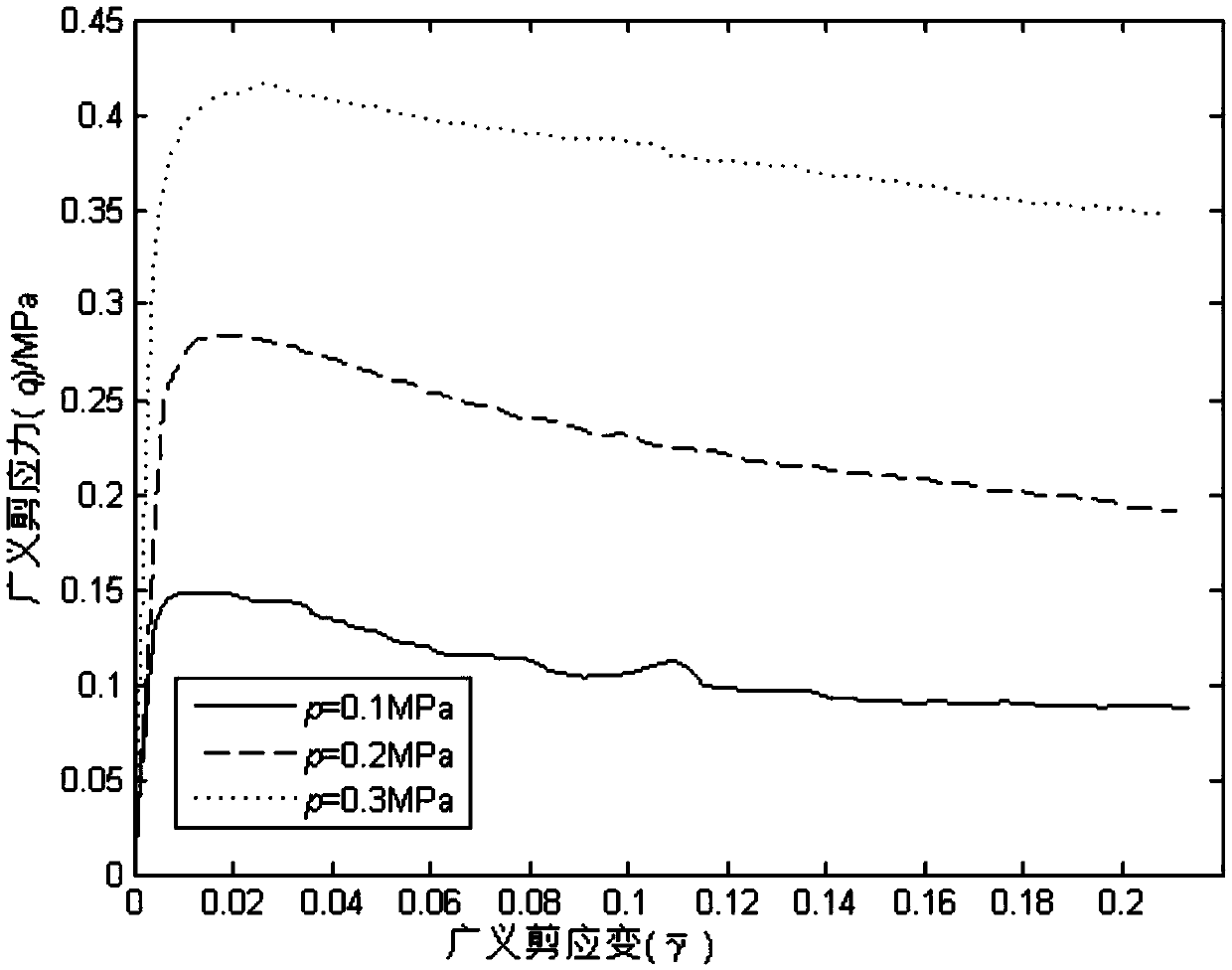
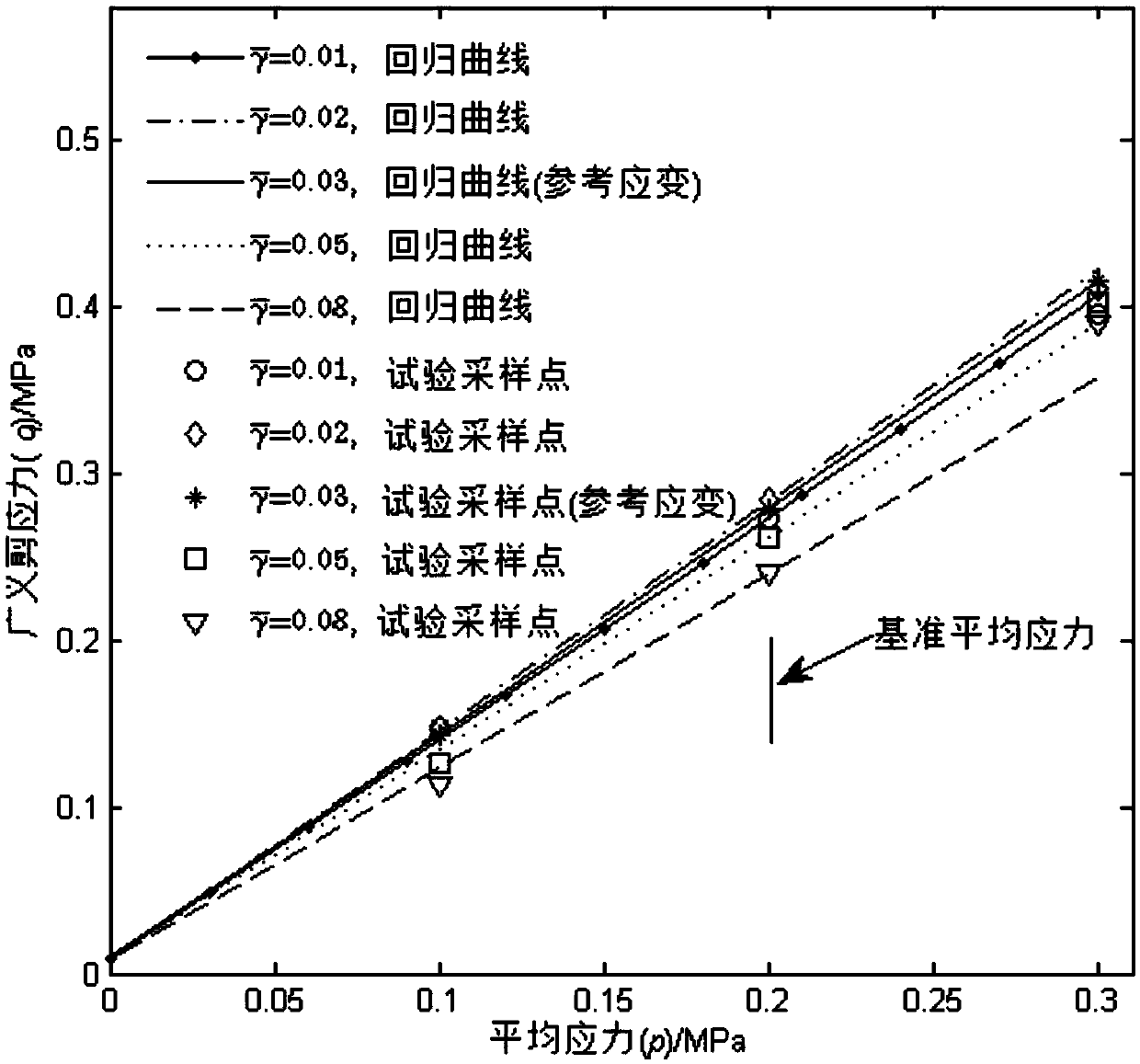
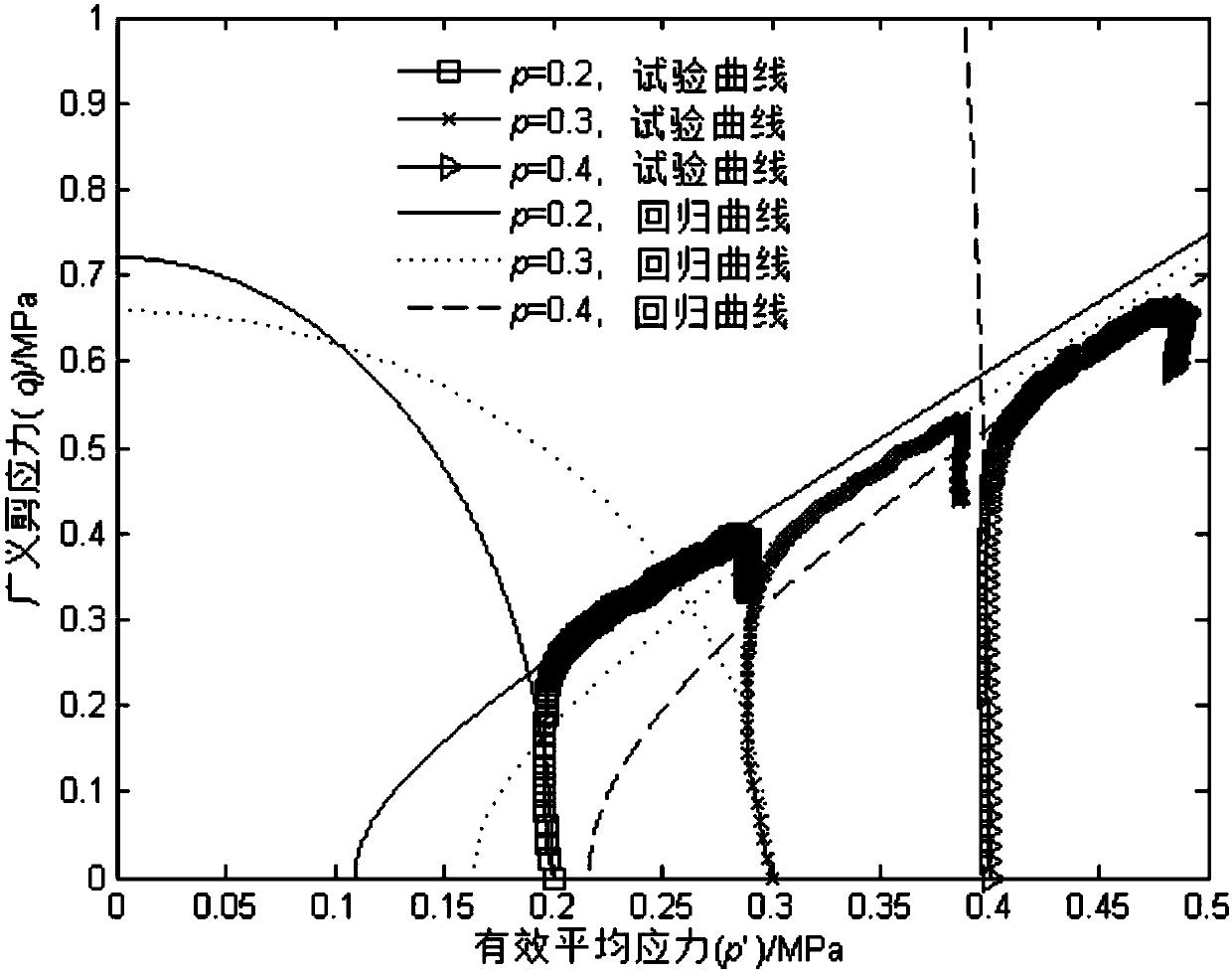
Method for determining shear yield surface and volume yield surface of geotechnical materials
ActiveCN109580388AImprove cohesionGood regression effectMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesTriaxial shear testEllipse
The invention relates to a method for determining the shear yield surface and the volume yield surface of geotechnical materials, and relates to the technical field of measuring solid deformation. Inorder to judge stress yield of the geotechnical materials, the shear yield surface is fitted by a quadratic polynomial, and the volume yield surface is fitted by an ellipse and a hyperbola; parametricregression of the shear yield condition of the quadratic polynomial is conducted through a constant average stress triaxial test and a conventional triaxial compression test; parametric regression ofthe volume yield conditions of the ellipse and the hyperbola is conducted through an undrained constant average stress triaxial test and the conventional triaxial compression test; a regression curveof the yield surfaces is drawn according to the shear yield condition, the volume yield conditions and relevant parameters; and according to specific response values of the shear yield condition andthe volume yield conditions in engineering, whether shear yield or volume yield occurs in the geotechnical materials or not is evaluated. According to the method for determining the shear yield surface and the volume yield surface of the geotechnical materials, whether yield of the geotechnical materials exists after stress or not can be judged in engineering, corresponding measures are taken to prevent material damage and collapse accidents.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Plasmonic multicolor meta-hologram
InactiveUS20170068214A1High plasma resonanceWide working wavelength rangeHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesNanoopticsYield surfaceEngineering
A phase-modulated optical component for the visible spectrum is provided and is capable of producing images in three primary colors. The phase-modulated optical component is primarily structured by a plurality of aluminum nanorods that are arranged in several two-dimensional arrays to form a plurality of pixels. The nanorods can yield surface plasmon resonances in red, green and blue light. By tuning the nanorod size in the arrays, the wavelength-dependent reflectance thereof can be varied across the visible spectrum, thereby realizing wavelength division multiplexing operations for the phase-modulated optical component.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Analysis method for forecasting periodic lattice-material yield surface
InactiveCN107368660AShorten the timeTheoretical results are accurateGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationFinite element analysis softwareYield surface
The invention relates to an analysis method for forecasting a periodic lattice-material yield surface. According to the analysis method, the coupling effect of the internal-structure axial force and bending moment when a material is actually stressed is considered, a yield condition of periodic lattice-material representative volume element (RVE) is obtained through theoretical derivation, and then through finite element analysis software, mass total calculation is achieved through programming. In post-processing, the calculating result is obtained in the mode that a yield point is automatically identified and extracted, the calculating result and the theoretical result are jointly visualized, and are compared mutually and verified, the accuracy of the result is guaranteed, and therefore forecasting of the strength performance of the periodic lattice material is achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
An elastic-viscous-plastic constitutive model construction method considering complex nonlinear behaviors of a fiber reinforced composite material
ActiveCN109902362APredicting Complex Nonlinear Elastoviscoplastic BehaviorSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsFiber-reinforced compositeYield surface
