Patents
Literature
40 results about "Material point method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
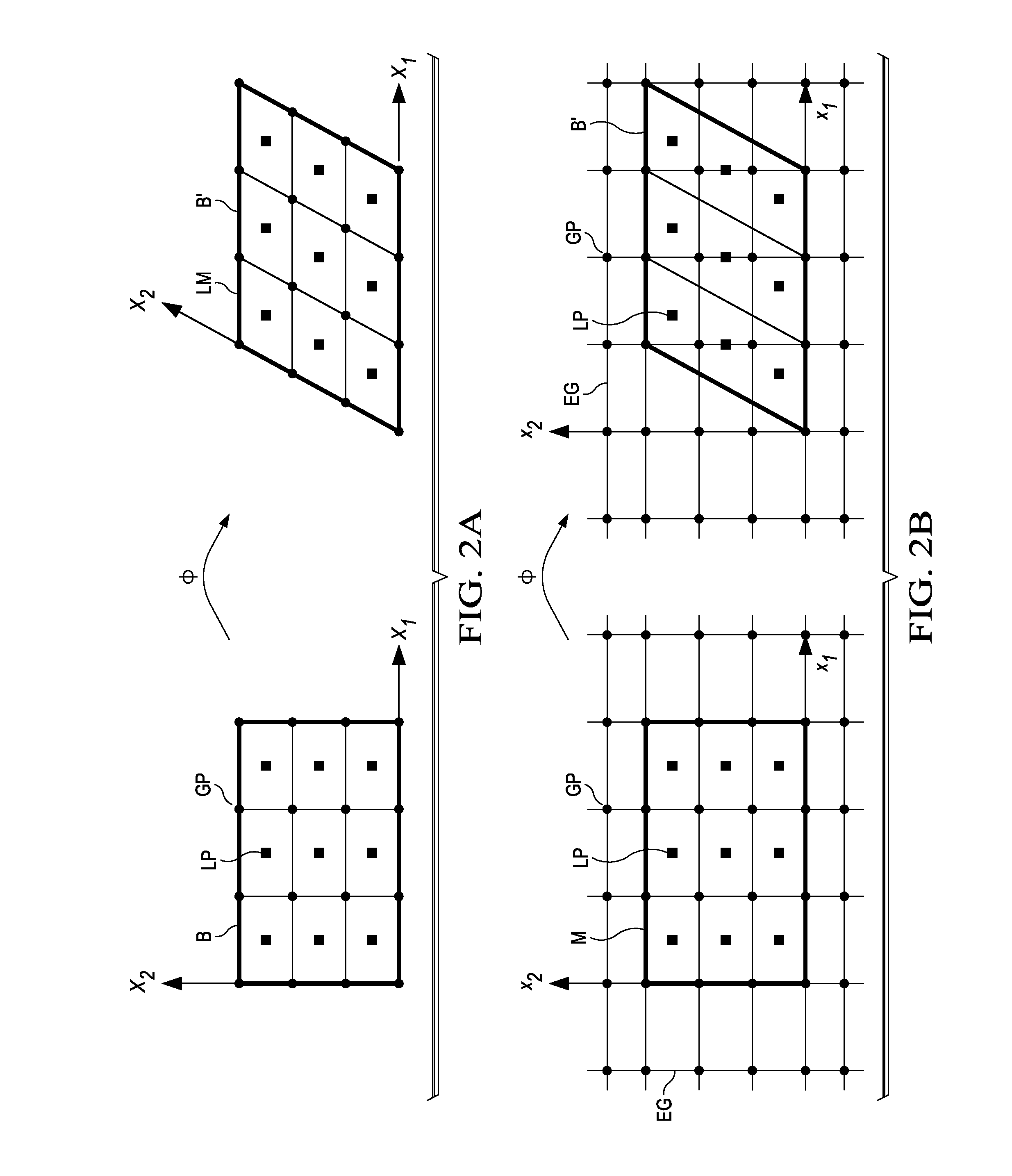
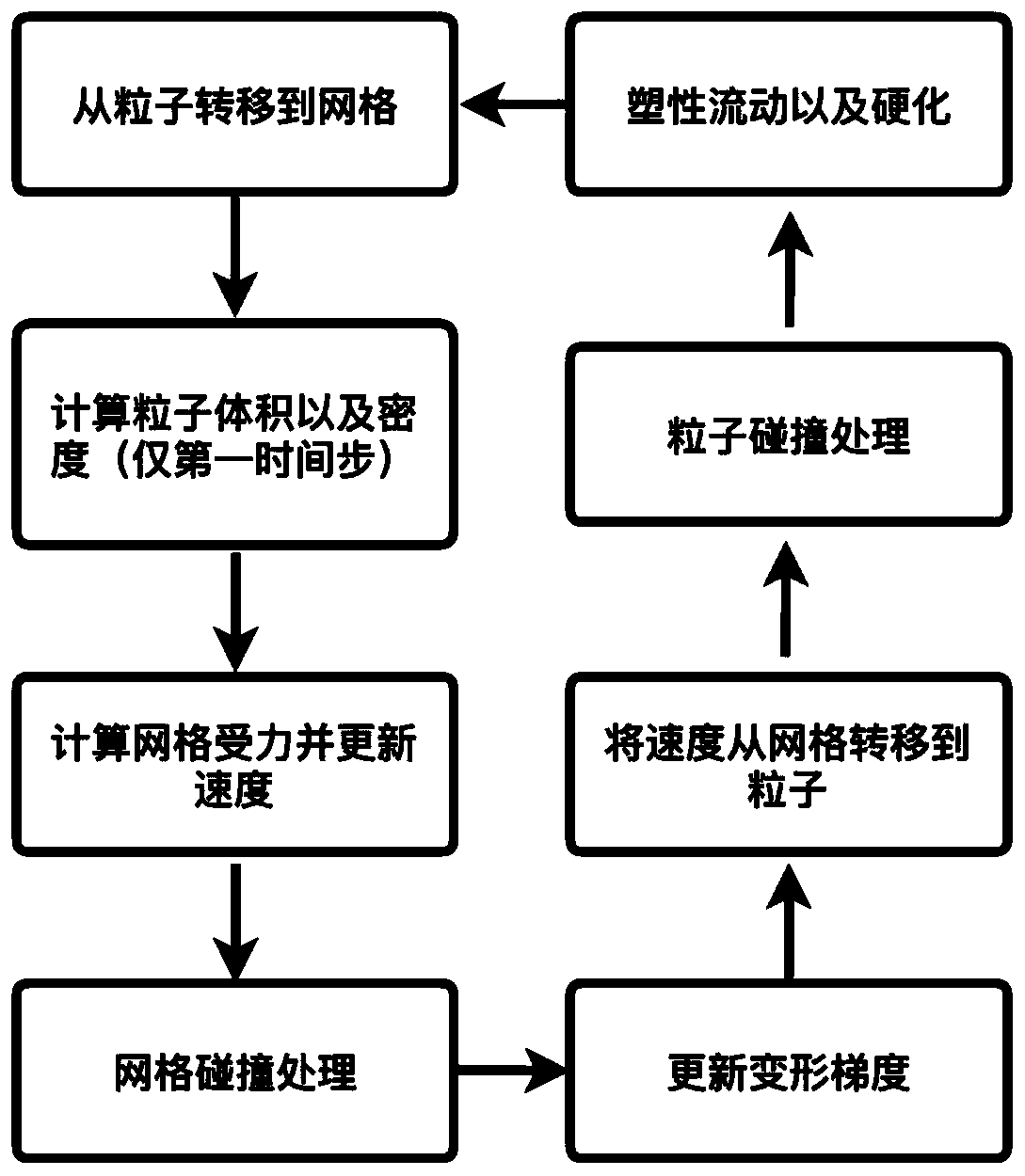
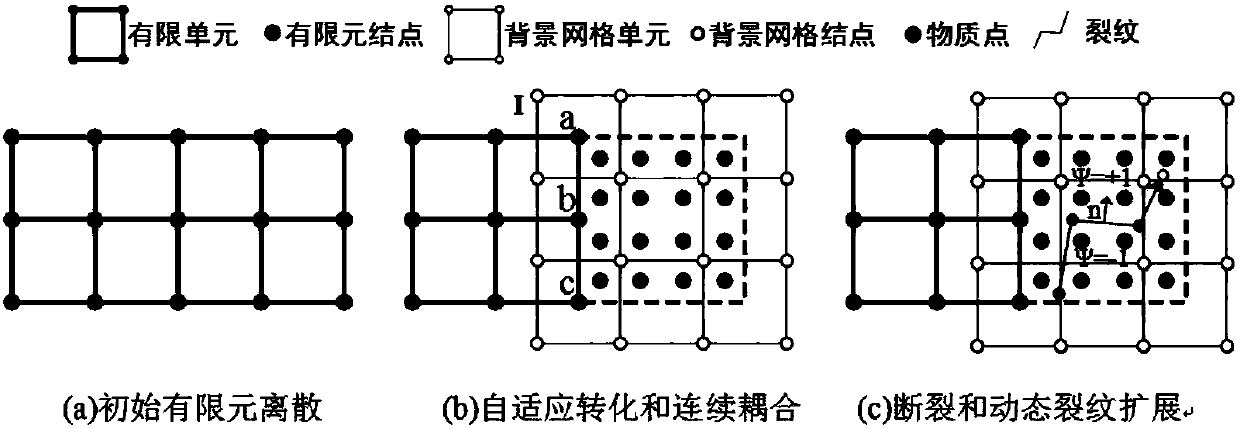
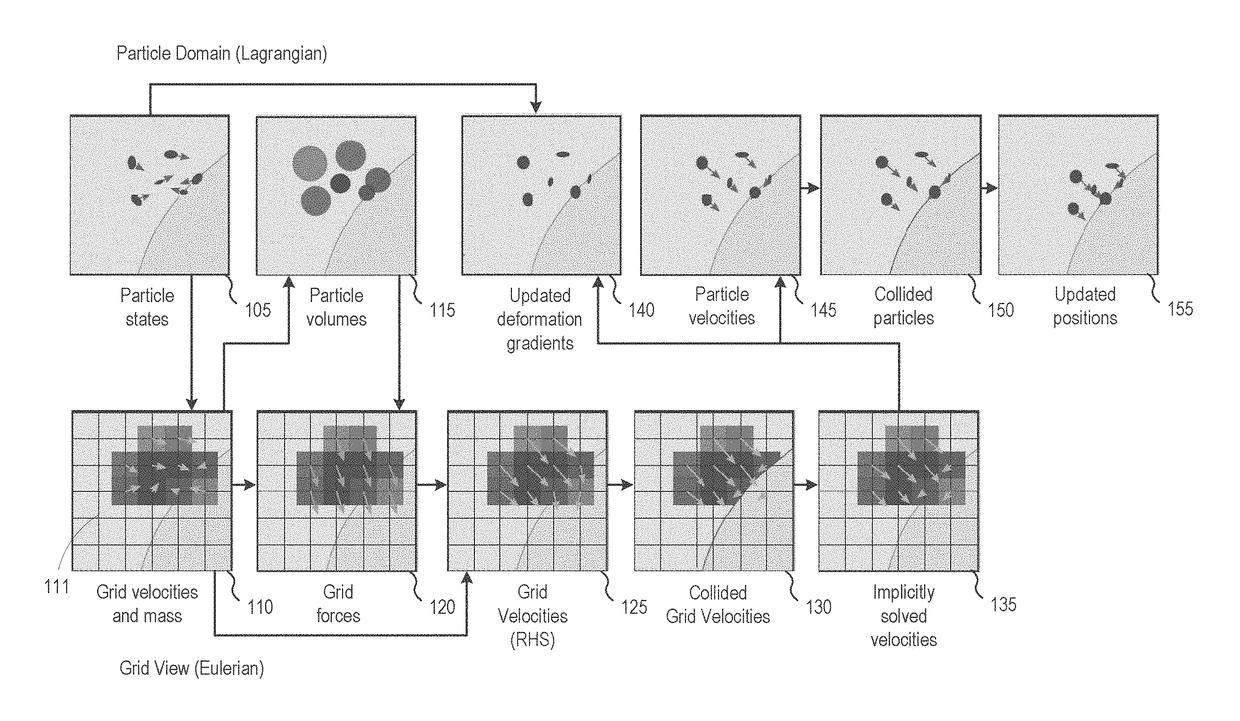
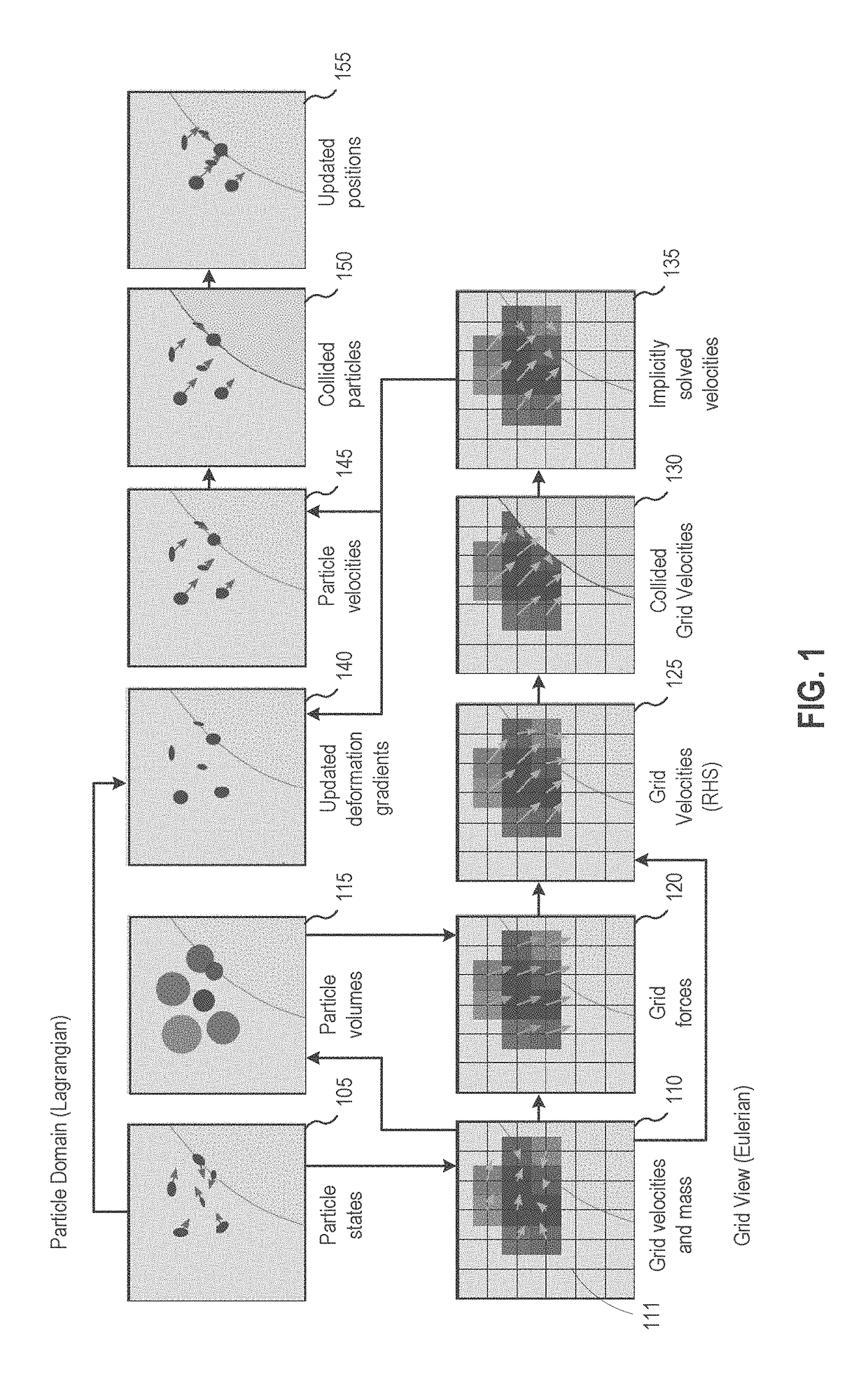
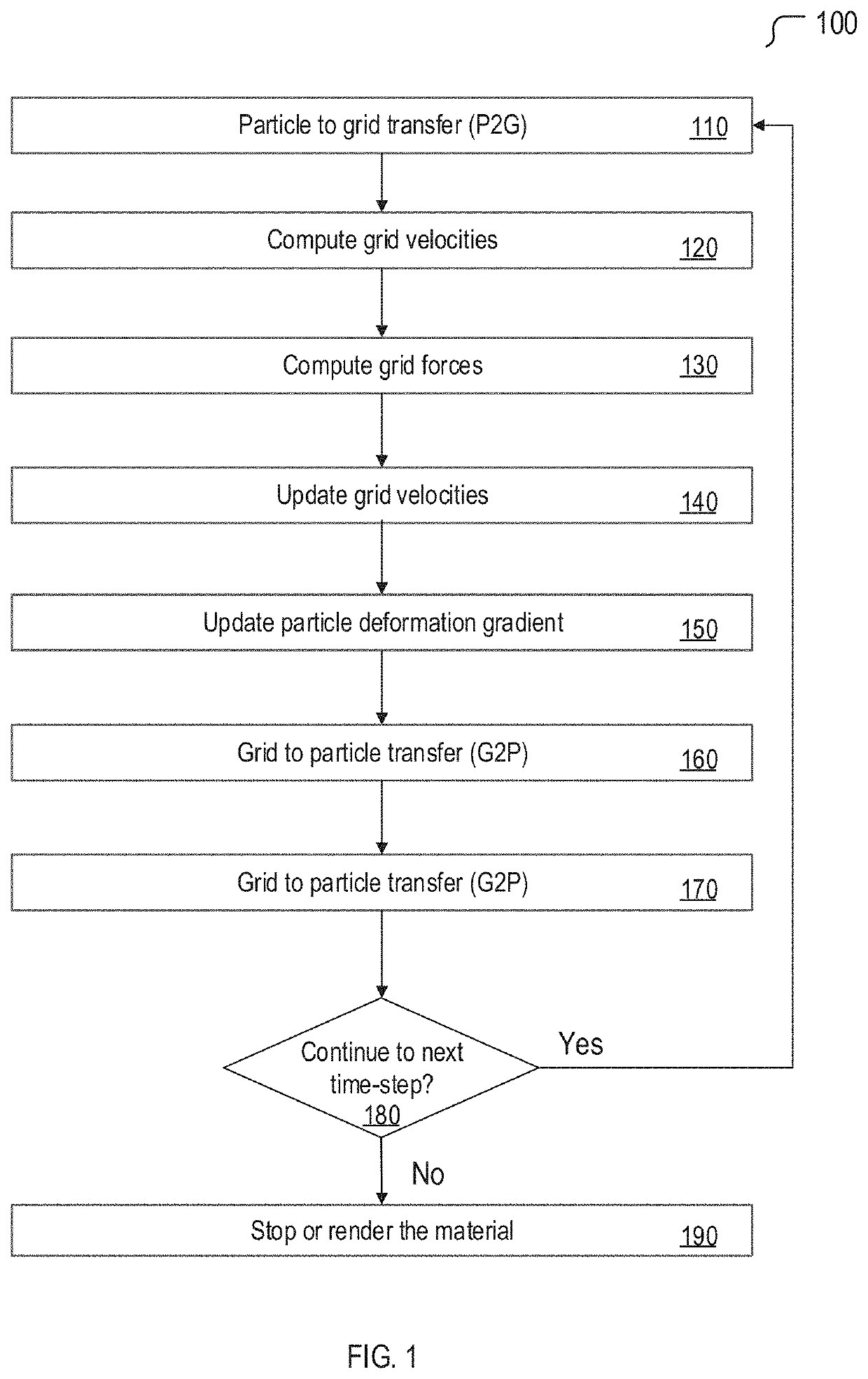
The material point method (MPM) is a numerical technique used to simulate the behavior of solids, liquids, gases, and any other continuum material. Especially, it is a robust spatial discretization method for simulating multi-phase (solid-fluid-gas) interactions. In the MPM, a continuum body is described by a number of small Lagrangian elements referred to as 'material points'. These material points are surrounded by a background mesh/grid that is used only to calculate gradient terms such as the deformation gradient. Unlike other mesh-based methods like the finite element method, finite volume method or finite difference method, the MPM is not a mesh based method and is instead categorized as a meshless/meshfree or continuum-based particle method, examples of which are smoothed particle hydrodynamics and peridynamics. Despite the presence of a background mesh, the MPM does not encounter the drawbacks of mesh-based methods (high deformation tangling, advection errors etc.) which makes it a promising and powerful tool in computational mechanics.
