Infrared small target distance estimation method with no need of atmospheric extinction coefficient
A technology of atmospheric extinction coefficient and target distance, applied in the field of photoelectric detection, can solve the problems of poor estimation accuracy and practicability, many restrictive conditions, and difficulty in practical application, so as to improve accuracy and practicability, avoid unreasonable restrictions, improve The effect of practicality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
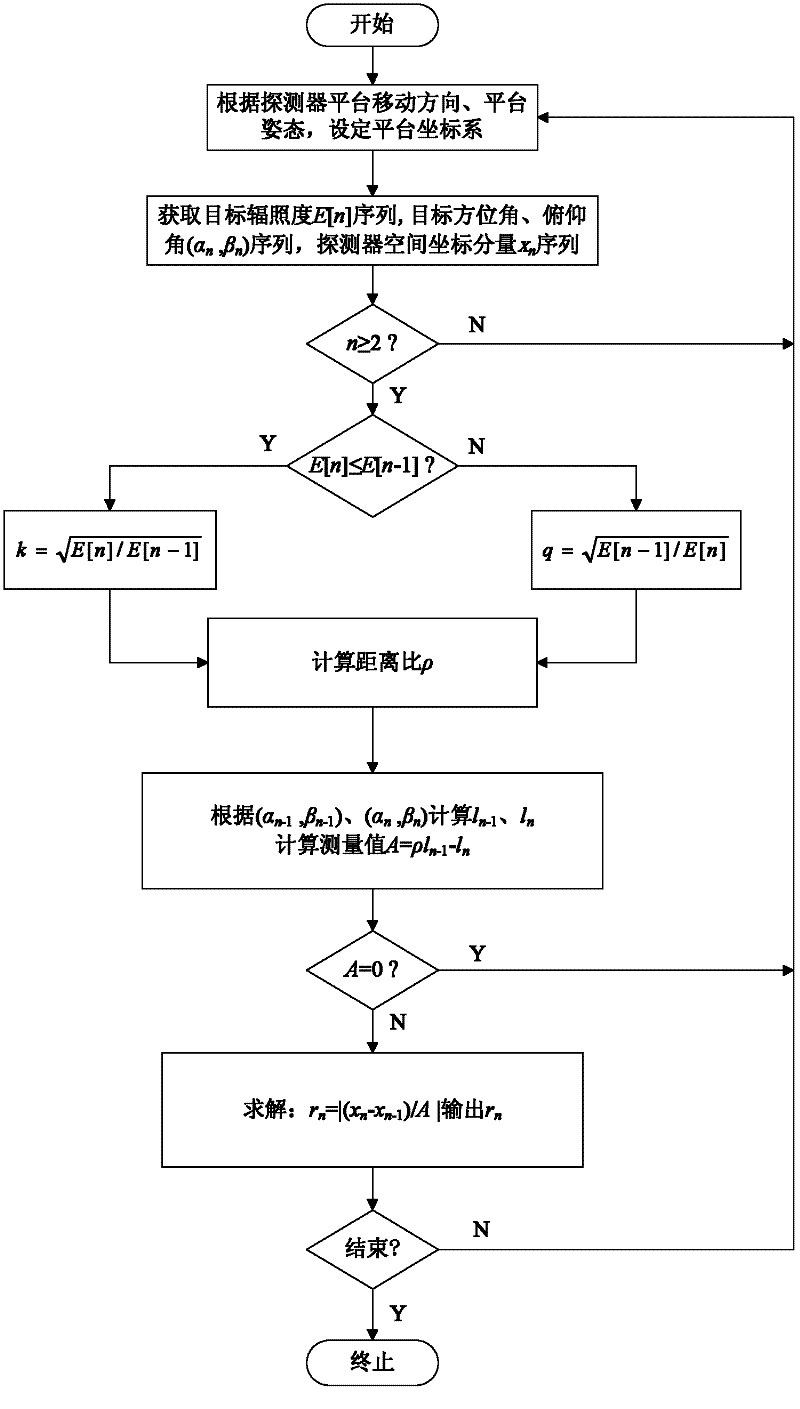
[0027] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0028] Step 1, set the detector observation coordinate system.
[0029] 1.1) Fix the single-band infrared sensor and the photoelectric theodolite lens barrel together so that their optical axes are parallel to the same direction, fix the GPS or Big Dipper positioning system on the base of the photoelectric theodolite to form a detector; fix the detector on the mobile platform It is connected with the central control computer to process and store the relevant parameters obtained, and realize the estimation of the target distance and information output;
[0030] 1.2) Set the detector observation coordinate system x-y-z, where the x-y plane is the plane where the detector platform is located, the negative direction of the x-coordinate axis is the projection direction of the motion direction of the detector on the x-y plane, and the positive direction of the z-coordinate axis is the upw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com