Method for controlling edge cracks of peritectic steel containing niobium or boron
A peritectic and steel edge technology, which is applied in the control field of edge cracking of medium and heavy plates, can solve the problems of reducing the amount of trimming of medium and heavy plates and cannot be effectively controlled, so as to reduce the amount of trimming, reduce unqualified products, and improve finished products. rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
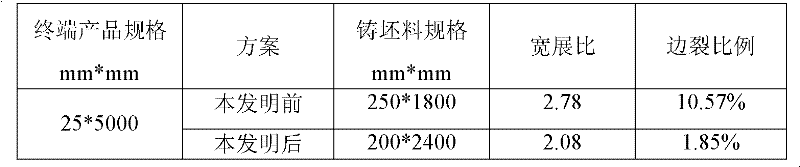
[0030] The final product specifications of the production thickness are: thickness: 25mm, width 5000mm Q370qEZ35 niobium-containing peritectic steel plate edge crack control method, the steps:
[0031] 1) Smelting, and controlling the weight percentages of the following components in the final molten steel: C: 0.14%, Nb: 0.020%;
[0032] 2) Continuous casting into billets;
[0033] 3) Carry out billet selection:
[0034] Since the thickness of the end product is required to be 25mm, that is, ≤40mm, a slab with a thickness of 200mm is selected; the current largest slab width is 2400mm,
[0035] 4) Carry out conventional heating to cast slab;
[0036] 5) Rolling:
[0037] Since the width of the terminal product is required to be 5000mm, that is, the width is ≥3360mm, it is rolled at a total width ratio of 2.08 until the terminal product is rolled;
[0038] 6) Carry out post-processing according to routine.
[0039] This example compares the detection situation:
[0040] ...
Embodiment 2
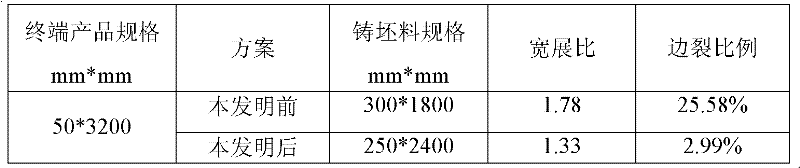
[0042] The final product specification of production thickness is: thickness: 50mm, width 3200mm Q390GJC niobium-containing peritectic steel plate edge crack control method, the steps:
[0043] 1) Smelting, and controlling the weight percentages of the following components in the final molten steel: C: 0.16%, Nb: 0.035%;
[0044] 2) Continuous casting into billets;
[0045] 3) Carry out billet selection:
[0046]Since the thickness of the end product is required to be 50mm, that is > 40mm ~ ≤ 60mm, a slab with a thickness of 250mm is selected, and the current largest slab width is 2400mm.
[0047] 4) Carry out conventional heating to cast slab;
[0048] 5) Rolling:
[0049] Since the width of the terminal product is required to be 3200mm, that is, the width is ≤3360mm, it is controlled to be rolled at a total width ratio of 1.33 until the terminal product is rolled;
[0050] 6) Carry out post-processing according to routine.
[0051] This example compares the detection si...
Embodiment 3
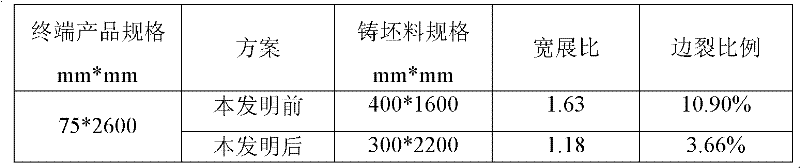
[0054] The final product specifications of the production thickness are: thickness: 75mm, width 2600mm Q345B niobium-containing peritectic steel plate edge crack control method, the steps:
[0055] 1) Smelting, and controlling the weight percentages of the following components in the final molten steel: C: 0.15%, Nb: 0.025%;
[0056] 2) Continuous casting into billets;
[0057] 3) Carry out billet selection:
[0058] Since the thickness of the end product is required to be 75mm, that is >60mm~≤80mm, a slab with a thickness of 300mm is selected; the width of the slab is selected as 2200mm.
[0059] 4) Carry out conventional heating to cast slab;
[0060] 5) Rolling:
[0061] Since the width of the terminal product is required to be 2600mm, that is, the width is ≤3360mm, it is rolled at a total width ratio of 1.18 until the terminal product is rolled;
[0062] 6) Carry out post-processing according to routine.
[0063] This example compares the detection situation:
[0064...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com