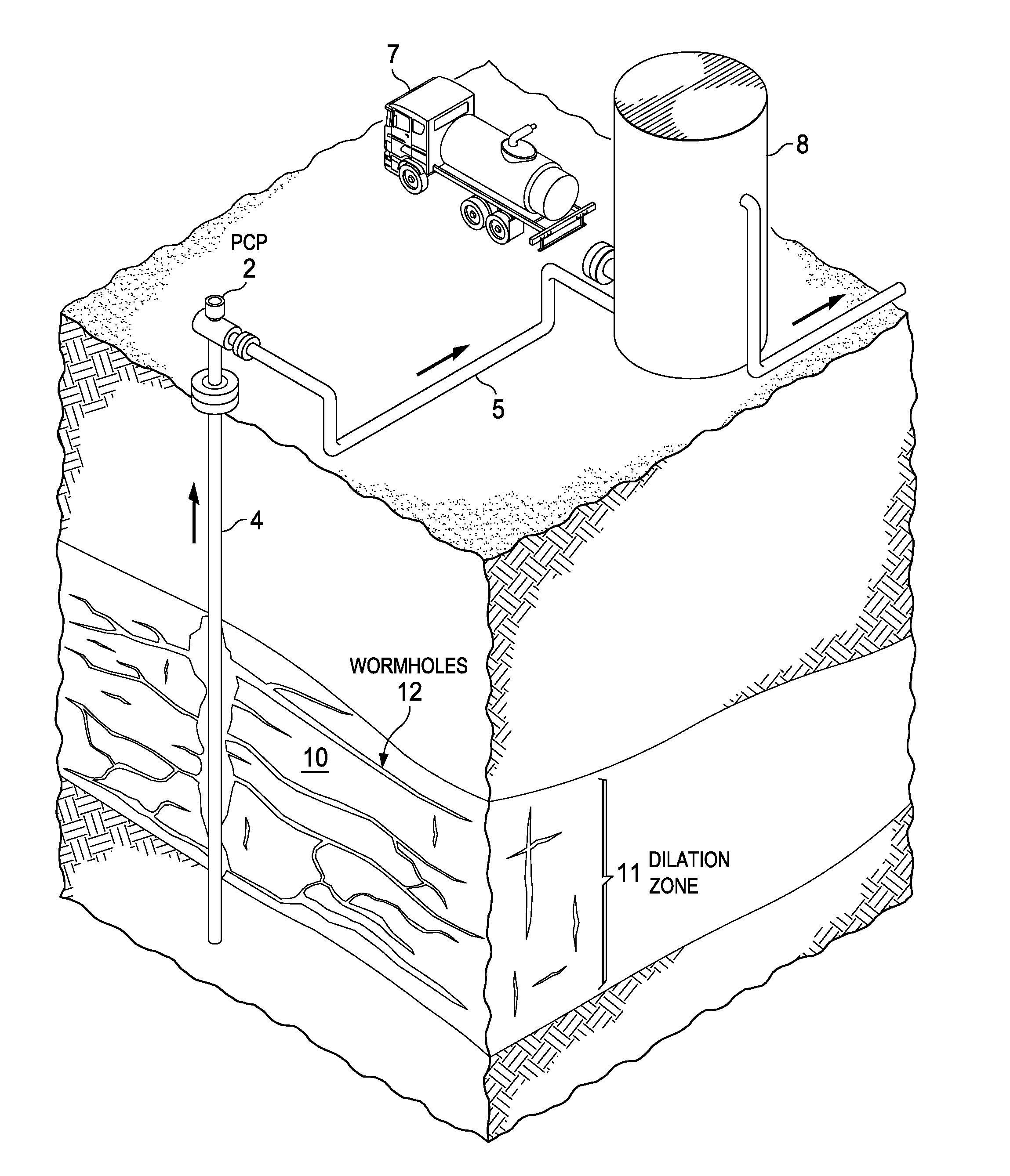
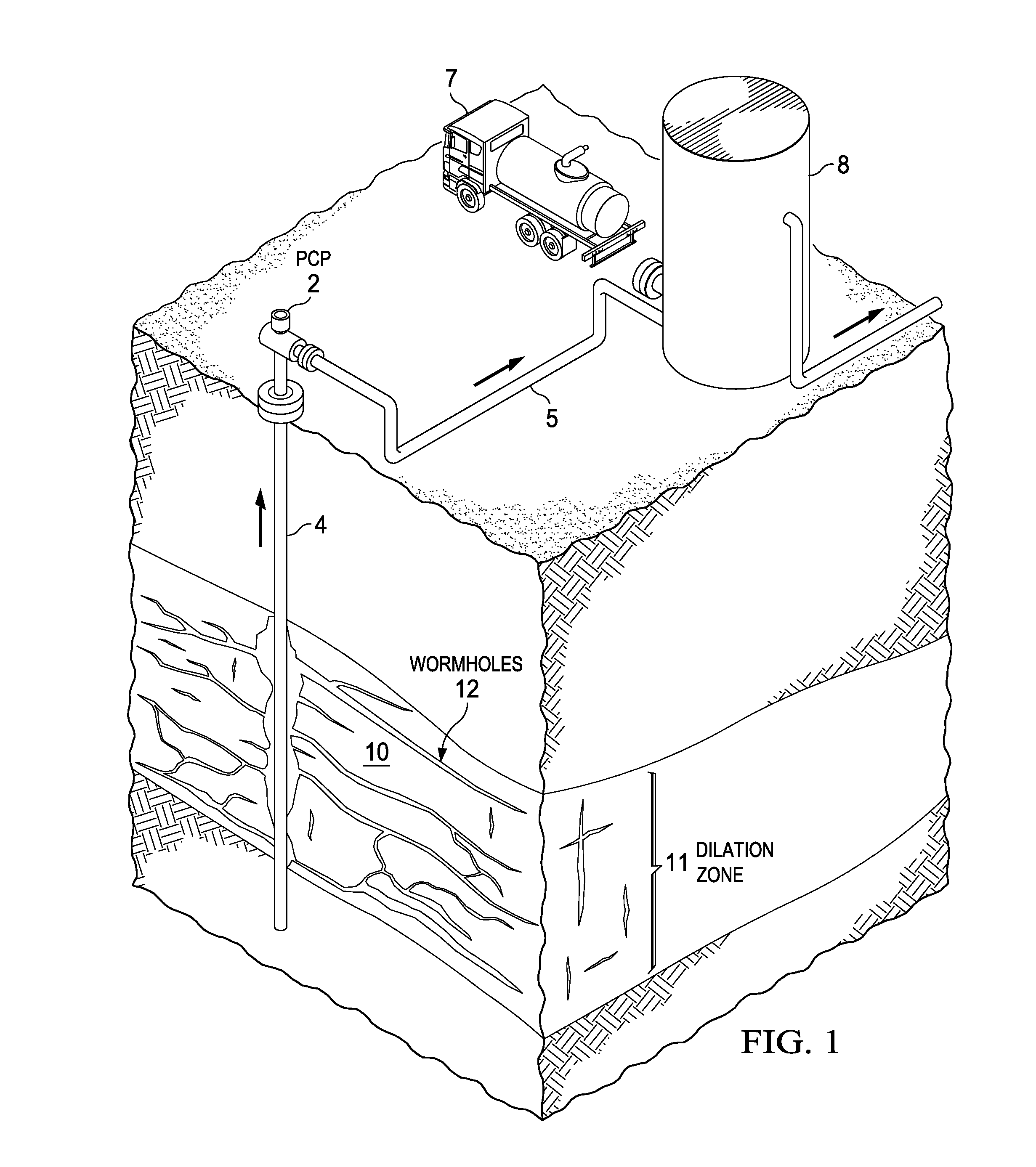
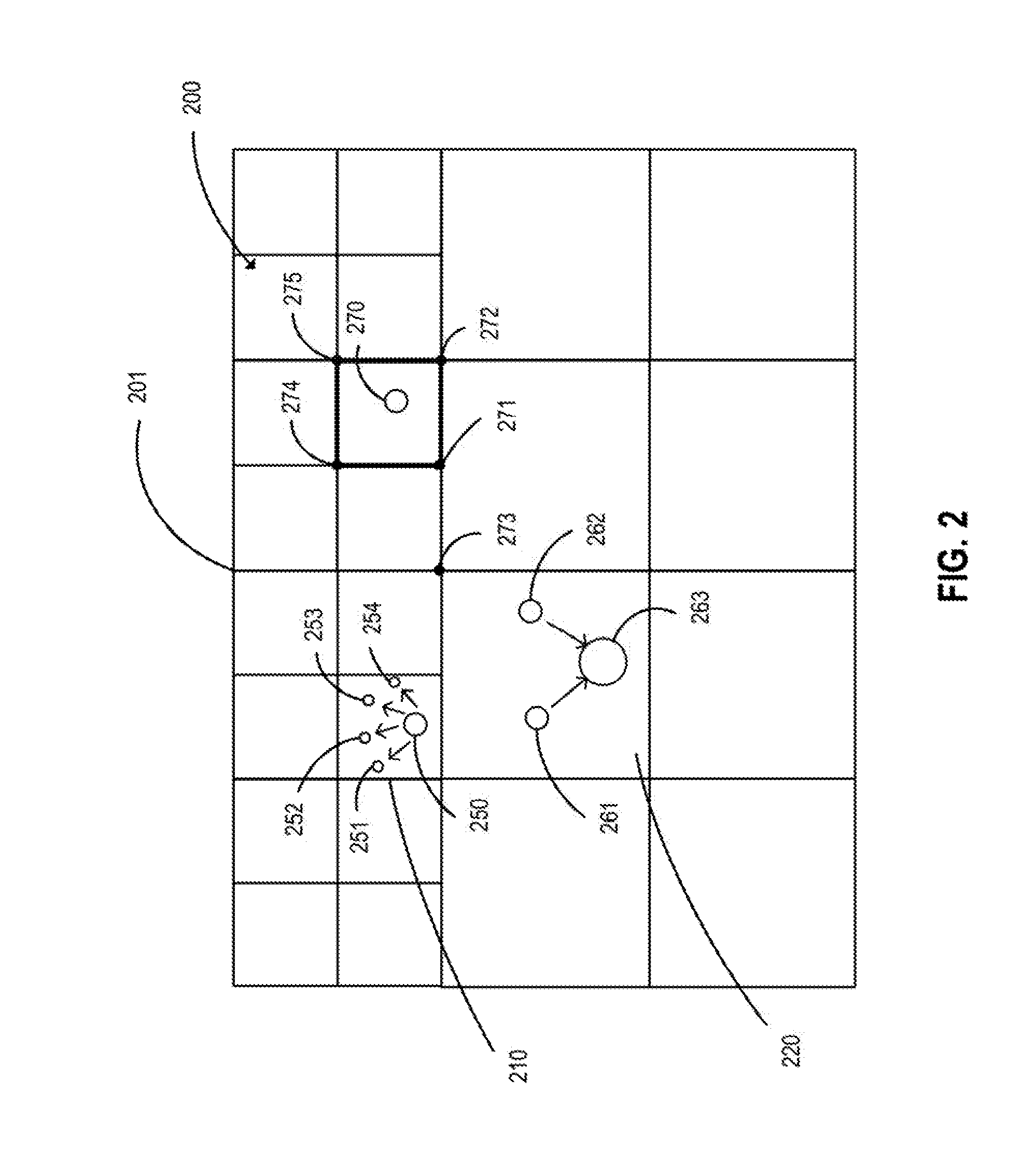
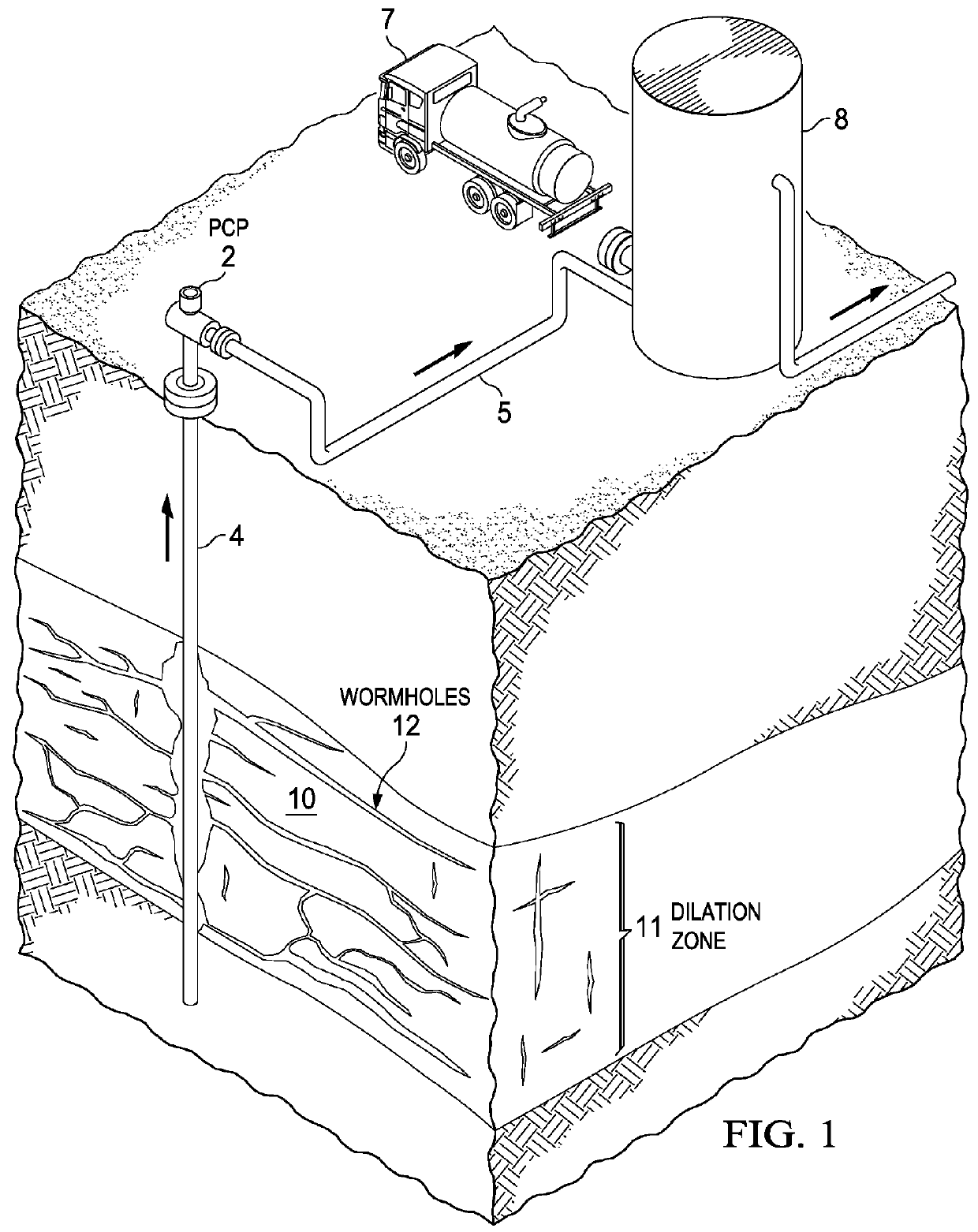
Material point method modeling in oil and gas reservoirs
InactiveUS20130096890A1Accurate modelingSimulation is accurateFluid removalSeismologyLaws of thermodynamicsEquation of state
A computer system and method of simulating the behavior of an oil and gas reservoir including changes in the margins of frangible solids. A system of equations including state equations such as momentum, and conservation laws such as mass conservation and volume fraction continuity, are defined and discretized for at least two phases in a modeled volume, one of which corresponds to frangible material. A material point model technique for numerically solving the system of discretized equations, to derive fluid flow at each of a plurality of mesh nodes in the modeled volume, and the velocity of at each of a plurality of particles representing the frangible material in the modeled volume. A time-splitting technique improves the computational efficiency of the simulation while maintaining accuracy on the deformation scale. The method can be applied to derive accurate upscaled model equations for larger volume scale simulations.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
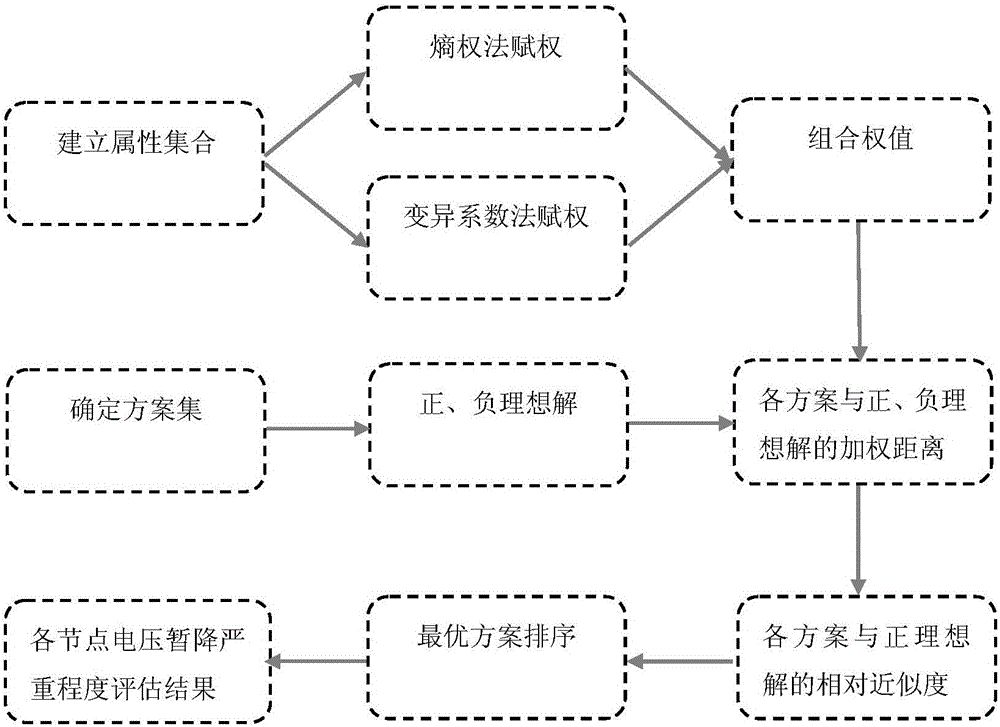
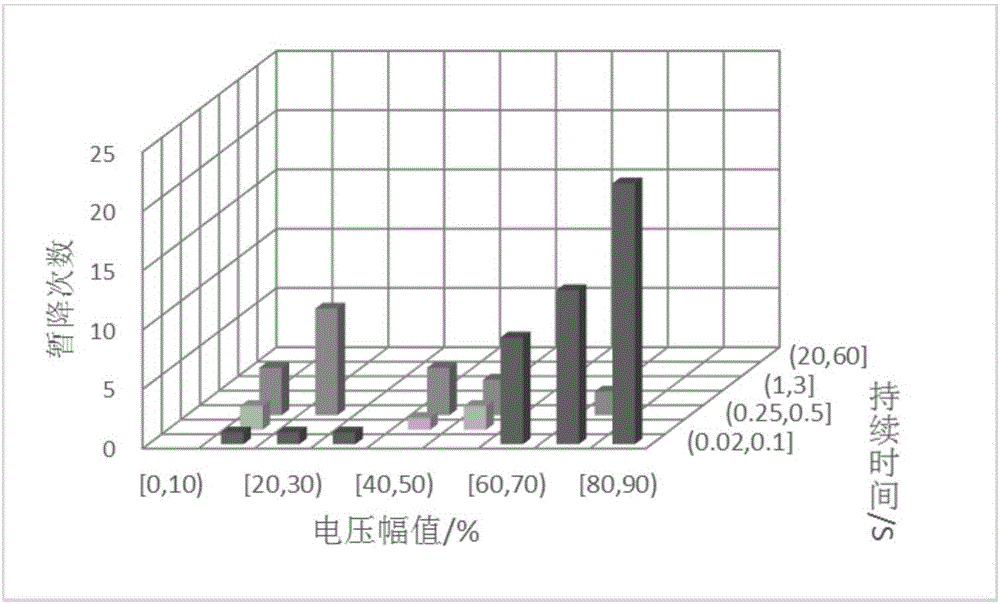
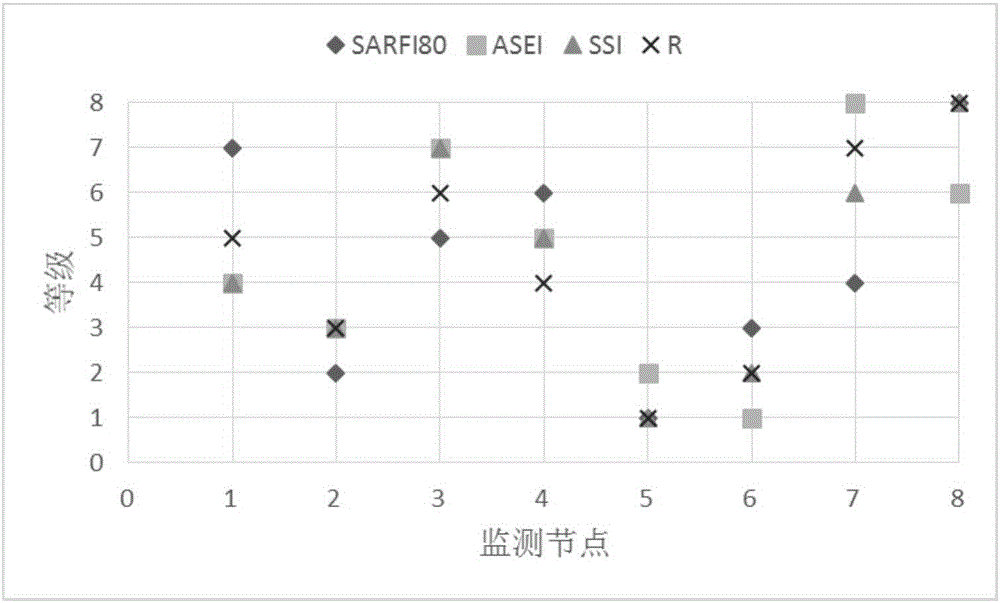
Node voltage sag severity comprehensive assessment method based on weighted ideal point method
The invention belongs to the technical field of power quality analysis and especially relates to a node voltage sag severity comprehensive assessment method based on a weighted ideal point method. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: to begin with, establishing an attribute set and a scheme set; then, determining combination weight of each index in the attribute set based on an entropy weight method and a variation coefficient method; and finally, carrying out voltage sag severity comprehensive assessment based on the weighted ideal point method. Weighted distance between each scheme and positive and negative ideal solutions in the ideal point method and relative closeness between the scheme and the positive ideal solution are calculated respectively, and the schemes are ranked in a descending order in sequence to obtain an optimal scheme order. The method reflects voltage sag severity from the perspectives of frequency, duration and amplitude angle, and reflects influencing characteristics of sag frequency on the voltage sag severity from perspectives of the part and the whole, so that erroneous judgment due to single-index assessment is effectively prevented, voltage sag information of each node can be reflected more comprehensively and accurately, and the obtained result is objective, accurate and more realistic.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
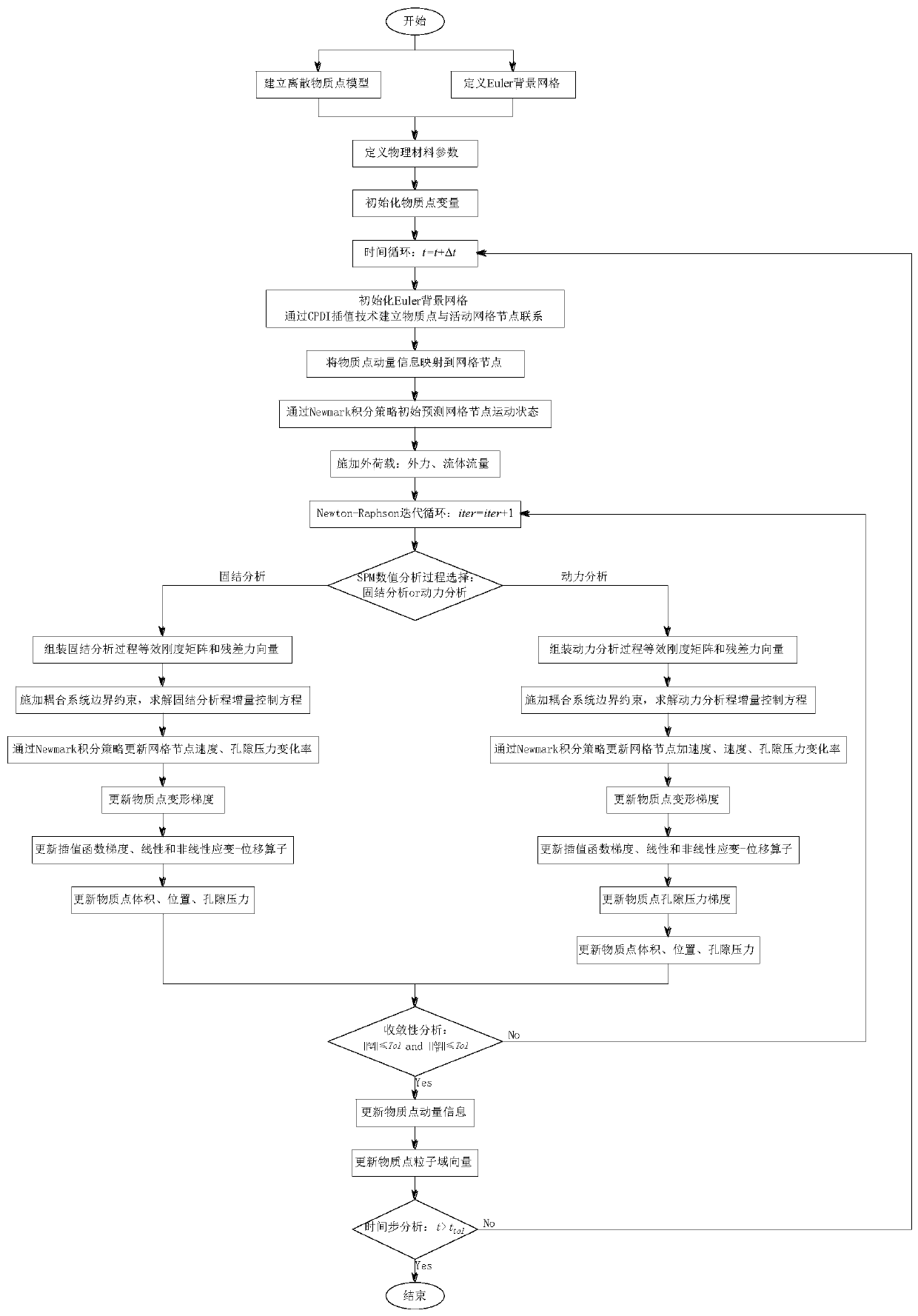
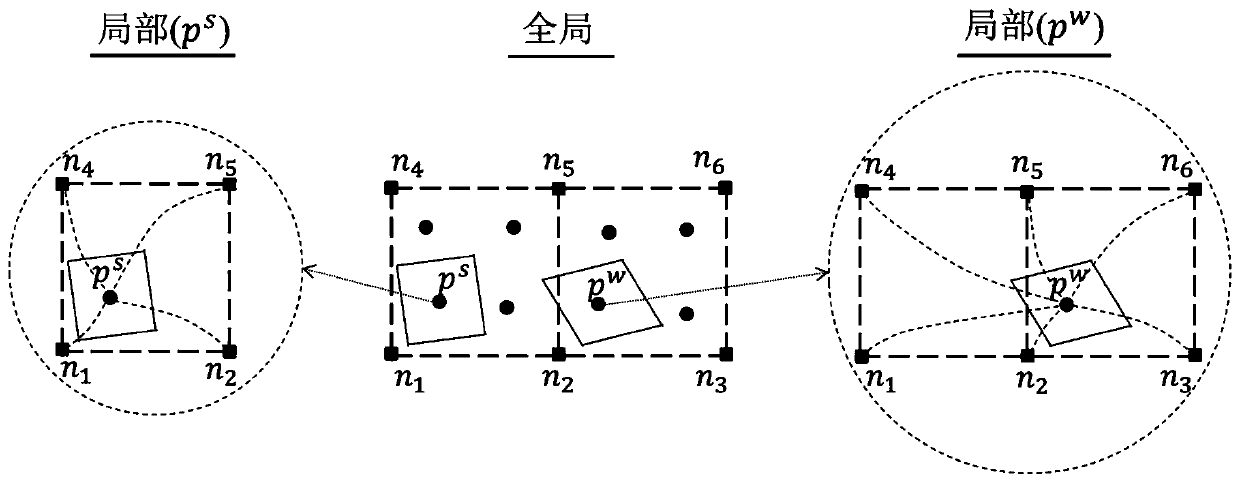
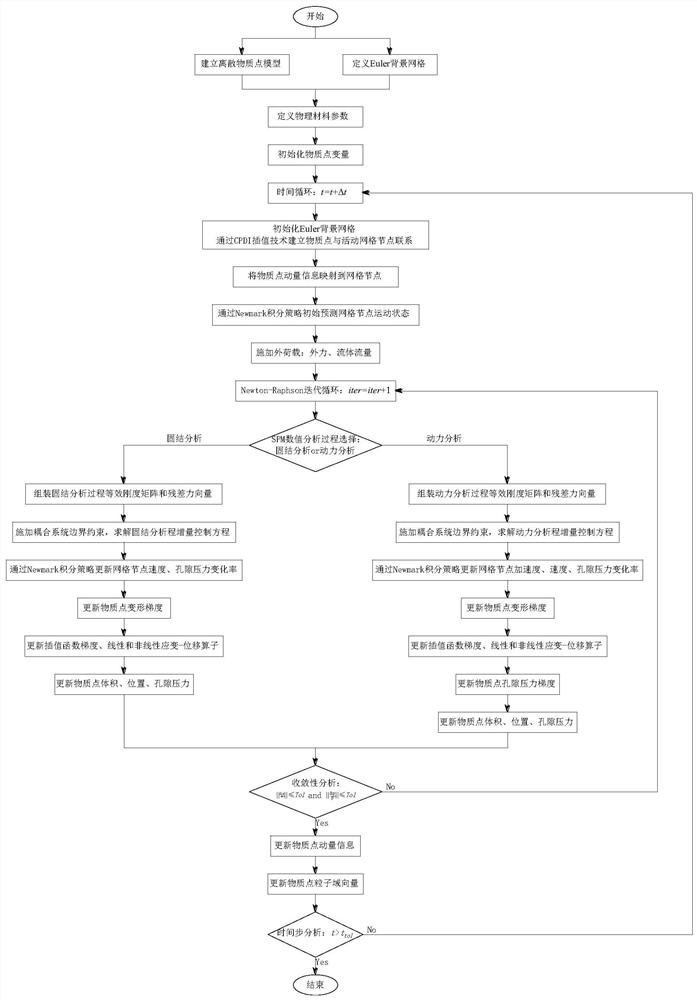
CCPDI-IMPM method for large deformation analysis of saturated porous medium
ActiveCN110298105AOvercome stabilityOvercome precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCritical timeSaturated porous medium
The invention provides a CCPDI-IMPM method for large deformation analysis pf a saturated porous medium based on a u-p control equation of a generalized Biot theory and a convective particle domain interpolation technology, and the method comprises saturated porous medium large deformation consolidation process analysis and saturated porous medium large deformation dynamic process analysis. According to the method, an implicit time integral strategy is adopted to overcome the defect that a traditional explicit material point method is limited by a critical time step length, and particularly, the calculation efficiency is remarkably improved when a quasi-static problem is solved; and the grid boundary smooth interpolation advantage of the CPDI and the Euler-Lagrangian description advantage of the implicit substance point method are combined, so that compared with the traditional FEM, the calculation performance is more stable when large deformation and extremely large deformation are processed. The invention further provides a method for expanding the substance penalty factor, and the method is used for processing the boundary condition of the fluid-solid coupling system more simplyand accurately.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