The invention discloses an elastic-viscous-plastic constitutive model construction method considering complex nonlinear behaviors of a fiber reinforced composite material, which comprises the following steps: constructing a viscoplastic potential function considering the influences of stretching, compression yield asymmetry and hydrostatic pressure of the composite material, and obtaining the viscoplastic strain in an incremental form through a non-associated flow criterion; Defining a dynamic yield surface based on an overstress function, and considering the difference of isotropic hardeningof the material under stretching and compression and the rate correlation effect of the dynamic yield surface; And considering the existence of lagging elastic deformation, defining the relationship between the overstress function at the loading stage and the relaxation stage and the equivalent viscoplastic strain rate, and forming an elastic-viscoplastic constitutive model for describing the complex nonlinear behavior of the composite material. The method can effectively describe the elastic-viscoplastic behavior of the fiber reinforced composite material, and can be applied to the scientificresearch and engineering technical fields of development of a continuous constitutive model of a commercial finite element software composite material, analysis and optimization of mechanical properties of a composite material engineering structure and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Collapsible loess foundation stress-strain simulating method for overhead transmission line
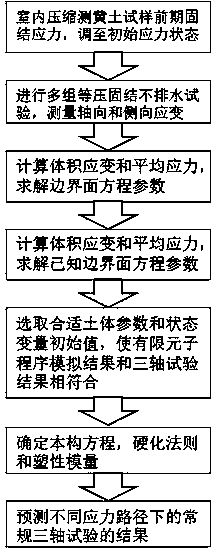
InactiveCN107860655AImprove accuracyWide applicabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress pointState variable
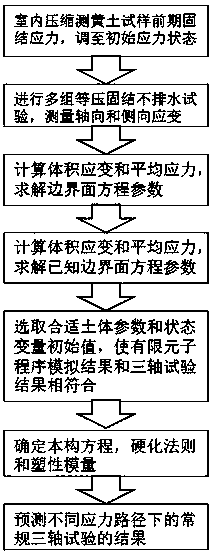
The invention discloses a collapsible loess foundation stress-strain simulating method for an overhead transmission line. The collapsible loess foundation stress-strain simulating method for the overhead transmission line comprises the following steps: (1) according to results of an indoor compression test and a constant-pressure consolidated undrained test of a saturated remoulded loess sample, measuring and recording average stress or axial stress of the tests, and drawing an e-lgp curve of the indoor compression test and a soil body stress-strain relationship curve and an lnv-lnp curve of the constant-pressure consolidated undrained test; (2) respectively determining the early consolidation stress of a soil body and material constants and the like involved in a constitutive model boundary surface equation, and obtaining a boundary surface equation of remoulded soil by utilizing a modified Cam-Clay model; (3) controlling the size of a yield surface and the change of a central position by adopting an associated flow rule and combining isotropic hardening and kinematic hardening rules, and solving plasticity modulus and determining a constitutive model through interpolation calculation of the distance between a current stress point and an image stress point; (4) selecting suitable soil body parameters and a state variable initial value to make a simulation result accord with the result of an undisturbed soil constant-pressure consolidated undrained shear test.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Landslide disaster scene simulation method based on material point method
ActiveCN109992830ASimulation of different hardening propertiesSimulated liquidityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsInterior point methodLandslide
The invention discloses a landslide disaster scene simulation method based on a material point method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) modeling and drawing a disaster phenomenon of the landslide in the field of computer graphics; 2) improving a yield surface criterion on the basis of a traditional MPM method, and introducing a modified Cambridge model. and 3) proposing a bidirectionalcoupling model based on the action of the granular material and the rigid body of MPM so that the soil-rock interaction in the landslide process is more real, and the efficiency of large-scale complex disaster scene simulation is improved. The landslide disaster scene simulation method solves the problem of landslide disaster scene simulation deficiency in computer graphics, and can simulate themovement between soil particles, the collision between stone rigid bodies and the coupling phenomenon between the soil particles and the stone rigid bodies in the landslide occurrence process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for determining yielding surface by crossed pre-stretching deformation and loading
ActiveCN107271273AReflect the evolution law of the yield surfaceStrongly Anisotropic Mechanical BehaviorMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress pointTest sample
