Heavy raw material boiling bed hydrogenation treatment method
A hydroprocessing and ebullating bed technology, which is applied in the treatment of hydrocarbon oil, petroleum industry, refining to remove heteroatoms, etc., can solve the problems of increased reactor scale, inability to optimize hydrogenation performance, unstable operation, etc., and achieve High hydrodesulfurization activity and metal removal activity, suitable asphaltene conversion performance, and the effect of improving comprehensive reaction performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0016] The preparation process of the ebullated bed hydrotreating catalyst is to firstly prepare the microspherical catalyst carrier, and then use the impregnation method to support the required hydrogenation active metal components. The preparation process of the catalyst carrier is as follows: the raw materials of the catalyst carrier with suitable humidity are made into particles of suitable size, and then the particles are spheroidized, and the spheres are dried and calcined to form a spherical catalyst carrier.
[0017] The drying and calcination of the catalyst carrier can adopt conditions well known to those skilled in the art, such as natural drying or drying at 80-150°C, and calcination at 600-1000°C for 1-6 hours. The impregnation method to support the active hydrogenation metal component can be carried out by methods well known to those skilled in the art, such as making a solution of the required active metal salt, impregnating the catalyst carrier with the solution...
Embodiment 1
[0021] Catalyst preparation
[0022] 1. Preparation of Catalyst A
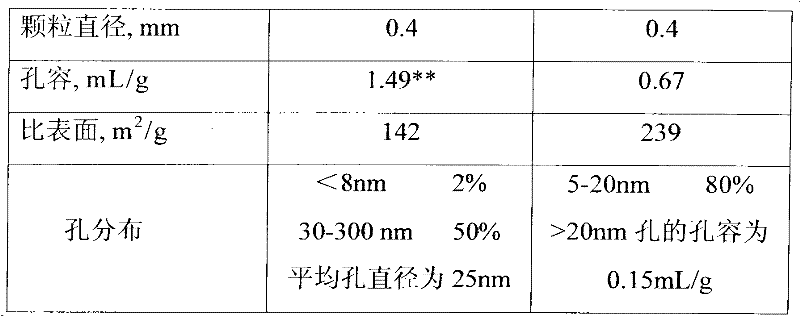
[0023] Prepare a spherical catalyst carrier with an average pore diameter of 22nm and a spherical particle diameter of 0.4mm. Other catalyst preparation processes refer to US4328127 and CN200710010377.5.
[0024] Prepare the Mo-Ni solution according to the conventional method, and the MoO in the solution 3 The NiO content is 4.01%, and the NiO content is 1.03%. The above-mentioned carrier was impregnated with this solution by an equal-volume impregnation method to obtain the final catalyst A, whose properties are shown in Table 1.
[0025] 2. Preparation of Catalyst B
[0026] A spherical catalyst carrier with an average pore diameter of 11nm was prepared, and the spherical catalyst particle size was 0.4mm. Other catalyst preparation processes were carried out according to the methods of US7074740 and CN200710010377.5.
[0027] Prepare the Mo-Co-P solution according to the conventional method, and the MoO ...
Embodiment 2
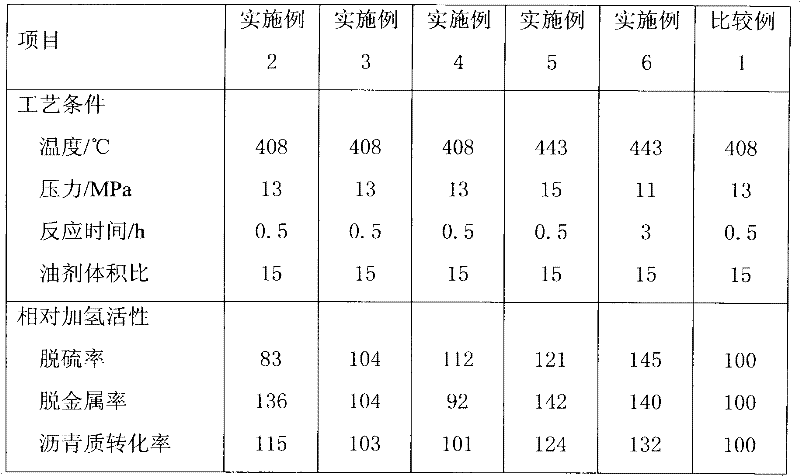
[0029] Catalysts A and B in Example 1 were selected and mixed in a ratio of 1:0.5 by volume and loaded into a 1L autoclave, and a vacuum residue hydrotreating test was carried out in the presence of hydrogen. The properties of the vacuum residue selected for the test are: distillation range 520°C + , the sulfur content is 2.8wt%, the metal (Ni+V+Fe) content is 357μg / g, and the asphaltene content is 6.8%. The test conditions are: reaction temperature 408°C, reaction pressure 13MPa, reaction time 0.5h, oil agent volume ratio 15, evaluation results are shown in Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com