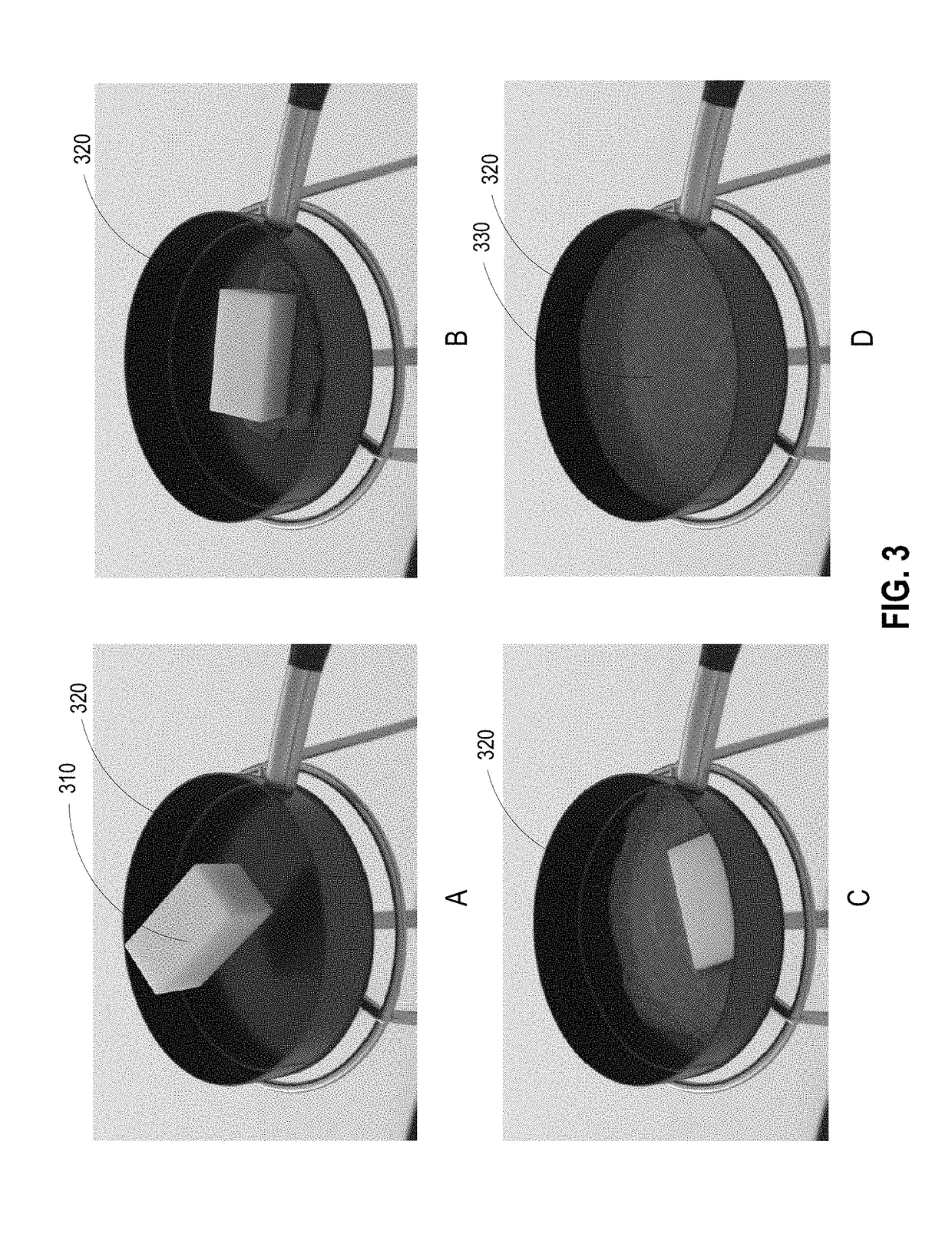
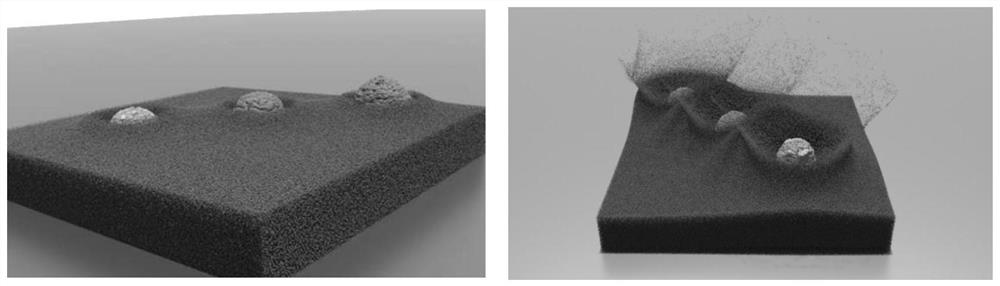
Material point method for simulation of granular materials
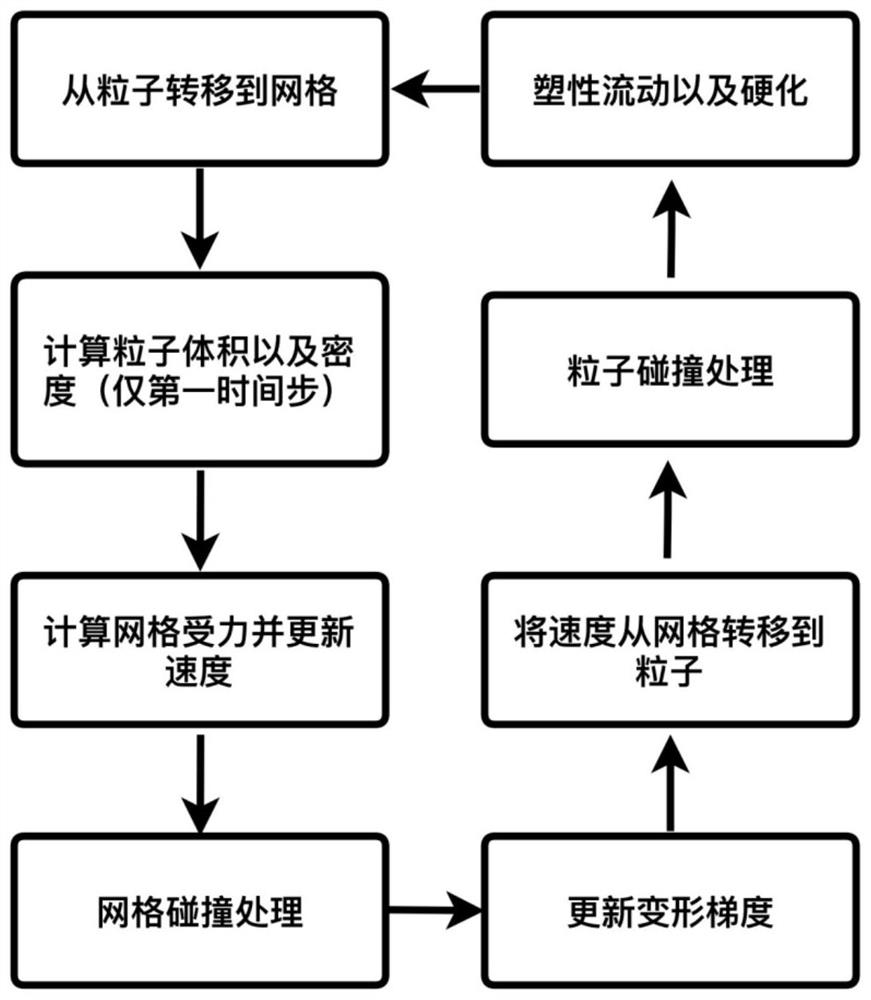
The disclosure provides an approach for simulating and rendering granular materials. A simulation application generates video frames depicting a granular material phenomenon using a strain based elasto-plastic constitutive model integrated with a hybrid Eulerian / Lagrangian material point method (MPM). The elasto-plastic constitutive model includes physical equation(s) which dictate forces that affect the granular material during the simulation. In particular, the constitutive model may include user-controllable parameters defining threshold(s) to start plastic deformation, as well as a hardening parameter which controls how fast the granular material packs under compression. The MPM is a procedure in which particles of the granular material and a background grid are coupled, with the grid being used to assist in computing forces dictated by the physical equation(s) of the elasto-plastic constitutive model. In one configuration, the grid may further be rendered with volumetric rendering to generate video frames depicting the granular material.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
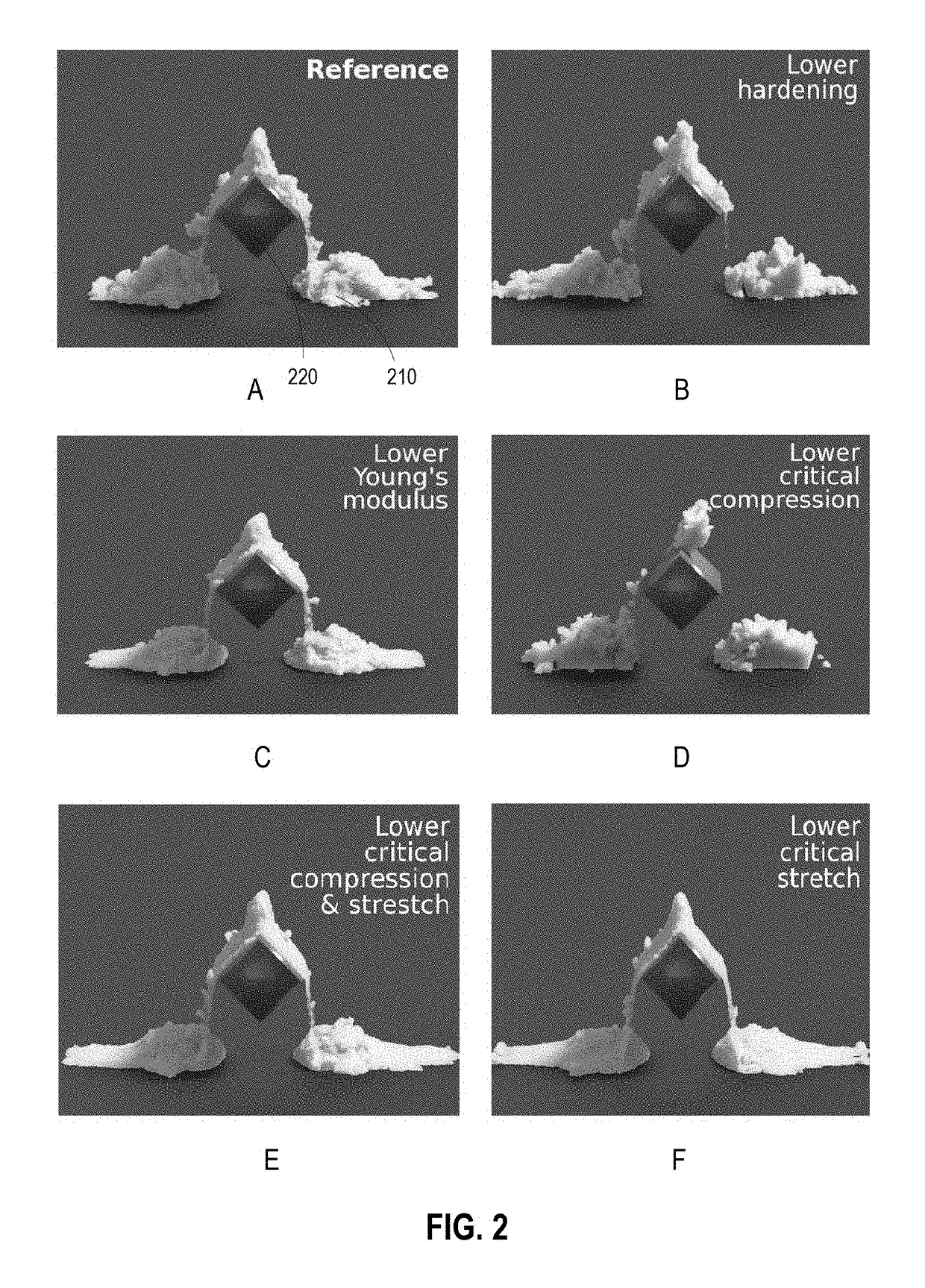
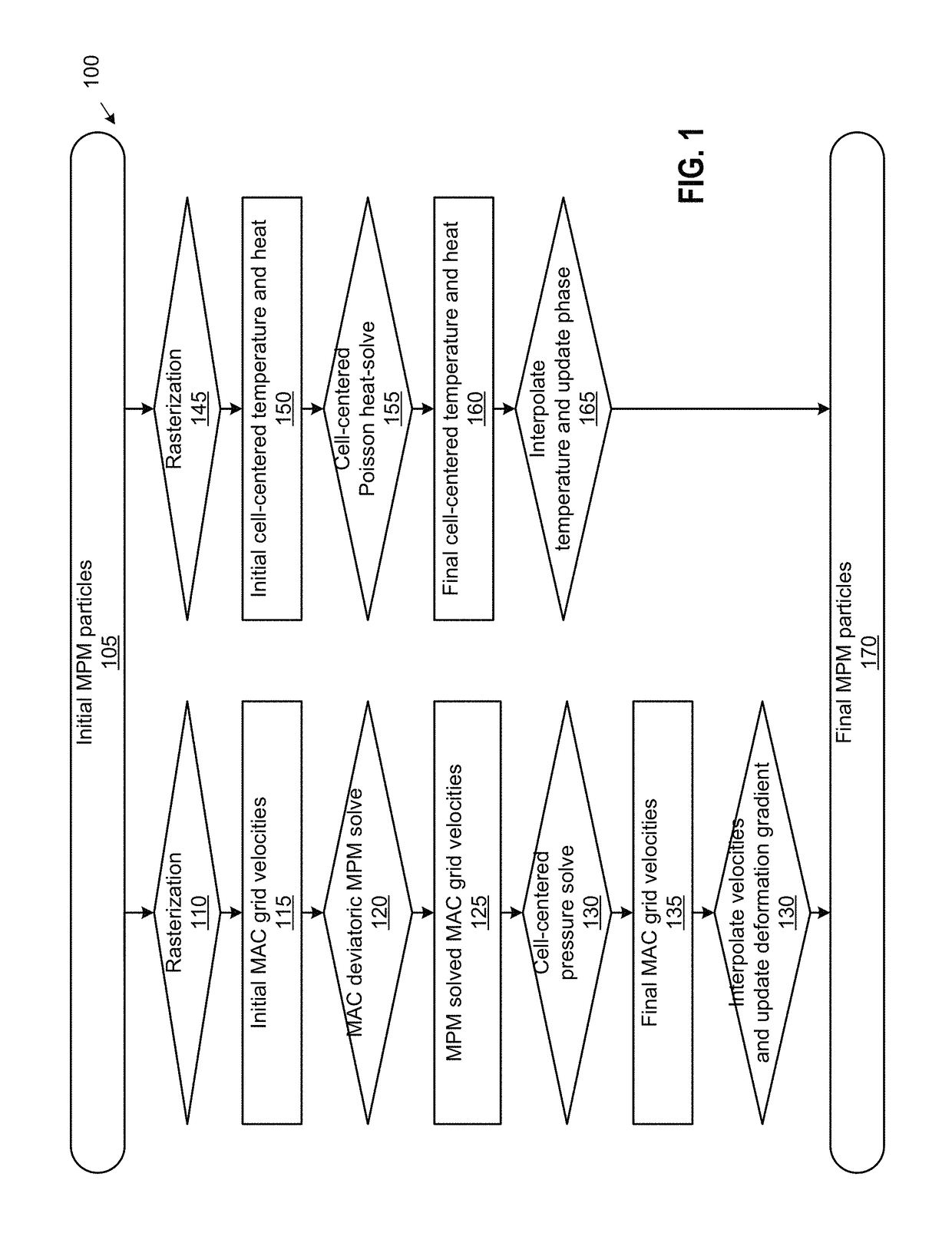
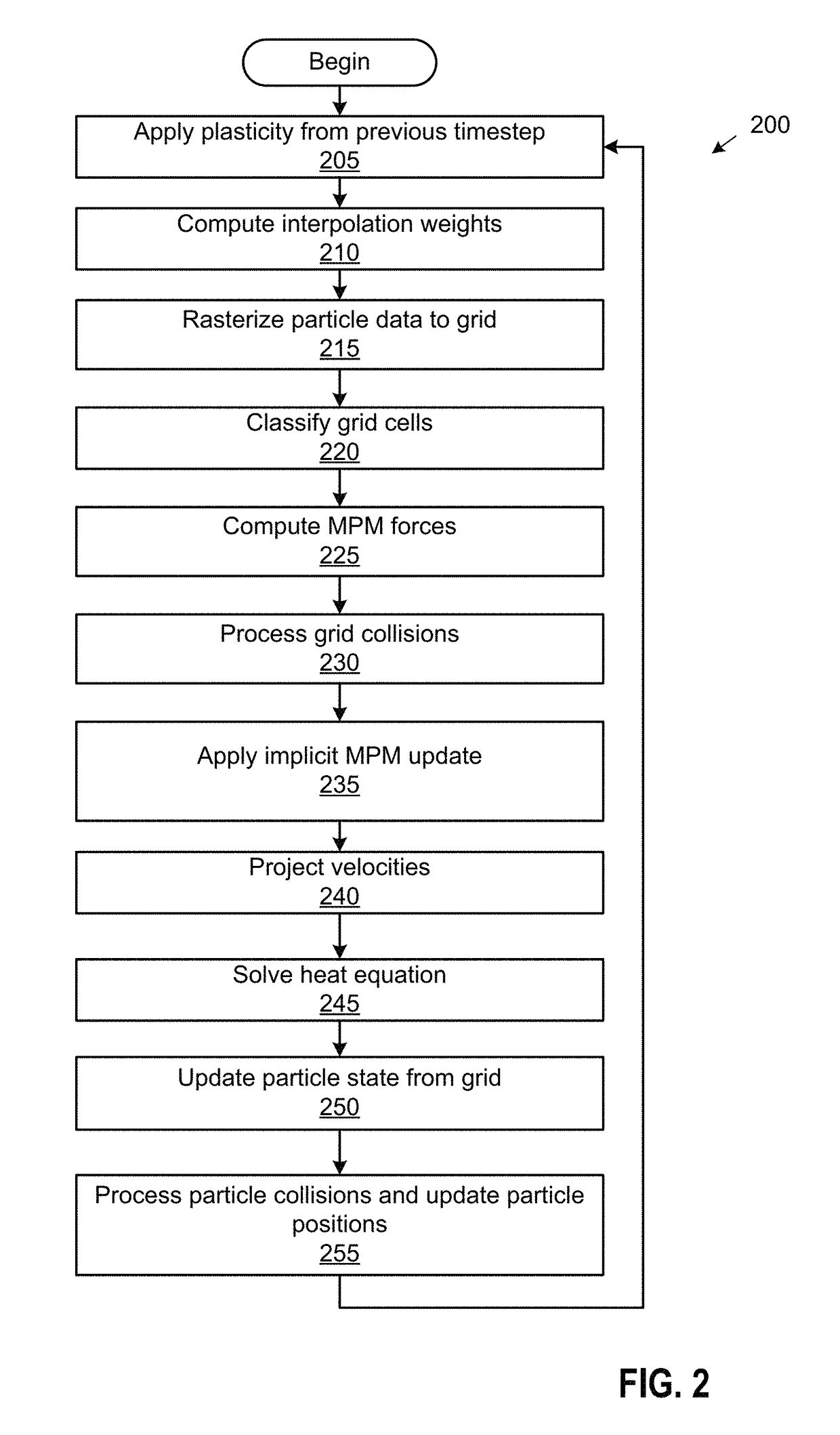
Augmented material point method for simulating phase changes and varied materials
ActiveUS20150186565A1Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsInterior point methodGrid based
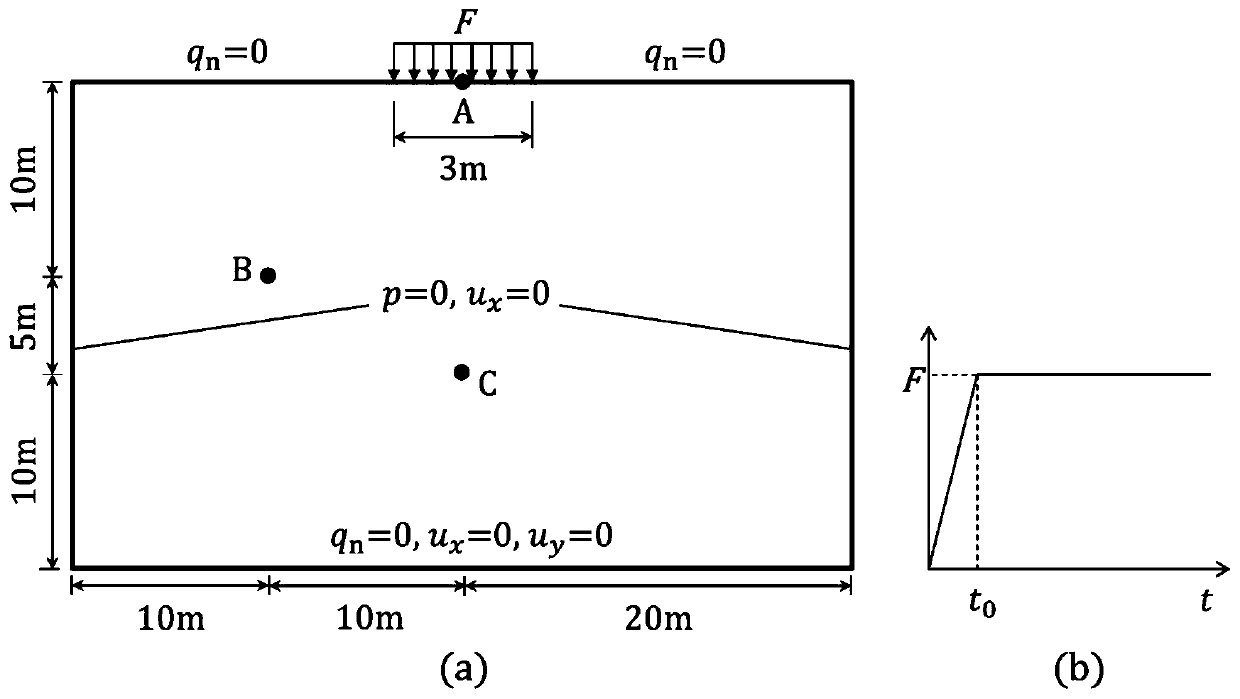
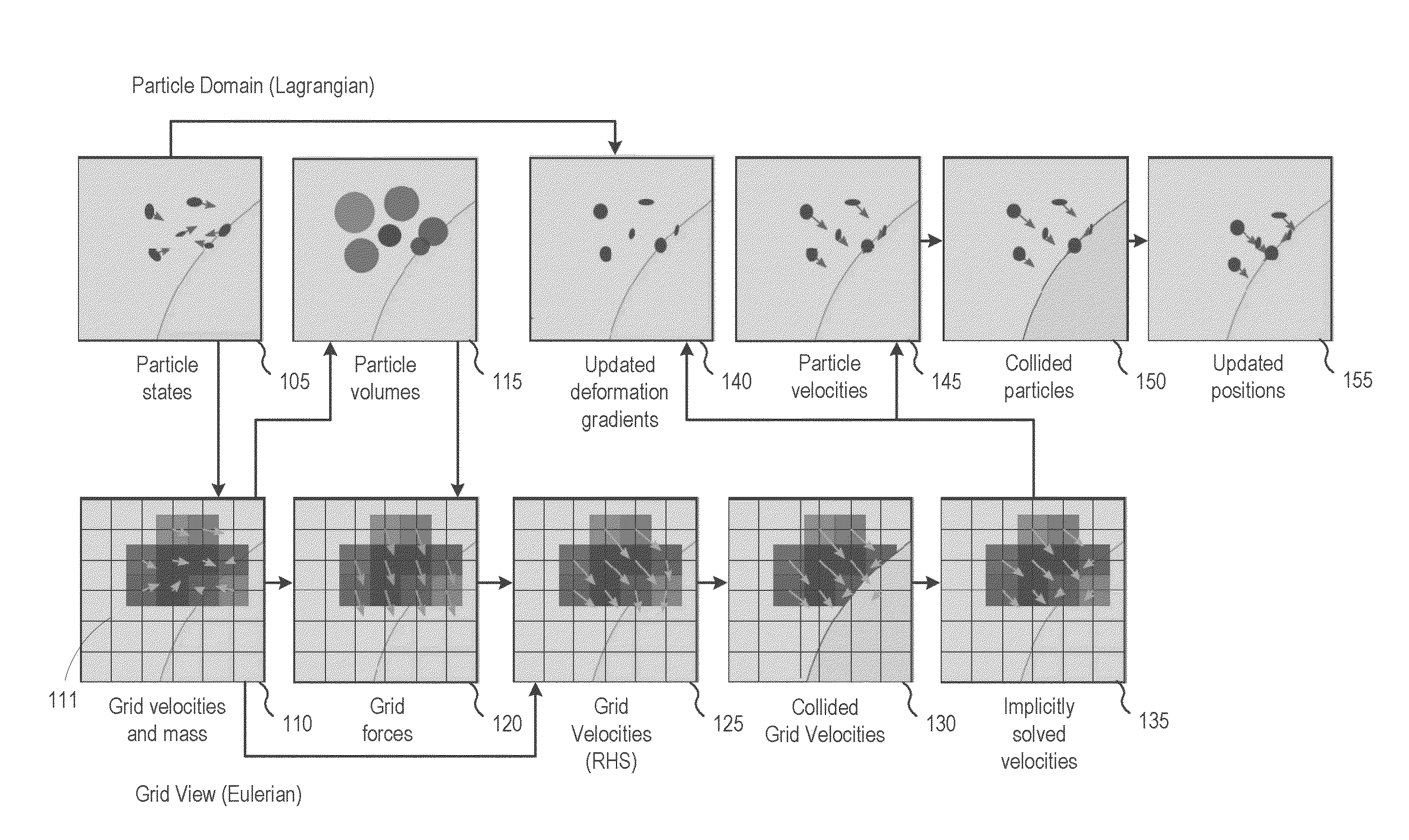
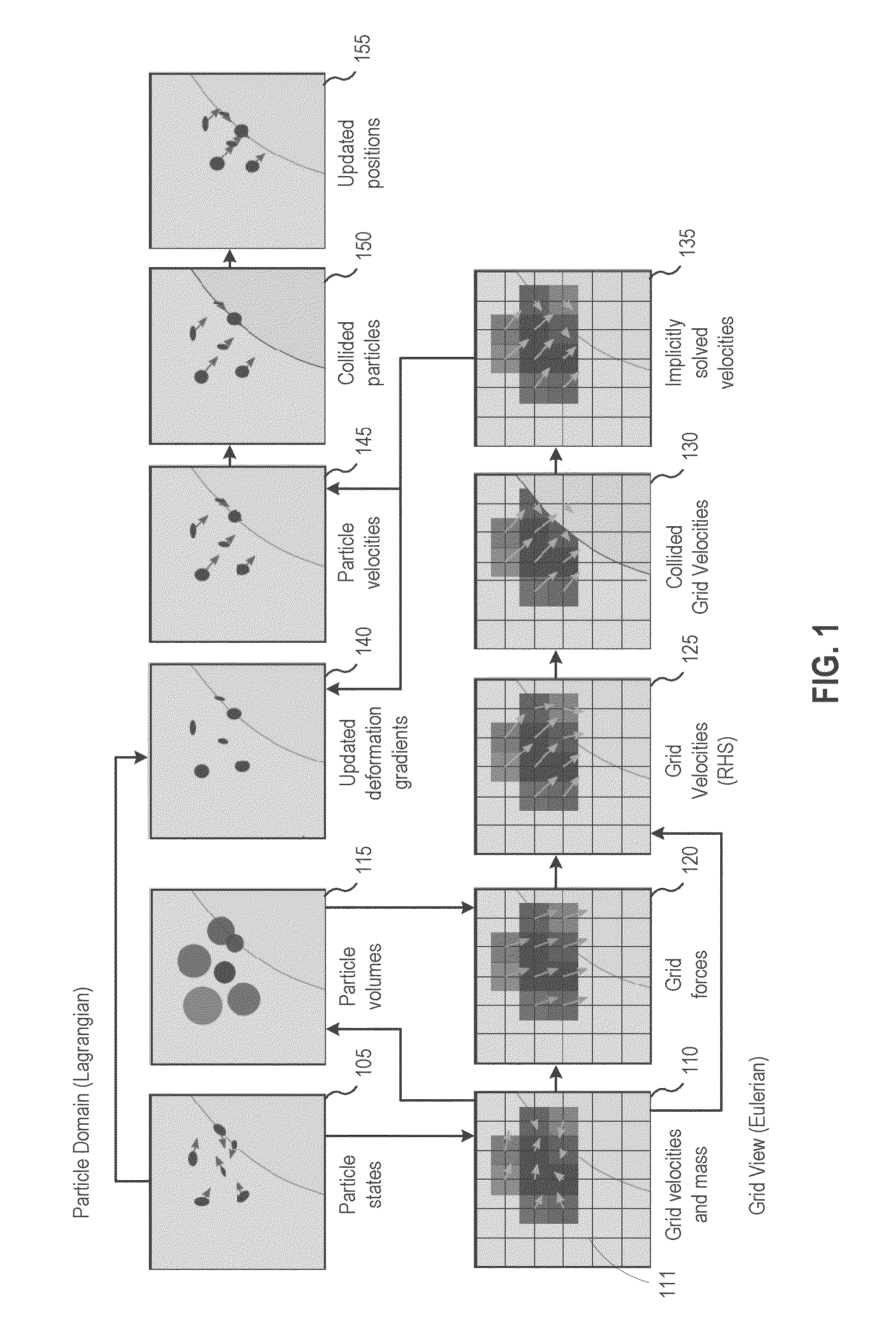
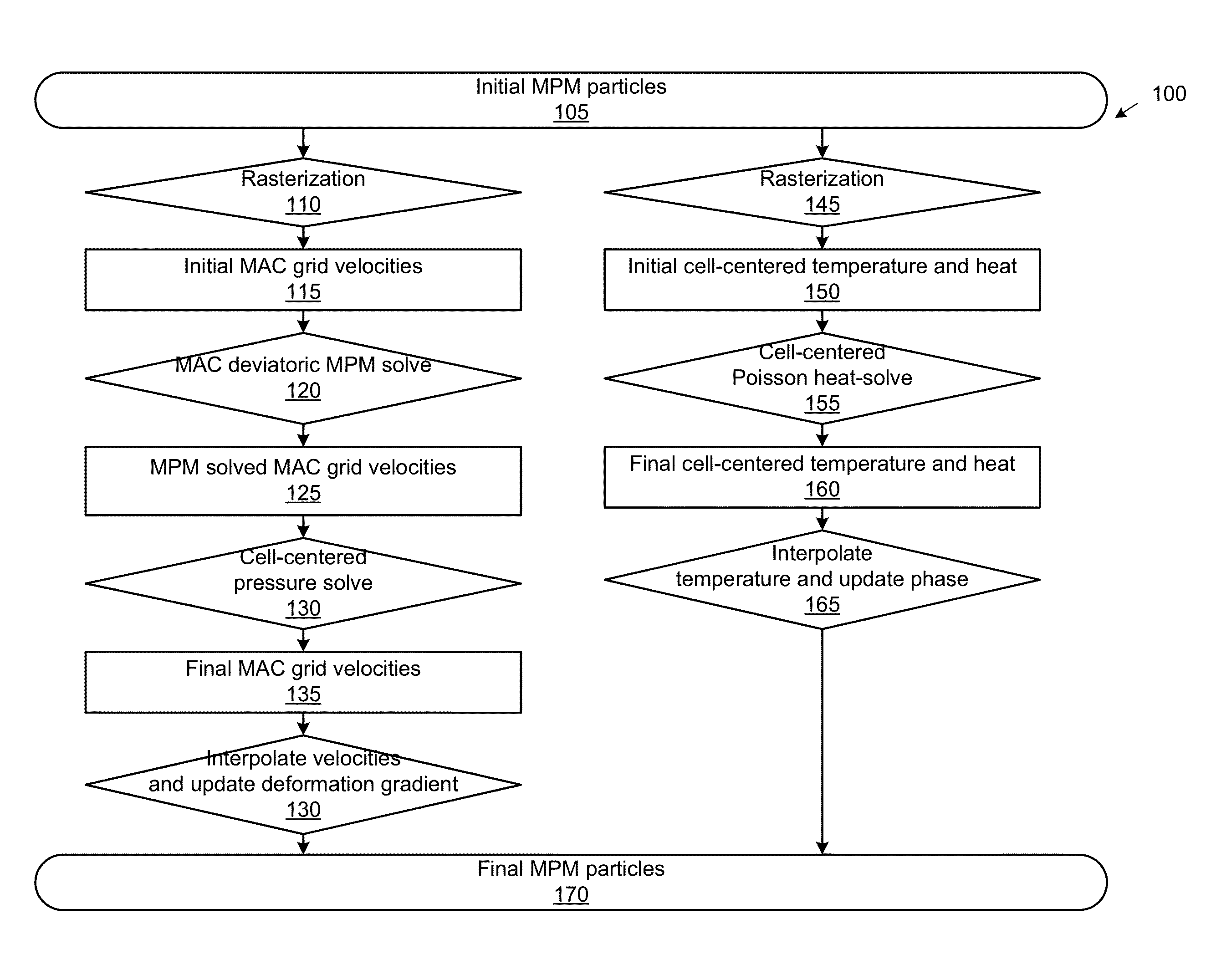
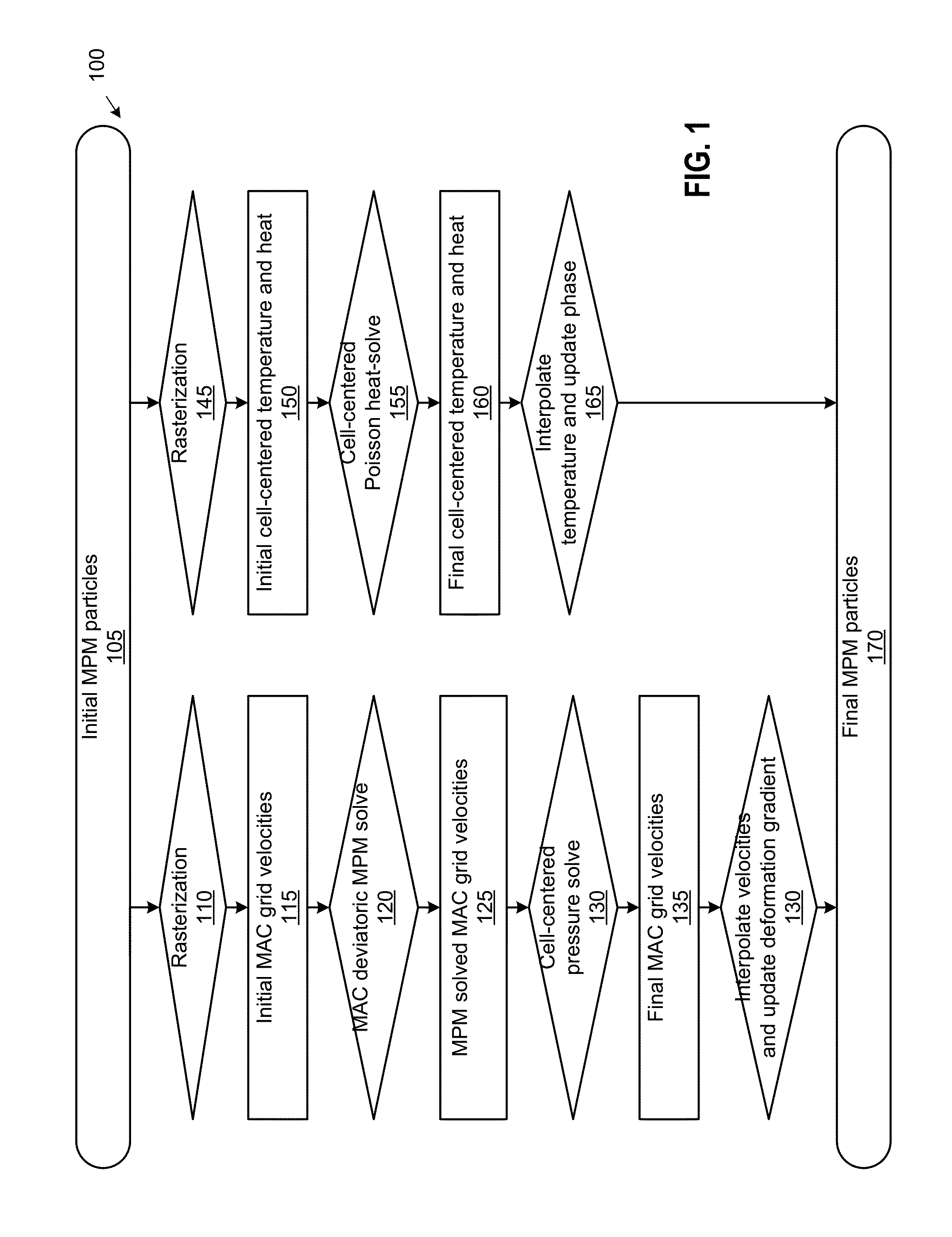
The disclosure provides an approach for simulating and rendering materials across different states and undergoing phase transitions. In one configuration, a simulation application generates video frames depicting a material phenomenon using an augmented material point method (MPM). Traditional MPM does not handle incompressible materials such as fluids. Techniques disclosed herein augment the MPM with a Chorin-style projection technique to enable simulation of arbitrarily incompressible materials. In one configuration, this is achieved with a marker-and-cell (MAC) grid based MPM solver, a splitting of stress used in the simulation into elastic and dilational parts, a projection-like implicit treatment of the Eulerian evolution of the dilational part of the stress, and particular techniques for rasterizing and updating quantities on the MAC grid. In addition, a heat model may be coupled to the MPM solver, allowing material changes to be driven with temperature and phase changes.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Adaptive material point method
ActiveUS20160210384A1Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsGratingImage resolution
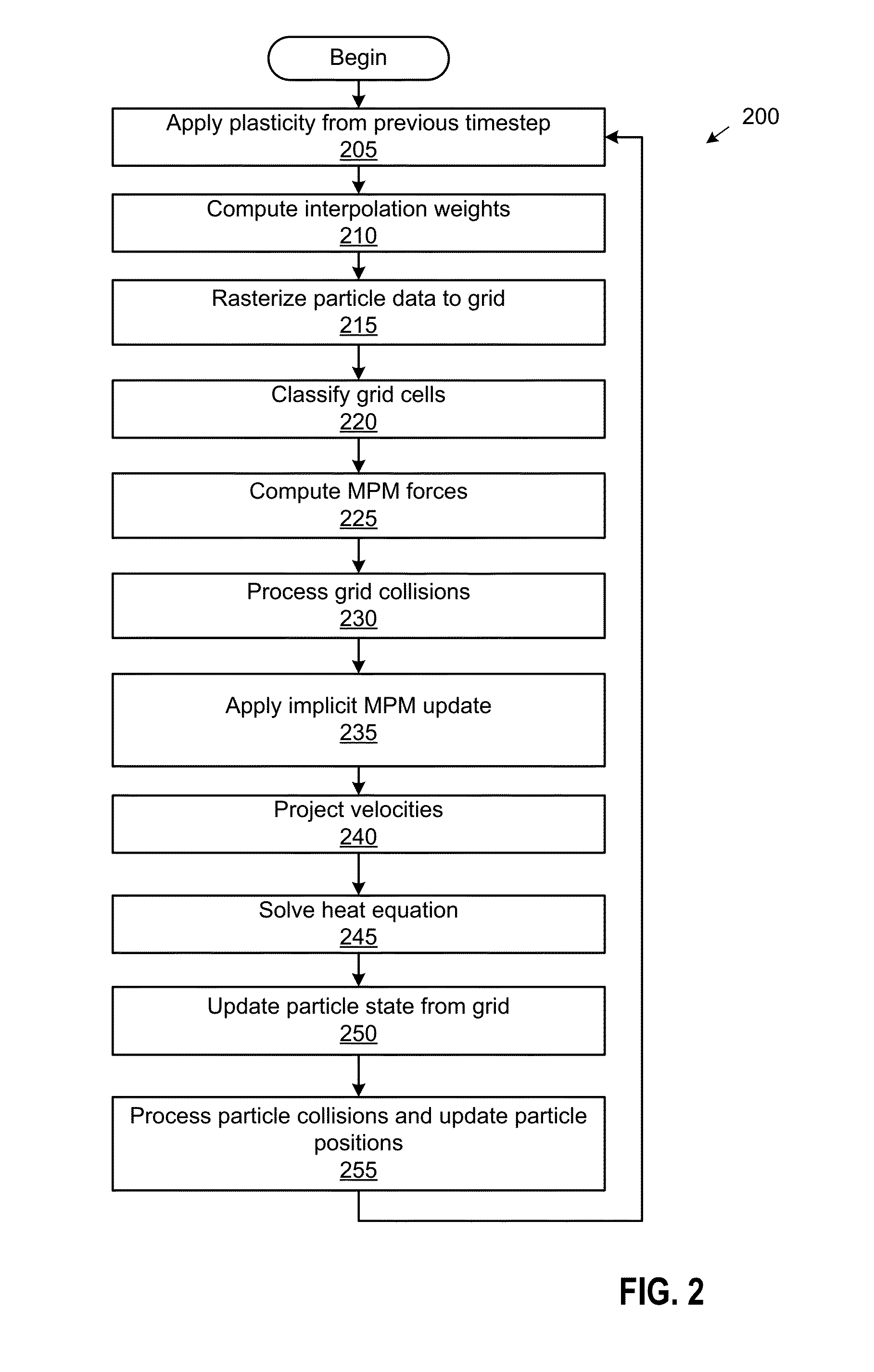
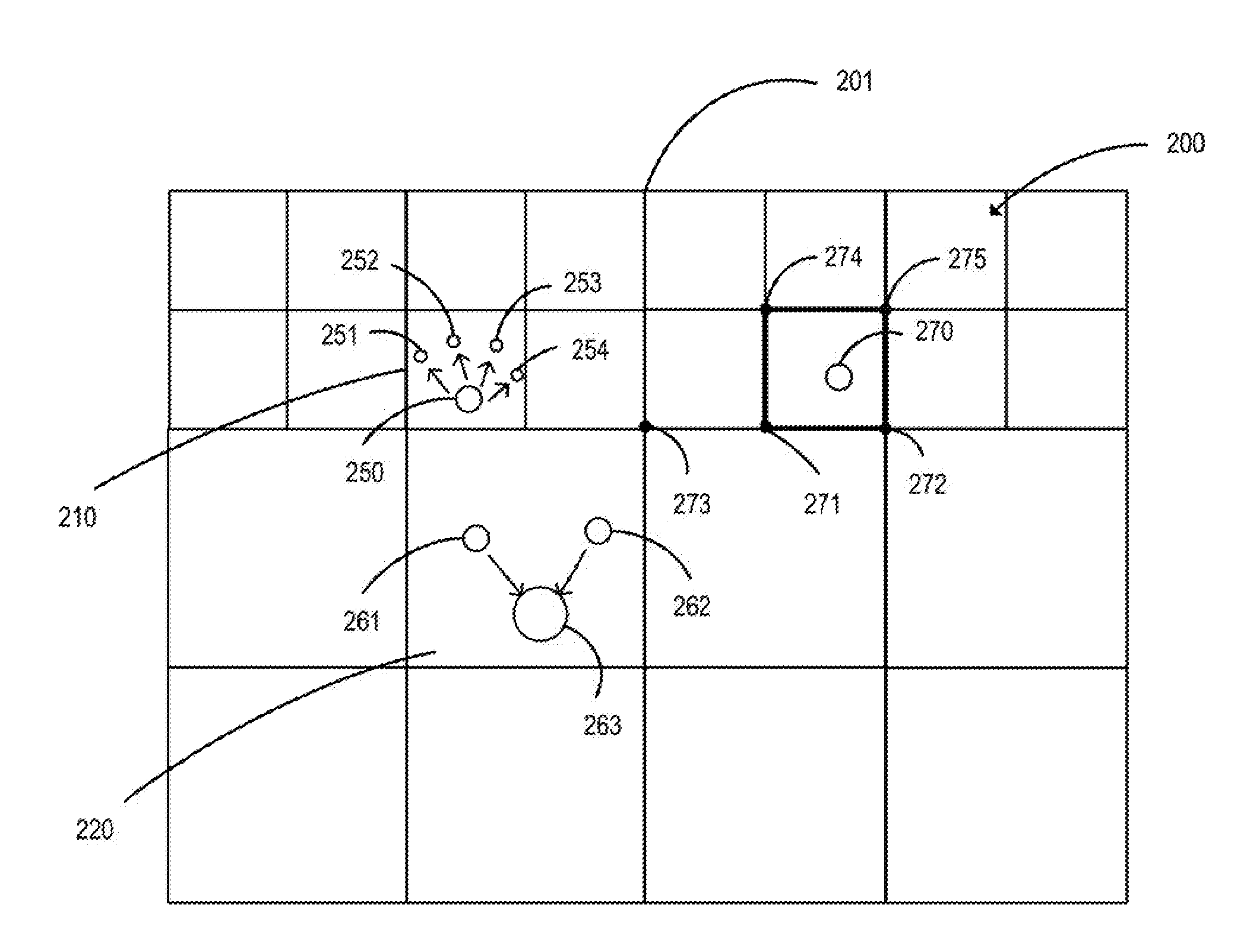
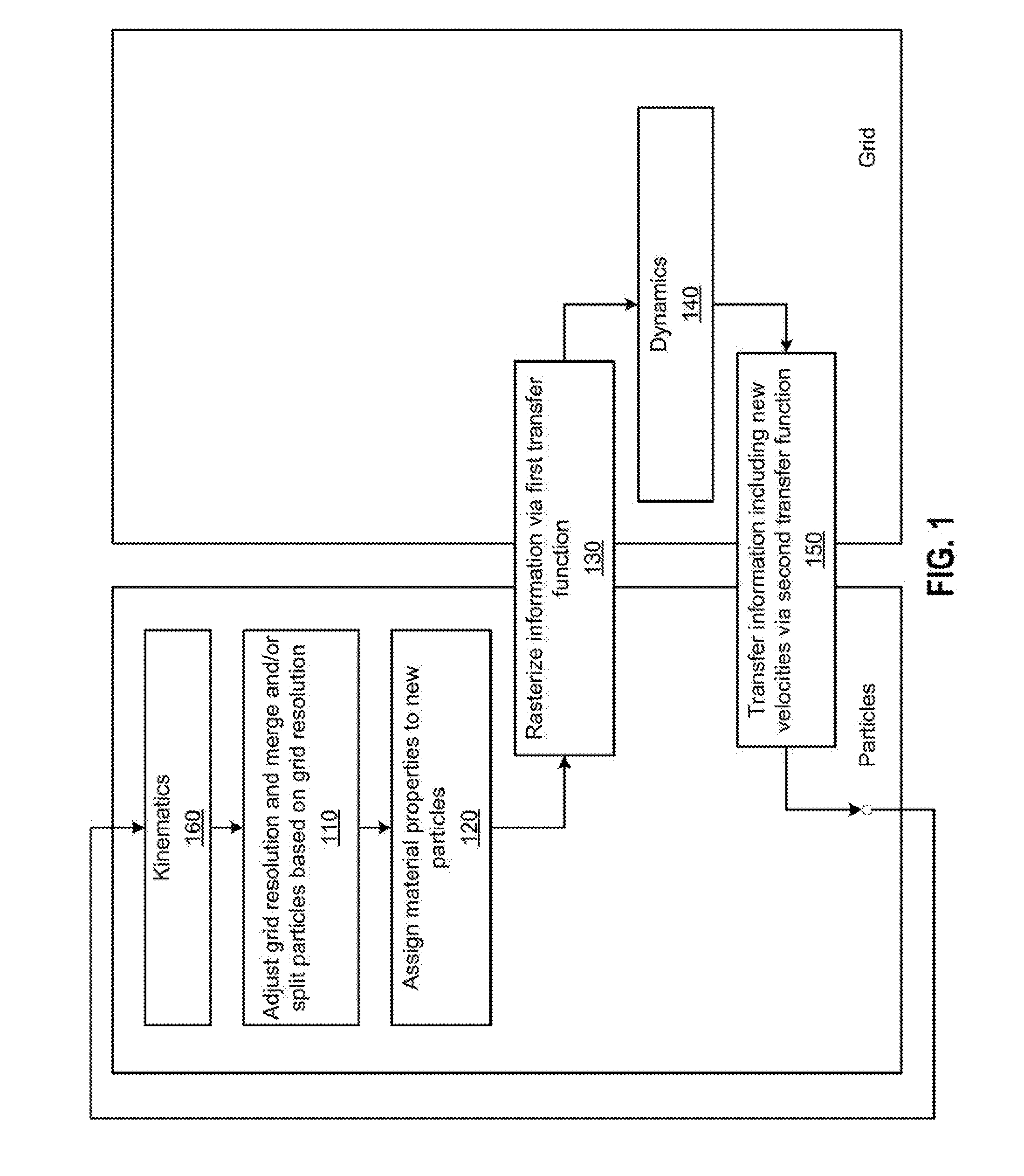
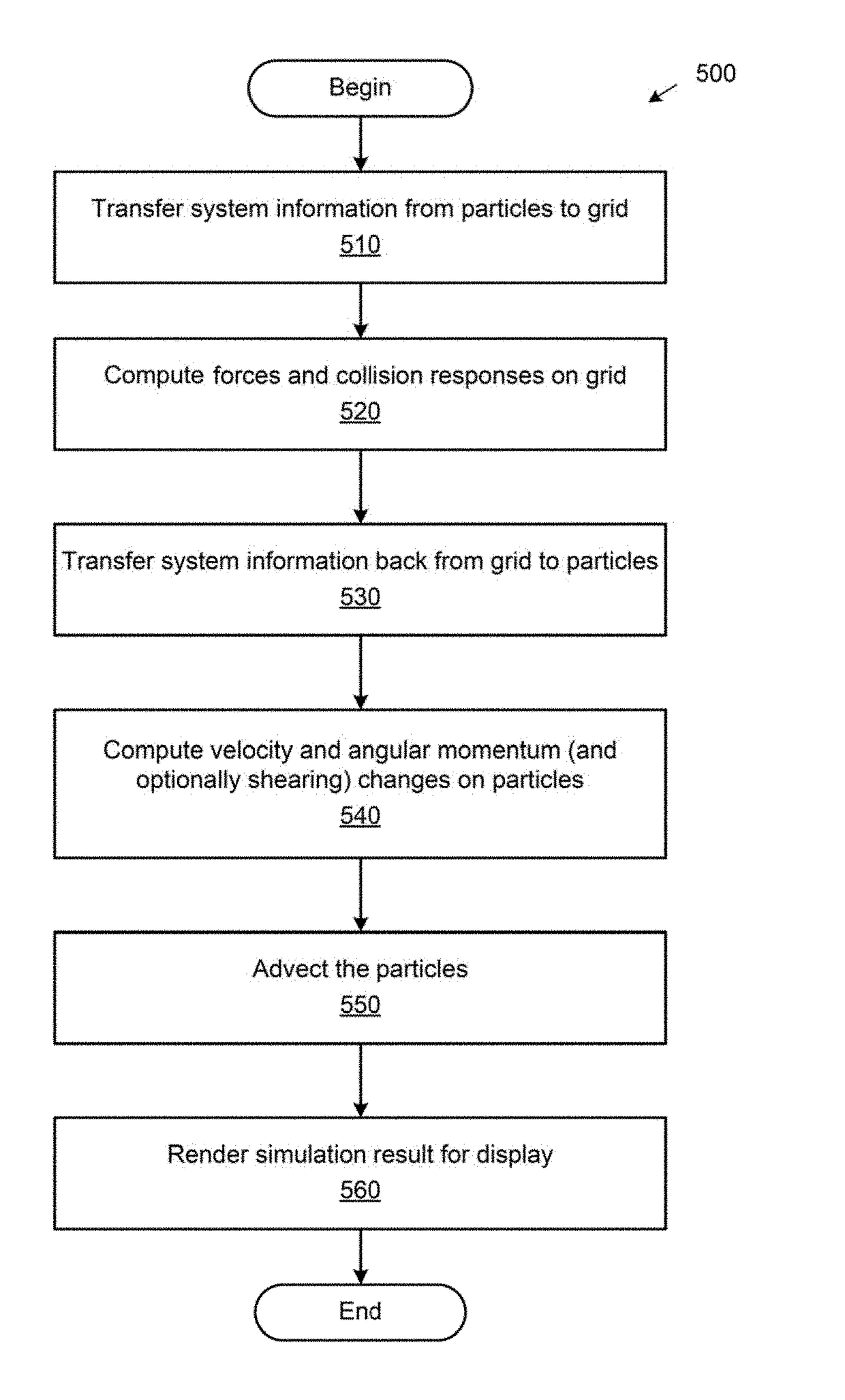
The disclosure provides an adaptive material point method for simulating and rendering of solid materials. During each time step, a simulation application splits and / or merges particles according to a resolution of a grid and assigns properties to the split / merged particles. The simulation application then rasterizes particle information, including masses and velocities, to the grid, on which forces and / or collisions are computed to obtain updated velocities. Grid information, including the updated velocities, is then transferred back to the particles. The transfer from particles to grid and back from grid to particles may employ different transfer functions. In particular, a quadratic transfer function may be used to transfer information from the particles to the grid, while a linear transfer function may be used elsewhere, including to transfer information back from the grid to the particles. After updated velocities are transferred to the particles, the simulation application advects the particles using the updated velocities.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
