Sensor device for magnetic particles with a high dynamic range
A technology of sensor equipment and magnetic particles, applied in the direction of instruments, scientific instruments, material analysis through electromagnetic means, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
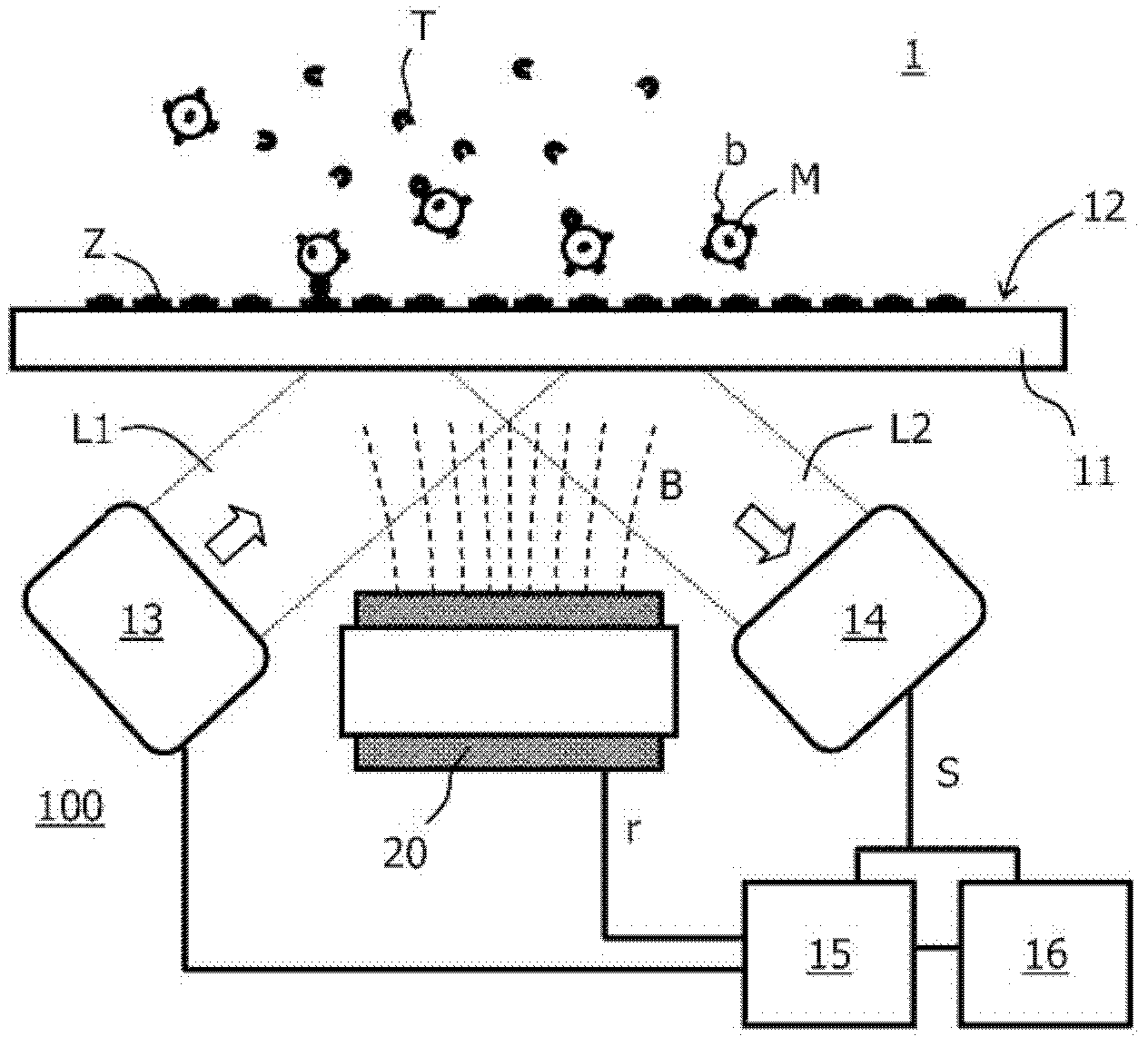
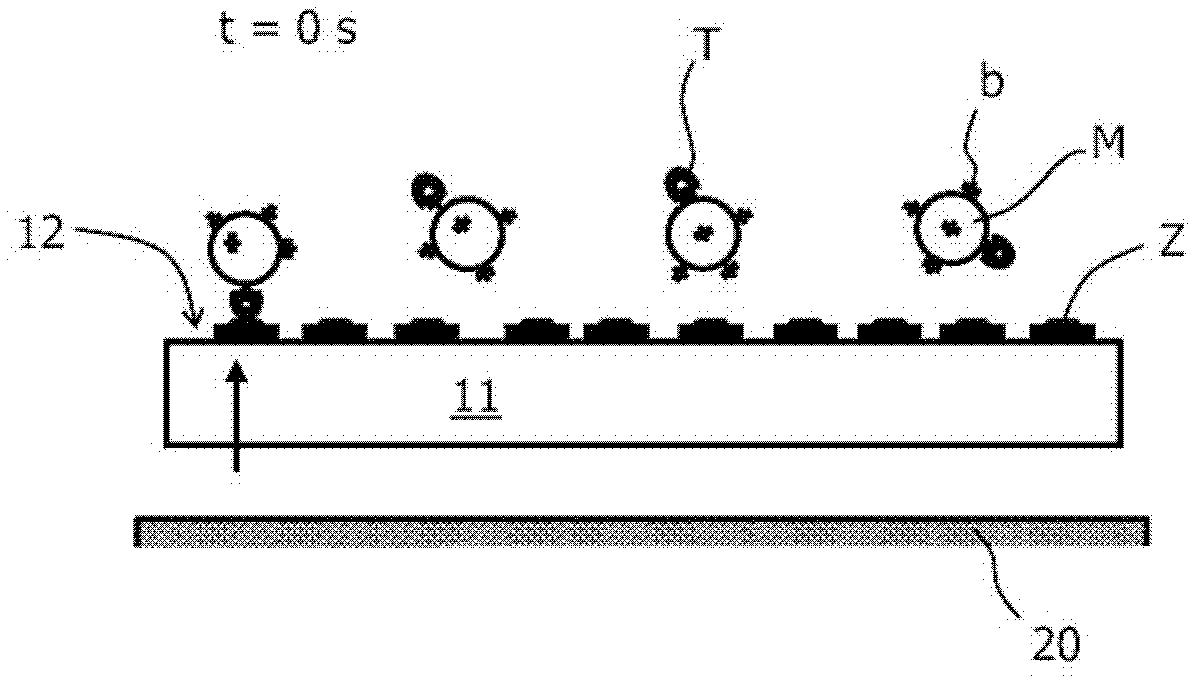
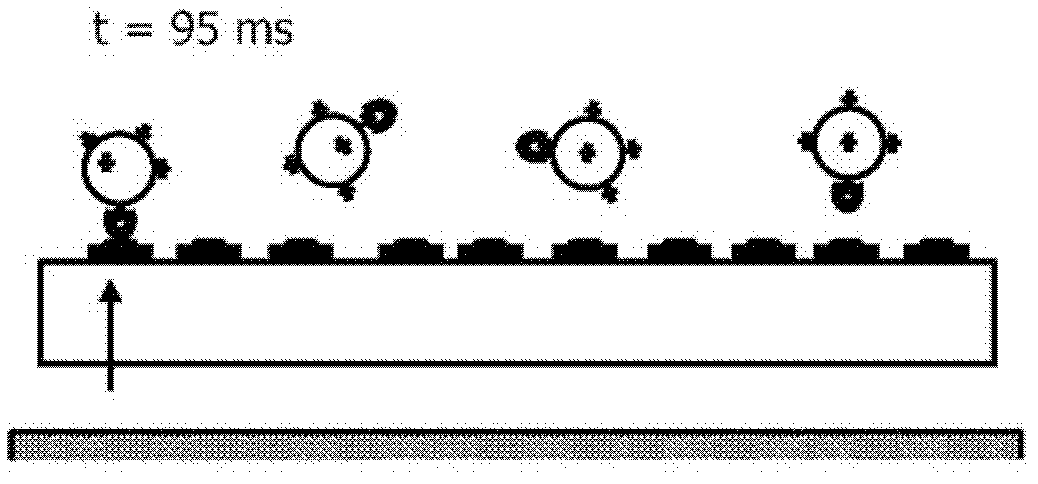
[0038] An important topic in the field of molecular diagnostics (MD) is the development of instruments for providing rapid diagnosis at point-of-care (POC) and in emergency situations. The primary requirements for an MD platform are speed of diagnosis, adequate sensitivity, and ease of use. In addition, disposables with microfluidic channels are preferred to increase the flexibility of the platform for a large number of manufacturers.
[0039] For many applications, the diagnostic method of choice is based on performing immunoassays. Here, possible detection methods include, inter alia, frustrated total internal reflection (FTIR) using magnetic labels and confocal fluoroscopy using molecular fluorescent labels. While both methods are sufficiently sensitive to detect small changes in labelling, robustness must be ensured for all physical aspects that can affect the inherent biochemical properties of the assay components. By using superparamagnetic beads, the kinetics of the a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com