The invention discloses a method for determining a yielding surface by crossed pre-stretching deformation and loading. The method mainly comprises the following steps: determining an initial yielding surface and a subsequent yielding surface; determining the yielding surface by adopting a loading path of carrying out pre-stretching deformation in one direction and then carrying out stretching deformation in the other direction. In the step of determining the initial yielding surface, firstly, a crossed stretching test sample is stretched to selected different stress points along one direction to keep load and then is stretched until the test sample is broken from the other direction; the initial yielding surface is drawn according to obtained yielding strength value; in the step of determining the subsequent yielding surface, firstly, the crossed stretching test sample is stretched to a selected pre-stretching point along a rolling direction and then is unloaded to zero or is unloaded to the selected different stress points; then the next step of a loading manner is selected according to different unloading manners to obtain the corresponding yielding strength value for drawing the subsequent yielding surface. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for reflecting an evolution law of the yielding surface in biaxial loading of a sheet material very well and can be used for effectively characterizing anisotropic mechanical behaviors of plastic deformation of a metal material.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Phase field material point method for large deformation fracture analysis of rock-soil structure
ActiveCN113360992AReduce complexityEasy to handleGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationPorosityYield surface
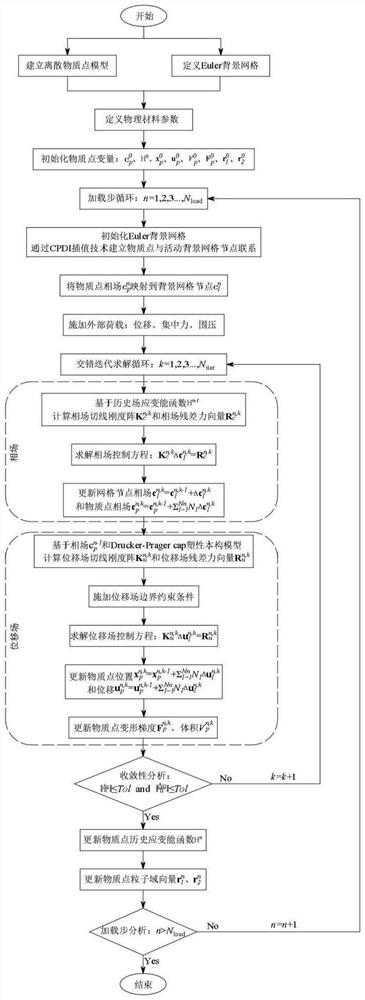
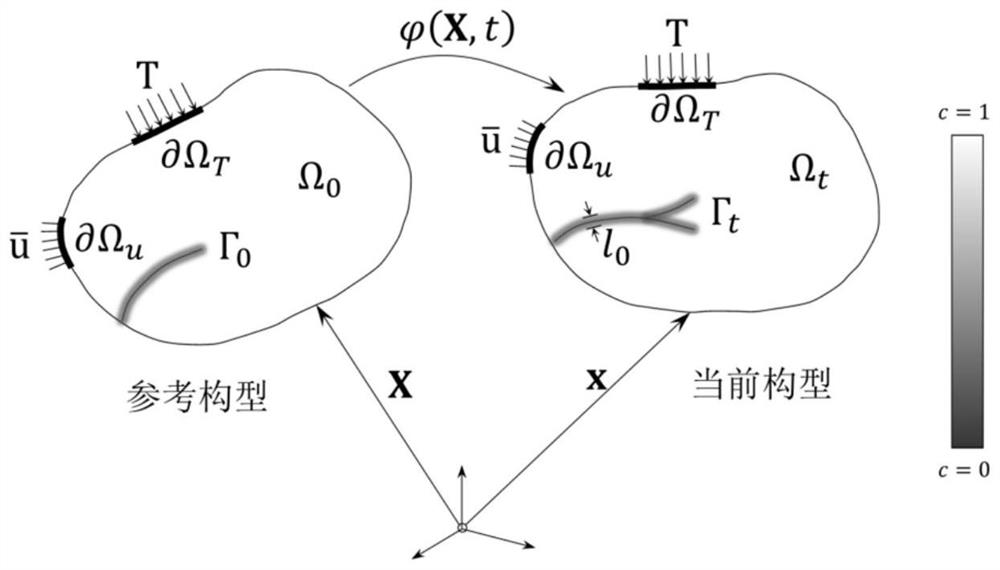
The invention belongs to the field of computational mechanics, and provides a phase field material point method for large deformation fracture analysis of a rock-soil structure, which considers the complex fracture phenomenon of brittleness-to-plasticity transformation of a high-porosity rock-soil material under the action of complex external factors, and widens the application range of the material point method in the field of solid material fracture. According to the method, a phase field fracture model is adopted as a damage function, so that a complex crack propagation path can be accurately and efficiently captured, and a smooth double-yield-surface Drucker-Prager cap plastic constitutive model is adopted to accurately and comprehensively describe complex mechanical behaviors of the pressure-sensitive geotechnical material; and the coupling effect of the phase field fracture model and the plastic constitutive model is realized by introducing the phase field effective stress. In addition, a CPDI interpolation method is adopted to improve the numerical stability and the boundary application accuracy, and an interlaced iteration solution strategy is implemented to improve the calculation efficiency and reduce the numerical implementation complexity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Variable-stiffness wind-resistant support for seismic isolation layer and mounting method of variable-stiffness wind-resistant support
InactiveCN107217751AReduce installation difficultySolve the problem of wind resistanceProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingIsolation effectVariable stiffness
The invention relates to a variable stiffness wind-resistant support for a shock-isolation layer, which comprises an upper connecting steel plate arranged above and a lower connecting steel plate arranged below, and several Wind-resistant steel plate, the wind-resistant steel plate is X-shaped with wide upper and lower ends and a retracted middle part, and the front and rear sides of the central retracted part of the wind-resistant steel plate are provided with circular arc surface notches for forming a weak yield surface ; The present invention also relates to an installation method for variable stiffness wind-resistant bearings used in shock-isolation layers. The structure design of the present invention is simple and reasonable, low in cost and superior in performance. It adopts the form of independent wind-resistant support, does not increase the installation difficulty of the original shock-isolation support, is convenient to disassemble, and makes full use of the characteristics of steel. To achieve the purpose of wind resistance without affecting the effect of seismic isolation, it can effectively solve the problem of wind resistance of seismic isolation buildings, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Embossing and laminating method and device for producing multi-ply web products and relative product
The embossing and laminating device comprises: a central embossing cylinder (1), provided with a plurality of protuberances (1P); at least three pressure rollers (3, 4, 5) disposed along the periphery of the embossing cylinder (1) and provided with a yielding surface, cooperating with the embossing cylinder; at least three paths to feed one or more plies (V1, V2, V3, V4) between the central embossing cylinder and each pressure roller; at least a first gluing unit (7) disposed between two consecutive pressure rollers and cooperating with said central embossing cylinder.