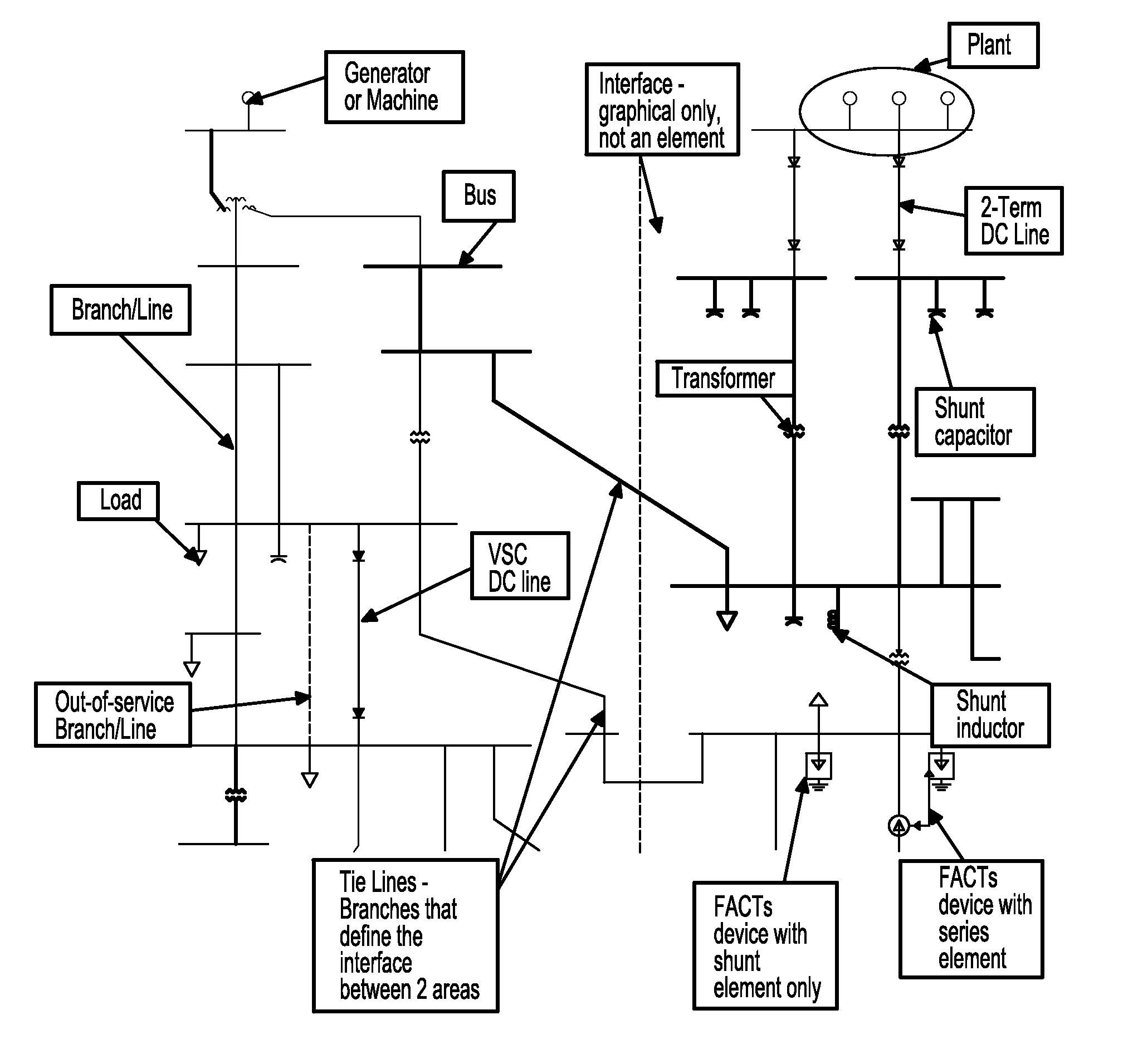
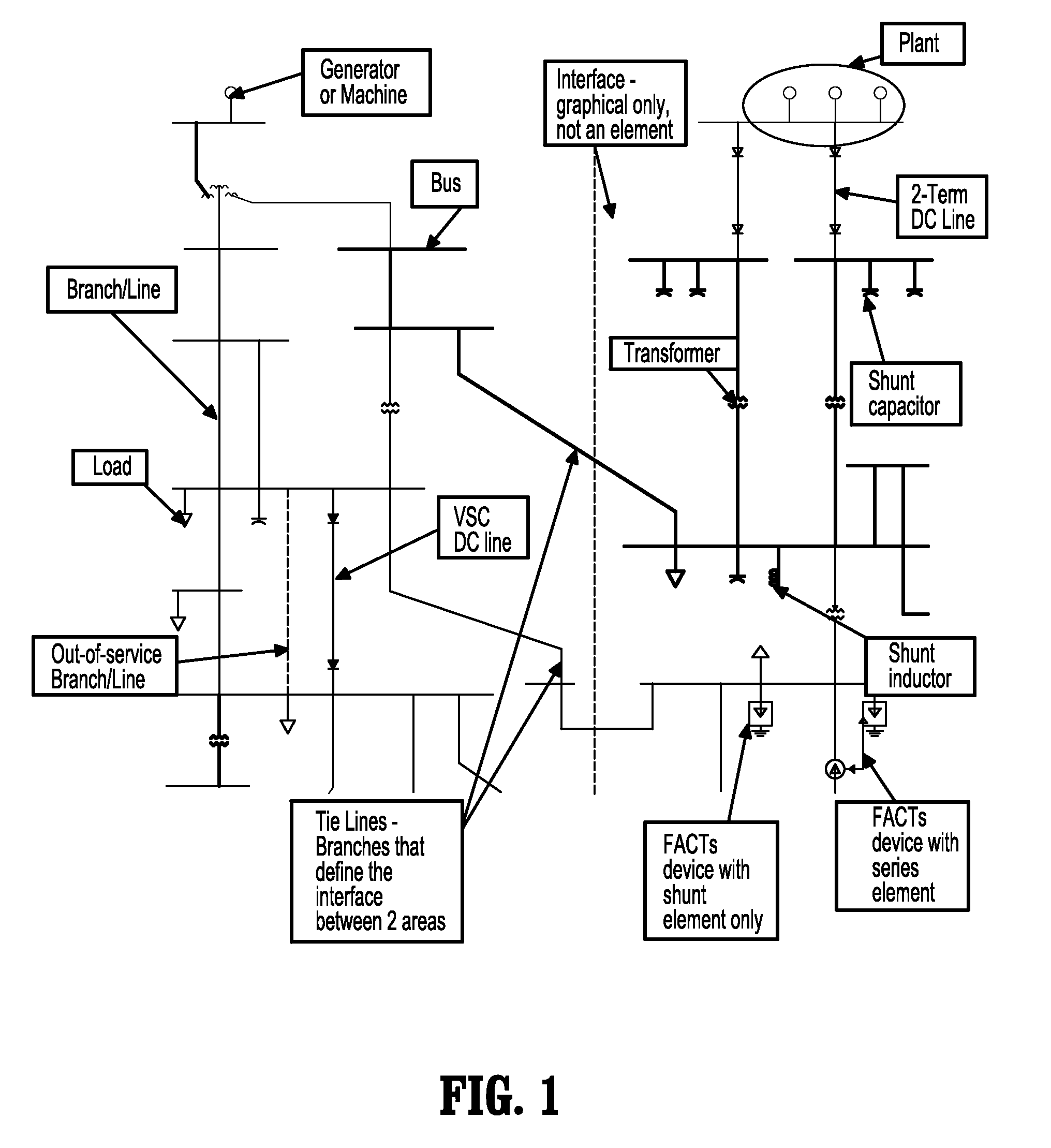
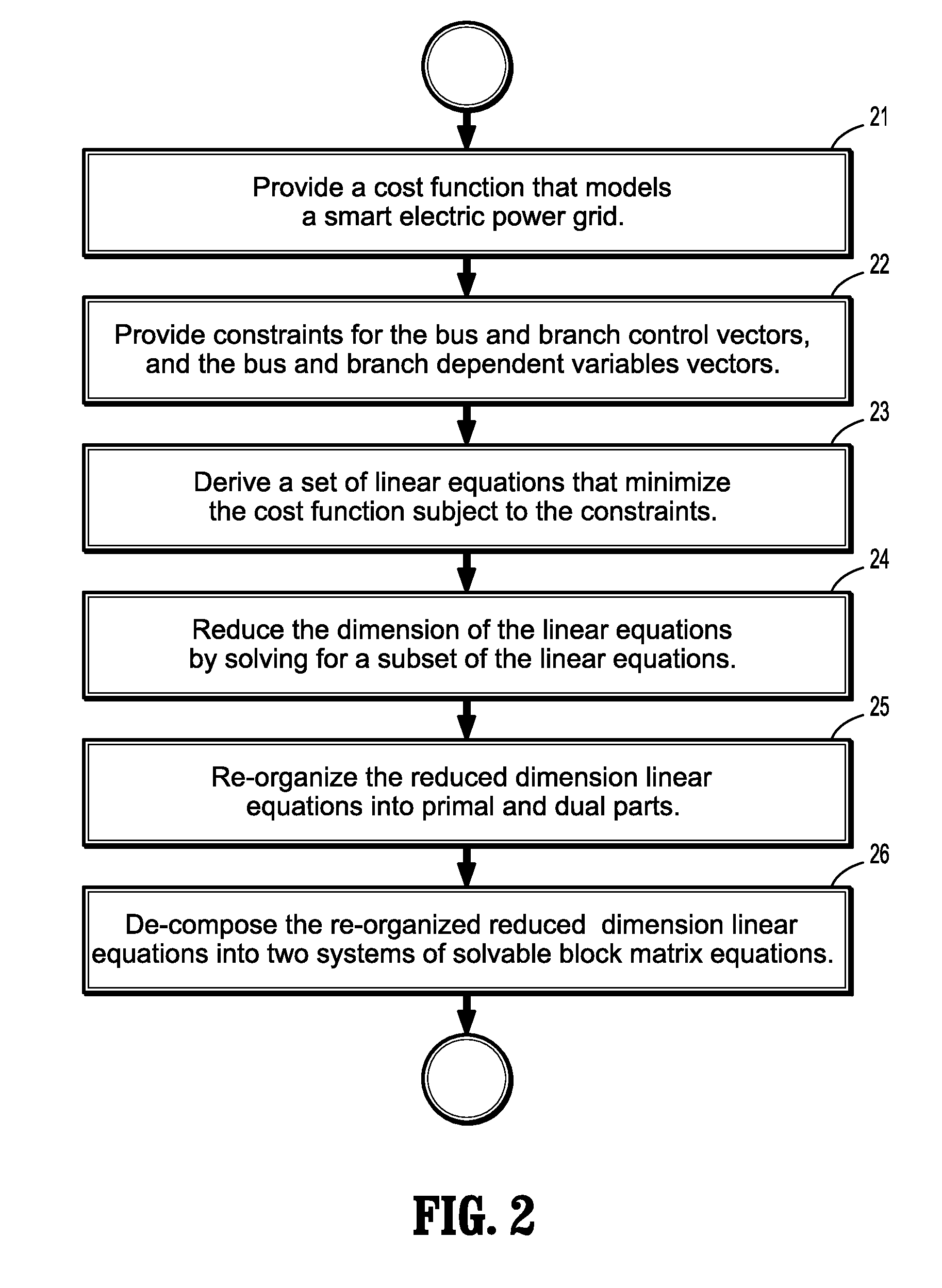
Interior point method for reformulated optimal power flow model
A method for approximating an optimal power flow of a smart electric power grid includes providing a cost function that models a smart electric power grid having buses connected by branches, deriving a set of linear equations that minimize the cost function subject to constraints from an expression of an extremum of the cost function with respect to all arguments, reducing a dimension of the linear equations by solving for a subset of the linear equations, re-organizing the reduced dimension linear equations into primal and dual parts, and decomposing the re-organized reduced dimensional linear equations into two systems of block matrix equations which can be solved by a series of back substitutions. A solution of the two systems of block matrix equations yields conditions for a lowest cost per kilowatthour delivered through the smart electric power grid.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Landslide disaster scene simulation method based on material point method
ActiveCN109992830ASimulation of different hardening propertiesSimulated liquidityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsInterior point methodLandslide
The invention discloses a landslide disaster scene simulation method based on a material point method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) modeling and drawing a disaster phenomenon of the landslide in the field of computer graphics; 2) improving a yield surface criterion on the basis of a traditional MPM method, and introducing a modified Cambridge model. and 3) proposing a bidirectionalcoupling model based on the action of the granular material and the rigid body of MPM so that the soil-rock interaction in the landslide process is more real, and the efficiency of large-scale complex disaster scene simulation is improved. The landslide disaster scene simulation method solves the problem of landslide disaster scene simulation deficiency in computer graphics, and can simulate themovement between soil particles, the collision between stone rigid bodies and the coupling phenomenon between the soil particles and the stone rigid bodies in the landslide occurrence process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multi-scale continuous calculation method for solving mesomechanics performance of energetic material
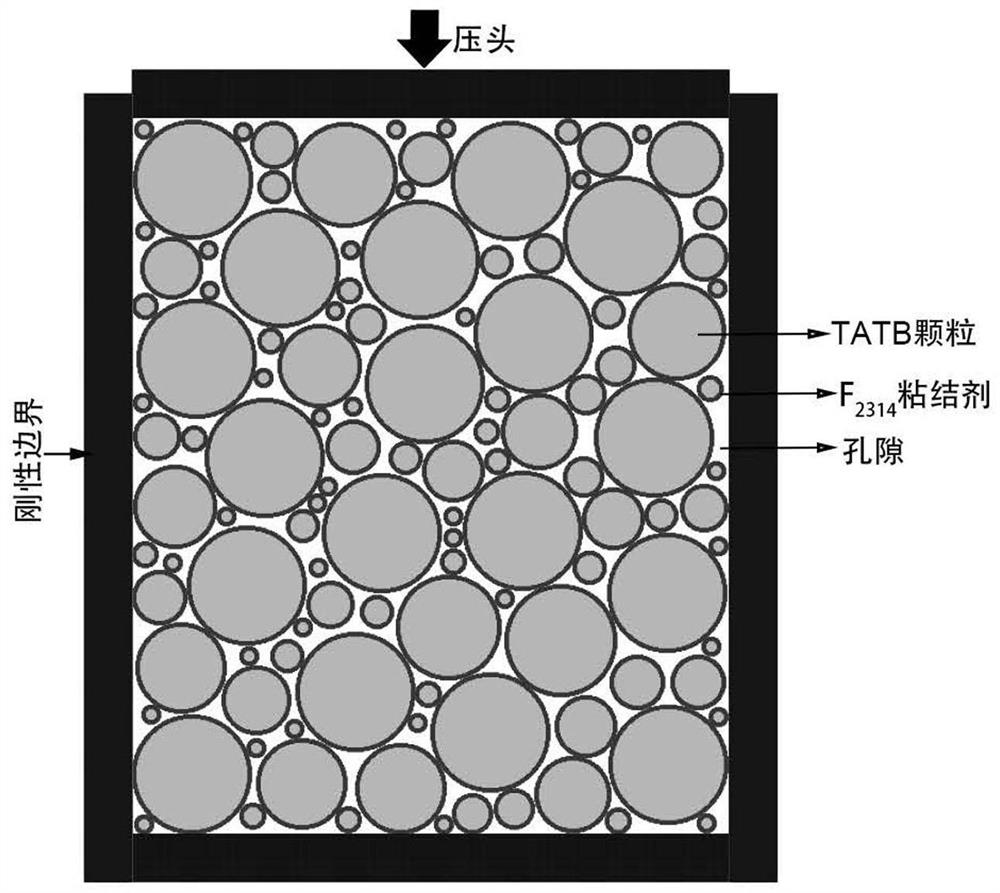
PendingCN111785331AThe calculation result is accurateReflect the mesoscopic boundary effectChemoinformaticsComputational theoretical chemistryExplosive AgentsMacroscopic scale
The invention discloses a multi-scale continuous calculation method for solving the mesomechanics performance of an energetic material. The method comprises the following steps: respectively carryingout molecular dynamics simulation and coarse graining molecular dynamics simulation on an explosive crystal component and a polymer binder component in PBX; converting a real PBX structure into a random round particle digital model through an effective approximation method; connecting key parameters from microcosmic scale to mesoscopic scale; calculating the mechanical properties of particles PBXunder a mesoscopic scale, establishing a representative volume meta-model of PBX on the mesoscopic scale by adopting a material point method, researching the mechanical behaviors of PBX under uniaxialcompression to obtain the elasticity modulus and state equation parameters of PBX, and inputting the elasticity modulus and state equation parameters into a continuum of a macroscopic scale as parameters for calculation. According to the invention, a composite energetic material cross-scale continuous calculation method completely based on theoretical calculation is realized from microcosmic scale to microcosmic scale and from single component to compound, and the method has important guiding significance for safety design of explosives.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Water and soil coupling landslide simulation method based on high-order double-set double-phase material point method
