Transparent substrate for photonic devices
A technology of transparent substrates and photonic devices, which is applied in the fields of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of optimizing OLED devices and not seeking in any way
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
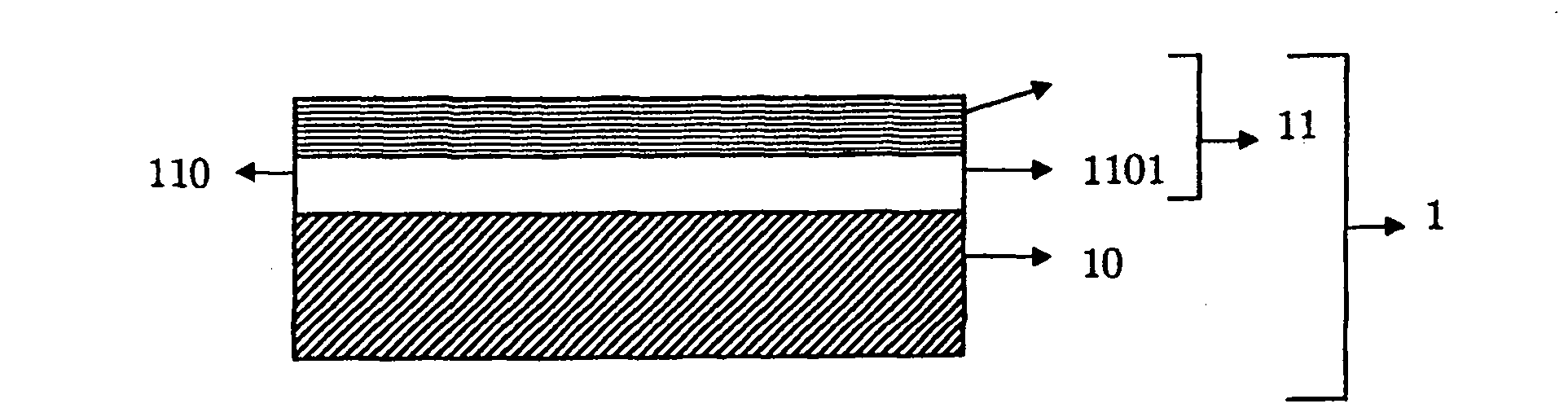
[0244] Table Ia gives in three columns examples of transparent substrates (1) comprising different types of electrodes (number of layers, chemical species of layers and thickness) and the results of measurements of the electrical and optical properties by including these Substrates for organic electroluminescent devices are obtained. The general structure of the electroluminescent device has been described above (page 28, lines 4 to 14). Examples 1R, 2R and 3R are three examples not in accordance with the invention. Example 1R is a transparent substrate comprising ITO electrodes. Example 2R is a transparent substrate comprising an electrode based on a structured low-emission stack comprising an Ag conductive layer. Example 2R is a transparent substrate not optimized for OLEDs because the electrode does not contain a leveling layer (114) and the thickness of the improving coating (110) is not optimized and thus outside the optical thickness range according to the following re...
Embodiment 2 and 3
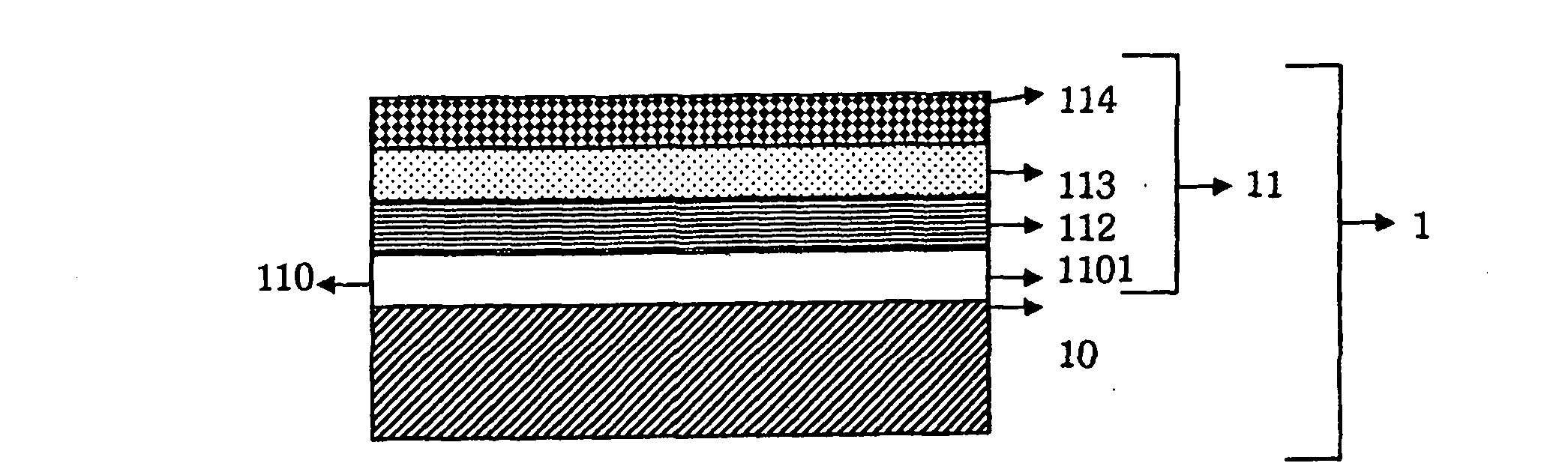
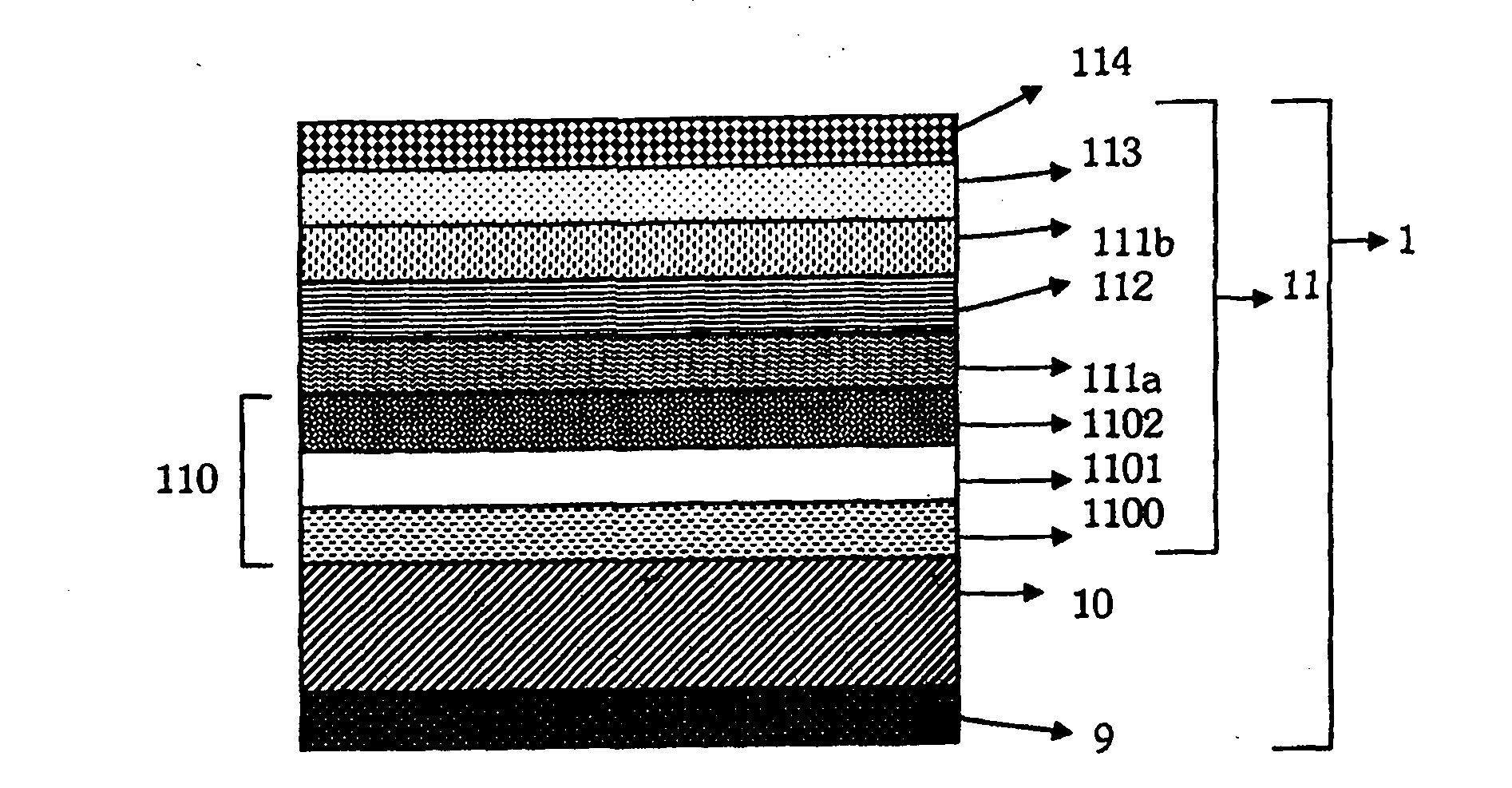
[0312] In Example 1R, the improving coating (114) comprises a barrier layer (1100) combined with a light transmission improving layer (1101) covered by a crystalline layer (1102). In addition, the crystalline layer (1102) and the insertion layer (113) are of the same kind. These layers consist of Zn