Owner:FABIO PERINI SPA
Numerical Model For Simulating Polymeric Material Properties
InactiveUS20110288827A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationBack stressNumerical models
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Numerical simulation method for generating three-dimensional damaged pattern
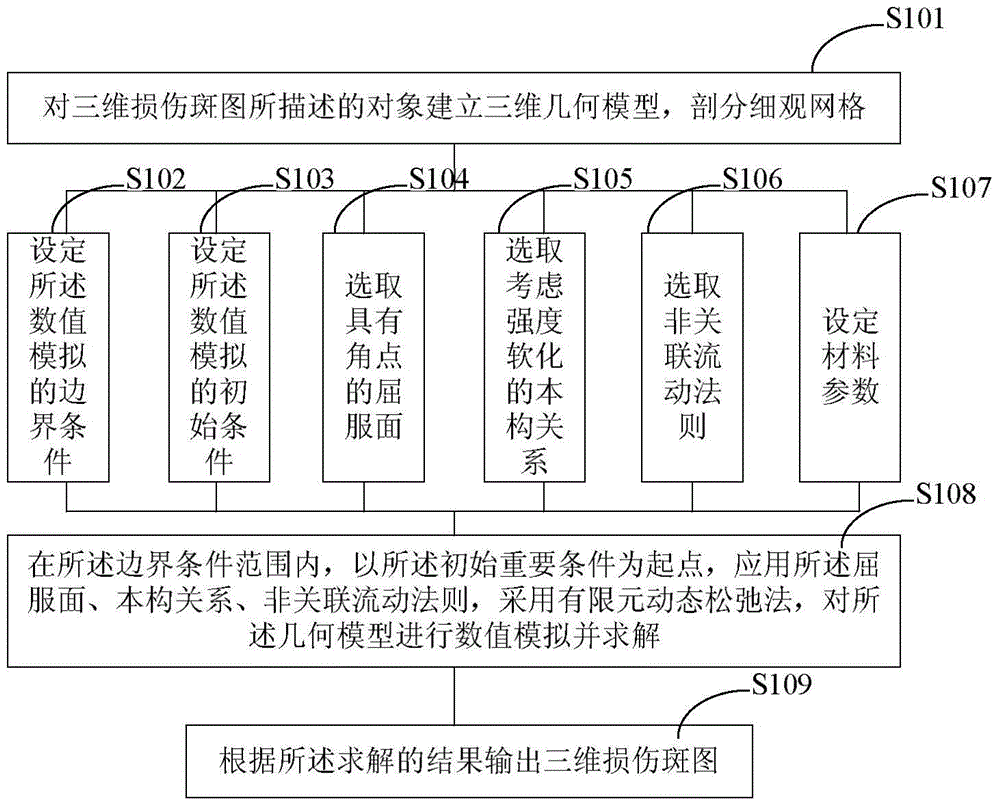
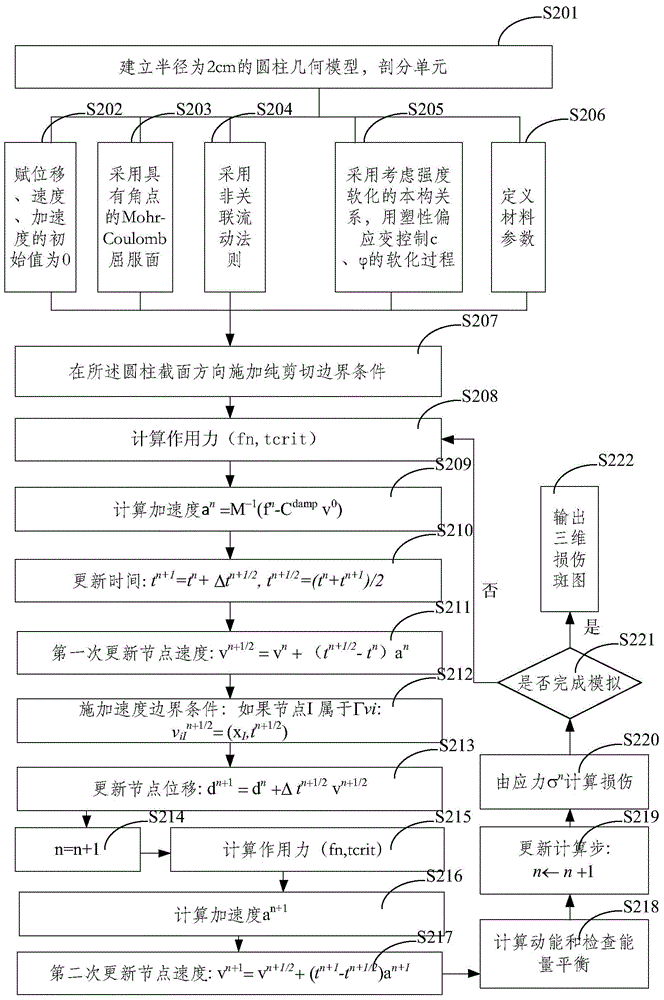
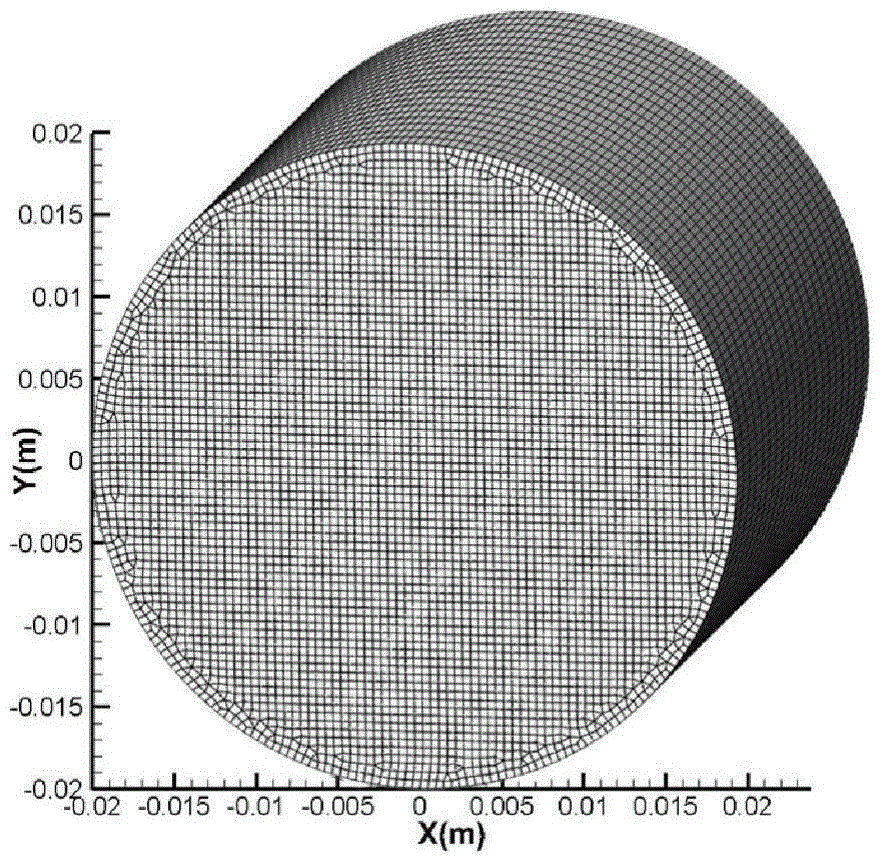
The invention provides a numerical simulation method for generating a three-dimensional damaged pattern. The method comprises the steps of establishing a three-dimensional geometric model for an object described in a three-dimensional damaged pattern, dissecting mesoscopic grids, setting a boundary condition, an initial condition and material parameters for the numerical simulation, selecting a yield surface with angular points, considering a strength-softening constitutive relationship and a non-associated flow rule, conducting the numerical simulation on the geometric model based on the finite-element dynamic relaxation method to get a solution, and outputting a three-dimensional damaged pattern. In this way, the three-dimensional damaged pattern can be generated directly based on a mechanical equation without the need of pre-assuming any physical mechanism. The above method provided in the invention is used for directly generating three-dimensional damaged patterns. Three-dimensional damaged patterns, generated based on the above method, can better reflect the actual damage situations of materials. Therefore, the mechanical performances of materials can be reflected more intuitively and more truly.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Complete water and soil coupling based land subsidence information processing method
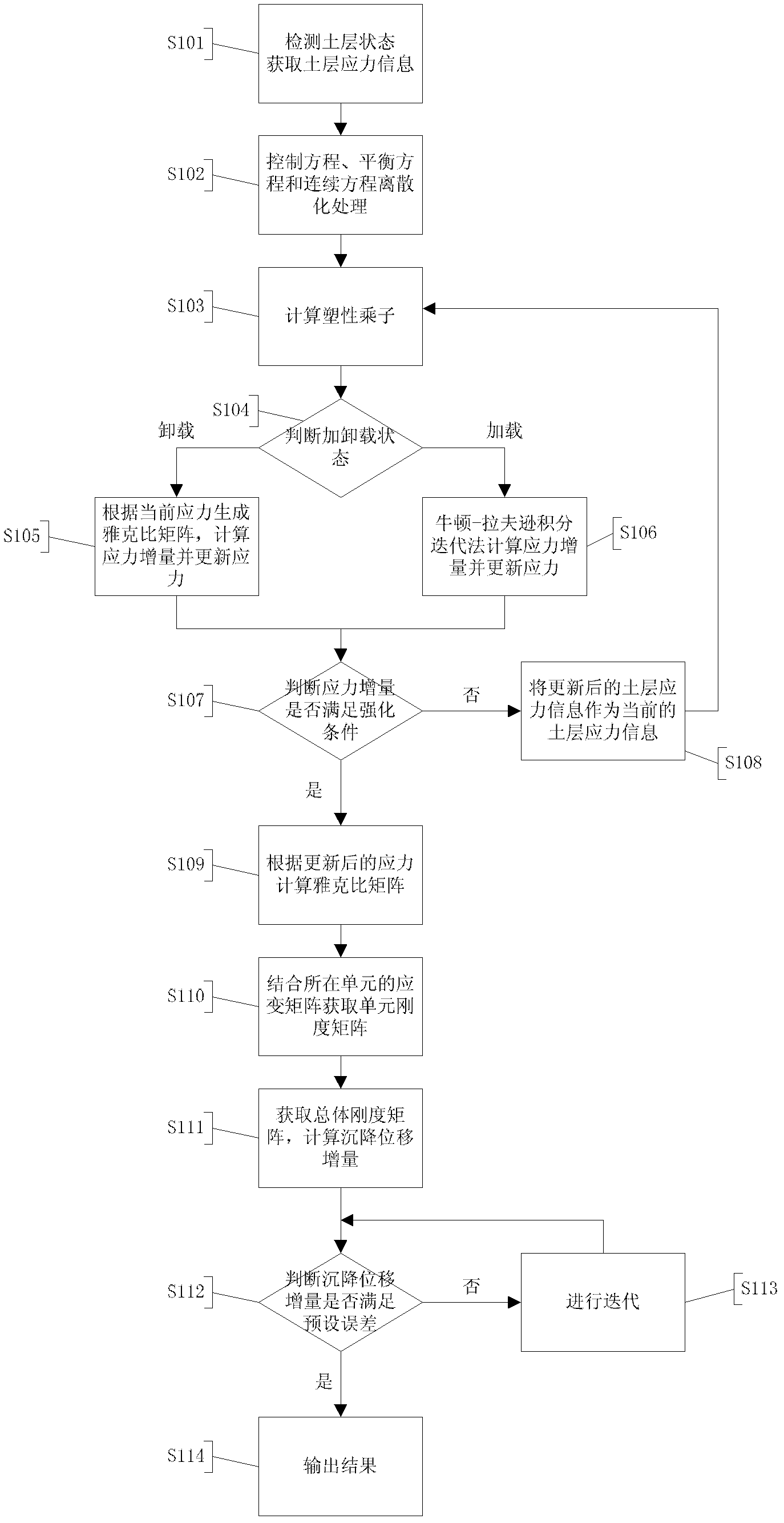
ActiveCN103258063AAvoid driftingImprove consistencySpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingYield surface
The invention relates to a complete water and soil coupling based land subsidence information processing method. The complete water and soil coupling based land subsidence information processing method includes steps of 1) detecting soil state to acquire soil layer stress information through a detecting module and transmitting the information to a discretization module and subsidence calculating module; 2) discretizing control equation, balance equation and continuity equation of complete water and soil coupling theory by the discretization module according to soil layer stress information and transmitting to the subsidence calculating module; 3) calculating complete water and soil coupling on the basis of a subloading cam-clay model by means of a finite element method according to the soil layer stress information and the control equation, the balance equation and the continuity equation subjected to discretization, and acquiring subsidence displacement increment. Compared with the prior art, characteristics of unloading and reloading of clay can be reasonably described, stress drifting from a yield surface can be accurately avoided on the basis of complete implicit-expression backward Euler diagram return algorithm during stress updating calculation, so it is unnecessary to judge whether to achieve yield or not by means of integral algorithm .