ActiveCN110008599AEffectively characterize and simulate water-soil coupling effectsSolve the problem of mesh distortionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDouble phaseLandslide
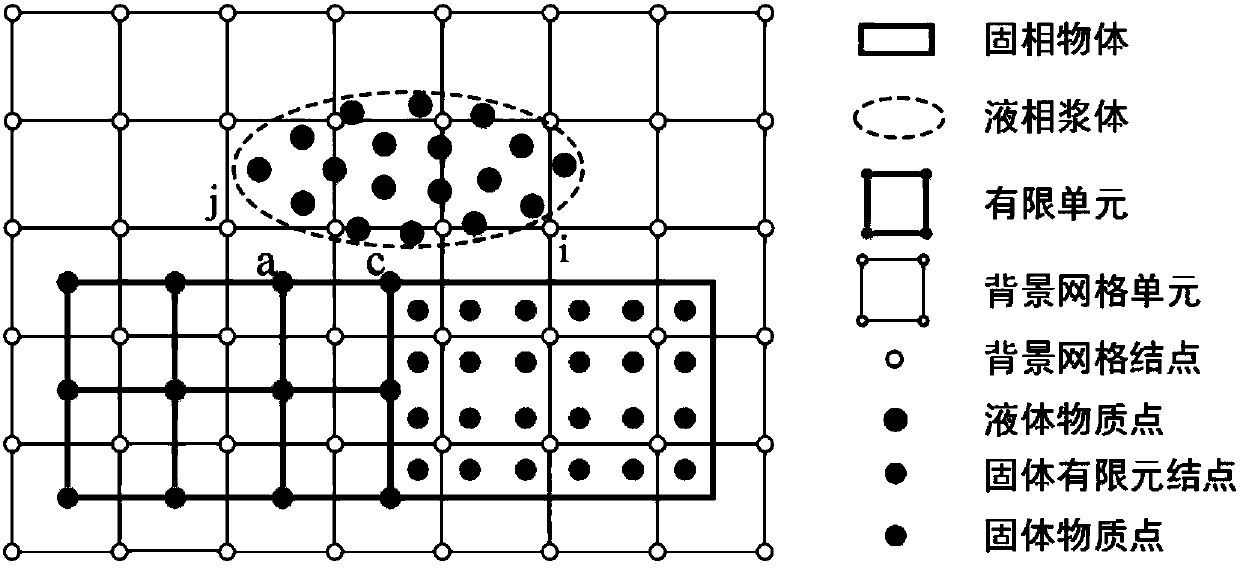
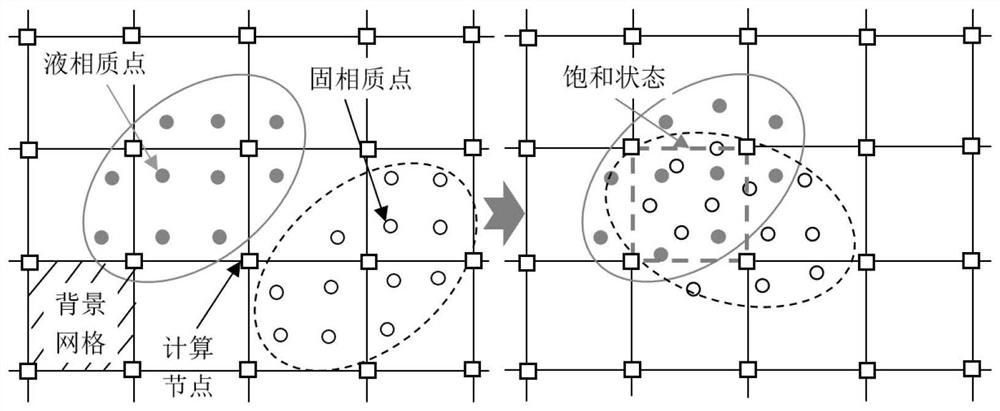
The invention provides a water and soil coupling landslide simulation method based on a high-order double-set double-phase material point method, and the method comprises the steps: employing two setsof material point division to disperse solid soil particles and pore fluid, and employing a regular background grid to realize the solving of a control equation; under a continuous medium mechanicalframework, establishing a solid-liquid two-phase substance point method control equation for dividing two sets of substances; realizing interaction between solid-liquid biphase material points and background grid nodes through a high-order B spline primary function; and based on the basic function of the B spline, updating the acceleration, speed, position and other information of the solid-liquidtwo-phase material point, mapping the calculated node information to the material point, updating the material information of the latest solid-liquid two-phase material point, and finally outputtingsimulation information. The method can accurately simulate the large deformation damage process and the water-soil coupling mechanism of the water-soil coupling soil landslide, and provides data support for disaster assessment and prevention of the water-soil coupling soil landslide problem.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
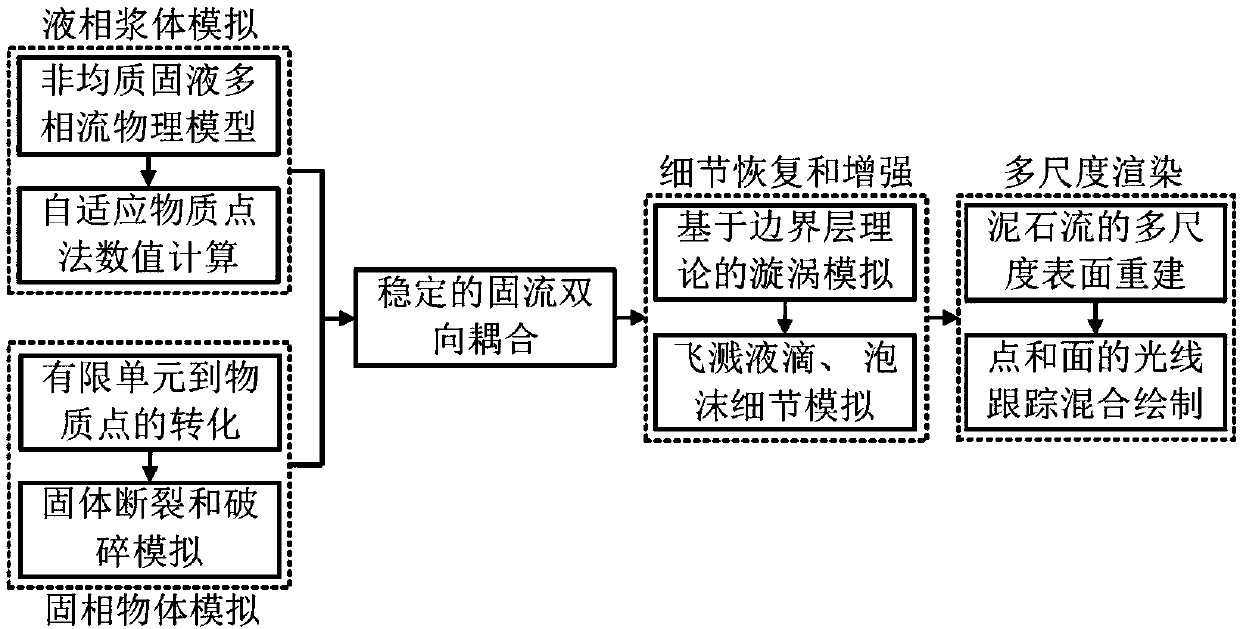
Multi-scale debris flow phenomenon simulation method based on material point method
The invention discloses a multi-scale debris flow phenomenon simulation method based on a material point method, and relates to the technical field of computer physical animation. The method comprisesthe following steps: S1, simulating multi-scale features of debris flow liquid slurry based on an adaptive material point method; S2, simulating multi-scale features of a debris flow solid phase object based on an adaptive material point finite element method; S3, simulating multi-scale liquid-solid coupling based on the material point method; S4, carrying out the multi-scale realistic renderingof debris flow animation. The method solves a problem of how to construct an effective physical model for describing multi-scale features of a debris flow disaster scene in the debris flow animation simulation process and a problem of building a consistency constraint between different models so as to achieve the multi-scale value solving and rendering. The method can achieve the realistic simulation of the multi-scale features of the debris flow phenomenon, achieves the generation of a debris flow animation with the fidelity of a picture, and provides the image data of the debris flow phenomenon for the disaster prevention, digital entertainment, film and television effects.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
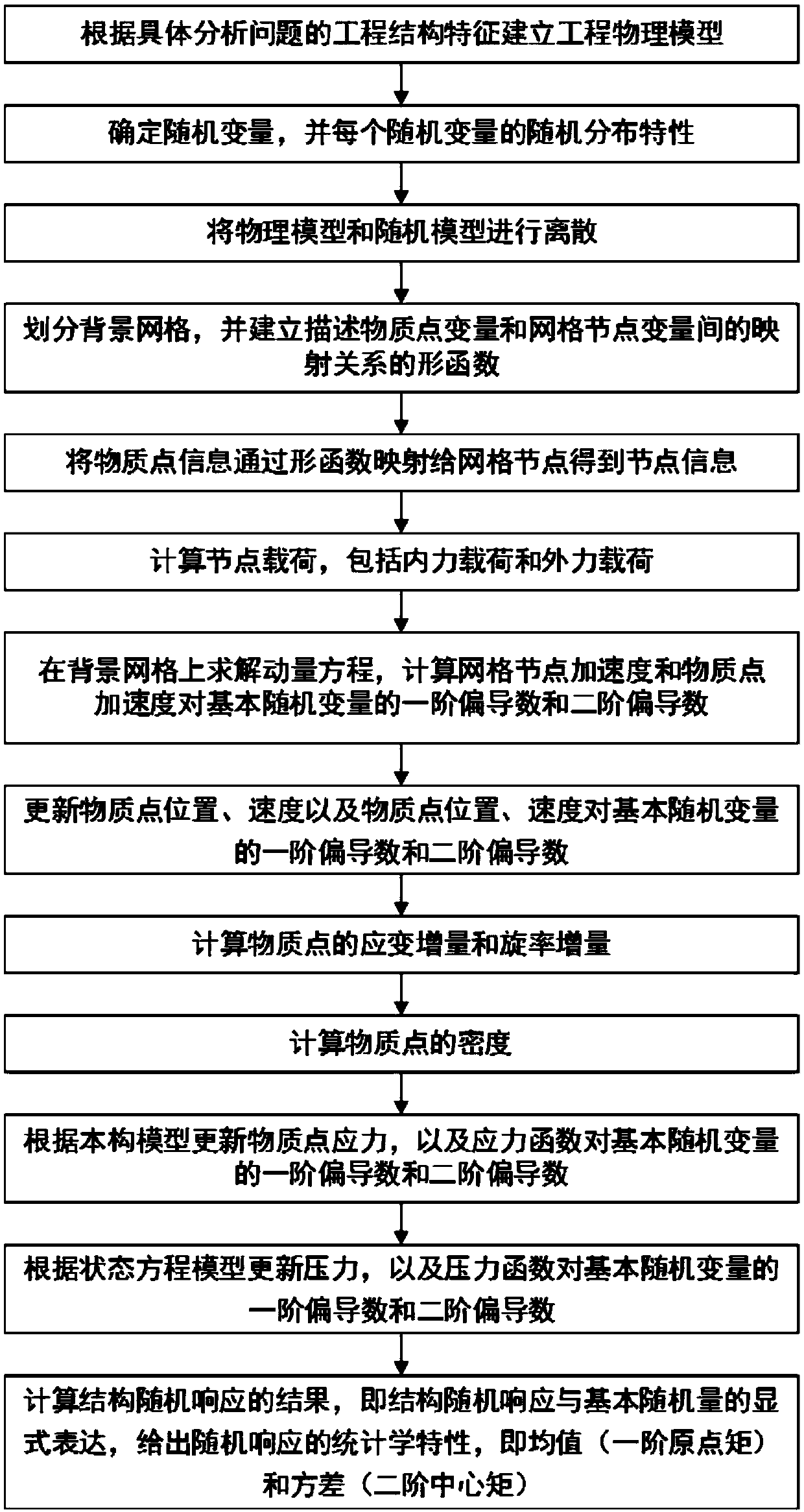
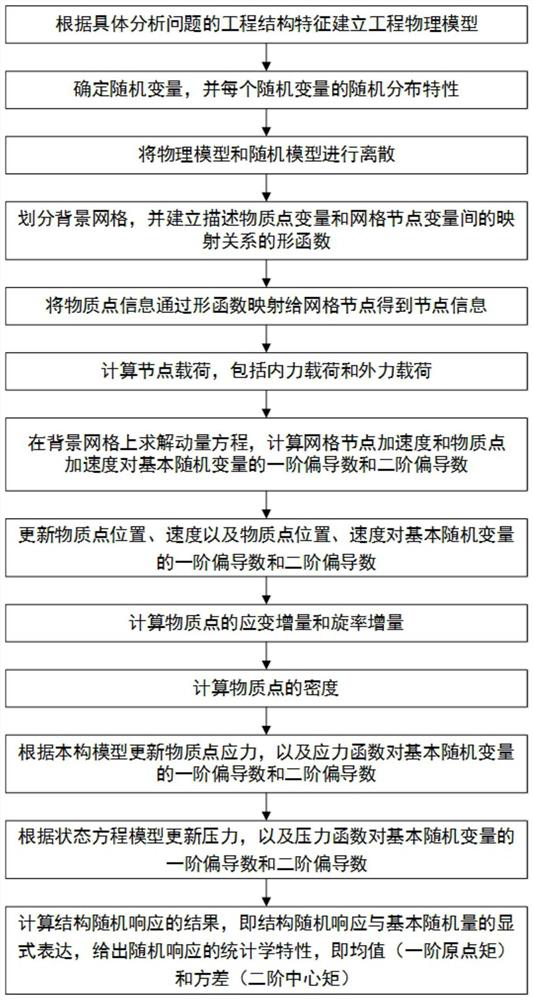
Material point method-based stochastic dynamics analysis method applied to explosion shock engineering
The invention provides a material point method-based stochastic dynamics analysis method applied to explosion shock engineering. The method comprises the steps of building an engineering physical model; determining stochastic variables and performing discretization; dividing a background grid for a calculation domain; calculating a node load of the background grid, solving a momentum equation, andcalculating first-order and second-order partial derivatives of an accelerated speed of a grid node and an accelerated speed of a material point to basic stochastic variables; updating the position and speed of the material point and first-order