x sn y o z (where x+y≥3 and z≤6), Zn x sny o z Up to 95% by weight of zinc is contained, the percentages by weight of zinc being expressed relative to the total weight of metal present in the layer. Examples 2 and 3 give examples consistent with the invention. In these embodiments, the improving coating (110) has an optical thickness that conforms to the following relationship:
[0313] T ME =T ME_0 +[B*sin(∏*T D1 / T D1_0 )] / (n 载体 ) 3
[0314] It comprises a barrier layer (1100) combined with an improvement layer (1101) covered by a crystalline layer (1102). Furthermore, the crystalline layer (1102) and the insertion layer (114) are of the same kind. These layers con...
Embodiment 3
[0317] Example 3 illustrates a transparent substrate comprising a thick silver layer which makes it possible to obtain a conductive layer with low resistance.
[0318] A comparison of the properties obtained for devices emitting quasi-white light comprising the transparent substrates of Examples 1R, 2 and 3 shows that:
[0319] The lifetime of the device comprising the substrate according to the invention is longer compared to Example 1R and also compared to a transparent substrate consisting of the same carrier (10) with an ITO electrode located thereon having Equivalent to a geometric thickness of 90 nm, its lifetime was 162 hours (results not shown in Table VII);
[0320] The sheet resistance (Ω / □) of Example 3 with a thick conductive layer is at least half lower than that of Examples 2 and 1R (Ω / □). The possibility of forming larger-sized devices under the circumstances;
[0321] • The optical properties obtained with organic electroluminescent devices comprising example...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com