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Collapsible loess constitutive simulation method for transmission lines
InactiveCN107894367AImprove accuracyWide applicabilityEarth material testingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTriaxial shear testState variable
The invention discloses a collapsible loess constitutive simulation method for transmission lines. The method comprises the following steps of 1, measuring and recording the test average stress or axial stress according to a loess sample indoor compression test and a triaxial undrained test result; 2, determining material constants involved in boundary surface equations of a constitutive model, and using a modified Cambridge model to derive the boundary surface equations of remolded soils; 3, using the associated flow rule and combining with the isotropic hardening and kinematic hardening rules to control the change of yield surface size and center position, using interpolation calculations to determine plastic modulus, and determining the constitutive model; 4, selecting appropriate soilparameters and state variables, so that simulation results and natural soil sample triaxial test results are consistent.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Method for representing fatigue characteristic temperature correlation of asphalt mixture in three-dimensional stress state
InactiveCN110286045APlay a guiding roleMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesRoad engineeringRoad surface
The invention discloses a method for representing fatigue characteristic temperature correlation of an asphalt mixture in a three-dimensional stress state, and particularly relates to the field of road engineering. The method concretely comprises the following steps of: S1, establishing a strength yield surface model based on a three-dimensional stress state; S2, establishing a response function of the yield surface of the asphalt mixture; S3, determining fatigue stress paths in different stress states; S4, providing a novel fatigue characteristic analysis method based on a yield criterion idea. The method redefines the fatigue equation from the three-dimensional angle, and represents the fatigue life by using the temperature in combination with the influence of the temperature on the fatigue life. The fatigue life equation determined by the method is more scientific and more practical, and can play a guiding role in the design of asphalt pavements in China.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for producing improved rubberized concrete using waste rubber tires
ActiveUS8338506B2Improve bindingImprove mechanical propertiesPlastic recyclingPaper coatingPartial oxidationWaste rubber