and second-order partial derivatives of the position and speed of the material point to the basic stochastic variables; calculating a strain increment and a spin rate increment of the material point; calculating the density of the material point; according to a constitutive model, updating a stress of the material point and first-order and second-order partial derivatives of a stress function to the basic stochastic variables; according to a state equation model, updating a pressure and first-order and second-order partial derivatives of a pressure function to the basic stochastic variables; and calculating a structure stochastic response result. The defects of a conventional numerical calculation method in researching nonlinear problems of explosion, impact and the like are overcome.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
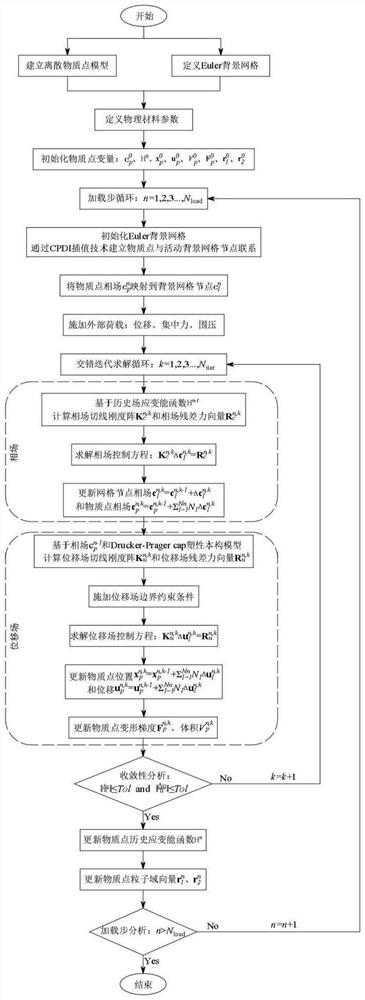
Phase field material point method for large deformation fracture analysis of rock-soil structure
ActiveCN113360992AReduce complexityEasy to handleGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationPorosityYield surface
The invention belongs to the field of computational mechanics, and provides a phase field material point method for large deformation fracture analysis of a rock-soil structure, which considers the complex fracture phenomenon of brittleness-to-plasticity transformation of a high-porosity rock-soil material under the action of complex external factors, and widens the application range of the material point method in the field of solid material fracture. According to the method, a phase field fracture model is adopted as a damage function, so that a complex crack propagation path can be accurately and efficiently captured, and a smooth double-yield-surface Drucker-Prager cap plastic constitutive model is adopted to accurately and comprehensively describe complex mechanical behaviors of the pressure-sensitive geotechnical material; and the coupling effect of the phase field fracture model and the plastic constitutive model is realized by introducing the phase field effective stress. In addition, a CPDI interpolation method is adopted to improve the numerical stability and the boundary application accuracy, and an interlaced iteration solution strategy is implemented to improve the calculation efficiency and reduce the numerical implementation complexity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
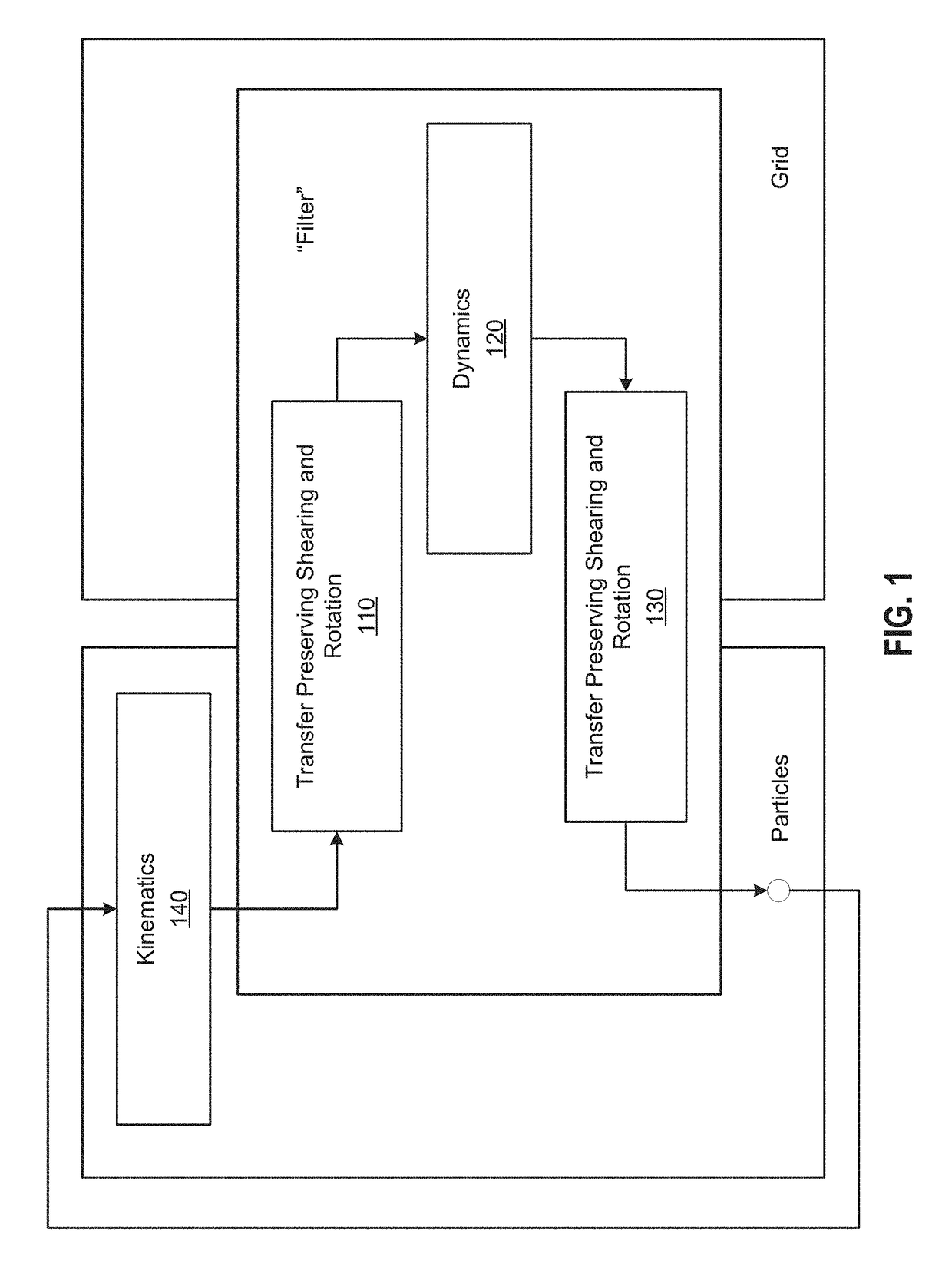
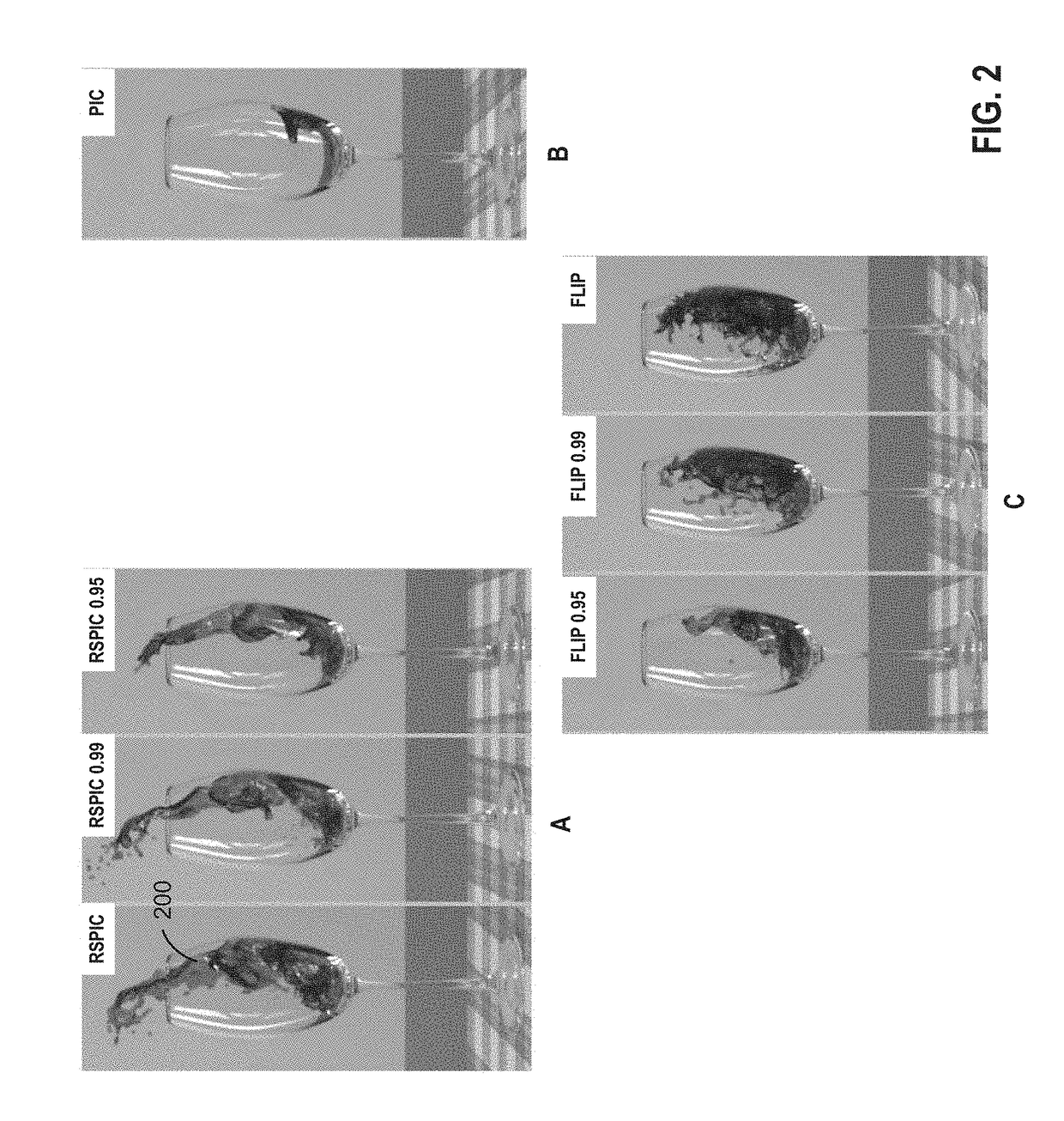
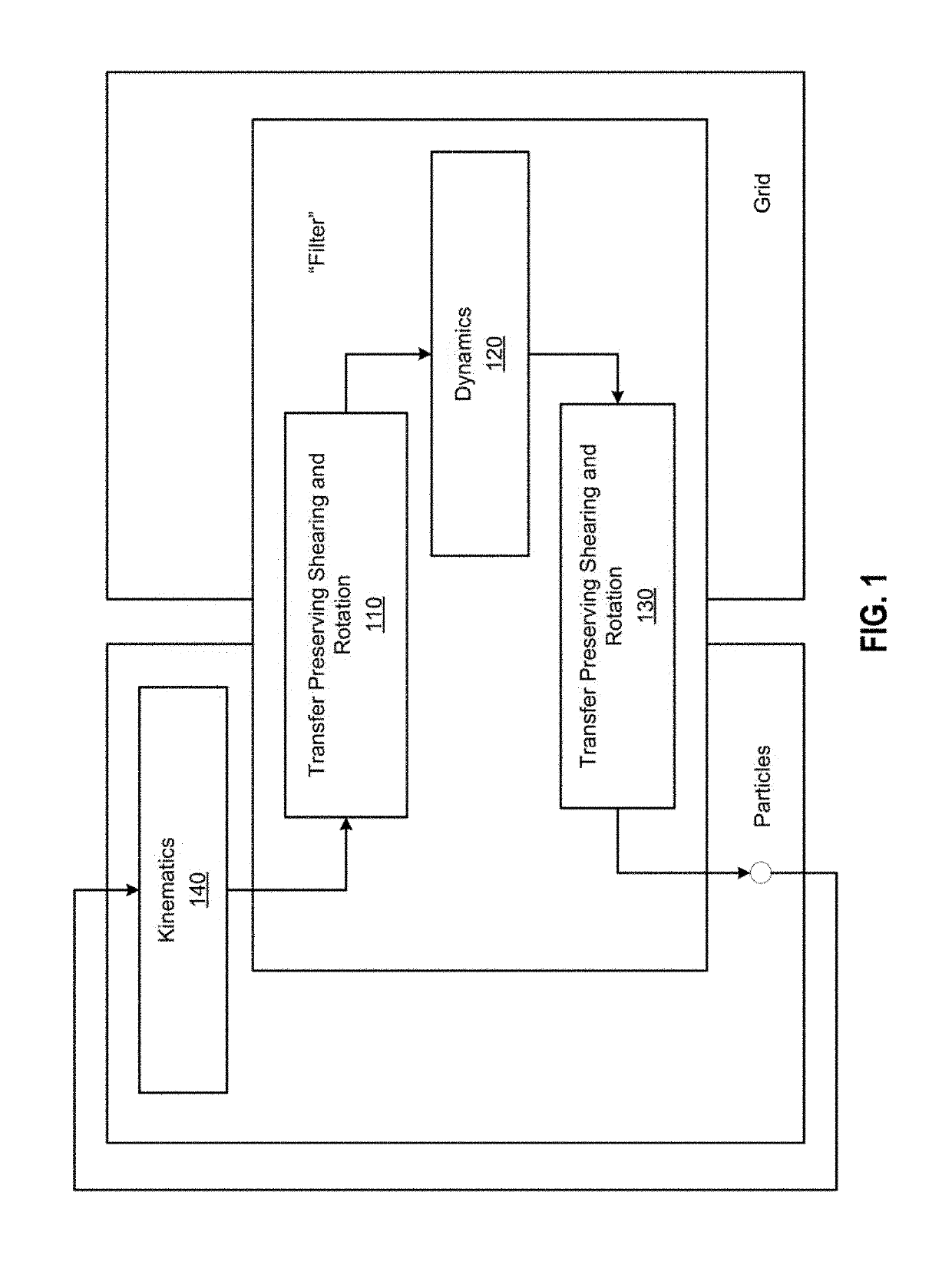
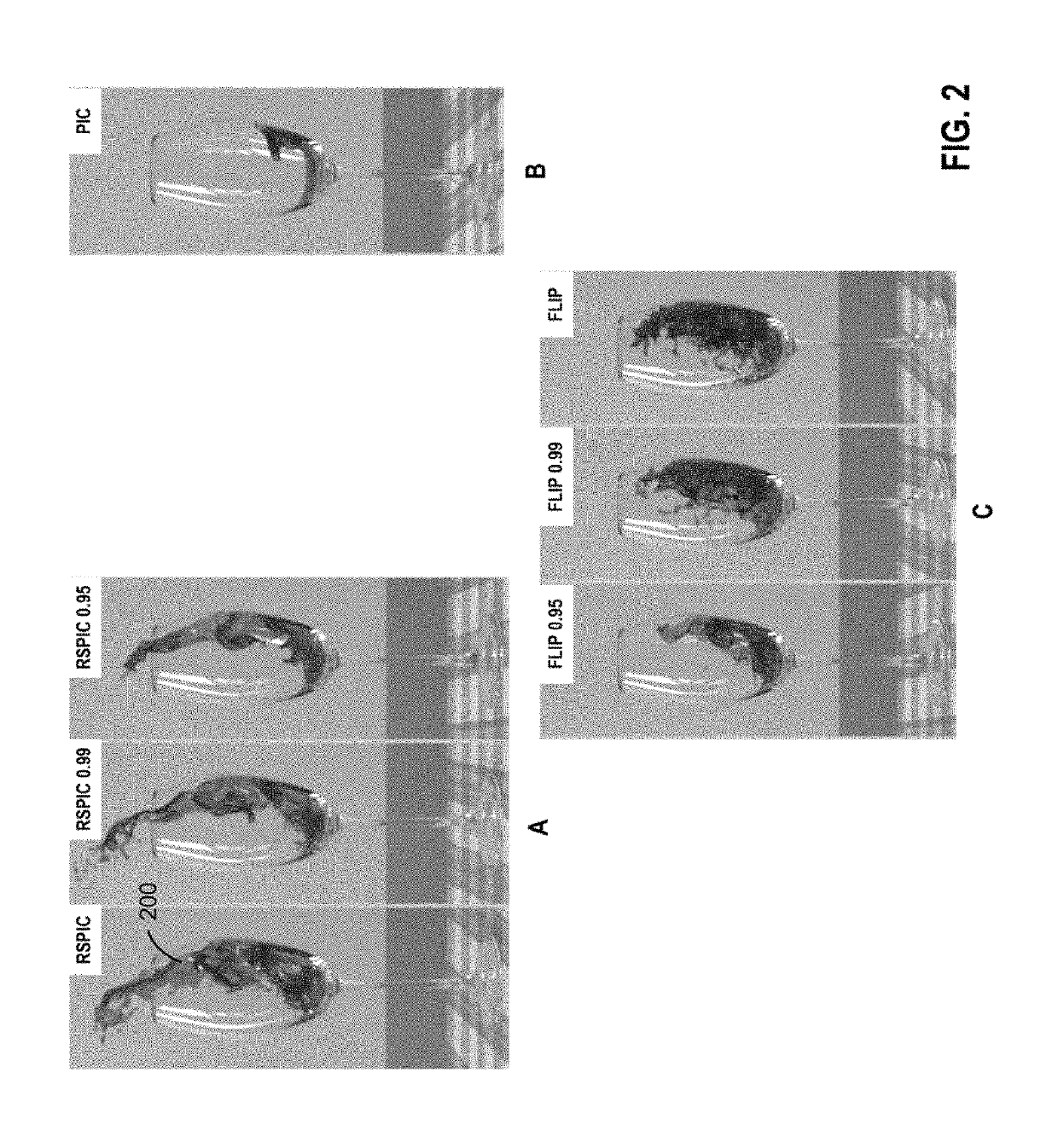
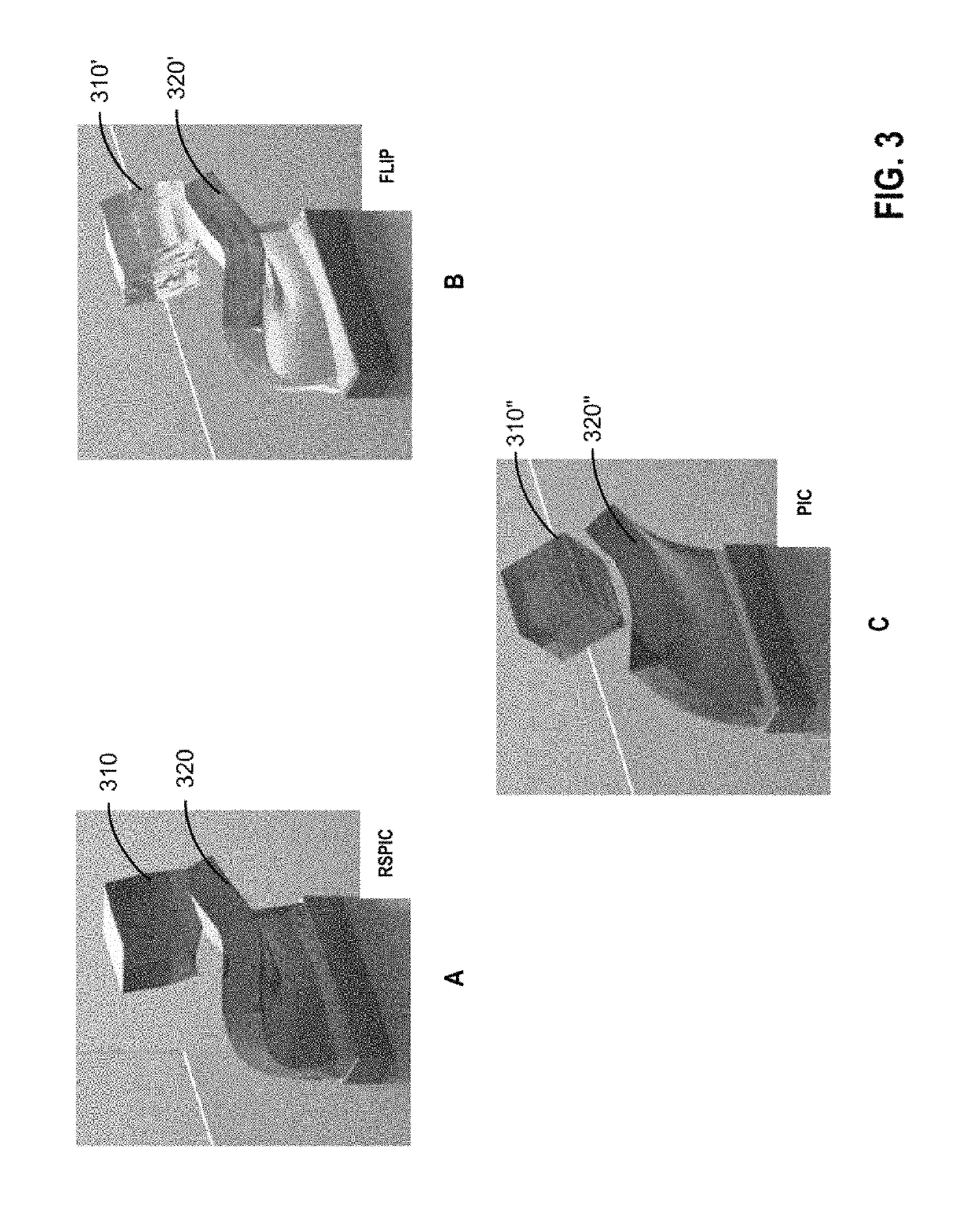
Particle-in-cell methods preserving shearing and rotation
The disclosure provides an approach for reducing information loss when transferring from particles to grid and vice versa in a hybrid Lagrangian / Eulerian simulation, while also preserving stability. In one aspect, referred to as the rigid particle-in-cell (RPIC) method, a simulation application stores a sampling of local angular momentum for each particle, helping to preserve the angular momentum that would otherwise be lost in the transfer from grid to particles. In another aspect that is more generally applicable and referred to herein as the rigid and shearing particle-in-cell (RSPIC) method, the simulation application stores, for each particle, a matrix with rotational and shearing information. The RSPIC method effectively reduces dissipation, preserves angular momentum exactly, and prevents instabilities. Further, the RSPIC method is applicable to both incompressible liquids and material point method (MPM) simulations of materials such as solids.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Material point method modeling in oil and gas reservoirs
InactiveUS9378310B2Accurate modelingSimulation is accurateFluid removalSeismologyLaws of thermodynamicsEquation of state