Partial oxidation of crumb rubber derived from environmental hazardous waste tires yields surface treated crumb rubber and a gas condensate which are used as blending stocks for making rubberized concrete with substantially improved mechanical strength as compared to the conventional rubberized concrete. The chemically more active rubber surface becomes hydrophilic, so it interacts with the hydrophilic surface of surrounding cement matrix much stronger. The gas condensate co-produced in the partial oxidation reactor consists of mainly active sulfur oxides (R—SOx—R) and serves as an excellent bonding agent to further enhance the bonding strength between the partially oxidized rubber particles and the cement mixes. The mechanically improved rubberized concrete is more versatile than conventional rubberized concrete.
Owner:SHIN CHUANG TECH CO LTD
Method for producing improved rubberized concrete using waste rubber tires
ActiveUS8536239B1Improve mechanical propertiesProductsRoof covering using tiles/slatesPartial oxidationWaste rubber
Partial oxidation of crumb rubber derived from environmental hazardous waste tires yields surface treated crumb rubber which are used as blending stocks for making rubberized concrete with substantially improved mechanical strength as compared to the conventional rubberized concrete. The chemically more active rubber surface becomes hydrophilic, so it interacts with the hydrophilic surface of surrounding cement matrix much stronger. The mechanically improved rubberized concrete is more versatile than conventional rubberized concrete.
Owner:SHIN CHUANG TECH CO LTD
Establishment method for fiber mixed concrete compressive strength destroying rule
InactiveCN105678018AApply compressive strength failure criteriaThe brief introduction is clearGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsFiberYield surface
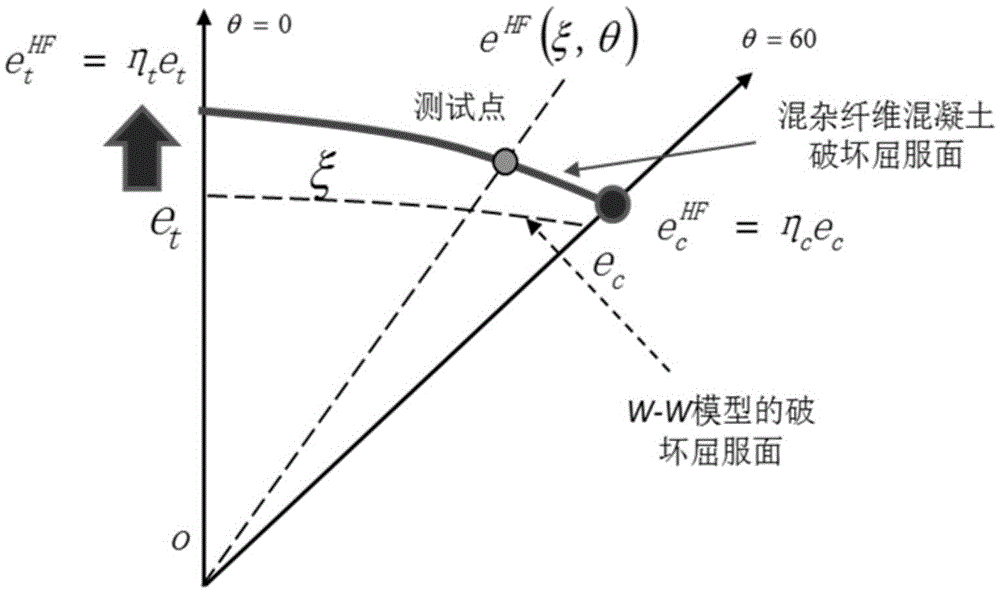
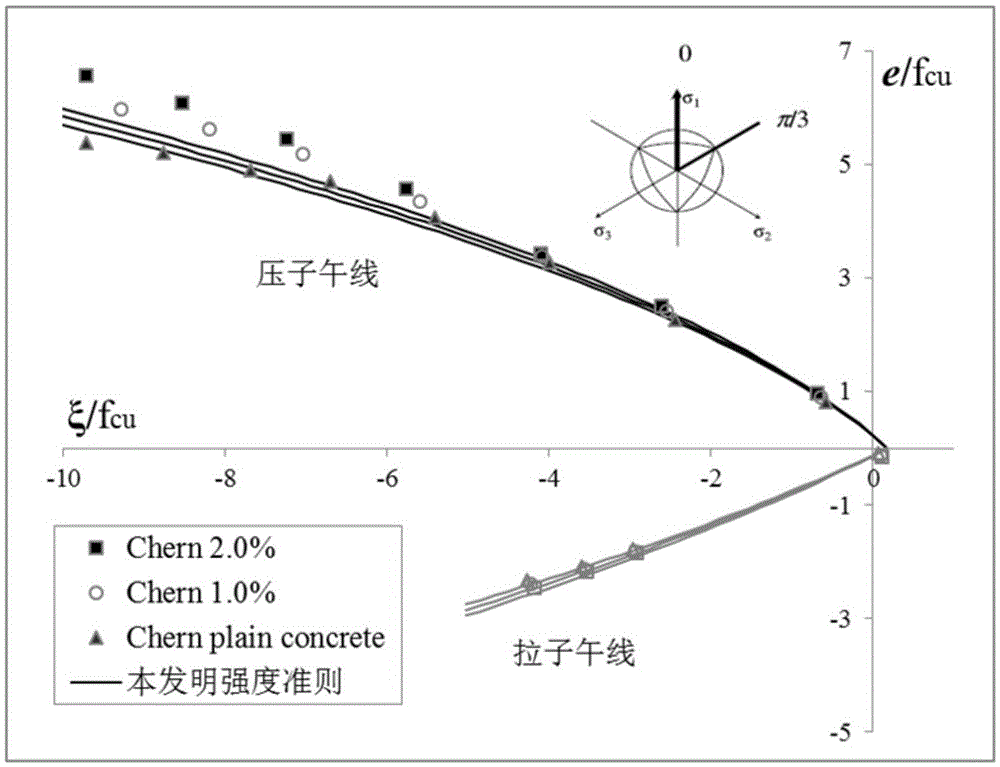
The invention discloses an establishment method for a fiber mixed concrete compressive strength destroying rule. The establishment method is based on a classic W-W five-parameter model, and comprises the following steps: using a special parameter demarcating method, introducing influence coefficients eta t and eta c of deviatoric stress which is applied by fiber to pull and compress meridian lines, and then fitting the influence coefficients with a fiber characteristic value lambda f to finally obtain the compressive strength destroying rule which is applicable to the fiber mixed concrete. The method is mature in theoretic foundation, clear in principal introduction, convenient in computation step, particularly strong in applicability, and applicable to determination of compressive strength destroying yield surfaces of concrete doped with various fibers in a plurality of doping manners and can obtain the result meeting the requirements for scientific research or engineering application.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Wood cross grain pressure-bearing constitutive relation model construction method and device based on wood weak phase structure, and storage medium