A computer system and method of simulating the behavior of an oil and gas reservoir including changes in the margins of frangible solids. A system of equations including state equations such as momentum, and conservation laws such as mass conservation and volume fraction continuity, are defined and discretized for at least two phases in a modeled volume, one of which corresponds to frangible material. A material point model technique for numerically solving the system of discretized equations, to derive fluid flow at each of a plurality of mesh nodes in the modeled volume, and the velocity of at each of a plurality of particles representing the frangible material in the modeled volume. A time-splitting technique improves the computational efficiency of the simulation while maintaining accuracy on the deformation scale. The method can be applied to derive accurate upscaled model equations for larger volume scale simulations.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Material sorting method
The invention relates to a material sorting method and belongs to the technical field of intelligent logistics. The material sorting method starts from a material sorting order which can be obtained according to a requirement list; the sorting order is divided into a plurality of sorting tasks; and the sorting tasks are sequenced, and thus sorting can be conducted more efficiently. In particular, indicator lights corresponding to the placing positions of sorting boxes are arranged on a sorting frame, and when the sorting tasks are executed, the corresponding indicator lights are lightened to remind sorting personnel to conduct accurate feeding, so that the working process is greatly simplified, and the sorting accuracy and efficiency are improved.
Owner:NANJING NANCHE PUZHEN IND LOGISTICS CO LTD
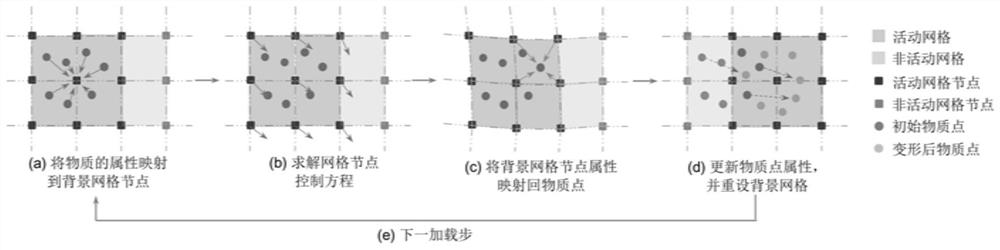
Material information mapping method for material point method for large deformation response of structure
ActiveCN110457785AAvoid complexityAvoid conditionsSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumInterior point method
The invention provides a material information mapping method of a material point method for large deformation response of a structure. The material information mapping method comprises the following steps: establishing a topological relation between a material point volume domain and a background grid by tracking the change of the material point volume domain in the large deformation process of the structure; dividing the volume domain of the material point into a plurality of volume sub-domains by the background grid node, respectively arranging virtual mapping material points in the centersof the volume sub-domains of the material point, and directly determining the material information on the virtual mapping material points by the material information on the material points; and mapping of mass, momentum, physical strength, surface force, stress and other material information of the background grid nodes is realized based on the virtual mapping material points. The material information mapping method can accurately give the material point method, can effectively eliminate the grid crossing error of the material point method when solving the large deformation problem of the structure, and solves a problem that the solving precision of the material point method is not high enough when solving the large deformation dynamic response of the structure.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Parallel meshfree method and system for solving strong heat fluid-structure interaction problem
PendingCN112163385AGuaranteed conservation of momentumGuaranteed energy conservationDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingThermodynamicsEngineering
The invention relates to a parallel meshless method and system for solving a strong heat fluid-structure interaction problem. The parallel meshless method is characterized in that time discretizationis carried out based on an optimal transportation theory, spatial discretization is carried out through adopting a material point method, and a local maximum entropy interpolation function is adoptedas a shape function. According to the parallel meshless method and the system, the mass conservation and the momentum conservation are strictly met in the aspect of time discretization, the Kroneckerattribute is met in the aspect of boundary, and extremely high precision and stability are shown in solving the problems of large deformation, fluid-structure interaction and the like of materials.