PendingCN113761729AEasy accessHigh degree of fitDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAgricultural engineeringYield surface
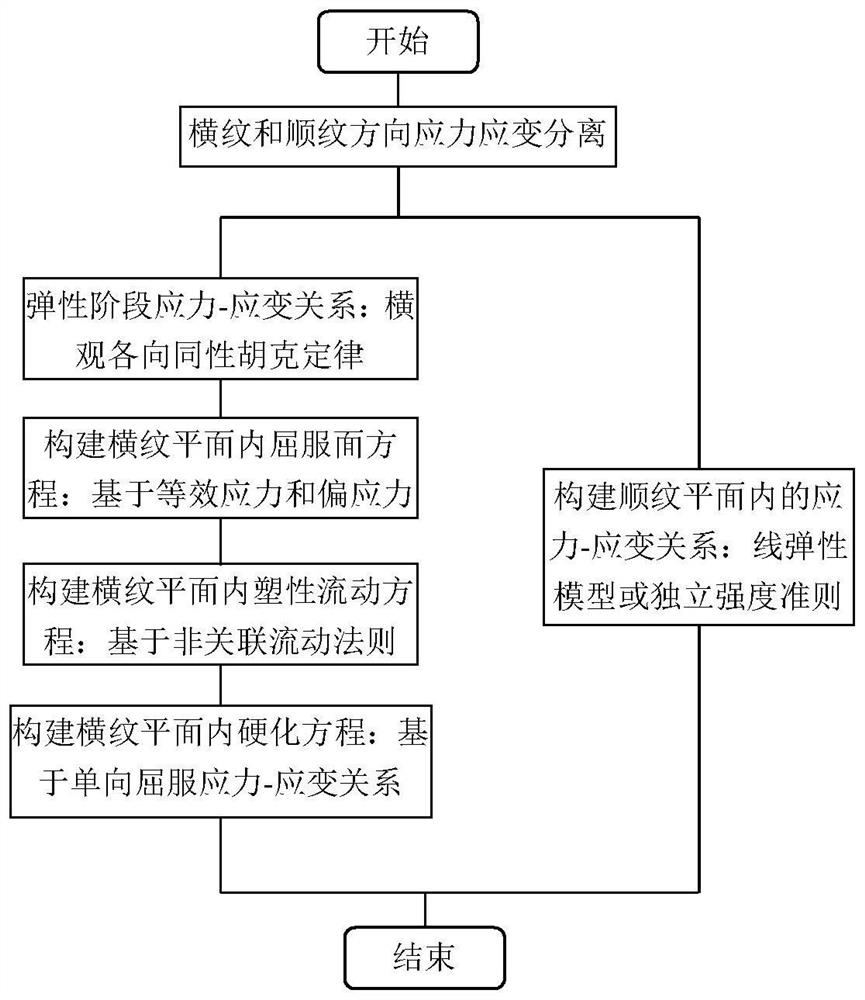
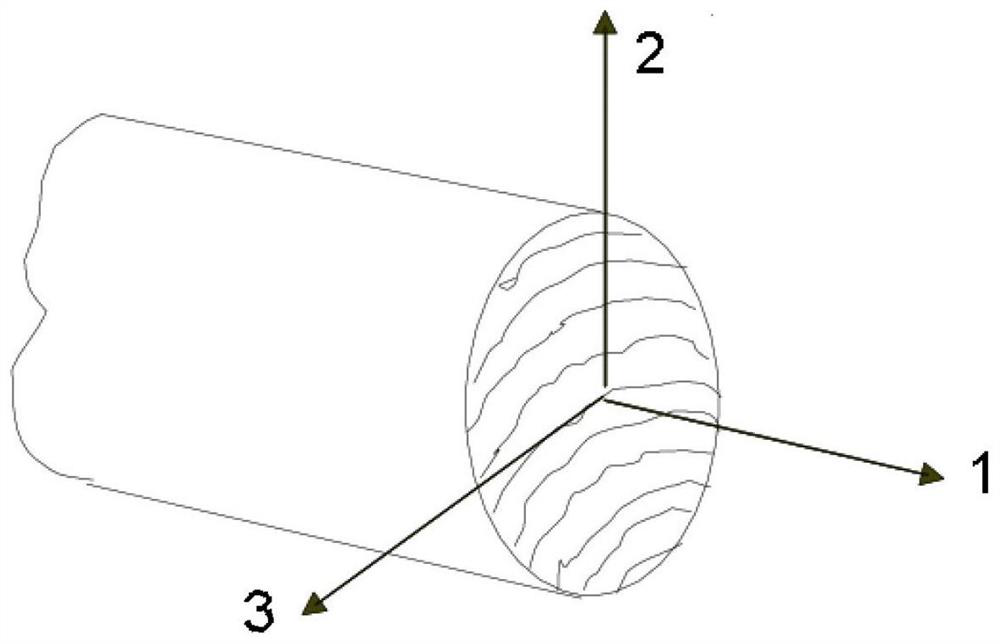
The invention provides a wood cross grain pressure-bearing constitutive relation model construction method and device based on a wood weak phase structure, and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps that: the stress-strain relation of wood in the elastic stage is constructed according to the Hooke law of a transverse isotropic material; according to stress characteristics of wood cross grain pressure bearing, equivalent stress causing wood volume deformation in a wood cross grain plane and deviating stress causing wood shear deformation are separated, and a yield surface equation of an elastic-plastic stage in the wood cross grain plane based on the equivalent stress and the deviating stress is constructed; according to a non-correlation flow rule, a plastic flow equation in a wood cross grain plane is constructed; according to the evolutionary relationship of the yield stress along with strain during unidirectional compression of the wood and the relationship between the yield stress during unidirectional compression of the wood and the yield stress during bidirectional compression of the wood, a hardening equation in a wood cross grain plane is constructed; and a stress-strain relationship in a wood rift-grain plane is constructed. The invention can better simulate the compression deformation of the volume when the cross grain of the wood is pressed.
Owner:INST OF WOOD INDUDTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Method and apparatus for altering material
InactiveUSRE37537E1High energyLow costVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyYield surface
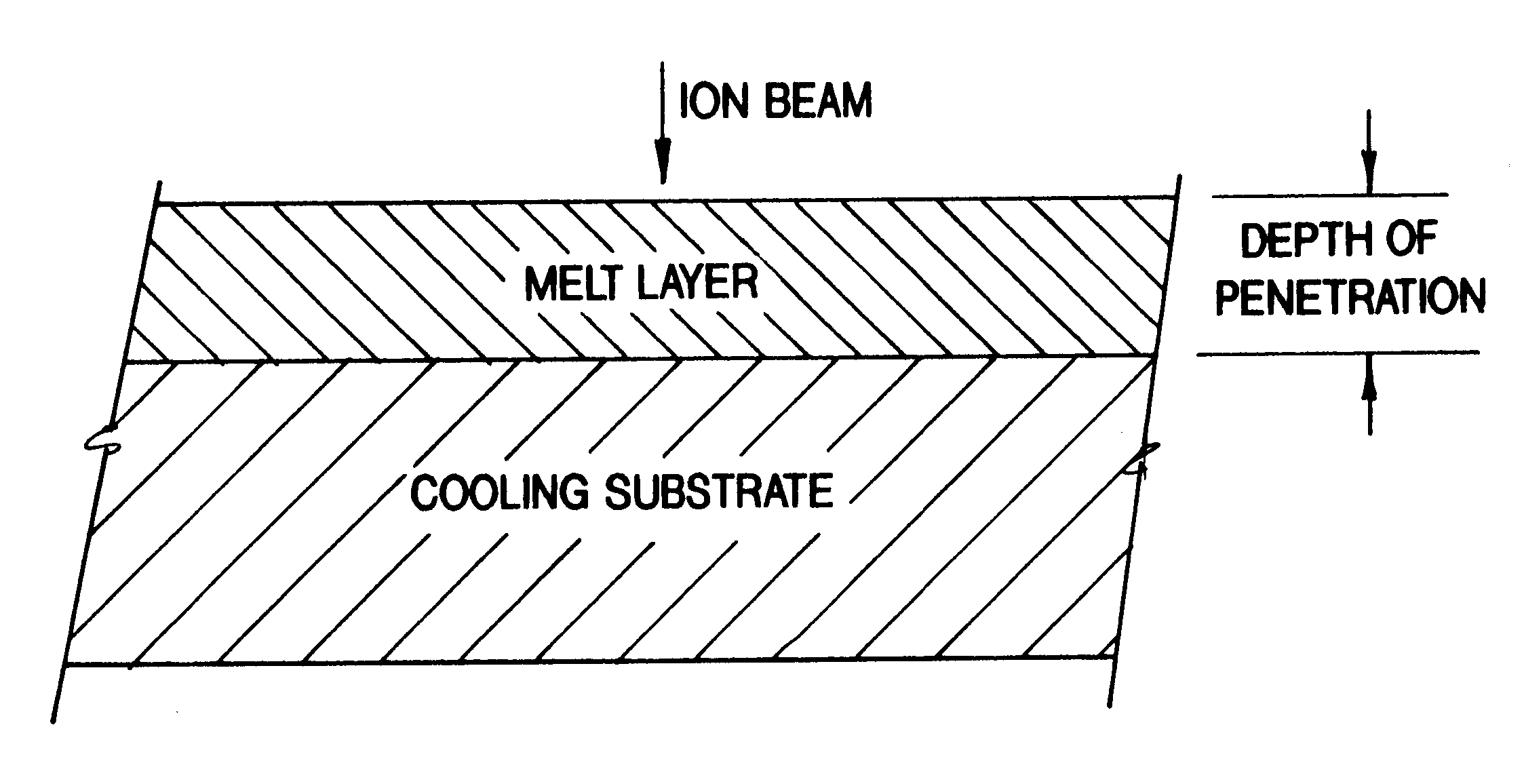
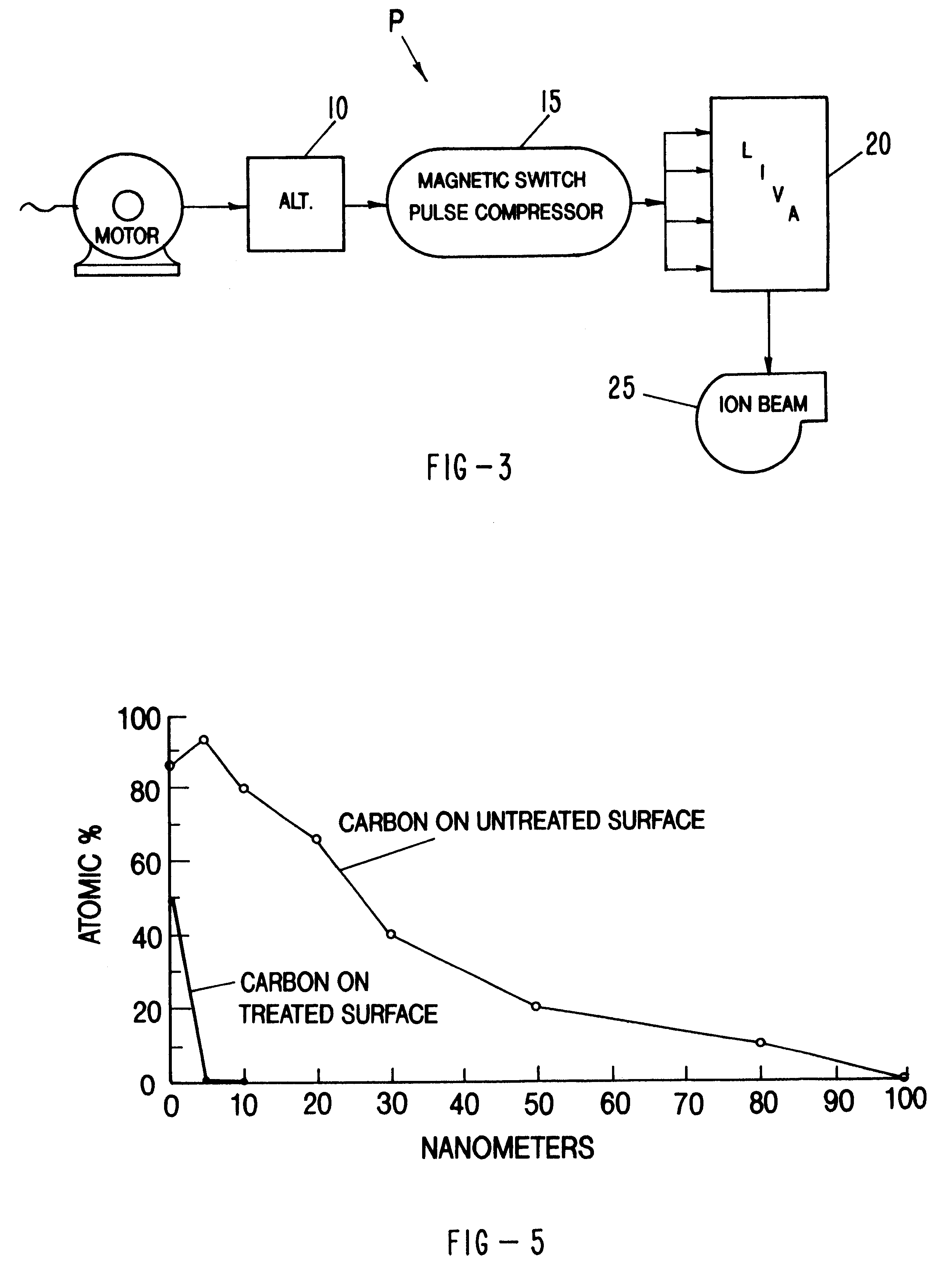
Methods and apparatus for thermally altering the near surface characteristics of a material are described. In particular, a repetitively pulsed ion beam system comprising a high energy pulsed power source and an ion beam generator are described which are capable of producing single species high voltage ion beams (0.25-2.5 MeV) at 1-1000 kW average power and over extended operating cycles (108). Irradiating materials with such high energy, repetitively pulsed ion beams can yield surface treatments including localized high temperature anneals to melting, both followed by rapid thermal quenching to ambient temperatures to achieve both novel and heretofore commercially unachievable physical characteristics in a near surface layer of material.
Owner:SANDIA
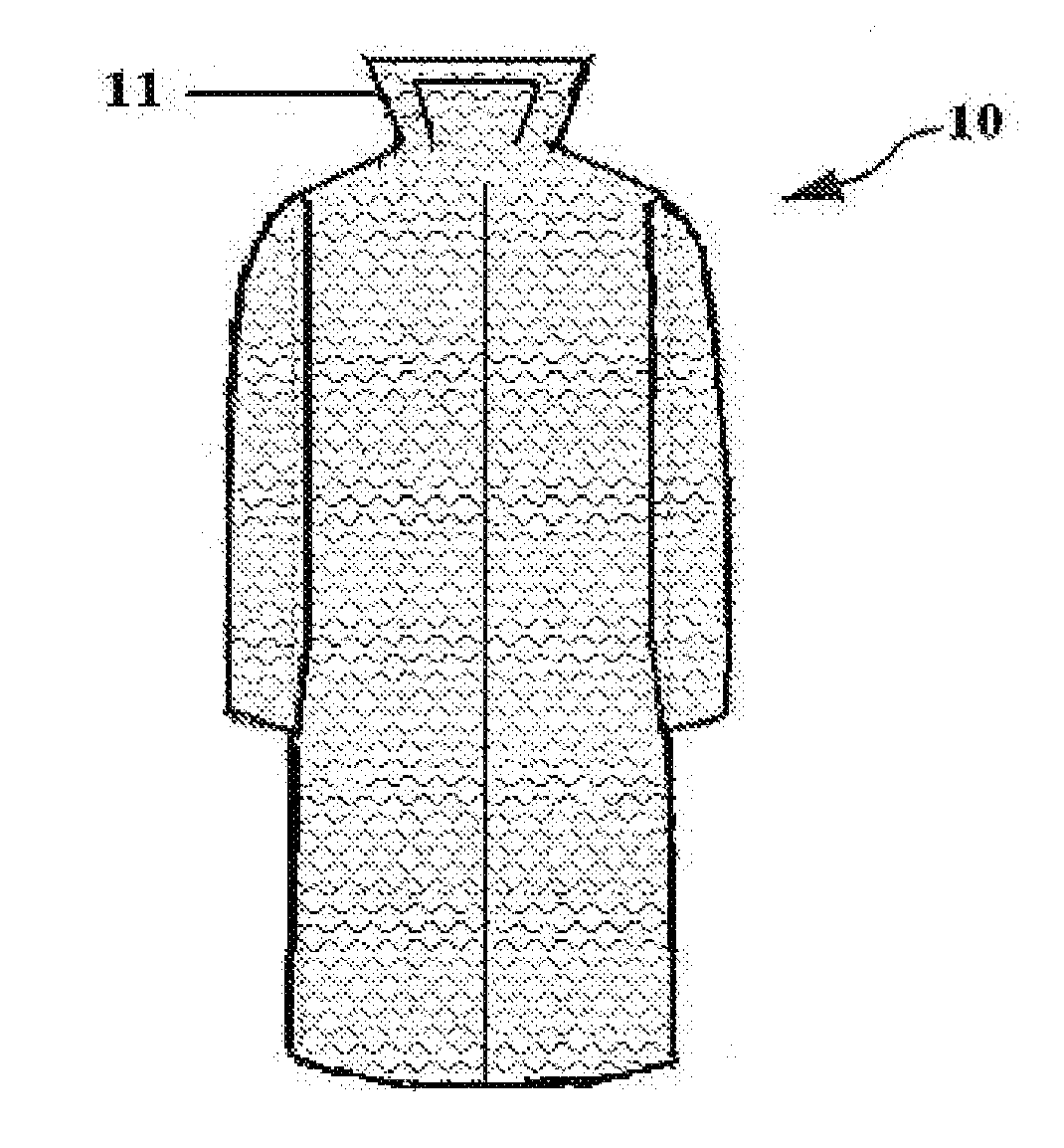
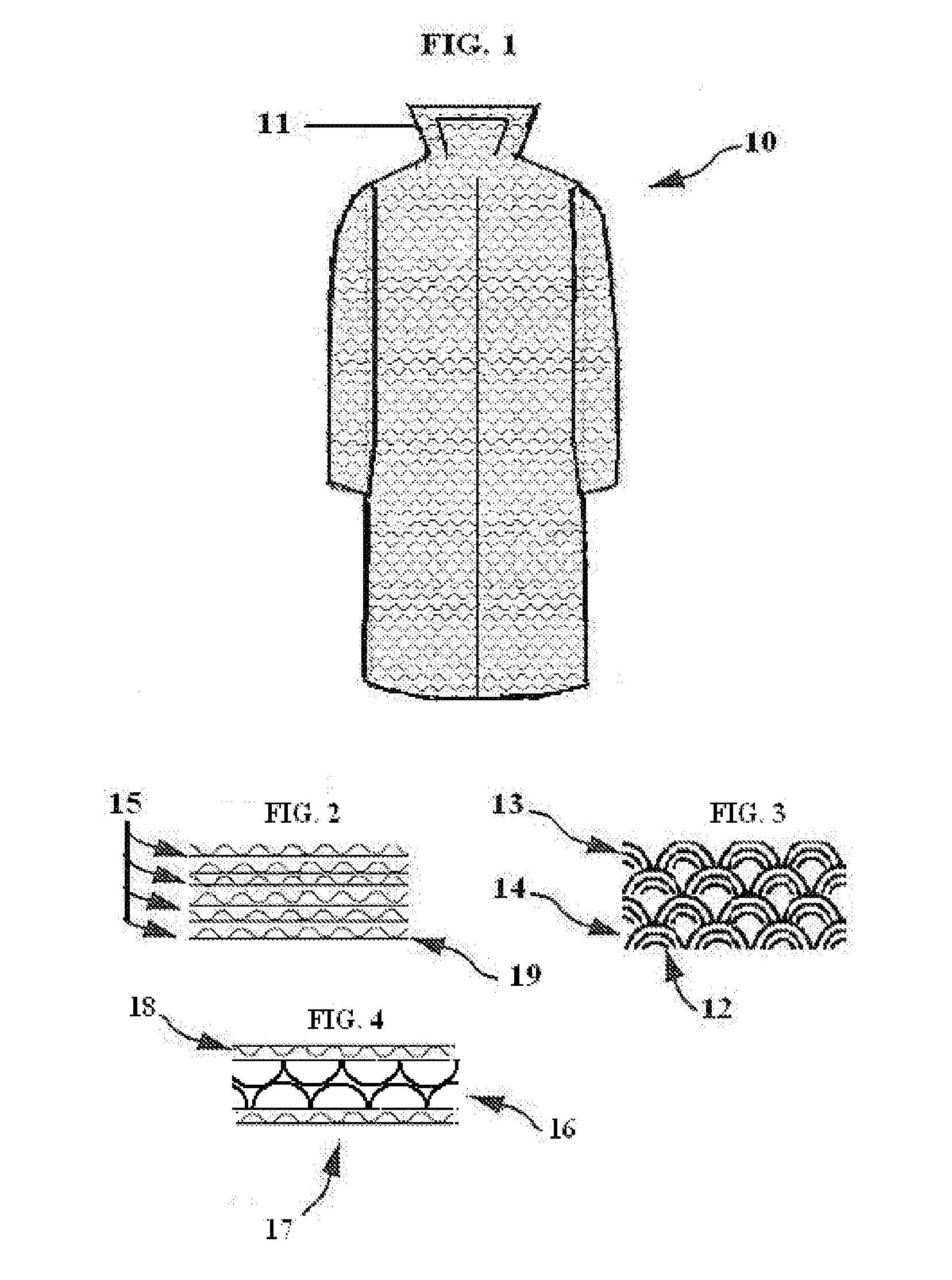
Body Protection Robe
InactiveUS20140143943A1Reduce shockDissipate impact energyChemical protectionHeat protectionEnergy transferMechanical energy
A protective garment that reduces the energy transfer from an impact or a fall by consuming some of the mechanical energy transferred to the person wearing the garment and decreasing the amount of injury to that person. The material used in the manufacture of the garment is a polymer, often termed “air bubble packing”. The protective action uses a design that has one or more layers of the air bubble packing or one air chamber fashioned into a robe style garment for the purpose of reducing the amount of injury to the wearer from an impact with an UN-yielding surface. The air chambers are intended to cushion or rupture as pressure is applied, after the collapse of the first air chamber the next air chamber or layer of chambers and the process is repeated.
Owner:CACAS CLAY
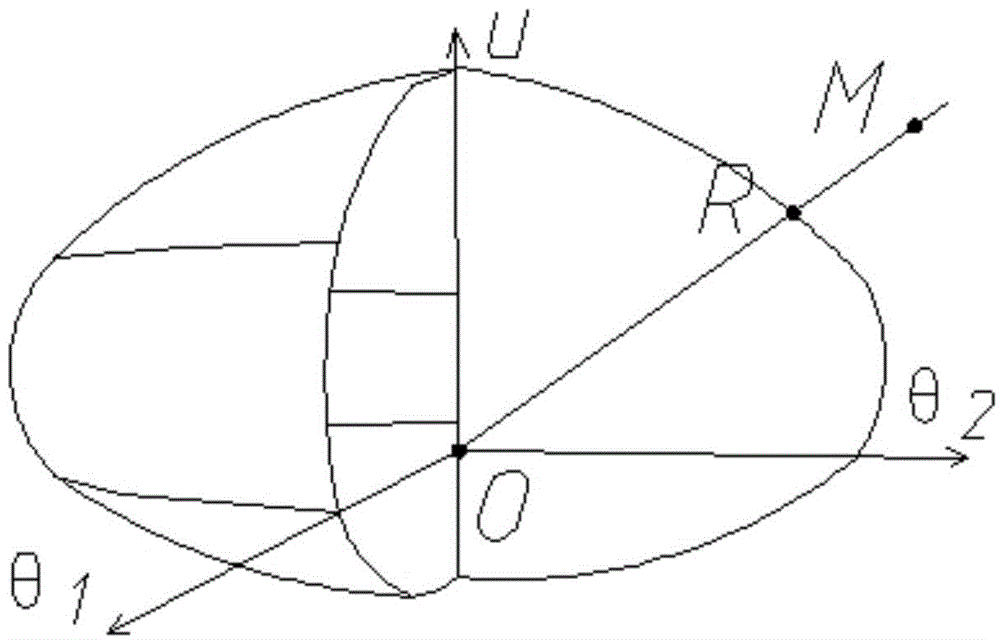
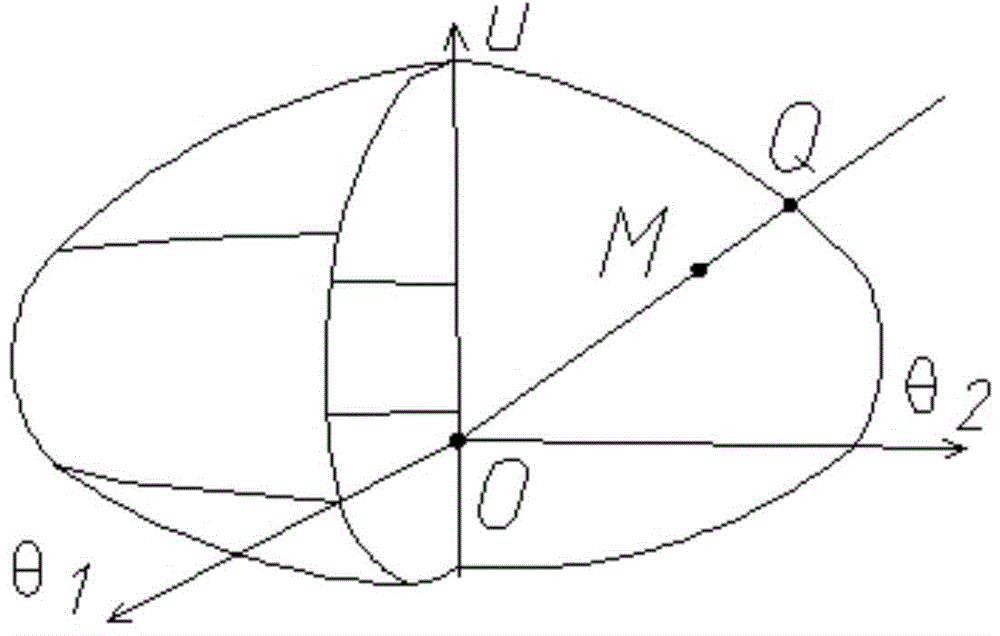
Method for determining performance state of any point in displacement space of three-dimensional plastic hinge
The present invention discloses a method for determining a performance state of any point in a displacement space of a three-dimensional plastic hinge. The method comprises: 1) determining an initial displacement yield surface of the three-dimensional plastic hinge; 2) determining a displacement performance surface of the three-dimensional plastic hinge; 3) selecting one point O on the initial displacement yield surface, and connecting any one point M in a displacement space to the point O to form a straight line, wherein the straight line intersects with the initial displacement yield surface at one point R and intersects with the displacement performance surface at one point Q, and MR / QR is defined as a correction energy-requiring ratio; according to the correction energy-requiring ratio, determining a performance state of the any one point M of the displacement space. By adopting the method, the performance state of any point in the displacement space of the plastic hinge can be easily determined to judge the performance of an actual structure under the action of a certain load and guide structural design, and the method is particularly applied to the design and the analysis of earthquake resistance of the structure.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com