Owner:云翼超算(北京)软件科技有限公司
Shock wave variable step size solving method based on B-spline mapping function material point method
ActiveCN111859646AReduce workloadShorten the timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEulerian methodEngineering
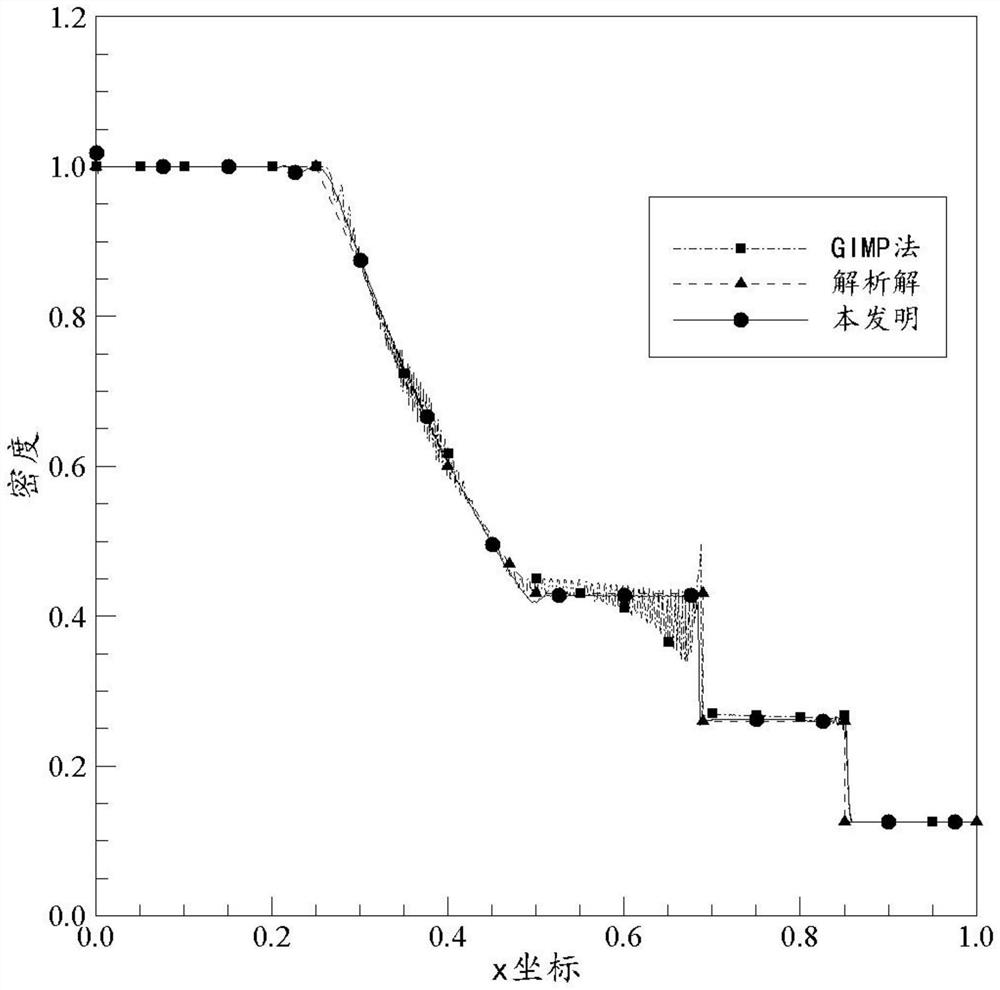
The invention provides a shock wave variable step size solving method based on a B-spline mapping function material point method. The method comprises the steps: firstly, establishing a B-spline mapping function; then, establishing a shock wave flow field model, and discretizing the shock wave flow field; giving an initial condition and a boundary condition of the shock wave flow field, and setting a calculation total length; calculating the time step length of the current calculation step according to the stability condition; solving a shock wave problem by using a material point method; andfinally, carrying out visualization processing on the shock wave flow field. According to the method provided by the invention, the problem of difficulty in processing a convection term in an Euler method and the problem of grid distortion in a Lagrange method can be avoided; and compared with a traditional standard substance point method and a traditional GIMP method, the method has the advantages that oscillation can be better suppressed, stability and robustness are higher, calculation efficiency is higher, and a new method can be provided for solving shock waves in engineering.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Particle-in-cell methods preserving shearing and rotation
The disclosure provides an approach for reducing information loss when transferring from particles to grid and vice versa in a hybrid Lagrangian / Eulerian simulation, while also preserving stability. In one aspect, referred to as the rigid particle-in-cell (RPIC) method, a simulation application stores a sampling of local angular momentum for each particle, helping to preserve the angular momentum that would otherwise be lost in the transfer from grid to particles. In another aspect that is more generally applicable and referred to herein as the rigid and shearing particle-in-cell (RSPIC) method, the simulation application stores, for each particle, a matrix with rotational and shearing information. The RSPIC method effectively reduces dissipation, preserves angular momentum exactly, and prevents instabilities. Further, the RSPIC method is applicable to both incompressible liquids and material point method (MPM) simulations of materials such as solids.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
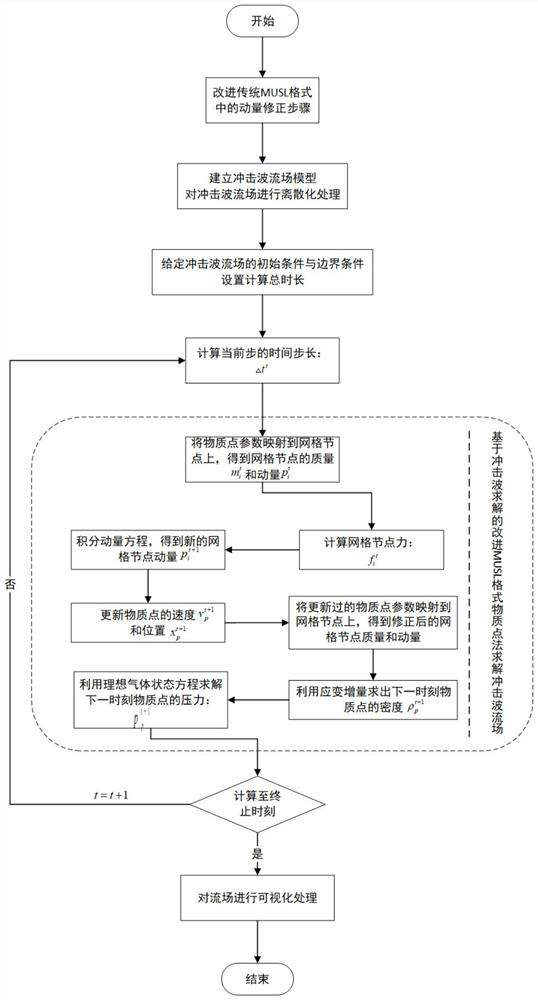
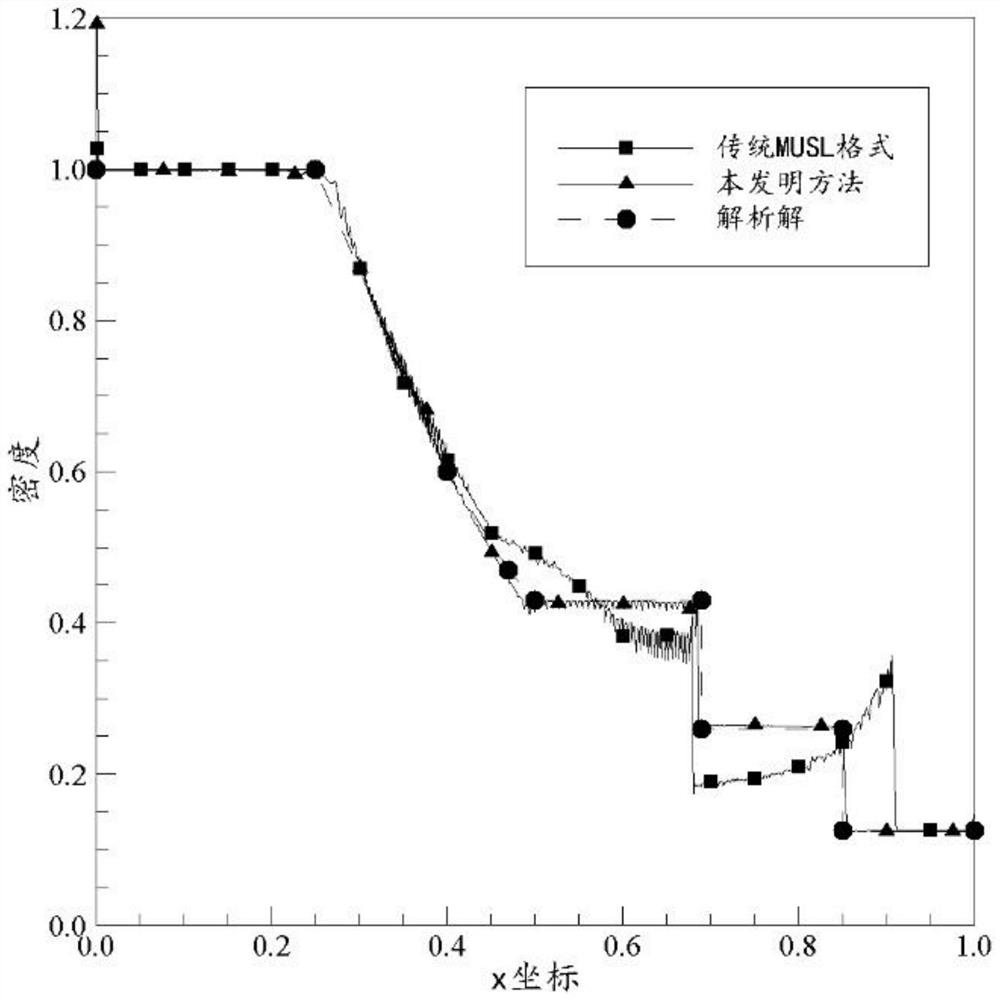
Improved MUSL format substance point method for shock wave solving
ActiveCN111859645AReduce workloadShorten the timeSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationEulerian methodEngineering
The invention provides an improved MUSL format material point method for shock wave solving. The method comprises the steps: firstly, improving a momentum correction step in a traditional MUSL format;then, establishing a shock wave flow field model, and discretizing the shock wave flow field; giving an initial condition and a boundary condition of the shock wave flow field, and setting a calculation total length; calculating the time step length of the current calculation step based on the stability condition; solving the shock wave flow field based on an improved MUSL format material point method of shock wave solving; and finally, carrying out visualization processing on the shock wave flow field. According to the method provided by the invention, the problem of difficulty in processinga convection term in an Euler method and the problem of grid distortion in a Lagrange method can be avoided; compared with the traditional MUSL format, the method has the advantages that noise generated when the material points pass through the grids can be effectively reduced, the requirement for the precision of the shape function is lower, robustness and stability are higher, calculation efficiency is higher, calculation energy consumption is lower, and a new method can be provided for solving shock waves in engineering.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Material point method for simulation of granular materials
The disclosure provides an approach for simulating and rendering granular materials. A simulation application generates video frames depicting a granular material phenomenon using a strain based elasto-plastic constitutive model integrated with a hybrid Eulerian / Lagrangian material point method (MPM). The elasto-plastic constitutive model includes physical equation(s) which dictate forces that affect the granular material during the simulation. In particular, the constitutive model may include user-controllable parameters defining threshold(s) to start plastic deformation, as well as a hardening parameter which controls how fast the granular material packs under compression. The MPM is a procedure in which particles of the granular material and a background grid are coupled, with the grid being used to assist in computing forces dictated by the physical equation(s) of the elasto-plastic constitutive model. In one configuration, the grid may further be rendered with volumetric rendering to generate video frames depicting the granular material.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Augmented material point method for simulating phase changes and varied materials
ActiveUS10210287B2Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsInterior point methodGrid based
The disclosure provides an approach for simulating and rendering materials across different states and undergoing phase transitions. In one configuration, a simulation application generates video frames depicting a material phenomenon using an augmented material point method (MPM). Traditional MPM does not handle incompressible materials such as fluids. Techniques disclosed herein augment the MPM with a Chorin-style projection technique to enable simulation of arbitrarily incompressible materials. In one configuration, this is achieved with a marker-and-cell (MAC) grid based MPM solver, a splitting of stress used in the simulation into elastic and dilational parts, a projection-like implicit treatment of the Eulerian evolution of the dilational part of the stress, and particular techniques for rasterizing and updating quantities on the MAC grid. In addition, a heat model may be coupled to the MPM solver, allowing material changes to be driven with temperature and phase changes.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Simulation method of landslide disaster scene based on material point method
ActiveCN109992830BEfficient and accurate simulationSimulation of different hardening propertiesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSoil scienceModelSim
The invention discloses a landslide disaster scene simulation method based on a material point method. The steps are as follows: 1) model and draw the disaster phenomenon of landslide in the field of computer graphics. 2) Based on the traditional MPM method, the yield surface criterion is improved, and the modified Cambridge model is introduced. 3) A two-way coupling model based on MPM for granular material and rigid body interaction is proposed, which makes the soil-rock interaction more realistic during the landslide process and improves the efficiency of large-scale complex disaster scene simulation. The invention solves the problem of lack of landslide disaster scene simulation in computer graphics, and can simulate the movement between soil particles, the collision between rock rigid bodies and the coupling phenomenon between soil particles and rock rigid bodies during the occurrence of landslides .
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Stochastic Dynamics Analysis Method Based on Material Point Method Applied in Explosion Shock Engineering
The invention provides a material point method-based stochastic dynamics analysis method applied to explosion shock engineering. The method comprises the steps of building an engineering physical model; determining stochastic variables and performing discretization; dividing a background grid for a calculation domain; calculating a node load of the background grid, solving a momentum equation, andcalculating first-order and second-order partial derivatives of an accelerated speed of a grid node and an accelerated speed of a material point to basic stochastic variables; updating the position and speed of the material point and first-order and second-order partial derivatives of the position and speed of the material point to the basic stochastic variables; calculating a strain increment and a spin rate increment of the material point; calculating the density of the material point; according to a constitutive model, updating a stress of the material point and first-order and second-order partial derivatives of a stress function to the basic stochastic variables; according to a state equation model, updating a pressure and first-order and second-order partial derivatives of a pressure function to the basic stochastic variables; and calculating a structure stochastic response result. The defects of a conventional numerical calculation method in researching nonlinear problems of explosion, impact and the like are overcome.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
The ccpdi-impm method for large deformation analysis of saturated porous media
ActiveCN110298105BOvercome stabilityOvercome precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
The invention provides a CCPDI-IMPM method for large deformation analysis of saturated porous media based on the u-p control equation of generalized Biot theory and convective particle domain interpolation technology. The method includes the analysis of large deformation consolidation process of saturated porous media and saturated Dynamic process analysis of large deformation in porous media. The invention adopts the implicit time integration strategy to overcome the defect of the traditional explicit material point method limited by the critical time step, especially when solving quasi-static problems, it significantly improves the calculation efficiency; The Euler-Lagrangian description advantage of the material point method is more robust than the traditional FEM calculation performance when dealing with large deformation and extreme large deformation. The invention also proposes an extended material point penalty factor method, which is used to deal with the boundary conditions of the fluid-solid coupling system more simply and accurately.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
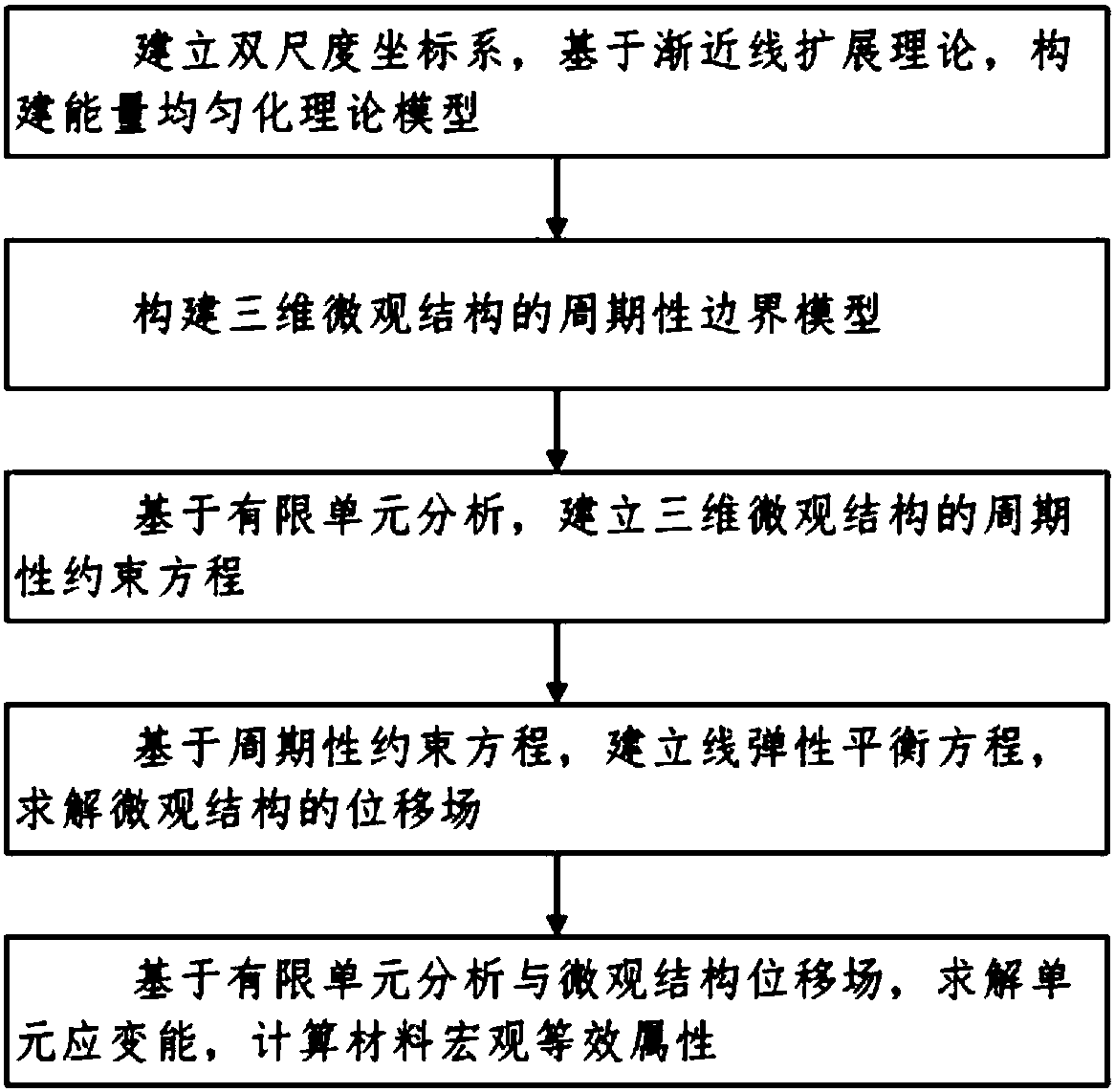
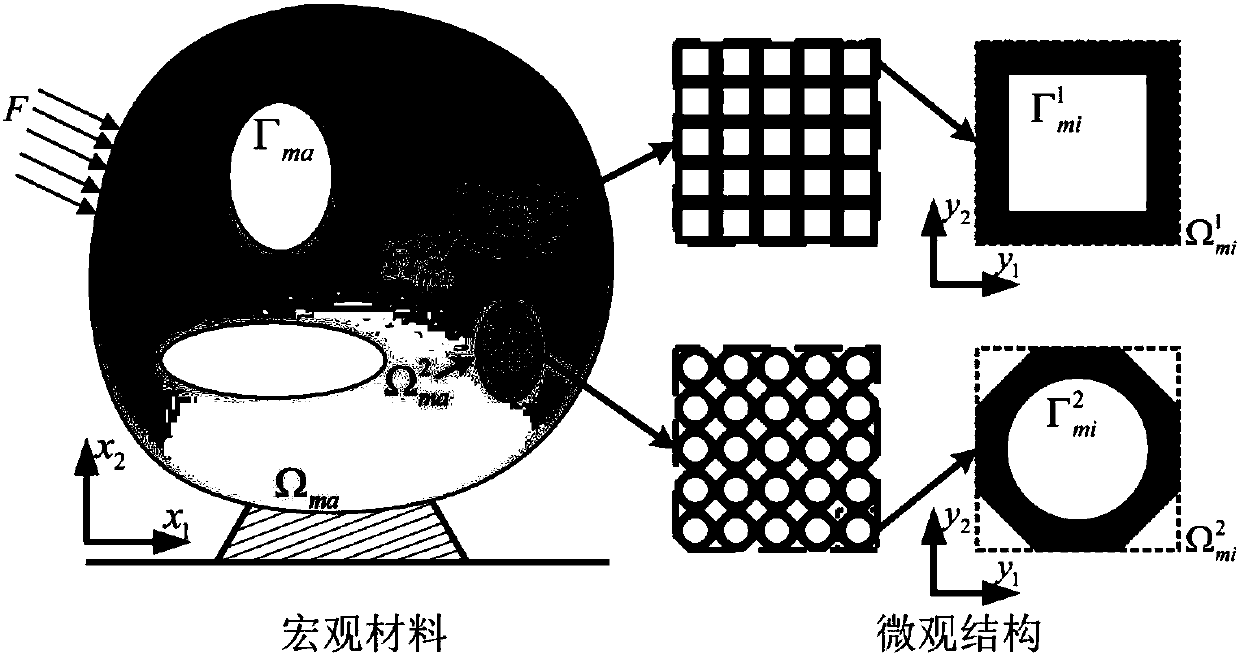
A method for obtaining macroscopic three-dimensional equivalent properties of materials
ActiveCN107451345BEfficient acquisitionSimplified homogenization techniqueDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleThree dimensional microstructure
The invention belongs to the technical field of material mechanics, and discloses a method for obtaining material macroscopic three-dimensional equivalent attribute. The method for obtaining material macroscopic three-dimensional equivalent attribute comprises the following steps of (1) establishing a double-scale coordinate system used for describing the material and the microstructure, and constructing a material macroscopic equivalent attribute model based on a progressive extension theory; (2) constructing a periodic boundary model of a three dimensional microstructure; (3) establishing a periodic constraint relation of the three dimensional microstructure through finite element analysis; (4) establishing a linear elasticity equilibrium equation of the three dimensional microstructure based on the periodic constraint relation, and obtaining a displacement field of the microstructure according to the linear elasticity equilibrium equation; and (5) solving unit strain energy based on finite element analysis and the displacement field of the microstructure, and obtaining the material macroscopic three-dimensional equivalent attribute. According to the invention, unit interactive energy is introduced in finite element analysis, a equivalence relation between the total strain energy of the microstructure under the unit test strain and the material attribute is established, and the material attribute is efficiently obtained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Heuristic scheme in material point method for simulating material
Owner:TENCENT AMERICA LLC
Simulation analysis method for rainfall-induced slope geological disaster scene
ActiveCN113240803ASimple and fast operationAdvanced technologyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSoil scienceSoil mass
The invention discloses a rainfall-induced slope geological disaster scene simulation analysis method, and the method comprises the following steps: reconstructing a three-dimensional model of a slope scene based on oblique photography data to obtain earth surface contour line data; processing earth surface contour line control points, and establishing a boundary model of the slope; generating a slope rock and soil mass point set in the range of the boundary model, and achieving the slope scene simulation; carrying out ground stress balance analysis under the self-weight acting force by adopting a material point method; analyzing historical rainfall data of the slope site to obtain distribution characteristics of rainfall intensity, duration and rainfall; randomly generating water quality points above the slope rock-soil body area to realize rainfall scene simulation; calculating the stress seepage coupling response of the slope rock-soil body under the infiltration condition in different time steps by adopting a two-phase material method, and realizing the whole process analysis of rainfall-induced slope geological disaster evolution; wherein the infiltration and surface runoff process of rainfall in the slope rock-soil body is fully considered. The method has the advantages of simple operation, advanced technology and high calculation precision.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Improved contact algorithm-based material point method applied to double-color coin imprinting forming simulation
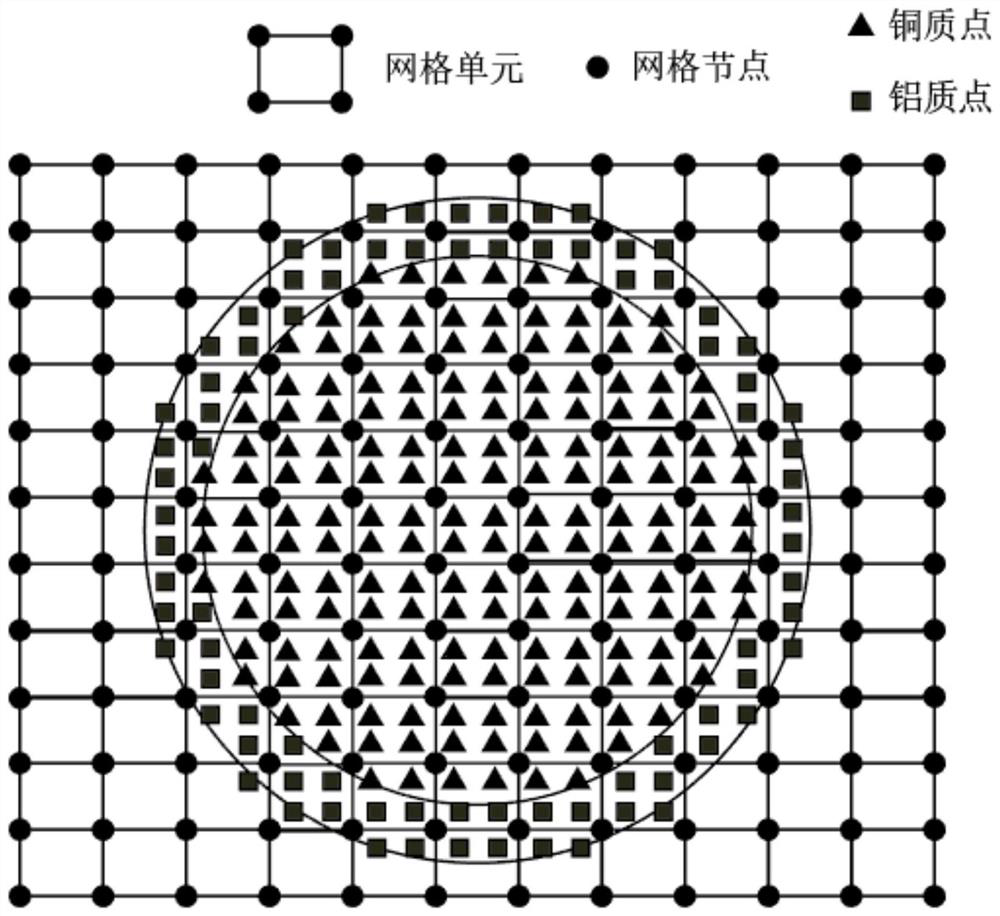
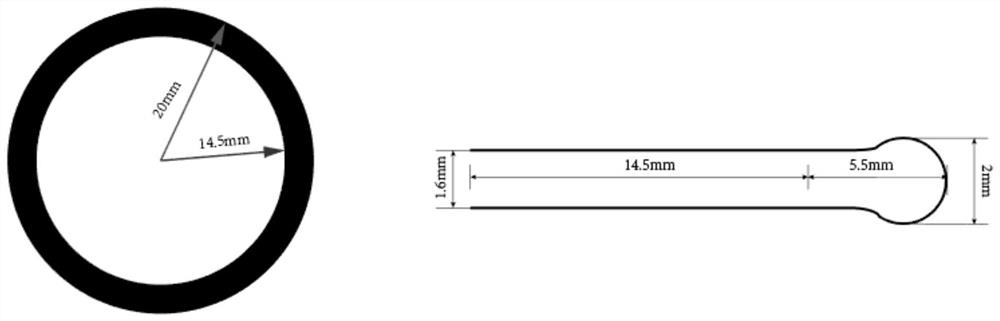
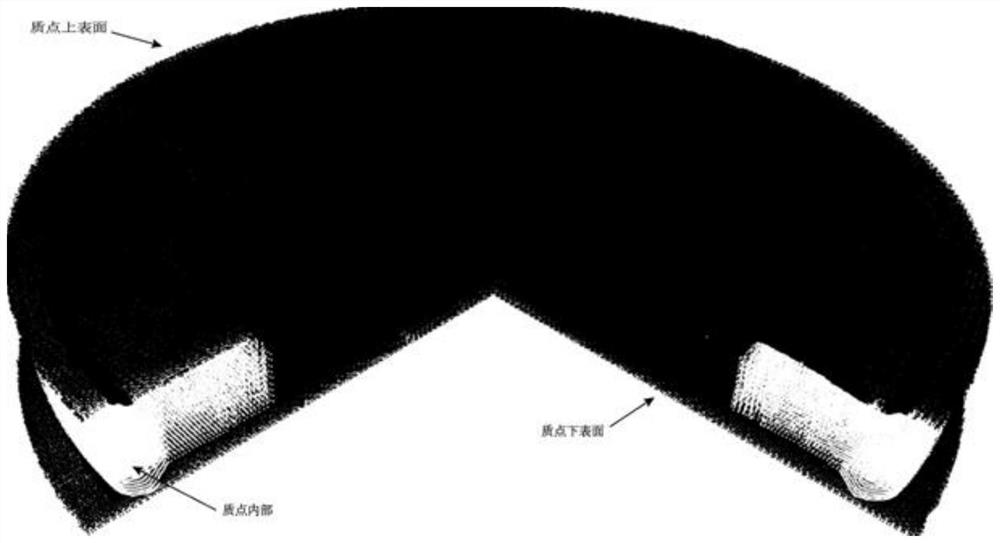
The invention provides a material point method based on an improved contact algorithm, which is applied to double-color coin imprinting forming simulation. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a dynamic physical model for a double-color coin imprinting forming process; carrying out material point integration on the dynamic model in the imprinting forming process; performing finite element triangle / quadrilateral unit discretization on the forming die; establishing a background grid according to the blank cake data model, performing tetrahedron / hexahedron unit discretization on the bicolor coin blank cake, and establishing a mass point set of a copper and aluminum material area; and calculating strain increment and rotation rate increment of the mass points, solving stress and elastic-plastic related variables of the mass points according to the constitutive model, and updating the density of all the mass points. According to the method, the problem of material self-contact judgment in double-color coin stamping forming finite element simulation is solved through a material point method.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com